Interference, Diffraction, and Optical Filters
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Interference
Superposition of overlapping waves creating patterns.
Diffraction
Bending of light around obstacles.
Young's Experiment
Demonstrates light wave interference using slits.
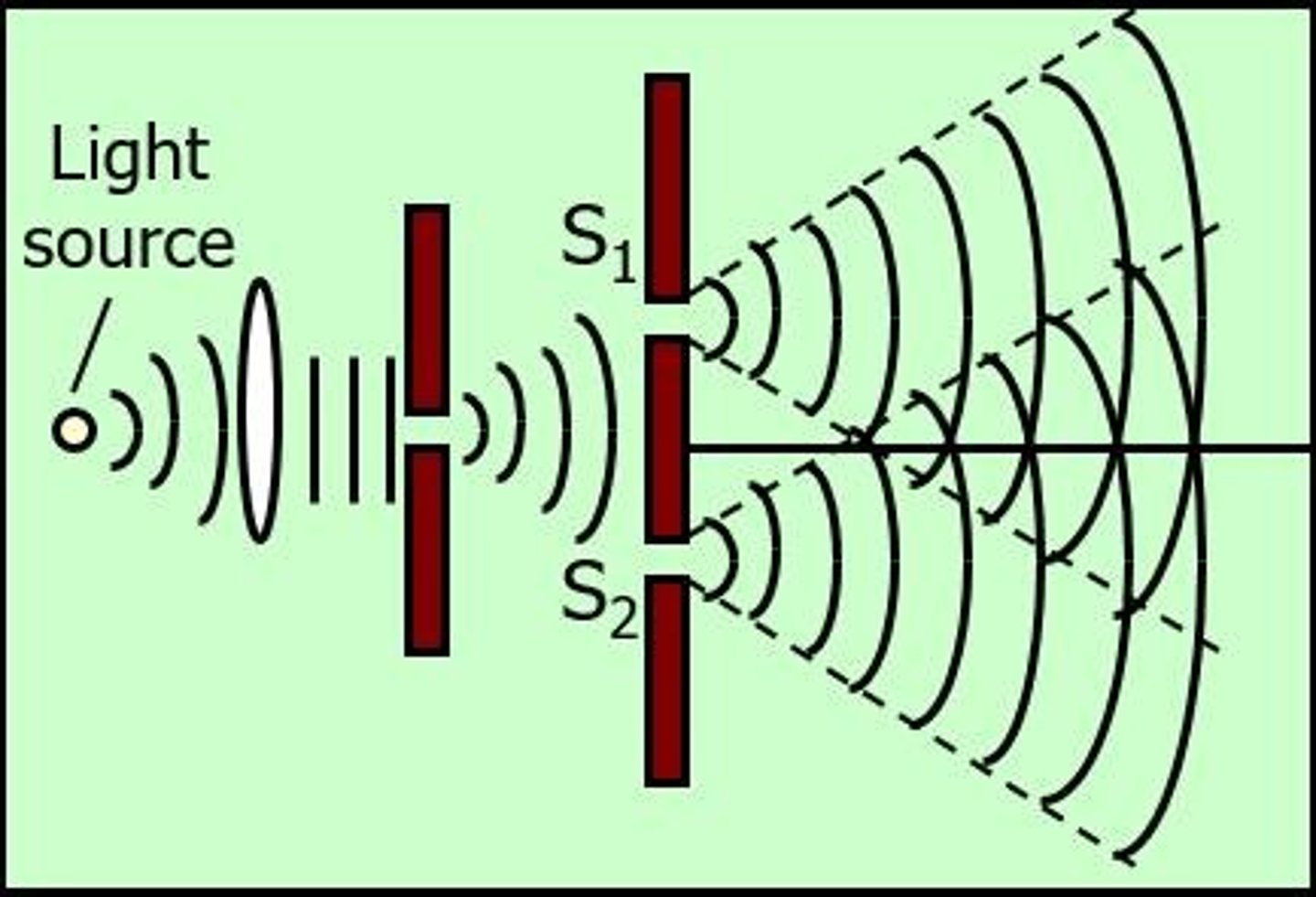
Constructive Interference
Waves combine for increased amplitude at bright fringes.
Destructive Interference
Waves combine for decreased amplitude at dark fringes.
Path Difference
Difference in distance traveled by two waves.
Fringe Pattern
Alternating bright and dark bands on a screen.
Sinc Function
Mathematical function describing diffraction patterns.
Airy Disc
Central bright spot in diffraction pattern.
