Chapter 18: Gas Exchange and Transport単語カード | Quizlet
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
alveolar gas exchange
external respiration
O2: alveoli to blood
CO2: blood to alveoli
1. Pulmonary ventilation
2. Alveolar gas exchange
3. Gas transport
4. Systemic gas exchange
5. Cellular Respiration
What is the overview of respiratory ventilation?
systemic gas exchange
internal respiration
O2: blood to cell
CO2: cell to blood
maintain partial pressures of blood gases
What is the function of chemoreceptors?
1. Monitor systemic arterial PO2 to prevent hypoxia
2. Monitor systemic arterial PCO2 to prevent hypercapnia
3. Monitor systemic arterial pH to prevent acidosis & alkalosis
How do chemoreceptors maintain partial pressures of blood gases?
Alveoli:
PO2 = 100 mm Hg
PCO2 = 40 mm Hg
What are the normal PO2 and PCO2 ranges in the alveoli?
Systemic Arterial Blood:
PO2 = 100 mm Hg
PCO2 = 40 mm Hg
What are the PO2 and PCO2 ranges in systemic arterial blood?
Systemic Cells:
PO2: less than or equal to 40 mm Hg
PCO2: more than or equal to 46 mm Hg
What are the PO2 and PCO2 ranges in systemic cells?
Systemic Venous Blood:
PO2: less than or equal to 40 mm Hg
PCO2: more than or equal to 46 mm Hg
What are the PO2 and PCO2 ranges in the systemic venous blood?
veins (towards) heart (moving away) arteries
so after blood has been oxygenated in the lungs, it moves back to the heart
1. pulmonary veins (towards) heart (moving away) systemic arteries
PO2 = 100 mm Hg
PCO2 = 40 mm Hg
After blood has circulated towards tissues, it makes its way back to the heart
2. systemic veins (towards) heart (moving away) pulmonary arteries
**** Focus on veins and arteries movement to and from the heart
What is the movement of blood for gas exchange throughout the body?
1. Alveolar PO2 and availability of O2
- can O2 reach the avleoli?
2. Diffusion problems
- can gas diffuse between alveoli and blood?
3. Perfusion, partial pressure, & gas solubility
- is there adequate perfusion of alveoli?
What are 3 factors that affect/influence Alveolar Gas Exchange?
1. Alveolar PO2 and availability of O2
- can O2 reach the avleoli?
Which factor affects/influences Alveolar Gas Exchange:
ex:
1. Altitude & O2 availability: the higher the altitude, the less O2 available = harder to breathe
2. Hypoventilation
- less compliance
- increase airway resistance (asthma, chronic bronchitis)
2. Diffusion problems
- can gas diffuse between alveoli and blood?
Which factor affects/influences Alveolar Gas Exchange:
ex:
1. Surface area of alveoli (type 1 cell)
- Emphysema: loss of type 1 cells and elastin
- increase compliance & decrease recoil
= less S.A. = less diffusion
2. Diffusion barrier permeability
- Fibrosis lung disease: thickened alveolar membrane slows gas exchange
= takes longer to get through membrane
3. Diffusion Distance
- Pulmonary edema: fluid in longs
= fluid in interstitial space increases diffusion distance
3. Perfusion, partial pressure, & gas solubility
- is there adequate perfusion of alveoli?
Which factor affects/influences Alveolar Gas Exchange:
ex:
1. Adequate blood supply to alveoli
2. Pressure gradient
- Partial pressure gradient to move
- Compare Alveolar PO2 = 100 mm Hg to pulmonary arterial blood PO2 less than 40 mm Hg
3. Temperature
- Air warmed & moistened in airway facilitates absorption
4. Solubility of O2
- not good at dissolving in water
- Plasma can't transport much dissolved O2
= Hemoglobin!!!! - helps transport
5. Solubility of CO2
- 20x more soluble in water than O2
- plasma can transport more dissolved CO2
Total Blood [O2] = (dissolved O2) + (bound O2)
=
1.5% dissolved O2
98.5% bound O2 to Hb
What is the % of (dissolved O2) + (bound O2) in total blood [O2]?
