Microbial Genetics and Genetic Engineering Overview
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
DNA Structure
Double helix composed of nucleotides.
Gene Expression
Process from genotype to observable phenotype.
Transcription
Synthesis of RNA from a DNA template.
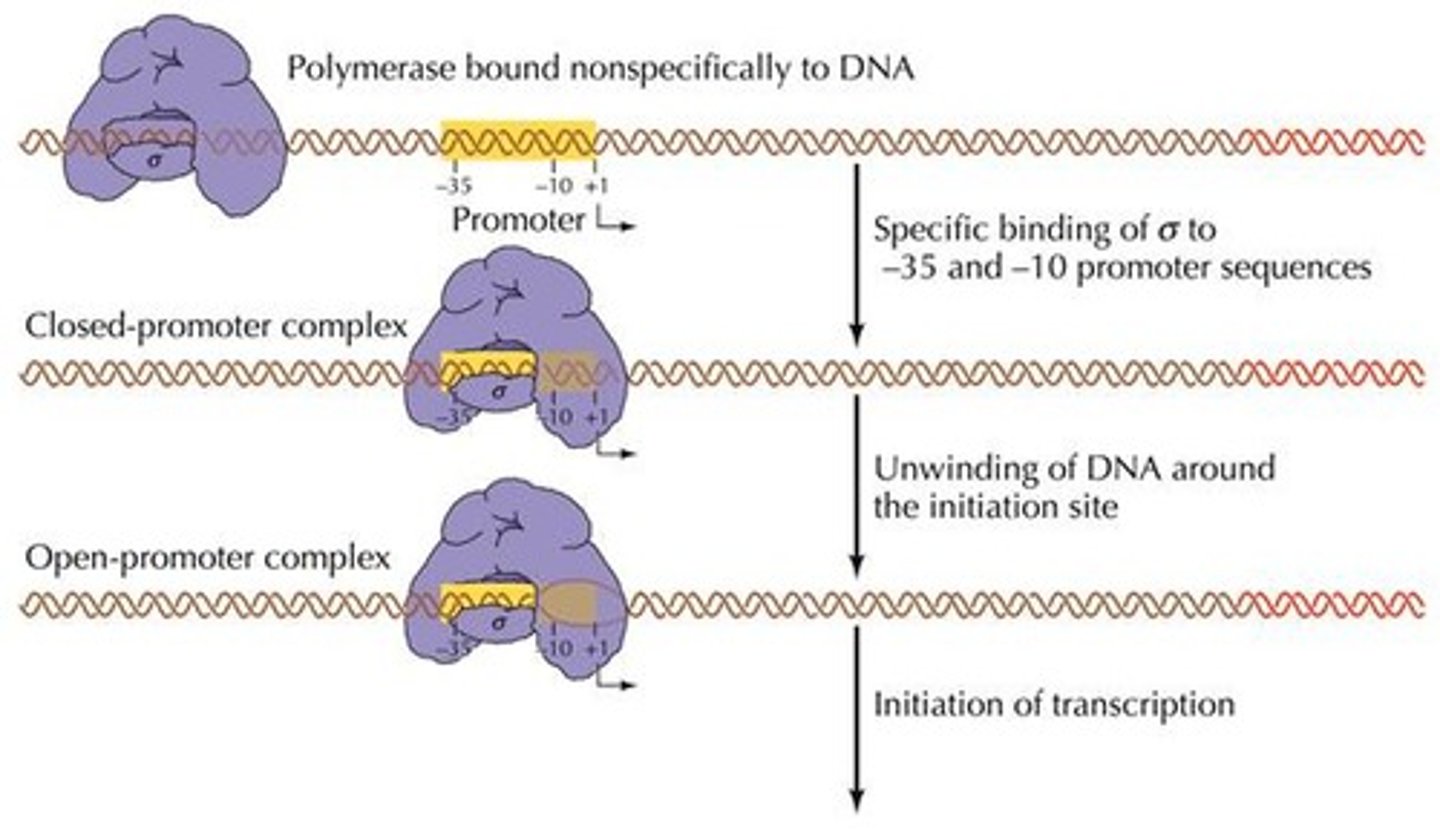
RNA Polymerase
Enzyme synthesizing RNA from DNA.
NTPs
Ribonucleoside 5′-triphosphates used in RNA synthesis.
