2 - Visual Acuity
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
When must VA testing be performed?
Always done AFTER case history
MUST be taken on EVERY patient at EVERY visit
Why is VA documented before the examination?
b/c you need to legally document VA prior to your examination.
How should established patients be tested?
Test them with glasses (D or N)
don’t need to test them w/out glasses
How should new patients be tested?
Test their vision both with AND without glasses
When doing VA, where should the examiner stand?
To the side to observe squinting, reactions & cheating
What is the standard procedure for eye coverage?
Cover the left eye first with an occluder, then test the right eye first
What are key things to observe and monitor during VA?
Facial expressions
Head and chin position (watch for tilting up to use bifocals)
Speed of reading (especially in children)
Watch for cheating (looking around the occluder)
Rule regarding parents during a child’s VA test?
Parents should remain silent to avoid negative influence; avoid letting parents scare or pressure the child
What does a ≥5 letter (1 Snellen line) change between eye exams indicate compared to a 1–2 letter change?
1–2 letters difference → Normal variability (due to fatigue, attention, etc)
≥5 letters difference → Real VA change, equal to about 1 full Snellen line (e.g., from 20/25 to 20/40)
needs to be documented & explained
What is the difference in VA between eyes suggest a normal vs abnormal issue?
Normal - 1-2 lines diff b/w both eyes
Abnormal - 2> lines (20/100 vs 20/40)
If a patient cannot see 20/20, what must be documented?
WHY they can’t see 20/20
Uncorrected ametropia? Ocular disease? Systemic disease? Amblyopia/strabismus?
When doing a Distance or Near VA on a new patient, what's normal when they read the letters w/out the occluder?
common for the patient to obtain 1-2 lines of better acuity measurement with both eyes open
If the patient attempts a line they believe they can see clearly but gets all the letters incorrect, what do you do?
Don't write the previous line as their final acuity
Instead, have them read the line above again to confirm accuracy before recording it as their end point
What is the required accommodation at 40 cm?
+2.50 D
Why do patients 40+ years old often struggle with near tasks without correction?
→ Natural accommodation decreases (b/c lens "hardens")
Fully presbyopic patients need +2.50 D add to see clearly at 40 cm
What is the primary purpose of PHVA?
helps distinguish refractive error vs ocular pathology
When should PHVA be performed?
Only if the patient is wearing their best correction (glasses/CL) AND cannot read 20/40 (corrected vision 20/40) at distance and near
When is PHVA NOT needed?
If the patient can see 20/20 with correction; or if distance is 20/40 but near is 20/20 (indicating the macula is functioning
How does a pinhole work?
→ tiny holes allow only the central, parallel rays of light to pass through
rays focus directly on the retina (macula), while out-of-focus rays are blocked
What can be interpreted if the pt’s vision improves with pinhole, vs doesn’t improve?
Improves = refractive error → needs glasses/refraction
No improvement/worse = possible ocular disease → requires slit-lamp or problem-focused exam
Why might vision worsen with pinhole in macular pathology?
→ pinhole directs light onto the macula only
Peripheral rays (which may have been using healthier retinal areas) are blocked
Why is PHVA only tested at distance and not near?
Near VA is already tested at short range with increased depth of field, so pinhole doesn’t add useful info
What is recorded if PHVA does not improve vision?
PH NI (pinhole no improvement)
What are key things to remember when doing VA on someone?
Only test with the patient’s own glasses/contacts (not someone else’s)
Always use an occluder (not the hand)
Always test vision with the patient’s habitual correction (the glasses/contacts they normally wear daily)
New patient with glasses: Take VA with + without glasses
Always test right eye first
unless the pt is returning and left eye acuity is uncertain (common in pediatric visits), test left eye first
How to test VA if pt can’t read largest letters on the screen
If the patient cannot read the largest letters (20/400), what’s the next measure?
Move them closer to the chart (or move the chart closer to them).
How to test VA if pt can’t read largest letters on the screen
If the patient cannot read the largest letters (20/400) after moving closer to the chart, what’s the next measure?
Show fingers at 1 ft (Finger Counting/FC)
Move further away until they can’t count
How to test VA if pt can’t read largest letters on the screen
If patient cannot count fingers, what is the next measure?
Wave your hand at 1 ft (Hand Motion/HM). Move further back until they cannot detect movement.
How to test VA if pt can’t read largest letters on the screen
If patient cannot detect hand motion, what is the next measure?
Light projection
Shine a penlight/transilluminator ~20″ away in different quadrants
Ask them to point toward the light
How to test VA if pt can’t read largest letters on the screen
If patient cannot locate the light source, what is the final measure?
Light perception
Patient can tell light is present but not where it’s coming from.
LP = can see light but don’t know where it is
What does NLP mean?
No Light Perception = completely blind
Distance VA
List the characteristics of the Snellen chart.
Variable spacing b/w letters and lines (no mathematical progression)
Variable numbers/letters per line (not the same # of letters per line)
High-contrast black/white
uses letters A-Z
Use: Most common in the US
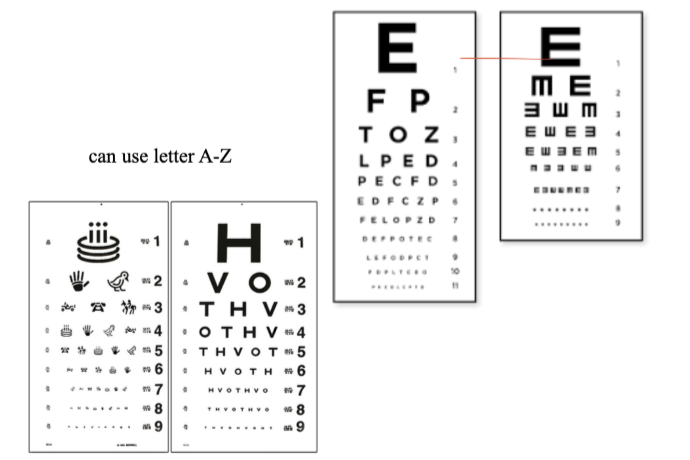
Distance VA
List the characteristics of the Bailie Lovie/EDTRS chart.