1. Amount of dissolved O2 in Plasma
- O2 solubility in water is poor
2. Amount of hemoglobin
- can only hold 4 O2 molecules
The amount of Oxygen bound to Hb depends on what?
cooperative binding
each successive oxygen bound to hemoglobin increases the affinity of the other subunits, while each successive oxygen released decreases the affinity of the other subunits
% Saturation
(O2 bound to Hb/max possible) x 100
small changes in % saturation
O2-Hb binding curves or O2-Hb dissociation curve
PO2 70-100 mm Hg: plateu
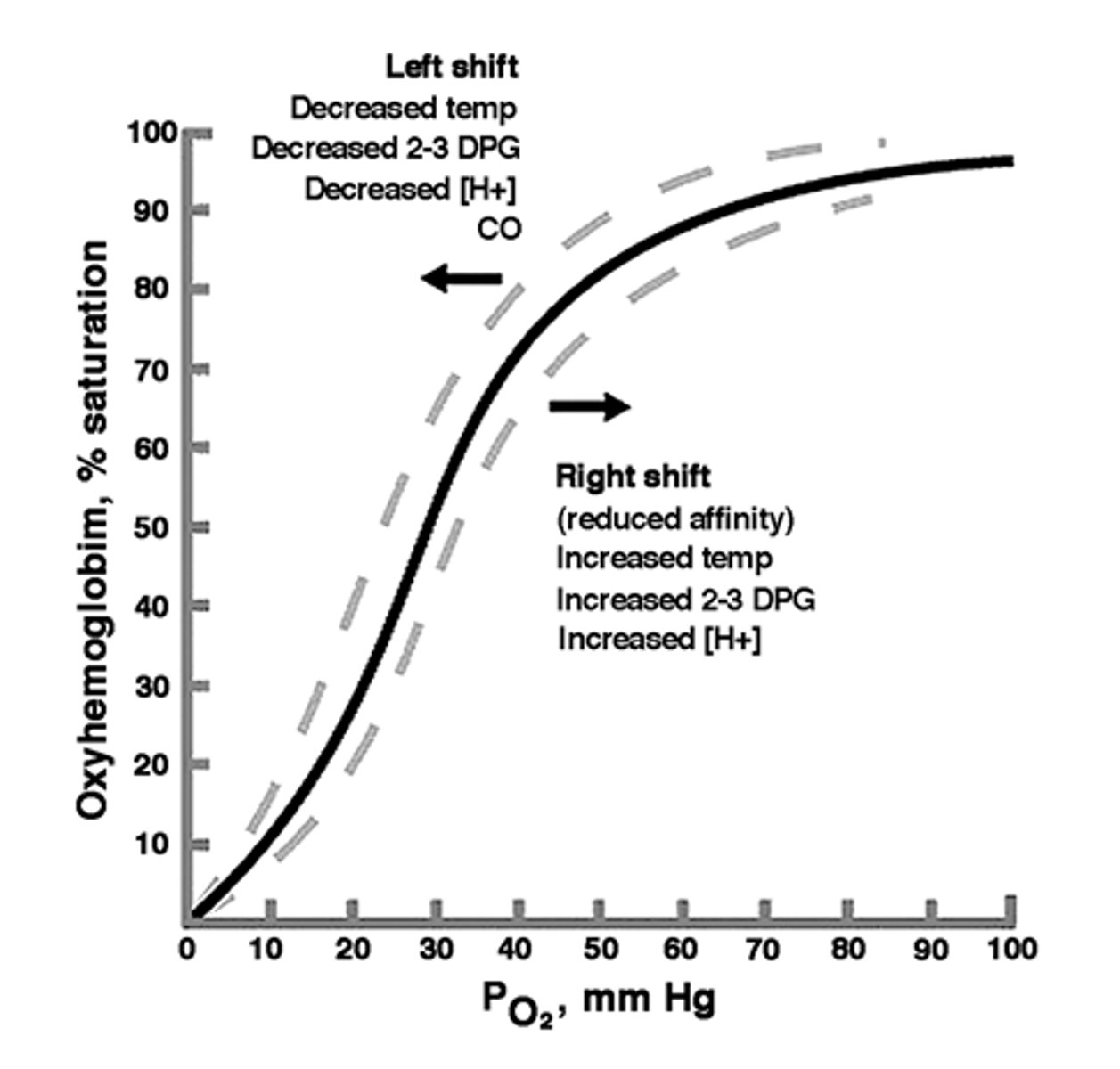
still about 90% saturated
O2-Hb binding curves or O2-Hb dissociation curve
PO2 60 mm Hg
