Beef Cattle Industry and Meat Industry
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Describe what age of beef animals are slaughtered and why?
-Young animals
-Have a high carcass quality
-Have good food conversion efficiency
What are the two main methods of rearing beef cattle
-Aim for maximum growth rates (more expensive but faster)
-Use maximum utilisation of cheap feed (Slower but much cheaper)
What are some common beef breeds in the UK?
Dual purpose (not in large numbers):
-Gloucester
-Simmenthal
Beef type (most prevalent):
-Continental (Cherolet, Belgian blue, Limousin)
-Traditional British breeds (Aberdeen angus, Belted Galloway, Hereford)
What are the characteristics of a beef cow?
-Very heavy muscle
-Low milk yield
-Good feed conversion
Compare traditional British beef breeds to continental beef breeds
-Smaller mature size (so lower maintenance cost)
-Early maturing
-Hardy (to climate, feed and environment)
-Good suckler cow
-Worser terminal sires
Continental breeds are the opposite
What does early maturing mean?
They reach the fatty deposition stage earlier than "late maturing".
What are the implications of early maturing cattle rearing?
-You have to monitor their feed intake to maintain lean muscle. -Need to grow them slowly over time by using low amount of concentrates and higher forage % in their diet.
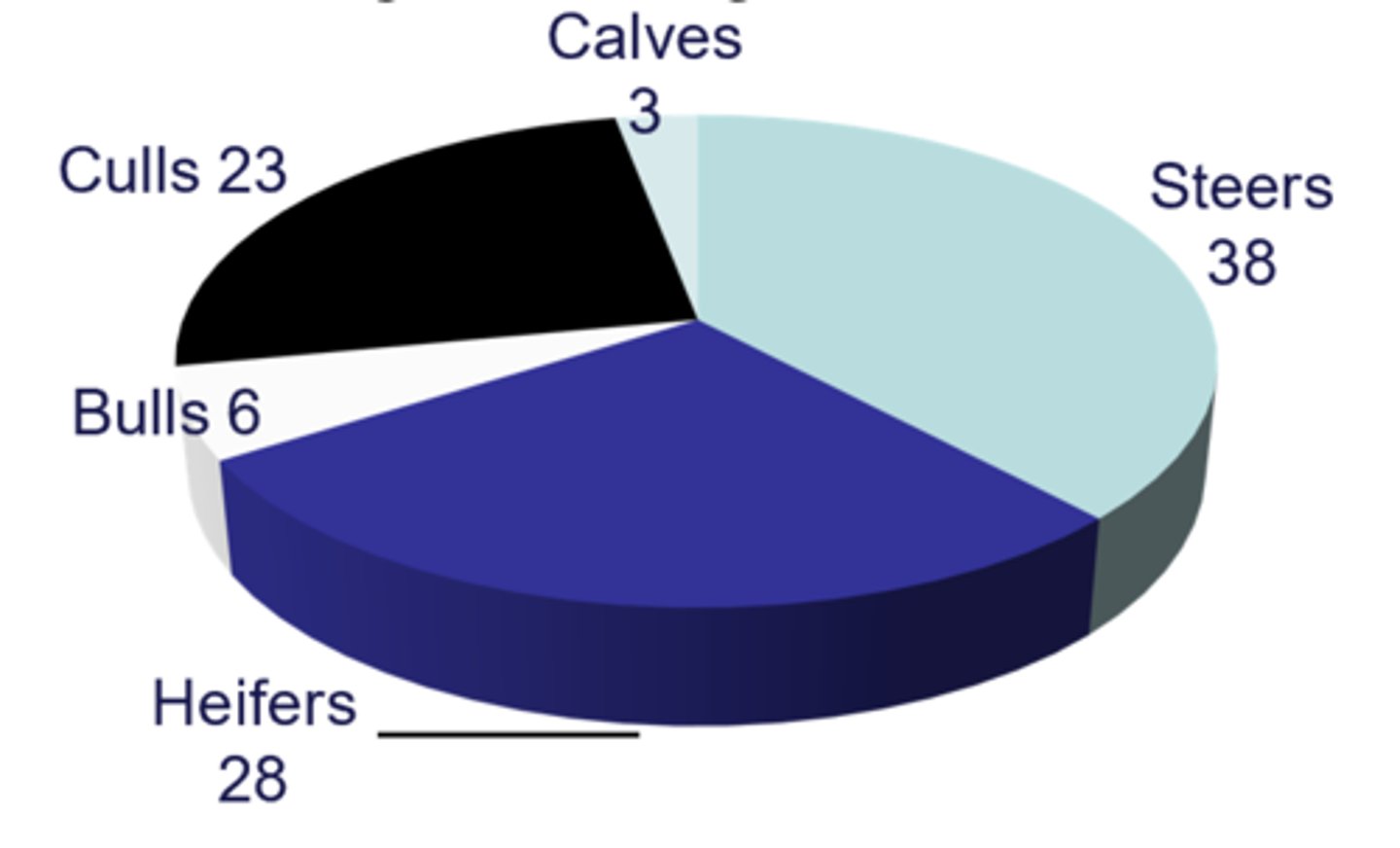
Outline the beef industry in the UK
-7/10 beef units have breeding cows
-Average breeder herd size = 28
-1.6 million breeding cows
-0.4 million breeding heifers
-2.5 million fattening
Outline the interactions that occur between the beef and dairy industry
Common for farmers to have 50% dairy sires and 50% beef sires so at least 50% of calves are purebred beef
-Surplus dairy females are sent into the beef herd for slaughter
-Dairy male calves are sent into the beef herd for slaughter
-Beef sires can be used on dairy cows for breeding
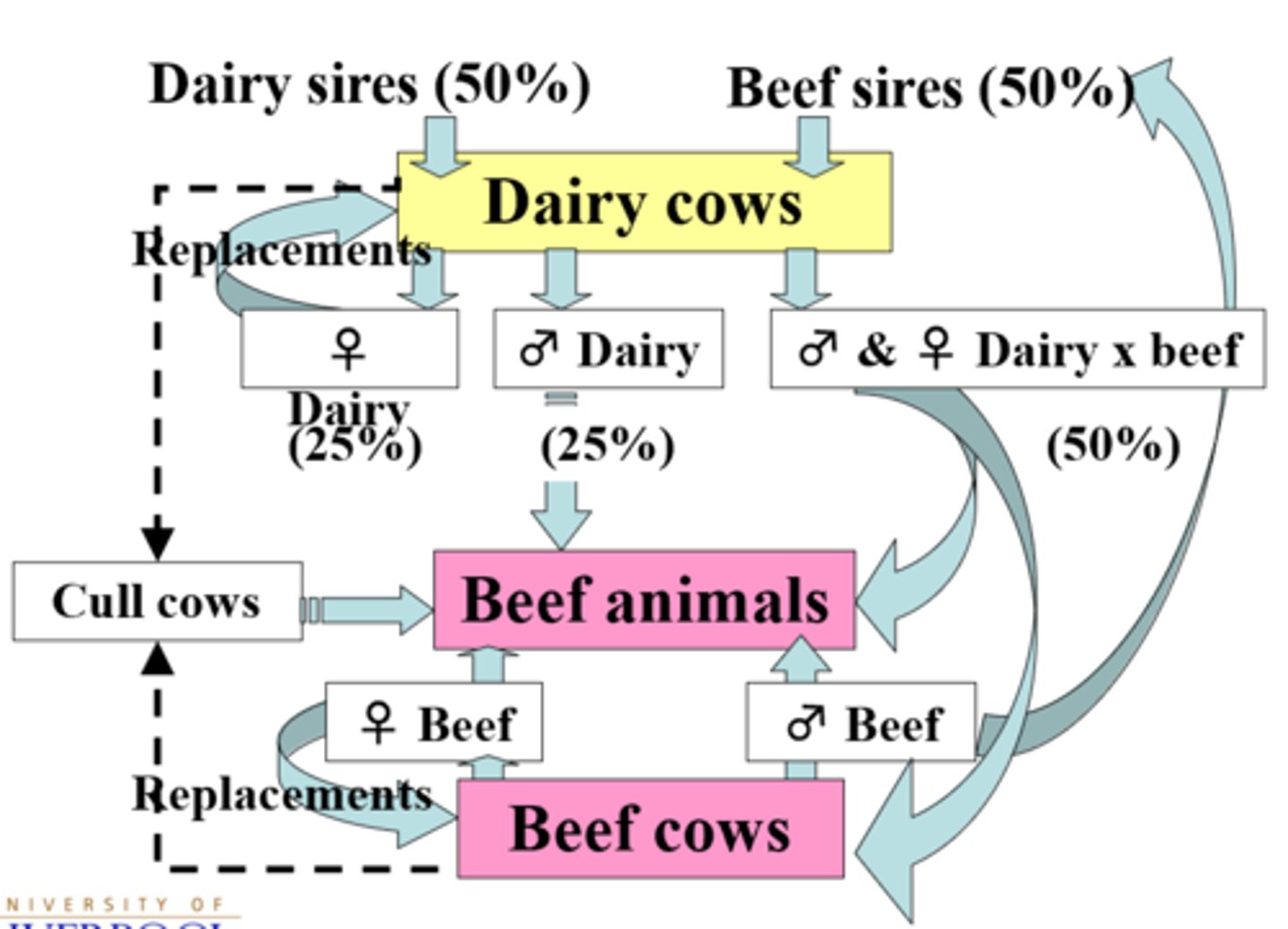
Is crossbreeding in the dairy and beef industry common?