5' to 3' Direction
Direction of RNA synthesis during transcription.
De Novo Synthesis
RNA synthesis without a primer.
Prokaryotic RNA Polymerases
Enzymes responsible for transcription in prokaryotes.
Sigma Subunit
Promoter recognition component of prokaryotic RNA polymerase.
Prokaryotic Promoters
DNA sequences initiating transcription in prokaryotes.
Initiation of Transcription
Binding of RNA polymerase to promoter region.
Elongation
RNA polymerase extends RNA strand during transcription.
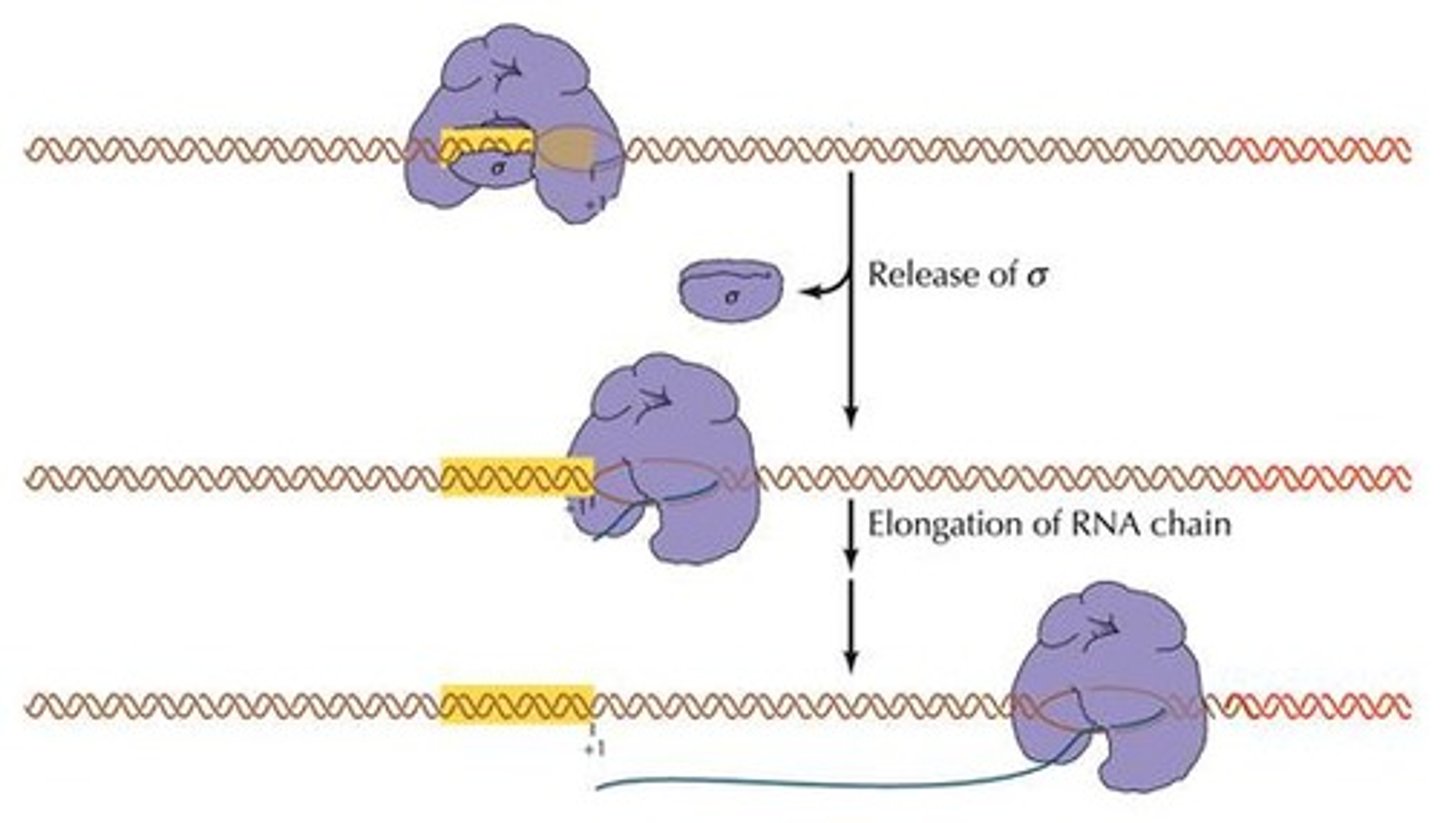
Termination of Transcription
Process ending RNA synthesis at specific sequences.