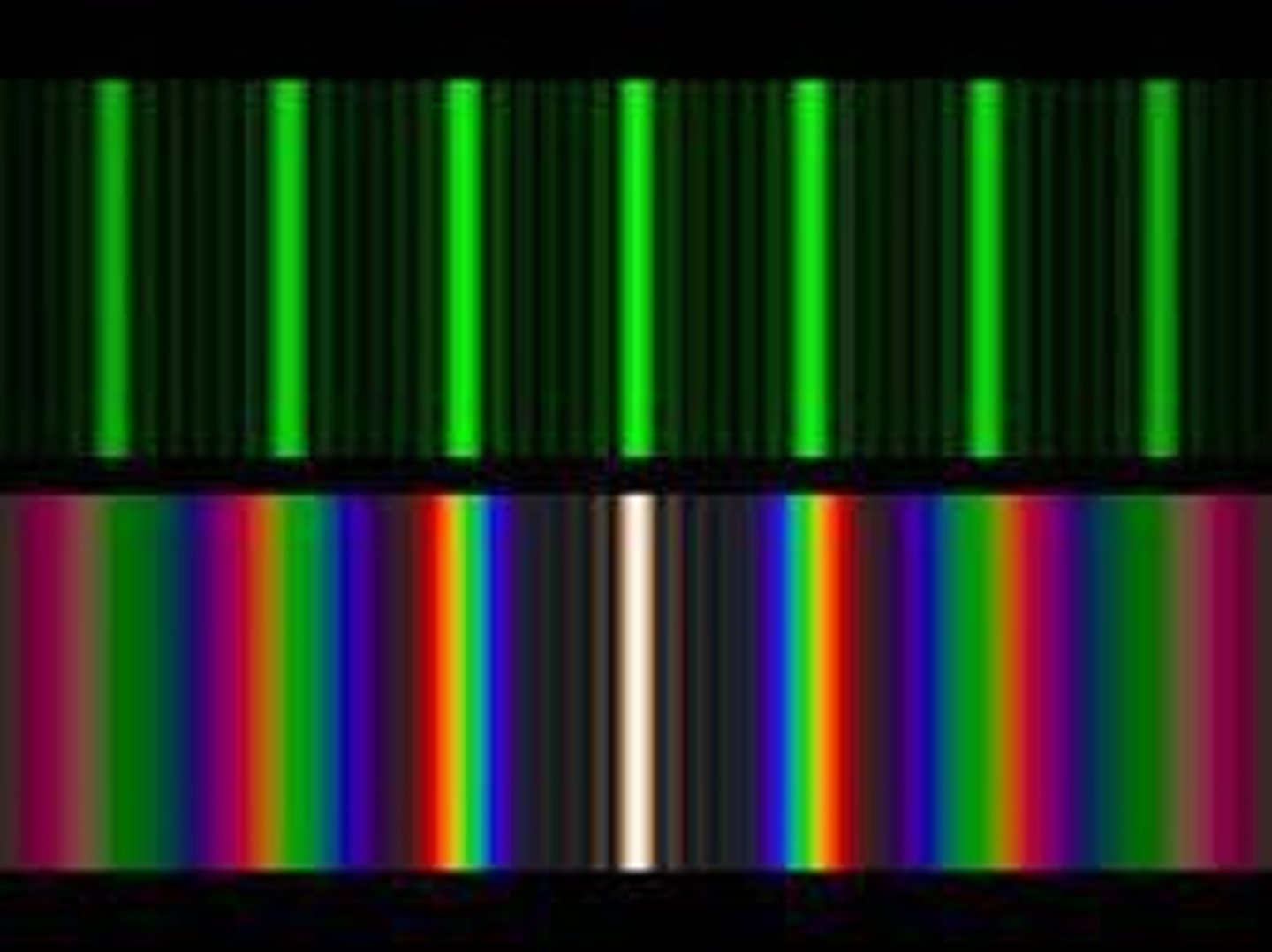
Resolution Limit
Minimum separation to distinguish two images.
Rayleigh Criterion
Condition for resolving two close objects.