Features 5 equally legible optotypes per line
Constant spacing
Constant logarithmic progression line-to-line
Use: Low Vision & Research Clinics
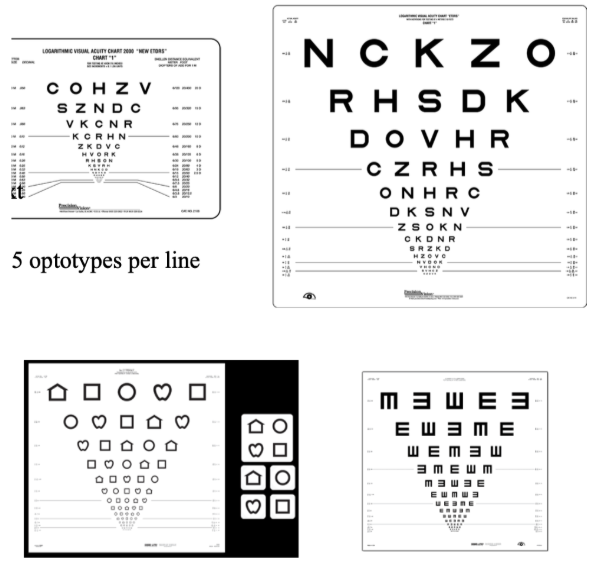
Distance VA
List the characteristics of wall charts.
Simple for screenings
Fixed illumination
Use: Vision screenings, medical offices
Distance VA
List the characteristics of Projectors.
Bulbs may reduce contrast
Limited randomization
Use: Pediatric practices
Distance VA
List the characteristics of Electronic Charts.
Excellent contrast
Fast
Randomizable
Multiple chart types (Snellen, EDTRS, LEA)
Use: Modern exam rooms
Near VA
List the characteristics of the reduced Snellen Acuity Card.
→ Tests at 40 cm (16")
20/20 letter subtends 5 minutes of arc
Not 5 letters per line
Near VA
List the characteristics of the Bailey-Lovie Format Near Card
→ Test at 40 cm/16"
More standardized than Snellen
Logarithmic progression and uniform spacing
Near VA
List the characteristics of the Jaeger Acuity Card.
→ Test at 14"
Not standardized
has no Snellen equivalent
List some examples of charts used in Non-Literate individuals or Children.
Tumbling E
Landolt C
Cardiff Cards
Broken Wheel
LEA Symbols
Patti Pics
HOTV
What are rods?
120 million
High sensitivity in dim light (scotopic vision)
↓ VA potential
Located in peripheral retina
What are cones?
6 million
High acuity & color vision (photopic vision)
↑ VA potential
Densest in the macula/fovea
Why does the fovea offer the best VA?
In fovea (1 cone: 1 ganglion cell) → extremely sensitive input
Outside fovea: 3-6 cones: 1 ganglion cell → signals combined, less detail
Rods: 75,000 rods: 1 ganglion → signals heavily summed, much less detail
Visual acuity is a ___________ Measurement. This is because it combines _______ + ____________.
Visual acuity is a Psychophysical Measurement.
combines physical process (light capture) & psychological process (interpretation of neural signals)
Define spatial vision.
ability to detect variations in luminance/contrast
Define Detection Acuity.
→ Distinguish target from background (e.g., spotting a star)
10 – 20 sec of arc
Define Resolution Acuity.
→ Detect 2 objects as separate (e.g., two distinct stars)
1 minute of arc
Define Vernier Acuity.
→ Detect small misalignments b/w two lines
5 sec of arc
Define Recognition Acuity.
→ Identify symbols (letters, numbers)
requires resolving and recognizing (Snellen chart)
What is the current Minimum Angle of Resolution (MAR) potential (Snellen)?
1 min of arc
What is the MAR potential for a "Perfect eye in a Perfect world"?
0.5 min of arc (30 seconds of arc)
Why doesn’t everyone see 20/10?
1) Anatomical arrangement of cones
if grating is too small brain can't perceive the grating
2) Aberrations of the optical system of the eye (e.g., corneal curvature)
How to calculate Optotype Size?
H = ____m x (tan 0.08333°)
multiply answer by 1000
round to 3 decimal places (e.g., 8.726mm)
What are the main limitations of VA?
1) Optical Clarity – Light must pass clearly through cornea, aqueous, lens, vitreous
Aberrations & diffraction can blur the image
2) Retinal Focus – Image must be focused on the retina
Errors: myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism.
3) Retinal Integrity – Requires healthy photoreceptors
Diseases: macular degeneration, dystrophies
4) Neural Pathway – Signal must travel from retina → V1
Damage (stroke, tumor, trauma, MS) ↓ VA.
5) Visual Processing – Cortex interprets the signal.
Impaired by TBI, seizures, intoxication
6) Physical Limitations
Glare: light scattering reduces contrast