Yes.
Why do cattle have passports?
-Due to BSE
-Needed to track movements, ID, dam and death

Compare cattle passports with horse passports
-Don't ID appearance as much (e.g. colour)
-Don't record the medication
What traits are desirable for the suckler herd?
-Low feed cost
-Longevity
-Tight calving pattern
-Fast growth and early sexual maturity
-Docile temperament
-Good feed conversion ability
-1 calf every year
-Low calf mortality
-Solid replacement policy
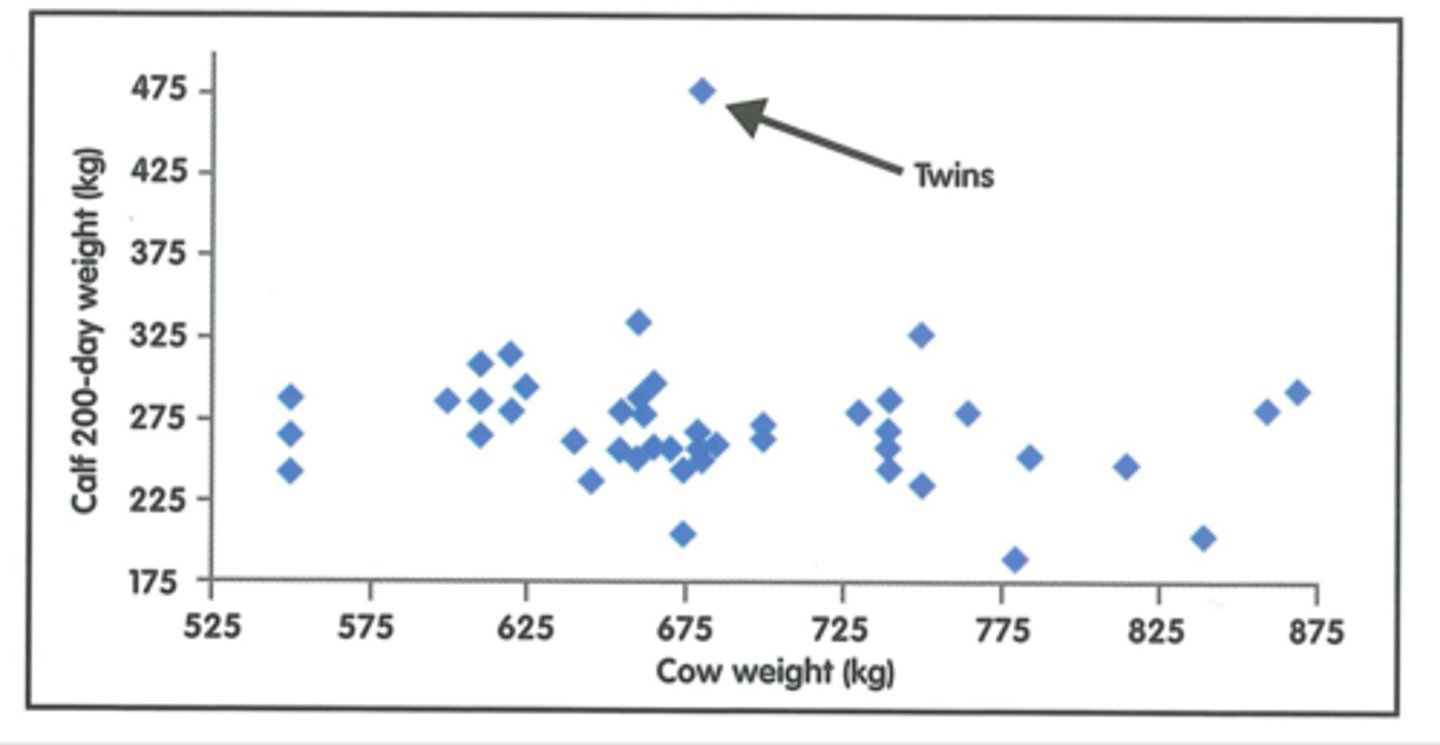
How is the suckler herd reared? Why?