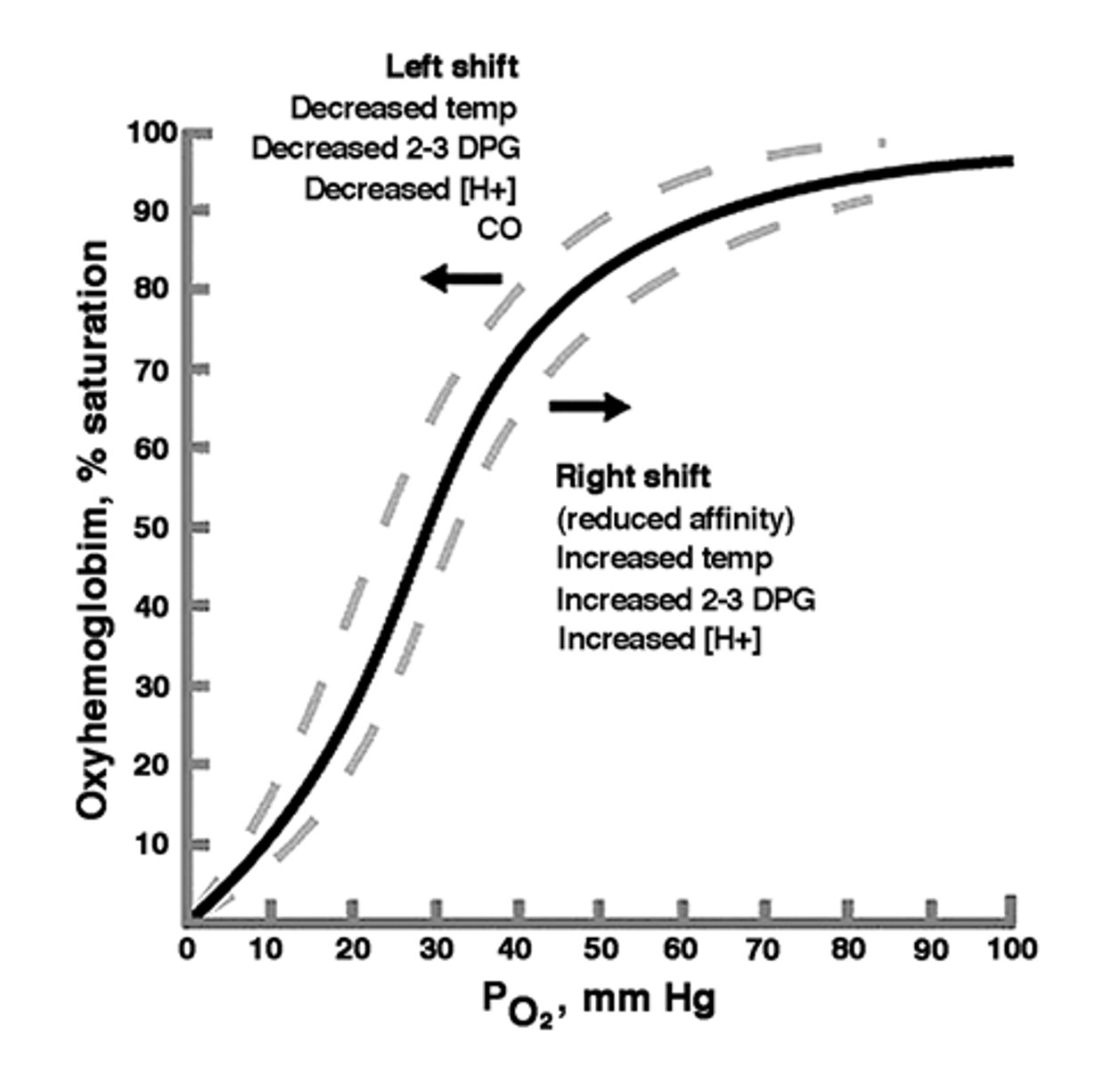
rapid dissociation
- dissoiation at systemic capillaries
- association at pulmonary capillaries
O2-Hb binding curves or O2-Hb dissociation curve
PO2 40 - 20 mm Hg
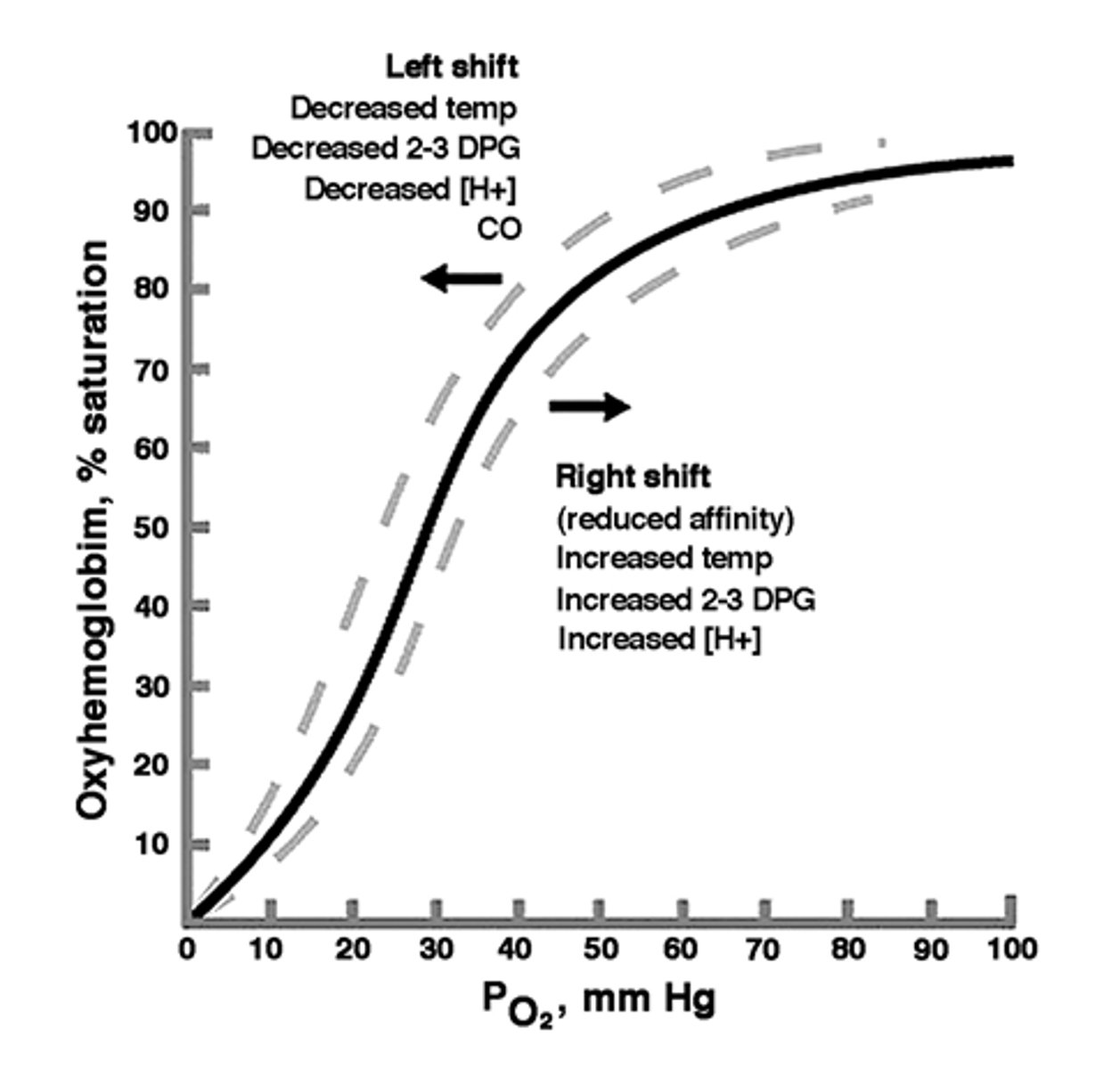
70%
If the PO2 = 20 mm Hg
and Hb % saturation is 30 %
how much O2 was extracted from blood?
