Week 10 - impulsivity and delayed discounting/ trust and coop
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
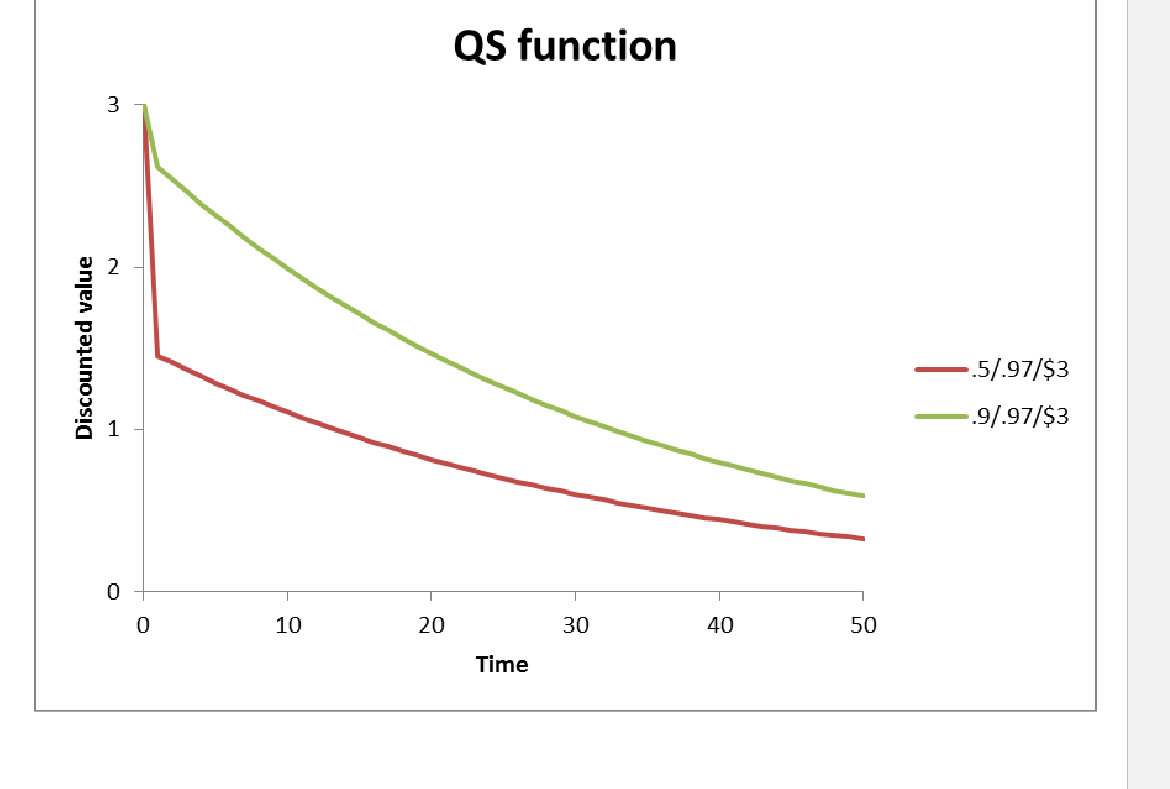
McClure et al (2004) - seperate neural systems value immediate and delayed monetary rewards
Q U A S I - H Y P E R B O L I C D I S C O U N T F U N C T I O N
smaller β =?
β × δ^t × u
β = beta is the special value placed on immediate rewards relative to future rewards (immediate - impulsive) > impact how much curve decrease near the orgin
δ = discount rate (delays - self-control) > impact how much curve decrease as delays get longer
t = time
u = value
samller β = more impulsive = faster decline in graph
activity in beta > delta
activity in delta > beta
activity in beta > delta = impulsive
activity in delta > beta = self-control
McClure et al (2004)
experimetnal design and regions of interest
subejcts choose between small/early reward and large/delayed reward
Example trials:
• $5 today and $10 in two weeks
• $5 two weeks and $40 in a month
regions of interest = PCC, MPFC, VStr, MOFC
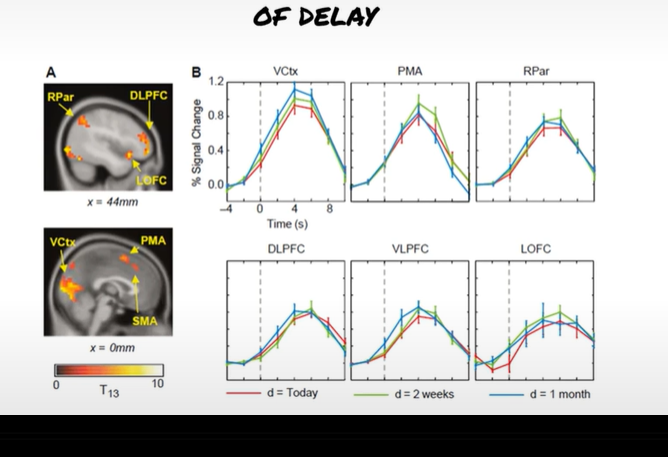
McClure et al (2004)
data tells us what?