Extensive system
-Low input, low output
-Forage-based
-Want to keep body condition constant all year (2.5) to minimise calving losses
-Spring calves may gain condition when put onto grass
-Attempt to get BCS to 2.5 in last trimester of pregnancy (Obesity NOT good)
The only way this herd will make profit is through calf production (not milk).
What is the target for an efficient suckler cow?
Rear her calf to atleast 50% of her own body weight at weaning (by 200d).
What are the pros and cons of spring calving?
Pros:
-Cow goes onto good quality grass at lactation (cheap feed)
-Good conception rates
Cons:
-Cow is heavily pregnant over winter (higher feed cost)
-Calf is weaned at autumn where no grass available (can have compensatory growth later though)
-Supervision more difficult if calving outside
-Can't predict when spring starts

What are the pros and cons of autumn calving?
Pros:
-Cow is in good condition in autumn (due to summer grass)
-Easy supervision
-Weaned calfs are more valuable
Cons:
-Must breed in winter
-Higher winter feeding cost
-Lactating over winter ^^

Outline the nutrition guidelines for a beef cow
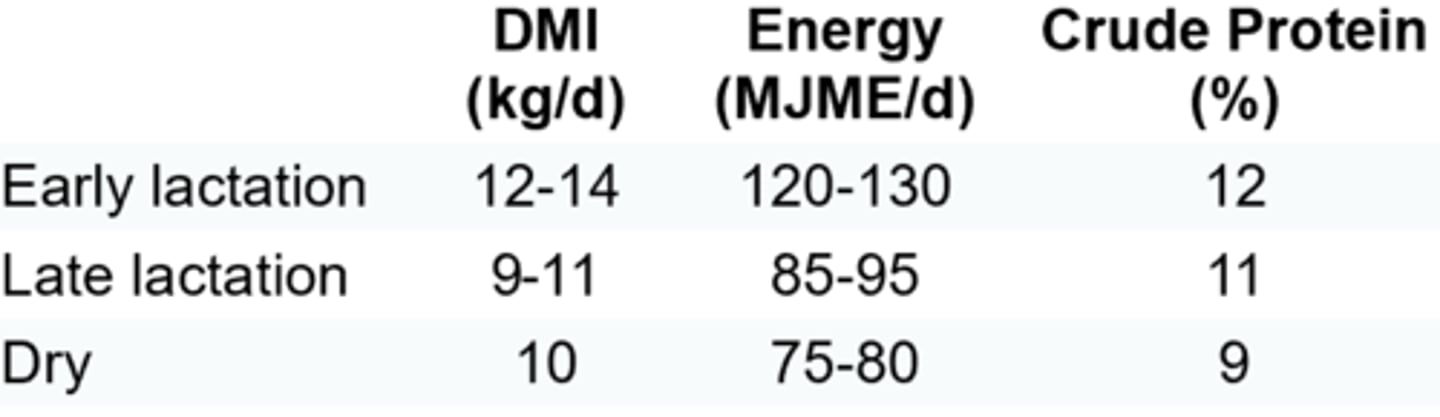
Outline a ration for an autumn calver in the first 3 months of lactation
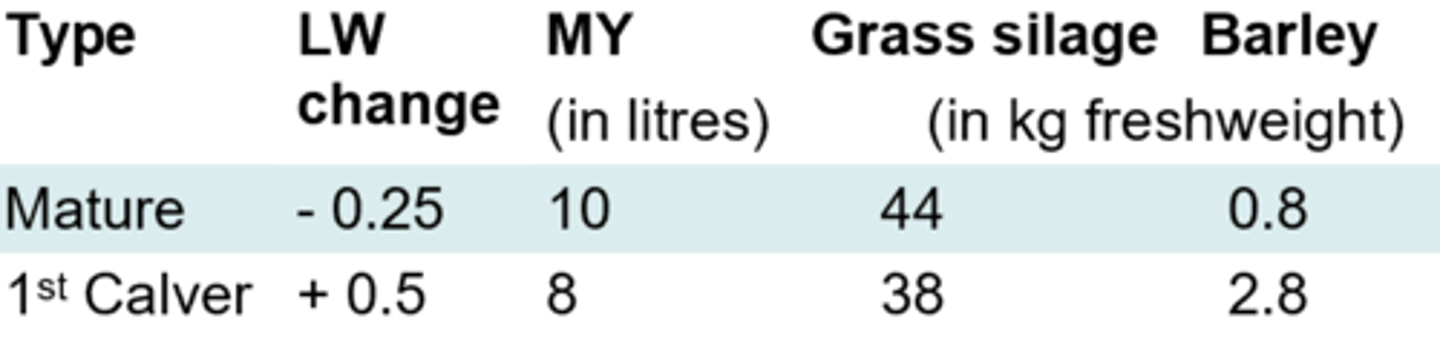
When would you normally wean off a beef calf? What scenario would it be later and earlier?