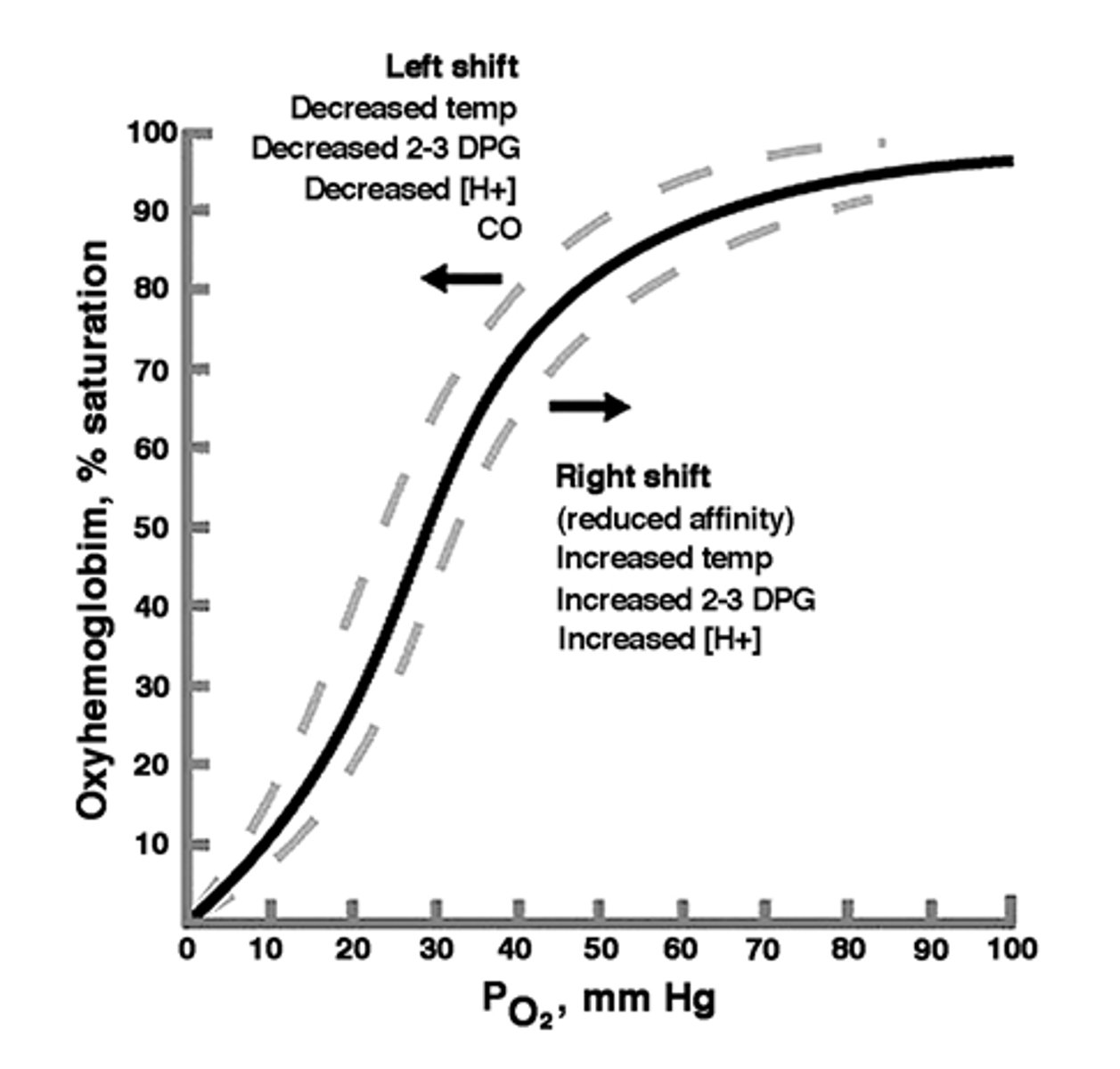
↑ PO2 = increased binding (high affinity)
↓ PO2 = decreased binding (low affinity)
PO2 determines binding
↑ PO2 = ?