delta regions = RPar, DLPFC, LOFC, PMA, SMA, VCTx = higehr signal to immediate regions
beta regions = PCC, MPFC, Vstr, MOFC = signal ireespective of delay > same repsosne all choices.
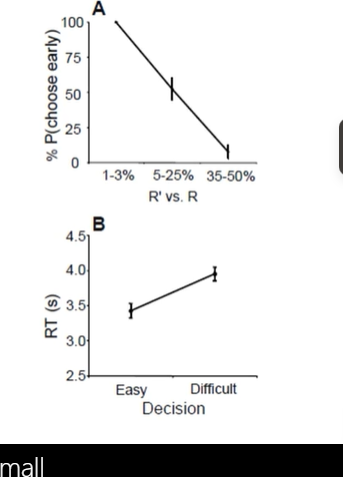
choice diff between easy and hard trials McClure et al (2004), show what about preference as diff between immedate reward and delay reward change?
when money amount differ by small (1-3), = choose immediate ($3 now vs $5 later)
when money amount differ by large (5-25%) = indifferent (3 now vs 15 later
when money amount differ by really large (25-505) = choose delay (10 now vs 200 way later)
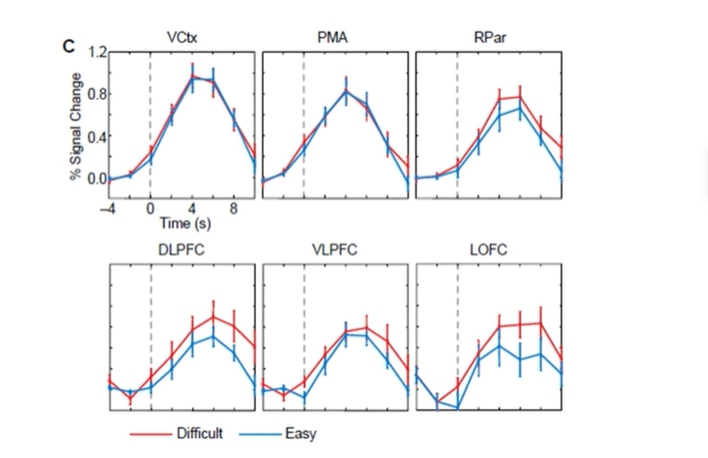
McClure et al (2004), then what?
which brains regions (beta vs delta) responded to easy vs difficult decisions
increased actiivty on diffcult trials in DLPFC, VLPFC, LOFC (delta)
the data suggest that the limbic system structures are engaged when immediate reward available
frontal brain regions are engaged when delay needs to be considered
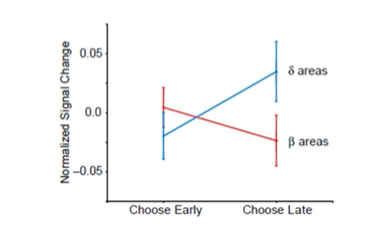
McClure et al (2004)
which brain regions are beta system
which brain regions are delta system
beta (immediate, impulsive) = PCC< MPFC, VStr, MOFC
delta (delayed, self-conftrol) = DLPFC, VLPFC, LOFC, RPar
choosing late option = delta activity higher, choosing early option = beta acitivty higher
what do McClure et al (2004) argue about choose?
math models guide neuro models
there is a competition between the beta and delta brain networks, the regions with the higher acitivty wins
beta = immediate valuation, limbic system
delta = involved in all valuation but contribute to self-control and evaluating trade-offs; prefrontal cortex
dual value system > system with greater level wins and winngin means controlling motor structure for action
while mcclure says there is a dual system, kables et al glimcher say there is a single system?
