Cognitive Psychology Chapter 2 : Goldstein 4th Edition
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Action Potential
Propagated electrical potential responsible for transmitting neural information and for communication between neurons. Action potentials typically travel down a neuron's axon.
Brain imaging
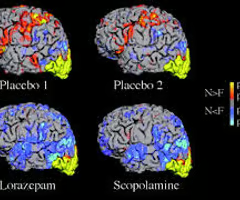
Techniques such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) that result in images of the brain that represent brain activity. In cognitive psychology, activity is measured in response to specific cognitive tasks.
Broca's aphasia
A condition associated with damage to Broca's area, in the frontal lobe, characterized by difficulty in using speech to express thoughts, but with a remaining facility for understanding speech.
Broca's area
An area in the frontal lobe associated with the production of language.
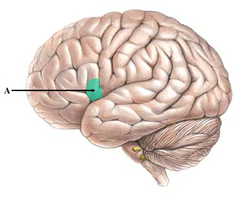
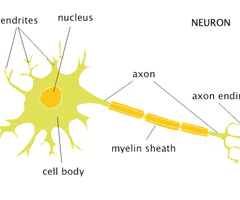
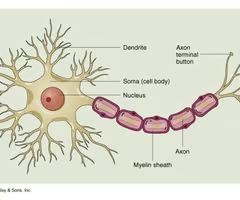
Cell body
Part of a cell that contains mechanisms that keep the cell alive. In some neurons, the cell body and the dendrites associated with it receive information from other neurons.
Cerebral cortex
The 3-mm-thick outer layer of the brain that contains the mechanisms responsible for higher mental functions such as perception, language, thinking, and problem solving.
Cognitive neuroscience
Field concerned with studying the neural basis of cognition.
Dendrites
Structures that branch out from the cell body to receive electrical signals from other neurons.
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)
A technique, based on detection of how water diffuses along the length of nerve fibers, for tracing nerve pathways and determining connections.
Distributed representation
Occurs when a specific cognitive function activates many areas of the brain.
Double dissociation
A situation in which a single dissociation can be demonstrated in one person and the opposite type of single dissociation can be demonstrated in another person (i.e., Person 1: function A is present, function B is damaged; Person 2: function A is damaged, function B is present)
Extrastriate body area (EBA)
An area in the temporal cortex that is activated by pictures of bodies and parts of bodies, but not by faces or other objects.
Feature detectors
Neurons that respond to specific visual features, such as orientation, size, or the more complex features that make up environmental stimuli.
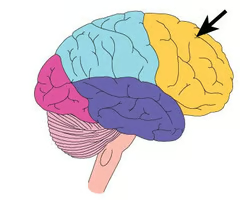
Frontal lobe
The lobe in the front of the brain that serves higher functions such as language, thought, memory, and motor functioning.
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
A brain imaging technique that measures how blood flow changes in response to cognitive activity. This technique does not involve the injection of a radioactive tracer.
Fusiform face area (FFA)
An area in the fusiform gyrus on the underside of the temporal lobe that contains many neurons that respond selectively to faces.
Hierarchical processing
Processing that occurs in a progression from lower to higher areas of the brain.
Levels of analysis
Refers to the idea that a topic can be studied in a number of different ways, with each approach contributing its own dimension to our understanding.
Localization of function
Location of specific functions in specific areas of the brain. For example, areas have been identified that are specialized to process information involved in the perception of movement, form, speech, and different aspects of memory.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Brain imaging technique that creates images of structures within the brain. Excellent for revealing structures, but does not indicate neural activity.
Microelectrodes
Small wires that are used to record electrical signals from the axons of neurons.
Nerve fiber
Part of the neuron that transmits signals from the cell body to the synapse at the end of the axon.
Nerve impulse
An electrical response that is propagated down the length of an axon (nerve fiber). Also called an Action potential.
Nerve net
A network of continuously interconnected nerve fibers (as contrasted with neural networks, in which fibers are connected by synapses).