↓ PO2 = ?
↑ pH (basic) = increased binding (high affinity)
↓ pH (acidic) = decreased binding (low affinity)
pH determines binding
↑ pH (basic) = ?
↓ pH (acidic) = ?
increased binding - harder to release O2
high affinity
decreased binding - easier to release O2
low affinity
↑ temperature = decrease binding (low affinity - release O2 easier; systemic capillaries)
↓ temperature = increase binding (high affinity - harder to release O2; pulmonary capillaries)
Temperature determines binding
↑ temperature = ?
↓ temperature = ?
↑ [DPG] = decreases binding (low affinity)
↓ [DPG] = increases binding (high affinity)
DPG determines binding
↑ [DPG] = ?
↓ [DPG] = ?
Total Blood [CO2] = (dissolved CO2) + (bound CO2) + (converted CO2)
=
7% dissolved
23% bound to Hb
70% converted to HCO3-
What is the % of (dissolved CO2) + (bound CO2) + (converted CO2) in total blood [CO2]?
Total Blood [H+] = (dissolved H+) + (bound H+)
=
dissolved
- very small amounts, depends upon PCO2 in blood
bound to Hb from CO2 conversion to HCO3-
- depends upon PCO2 in blood
What is the % of (dissolved H+) + (bound H+) in total blood [CO2]?
carbon monoxide (CO)
210 times the affinity for Hb as O2
- occupies the O2 binding sites on Hb
- reduces the amount of O2 transported by Hb
- Does not increase ventilation reflexes because there is no signal to breathe in more
- symptoms: sleepiness, muscles don't work, confusion, skin (veins are cherry red), eyes
brain stem
control pattern of inspiration and expiration of quiet breathing
Medulla: DRG & VRG
Pons: PRG
chemoreceptors & mechanoreceptors
monitor PO2, PCO2, pH and lung stretch
Higher centers
influence pattern by providing info regarding activity and emotions
Medulla - Ventral respiratory group (VRG)
- MAINTAIN OPEN AIRWAYS
- maintain muscle position pharynx, larynx, tongue
- stimulate forced ventilation
- Pre-Botzinger complex → possible pacemaker cells: stimulates DRG
Medulla - Dorsal respiratory group (DRG)
- STARTS CONTRACTION/INHALATION
- sensory info from chemo- and mechanoreceptors
- stimulates inspiratory muscles, esp. diaphragm
- Ramping pattern
Inspiration: positive feedback
Expiration: end stimulation
Pons - Pontine respiratory group (PRG)
- coordinate respiratory movement
- receives info from higher centers & DRG & sends info to DRG & VRG
triangle of communications
peripheral chemoreceptors
found in aortic body and carotid bodies
* Glomus cells: receptor cells
- inactivation of K+ channels
detects PO2, PCO2 & pH
central chemoreceptors
found in medulla oblongata
- stimulation sets respiratory rhythm & depth of ventilation
- respond to [H+] in CSF
- Blood-brain barrier: H+ vs. CO2
cough reflex
Receptors in larynx, trachea, and bronchi
Deep inspiration & forceful expiration
- lower respiratory system: particulates & mucus
- prevents aspiration
*Alcohol can inhibit the reflex
sneeze reflex
receptors in nasal cavity and pharynx
Deep inspiration and forceful expiration
- upper respiratory system: particulants & irritants
noxious chemicals: olfaction
bronchoconstriction & cessation of breathing
- skunk odor
smokers can lose this reflex
Hering-Breur inflation reflex: lung stretch receptors
extreme inflation - not effective in quiet breathing
- role in infants
- closed pneumothorax
Higher brain centers:
hypothalamus and cerebrum, limbic system
1. voluntary control
- speech
2. swallowing
- can't breathe and swallow at the same time
3. underwater swimming
- hyperventilate: reduces PCO2
4. voluntary apnea: breath holding
- skeletal muscle control & reflex override
oxygen debt
the amount of oxygen required after physical exercise to convert accumulated lactic acid to glucose