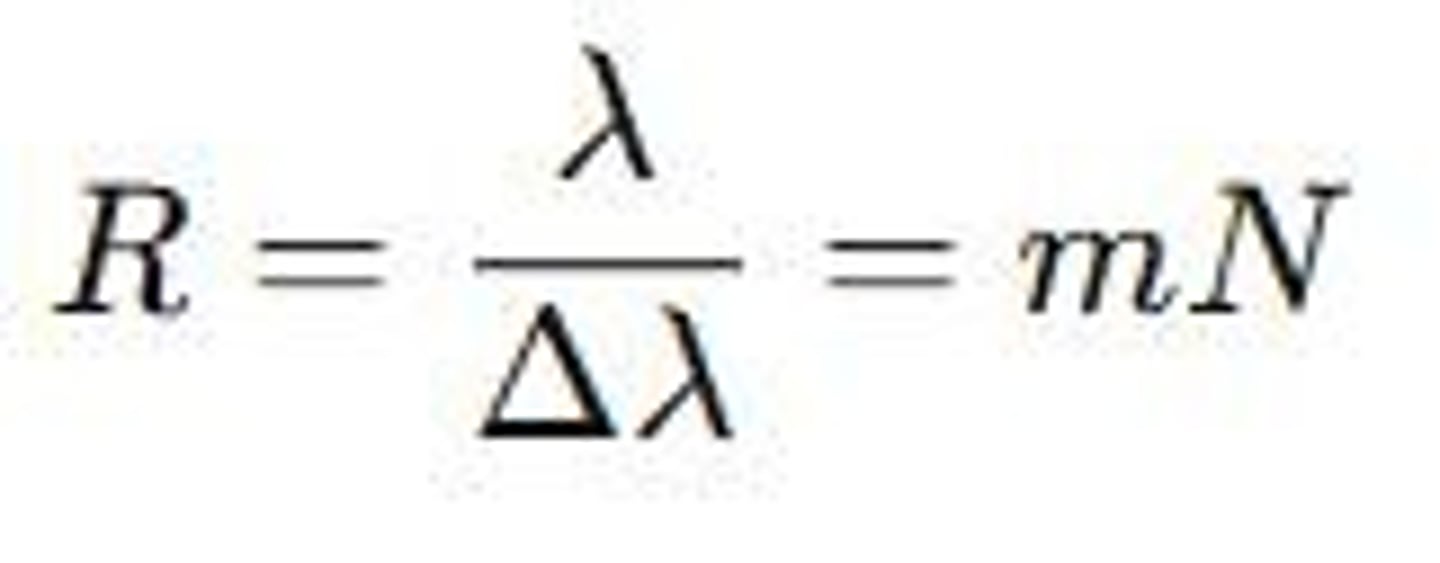
Diffraction Grating
Multiple slits creating enhanced interference patterns.
Grating Equation
d sin q = nλ relates angle and wavelength.
Resolving Power
Ability to distinguish closely spaced images.
Slit Width (d)
Distance between adjacent slits in a grating.
Wavelength (λ)
Distance between successive peaks of a wave.
Angular Deviation (q)
Angle at which light is diffracted.
Order of Diffraction (n)
Integer representing the fringe number.
Central Maximum
Brightest point in an interference pattern.
Dark Fringe Location
Position of minimum intensity in interference.
Bright Fringe Location
Position of maximum intensity in interference.
Example Calculation
Using given values to find fringe positions.
Slit Separation
Reciprocal of lines per mm measurement.
Angular Deviation
Angle of light change due to diffraction.
Grating Density
Number of lines per mm on a grating.
Order of Bright Fringe
Number indicating the fringe's position.
Laser Filters
Must sharply cut on/off due to narrow wavelengths.
Long Pass Filter
Transmits wavelengths above a specified cut-on.
Short Pass Filter
Transmits wavelengths below a specified cut-off.
Band Pass Filter
Transmits a narrow range of wavelengths.
Neutral Density Filter
Reduces intensity without wavelength discrimination.
Absorption Filter
Colored glass that absorbs unwanted light.
Dichroic Filter
Redirects light at 45° angle, allows transmission.
Diffraction
Departure from geometric optics causing light patterns.
Interference
Interaction of light waves causing patterns.
Thin Film Interference
Light reflected at interfaces alters interference patterns.