6-8 months
-Later if cow is high BCS
-Earlier if cow is low BCS
Which is better, abrupt weaning or gradual weaning for beef calves?
Abrupt.
What must you do once the calf has been weaned?
Ensure good separation distance between the two otherwise they will stress and lose BCS.
How much extra energy do beef cattle require if they are left out in pasture during winter?
Atleast 15% extra.
What are the two main types of beef products?
-Veal
-Rosé
Describe how veal is produced
-From dairy-bred males
-1.2-1.4 kg DLWG
-Slaughter at 6-7 months @300kg LW/ 150kg DW
-Crates are banned, must be group housing
-Minimum requirements for dietary iron and fibre
-Fed milk throughout plus hard feed and straw
Describe how rosé is produced
-Reared in approved system
-Wean off milk at 6-12 w/o
-Feed starchy feed (maize silage and cereal) and straw
-Slaughter at 8-12 m/o (e.g. at 10 mo @400 kg LW or 200 kg DW)
Describe the production of dairy calves in the beef industry from birth to weaning
-Bought at 10-14 d/o
-Fed milk until 6-8 w/o plus hay and calf pellets
-Expected DLWG = 0.9kg
Describe the production of suckler calves in the beef industry from birth to weaning
-Can creep feed
-Wean at 6-8 m/o
-Expected DLWG = 1.2 kg bulls/ 1.0kg steers and heifers
What are the requirements for the sale and transport of calves?
Sale:
-Illegal to sell at less than 7 d/o
-No resale within 28d
Transport:
-Illegal to transport before 10 d/o
-If less than 14 d/o the transport cant be longer than 8hr
Navel must be healed for both.
Describe creep feeding in beef calves
-Start at 6-12 weeks prior to weaning
-Preserves cows BCS
-Primes rumen for post-weaning diet
-Provides 14-16% CP
List the % weigh tgain from dams milk from 1-6 months
-1 m/o = 100%
-3 m/o = 66%
-6 m/o = 33%
What are the options for beef calves after weaning?
-Intensive system
-Extensive system
-Can sell as store cattle:
-Not taken to slaughter on farm where born
-Sold @ 6-12 m/o
What is the fattening period?
Where the calves are weaned and reared for meat.
What are finishing cattle?
-Cattle in their last few weeks prior to slaughter.
-System is optimised for maximum weight gain and kept clean to prevent rejection from abattoir
Describe the intensive system for beef rearing
-Must introduce cereal gradually
-Feed barley, silage, concentrate (truly ad-lib
-Must provide proper eating straw (not dirty)
-Finish at 12-14 m/o
-Target weight = 520kg
-DLWG atleast 1.2kg
-Housed
-Usually for late-maturing breeds
-Feed conversion 5:1
-Need protein supplement
-Need mineral and vitamin lick
-Need stable social group
What is the buller-steer problem?
-Bullying issue in social groups less than 20 cattle.