Neural circuit
group of interconnected neurons that are responsible for neural processing.
Neural network
groups of neurons or structures that are connected together
Neural representation
States that everything a person experiences is based not on direct contact with stimuli, but on representations in the person's nervous system.
Neuron
Cell that is specialized to receive and transmit information in the nervous system.
Neuron doctrine
The idea that individual cells called neurons transmit signals in the nervous system, and that these cells are not continuous with other cells as proposed by nerve net theory
Neuropsychology
the study of the behavioral effects of brain damage in humans
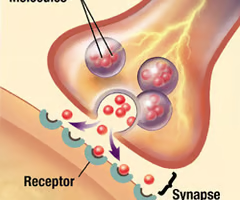
Neurotransmitter
A chemical that is released at the synapse in response to incoming action potentials.
Occipital lobe
The lobe at the back of the brain that is devoted primarily to analyzing incoming visual information.
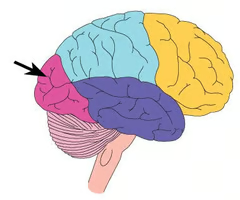
Parahippocampal place area (PPA)
An area in the temporal lobe that contains neurons that are selectively activated by pictures of indoor and outdoor scenes.
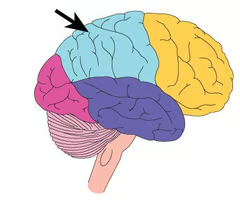
Parietal lobe
The lobe at the top of the brain that contains mechanisms responsible for sensations caused by stimulation of the skin, and also some aspects of visual information.
Population coding
Neural representation of a particular object or stimulus by the pattern of firing of a large number of neurons
Prosopagnosia
Condition caused by damage to the temporal lobe that is characterized by an inability to recognize faces.
Receptors
Specialized neural structures that respond to environmental stimuli such as light, mechanical stimulation, or chemical stimuli.
Recording electrode
When used to study neural functioning, a very thin glass or metal probe that can pick up electrical signals from single neurons. Also see Event-related potential (ERP).
Reference electrode
Used in conjunction with a recording electrode to measure the difference in charge between the two. Reference electrodes are generally placed where the electrical signal remains constant, so any change in charge between the recording and reference electrodes reflects events happening near the tip of the recording electrode.
Resting potential
Difference in charge between the inside and outside of a nerve fiber when the fiber is at rest (no other electrical signals are present).
Retina
A network of neurons that lines the back of the eye. The transformation of light into electrical signals and the initial processing of visual information occur in the retina.
Sensory code
How neural firing represents various characteristics of the environment.
Sparse coding
Neural coding based on the pattern of activity in small groups of neurons; with a majority of neurons remaining silent.
Specificity coding
The representation of a specific stimulus by the firing of neurons that respond only to that stimulus. An example would be the signaling of a person's face by the firing of a neuron that responds only to that person's face.
Synapse
Space between the end of an axon and the cell body or dendrite of the next axon
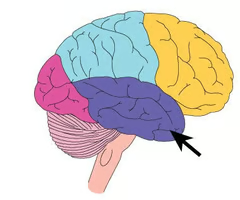
Temporal lobe
The lobe on the side of the brain that contains mechanisms responsible for language, memory, hearing, and vision.
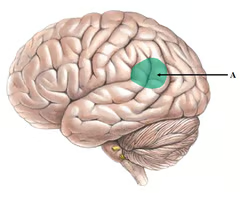
Visual cortex
Area in the back of the brain (occipital lobe) that receives signals from the eyes.
Voxel
Small cube-shaped areas in the brain about 2 or 3 mm on a side. They are not brain structures but are simply small units of analysis created by the fMRI scanner.
Wernicke's area
Area in the temporal lobe associated with understanding language. Damage to this area causes Wernicke's apahasia.
Axon
Transmits electrical signals, can be myelinated (surrounded by a fatty insulated layer)
Terminal Button
Dispenses neurotransmitters across synapse