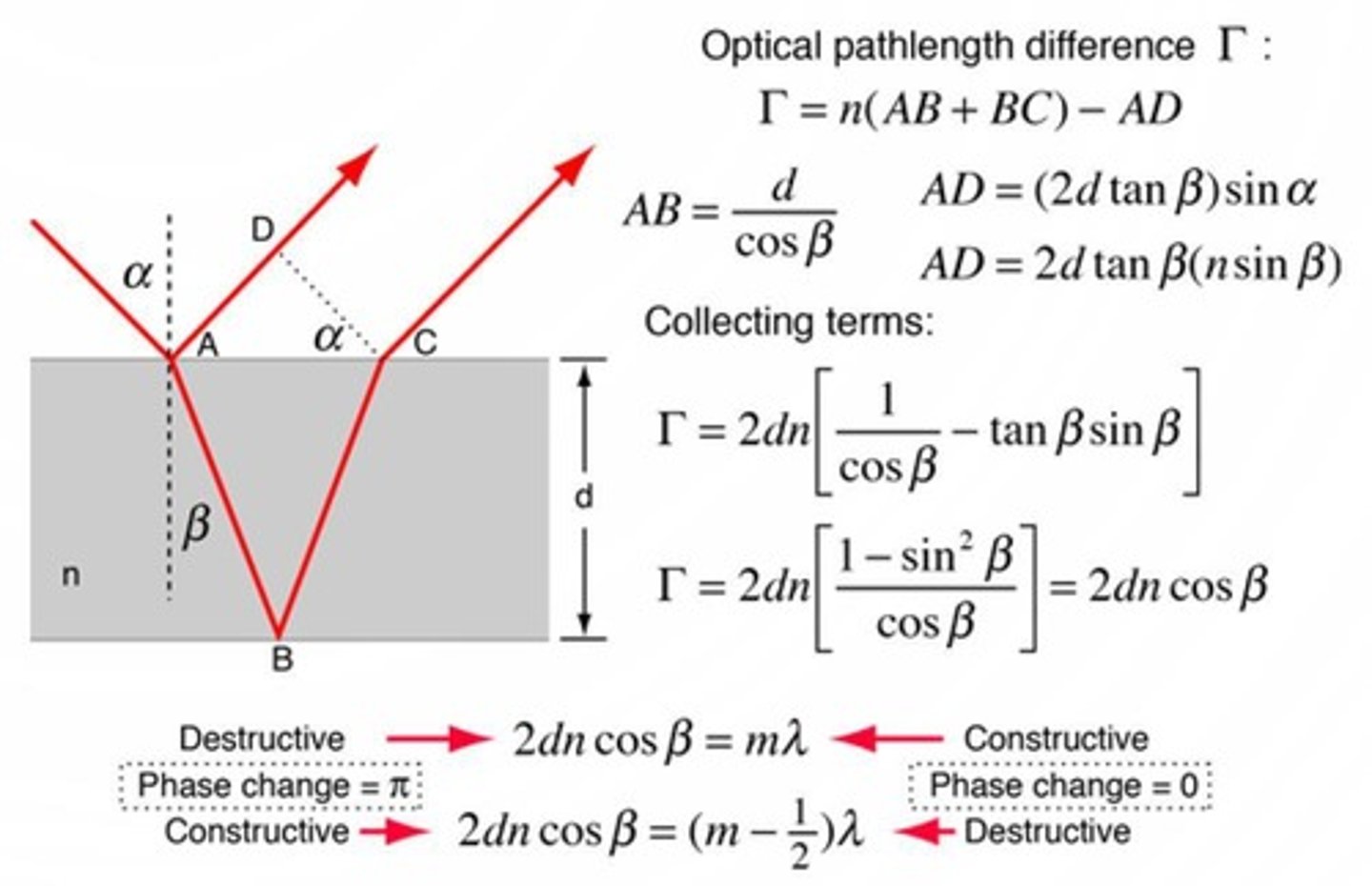
Interference Filters
Reflect unwanted wavelengths using thin layers.
Constructive Interference
Waves combine to amplify light intensity.
Destructive Interference
Waves combine to reduce light intensity.
Dielectric Material
Insulating material used in interference filters.
Bragg's Dielectric Mirrors
Used to direct light in different spectral regions.