true
Kables et glimcher (2007) - neural correlates of subjective value during intertemporal choice
experimental design
immediate option is always $20, present delayed options (6 hrs, 180 days) with 6 different outcomes (20.20-110)
the immediate option is held constant and delayed options range
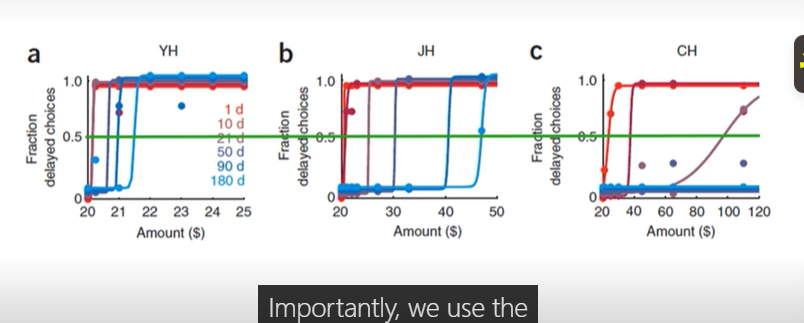
Kables et al (2007) rank from less to more impulsive
from left > right its less impulsive > most impulsive
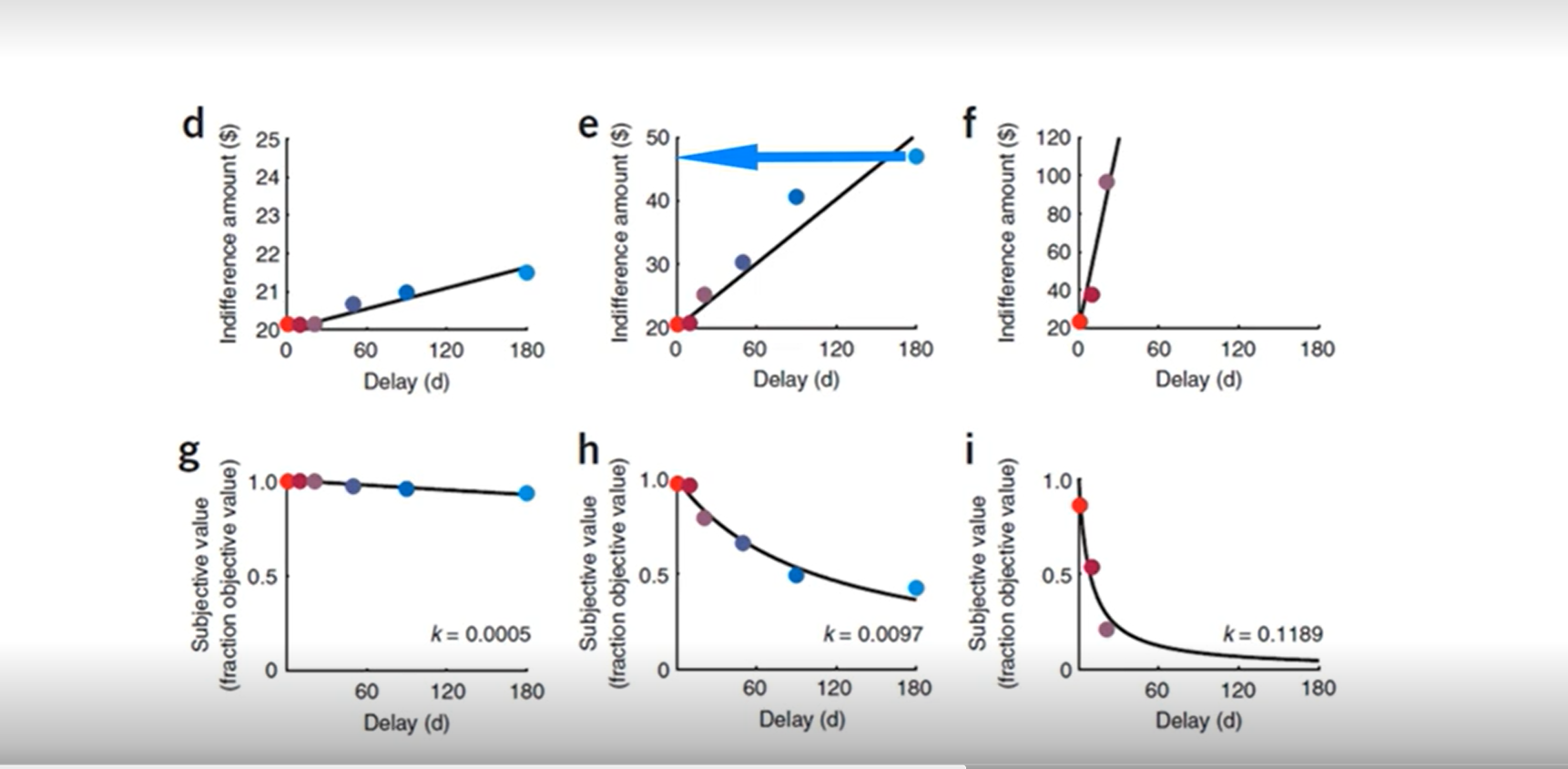
find indifference points for D-F and estimate subjective value match graphs
D) delay 180 for $21 = $20 immdeiate (20/21=0.95%) > g graph
E) delay 180 for $48 = $20 immediate (20/48=0.42%) > h graph
F) delay 50 for $99 = $20 immediate (20/99=0.20%) > i graph
objective value / subjective value = % fraction of objectice outcome delayed outcome represents
20/21
20/48
20/100
Kable et al (2007) what did brain acitvity data show?