RNA Processing
Modifications of RNA after transcription.
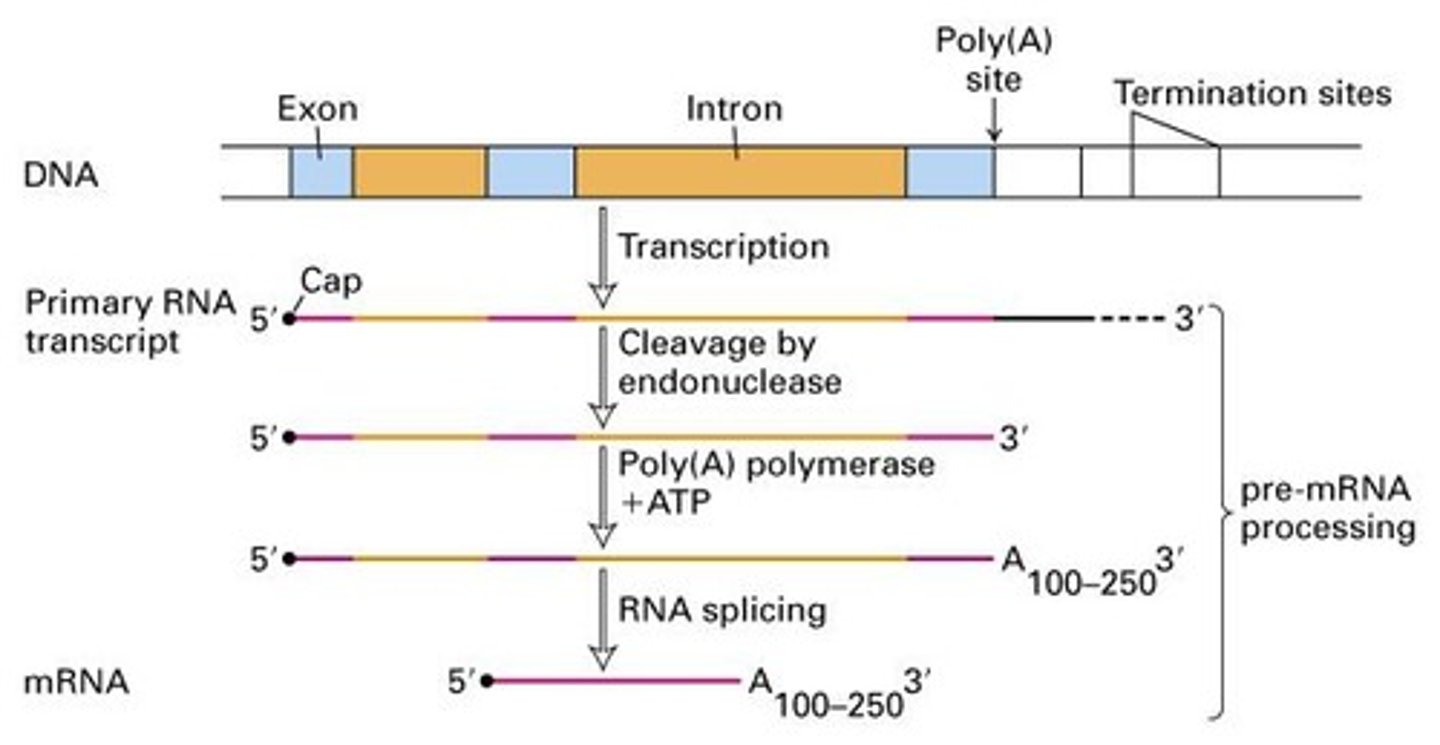
5' Capping
Addition of a methylated cap to mRNA.
3' Poly(A) Tail
Addition of adenine nucleotides for stability.