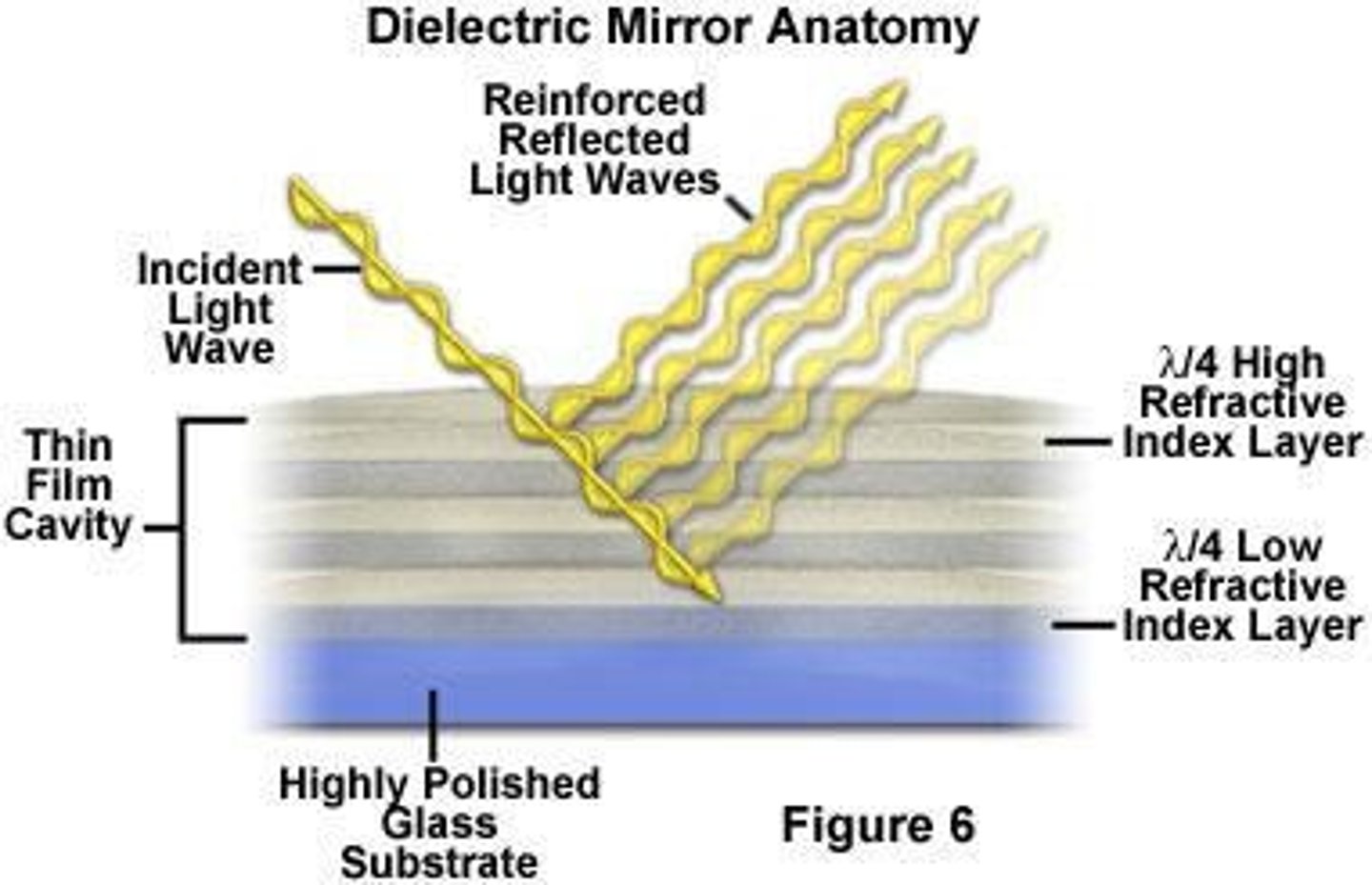
Optical Filter Design
Determined by layer thickness and light angle.
Dichroic Definition
Greek for 'two colors', used in filters.
Filter Thickness Calculation
Based on wavelength and refractive index.
Dichroic
Greek term for two colors in filters.
Dichroic Filter
Reflects and transmits specific light wavelengths.
Transmitted Light
Light that passes through a filter.
Reflected Light
Light that bounces off a surface.
Absorptive Filters
Filters that absorb unwanted light wavelengths.
Coloured Glass Filters
Filters made of dyed glass or plastic.
Fluorescence
Emission of light by a substance after absorption.
Bandpass Filters
Allow specific wavelength range to pass.
Full Width at Half Maximum (FWHM)
Width of a bandpass filter at half peak transmission.
Notch Filters
Inverted bandpass filters that block specific wavelengths.
Long Pass Filters
Allow wavelengths longer than a cutoff to pass.
Short Pass Filters
Allow wavelengths shorter than a cutoff to pass.
Fluorescein (FITC)
A fluorescent dye with specific excitation/emission wavelengths.
Interference Filters
Filters using interference to selectively transmit light.
Blocking Properties
Ability to prevent unwanted wavelengths from passing.
Transmission Properties
Ability to allow desired wavelengths to pass.
Neutral Density Filters (N.D)
Reduce light intensity without wavelength discrimination.
Beam Splitters
Divide light into two or more beams.
Optical Filter Evaluation
Assess filter performance using stained particles.
Light Loss by Optics
Reduction of light transmission through optical materials.
Quartz Filters
Used for wavelengths < 450 nm.
Spectrofluorometer
Instrument for measuring fluorescence and filter performance.
Filter Lifetime
Duration before filters degrade and need replacement.