-Need adequate space in pen and trough
List some common problems with the intensive rearing system
-Buller-steer problem
-Carbohydrate overload (bloat, rumen acidosis etc)
-Hypovitaminosis A
-Lameness
-Pneumonia
Describe the extensive system for beef rearing
-Can be no concentrate
-Mostly fed forage
-Can cull @ 18, 24 or 30 m/o based on market
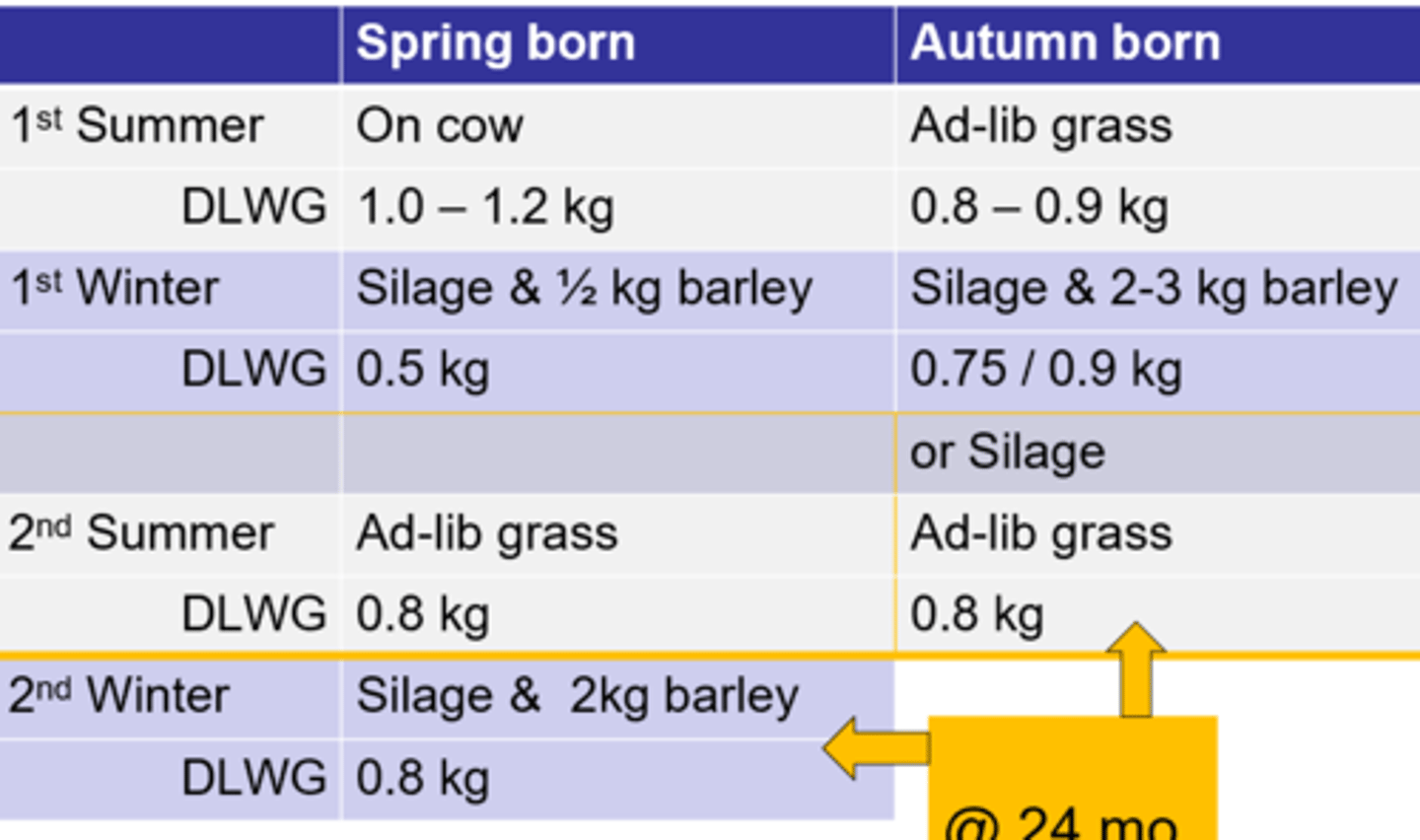
What are the critical check points for the extensive system for beef rearing?
-Target finish weight and gender to market
-Check body condition
-Check silage quality
-Endoparasite and pneumonia control
What are the common finishing weights for heifers and steers
18 months:
-Heifers = 360-480kg
-Steers = 530kg
22-24 months:
-Steer = 560kg
What are the target feed conversion ratios for the different rearing systems in beef cattle?
-Extensive = atleast 7:1
-Intensive = ~5:1
-Calf on creep feed = atleast 4:1
What is the killing out %?
(Saleable carcass weight/live weight) x100
Approximately, what proportion of the live weight is carcass?
55%.
Describe the factors that influence KO%
Nutrition:
-Higher roughage diets = lower KO% (gut fill)
Gender:
-Bulls greater carcass weight than steers
-Heifers less carcass weight than steers (higher fat content)
Age:
-Younger have a lower fat content
Breed:
-Traditional > Continental > Dairy cross beef > Dairy