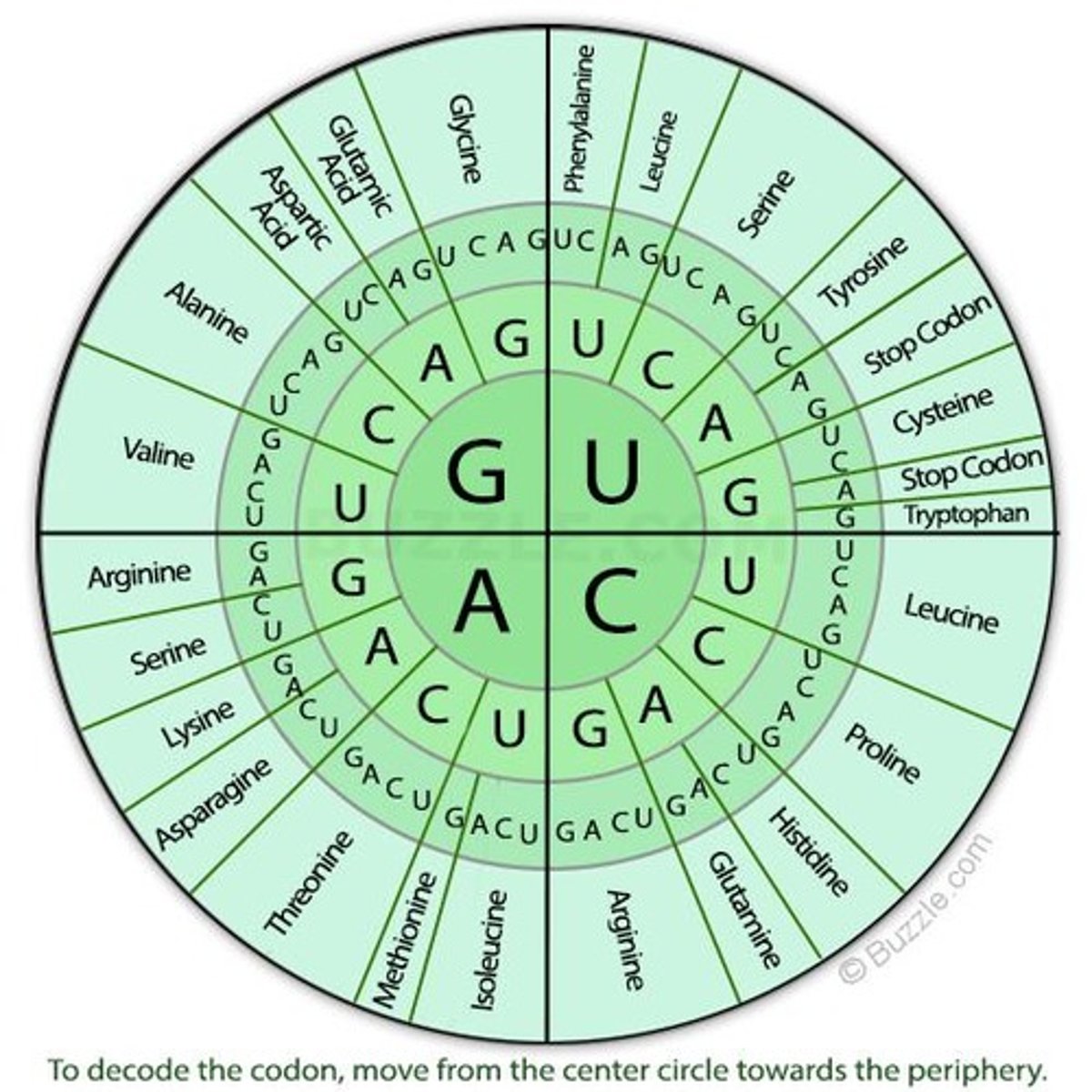
Codon
Three-nucleotide sequence coding for an amino acid.
Template Strand
DNA strand used for RNA synthesis.
Wobble Position
Flexible base pairing in codon-anticodon interaction.
tRNA
Transfer RNA transporting amino acids to ribosomes.
