Lecture 12 - Cryptography
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Cryptography
the art of secret writing
converts data into unintelligible form
must be reversible
process of encryption and decryption
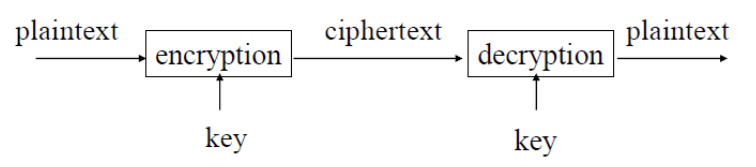
Plaintext
encryption (key)
ciphertext
decryption (key)
plaintext
plaintext
a message in its original form
Ciphertext
a message in the transformed, unrecognized form
Encryption
the process that transforms a plaintext into a ciphertextd
decryption
the process that transforms a ciphertext to the corresponding plaintextkey
Key
the value used to control encryption/decryption
Caesar Cipher
moving each letter of plaintext n number of times to the right
to decrypt, you move it backwards (left)
symmetric
single key
the key used to encrypt a message is the same as the one used to decrypt it
Asymmetric
Public key
key to decrypt a message is different from the key used to encrypt it
Algorithm & key
single key encryption
two pieces of identical information encrypted with the same algorithm but with different keys produce completely different ciphertexts
do not need to keep algorithm secret, just the key
key is small (number of bits)
brute-force attacks
try all possible keys on some ciphertext until get an intelligible translation into plaintext
on average half of all possible keys must be tried to achieve success
Key management
with symmetric encryption, the communicating parties must share the one key
Data Encryption Standard (DES)
Single Key
developed in mid 1970s
used 56-bit key
broken by experts in less than a day
Triple DES (3DES)
3 different keys to produce the encrypted text
Advanced encryption standard (AES)
most advanced computers and techniques available today
will require 150 trillion years to break by brute force
life span: 20 years
RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman)
most popular form of asymmetric encryption
two keys:
one key (public key) is used to encrypt message
second very different private key is used to decrypt the message.
from 512, 1024, 2048 bits in length
one way function: once it is encrypted by the one way function, the message cannot be decrypted without the private key
RSA Key Pair
Public key to encrypt the message
Private key to decrypt the message
RSA Key Length
RSA key sizes can be 512, 1024, or 2048 bits long. Larger key sizes provide stronger security.
RSA One-Way Function
RSA uses a one-way function—once encrypted, the message cannot be decrypted without the private key, ensuring secure communication.
Public key encryption benefits
reduce the key management problem
key management problem is reduced to the on-site protection of the private key