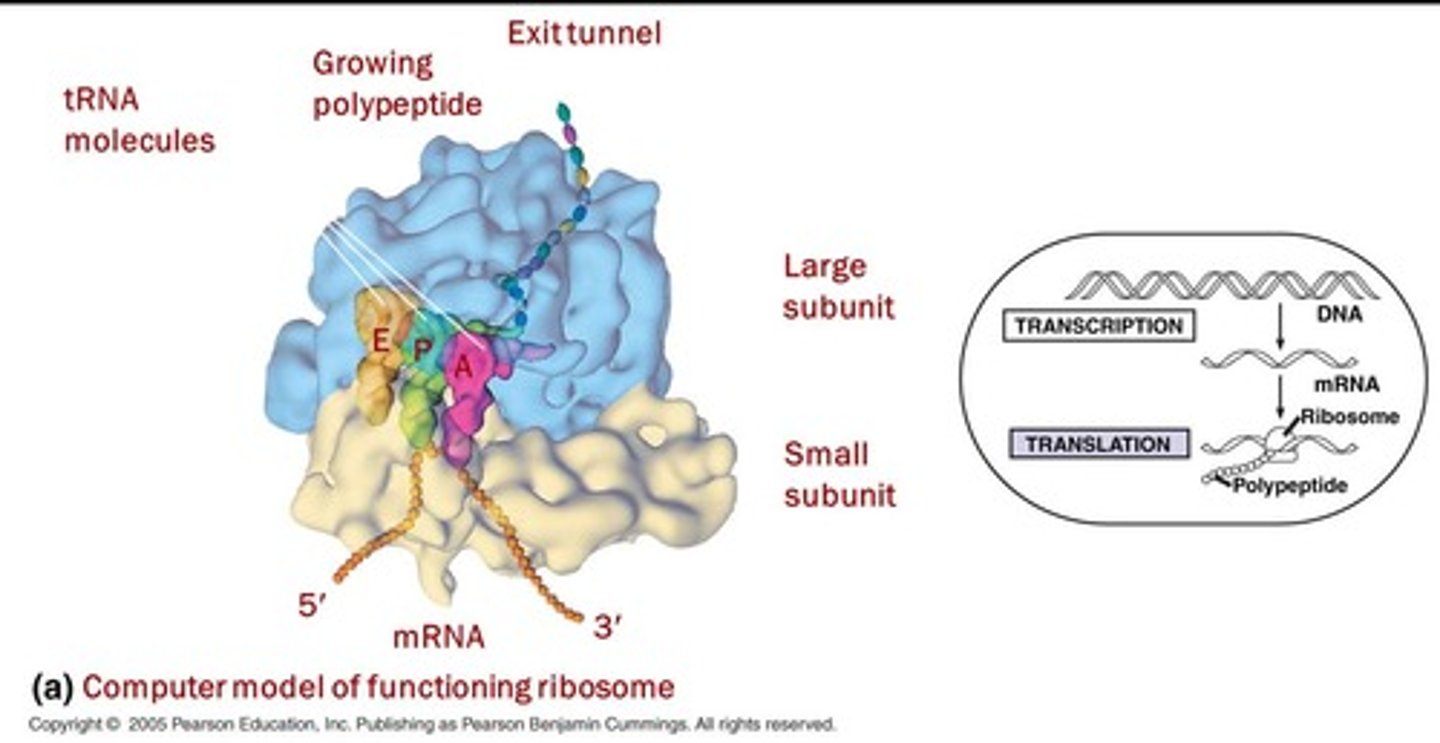
Ribosomes
Molecular machines synthesizing proteins from mRNA.
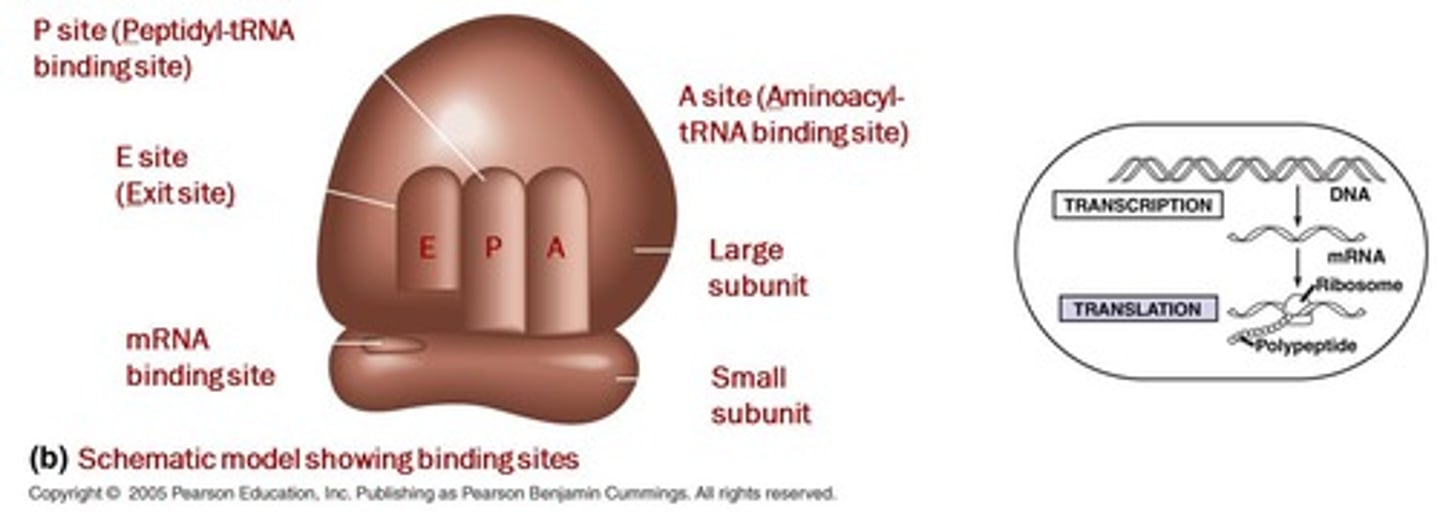
Ribosomal Binding Sites
P, A, and E sites for tRNA in ribosomes.
Charging tRNA
Attachment of amino acid to tRNA molecule.
Initiation of Translation
Assembly of mRNA, tRNA, and ribosomal subunits.
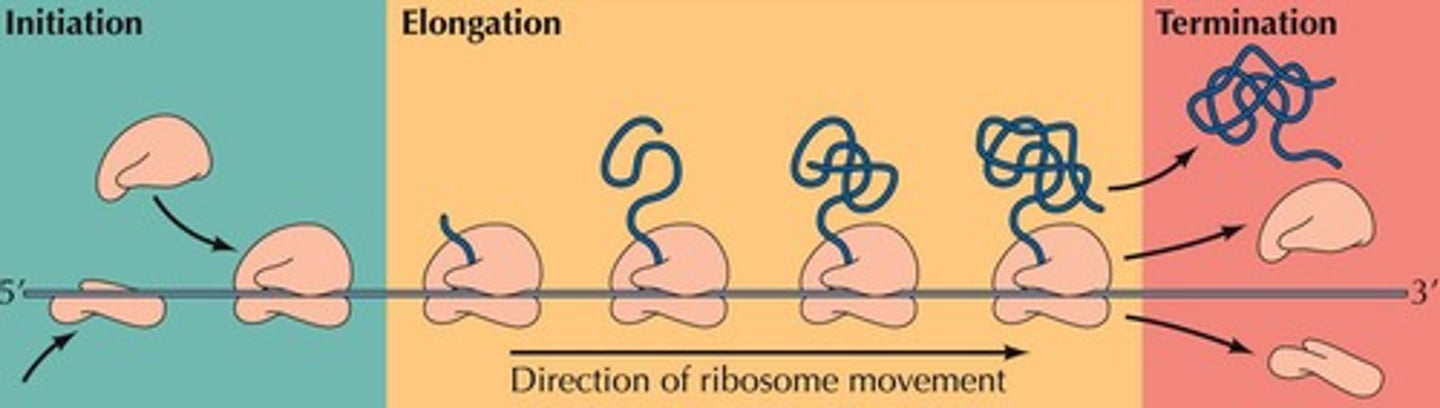
Elongation in Translation
Sequential addition of amino acids to polypeptide.
Termination of Translation
Release of polypeptide upon encountering stop codon.
Polyribosomes
Multiple ribosomes translating a single mRNA simultaneously.
Point Mutations
Single nucleotide changes affecting protein function.
Missense Mutations
Substitutions resulting in different amino acids.
Nonsense Mutations
Substitutions creating premature stop codons.
Frameshift Mutations
Insertions or deletions altering reading frame.
Mutagens
Agents causing genetic mutations.
Conjugation
Direct transfer of DNA between bacteria.
Transformation
Uptake of free DNA by a bacterium.
Transduction
DNA transfer via bacteriophages.
Recombinant DNA Technology
Combining DNA from different organisms.
Gene Therapy
Replacing faulty genes to treat diseases.
CRISPR
Genome editing tool for precise DNA modifications.
CAR T-Cell Therapy
Engineered T cells targeting cancer antigens.