brain activity coorelated with subjective value > data supports conclusion that a single system of brain region capable of represent immediate and delayed outcomes
MPFC, VS, PCC represent value of immediate and delayed rewards used by subjects to make decisions, directly against McClure et al.
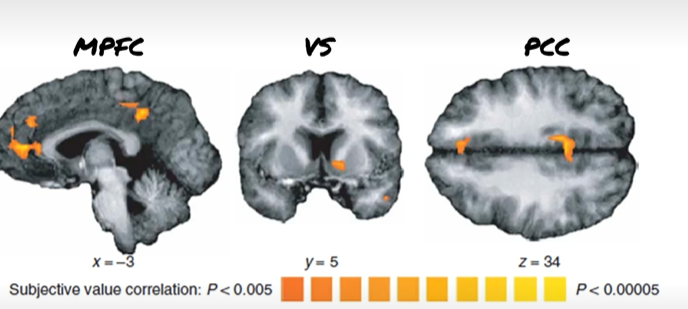
Kable et al (2007) conclusions
PCC, MFC, VS signal could reprsents subjective value of immediate and relayed outcomes
subjectively, immediate rewards are valued more than delayed rewards
Self Control
Hare et al. - self contron invovled modulatio of vmPFC
experimental design
recruited dieters for an fMRI study to look at activity in vmPFC and DLPFC > subjects rated foods from very unhealthy to very healthy and very bad to very tasty > monitored decisions related to health and taste preferences
during the decision block they are shown a netral food item and choose to eat the reference food item or the food item offered and categorized into self-controllers (SC) or non sef controllers (NSC)
Hare et al.
self-controllers (SC) vs non sef controllers (NSC)
SC = made decisions based on health and taste information; rejected most liked but unhealthy items
NSC = made decisions based on taste info only, ignored self-reported health informatoin when making decisions
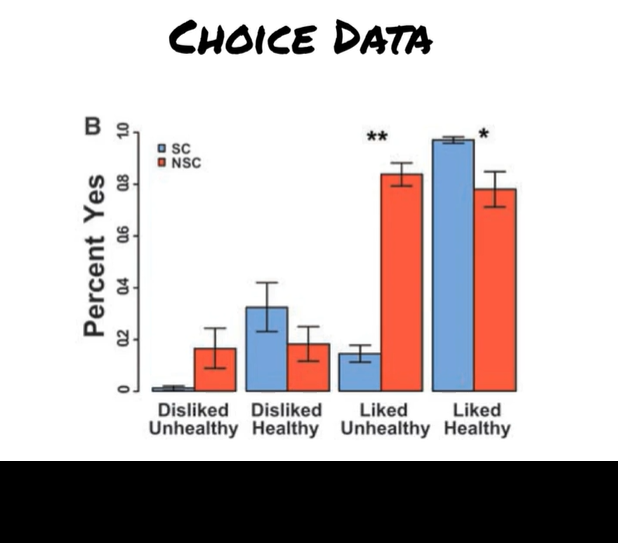
Hare et al. what does choice data show?
blue data = SC, red = NSC
SC disliked unhealthy more
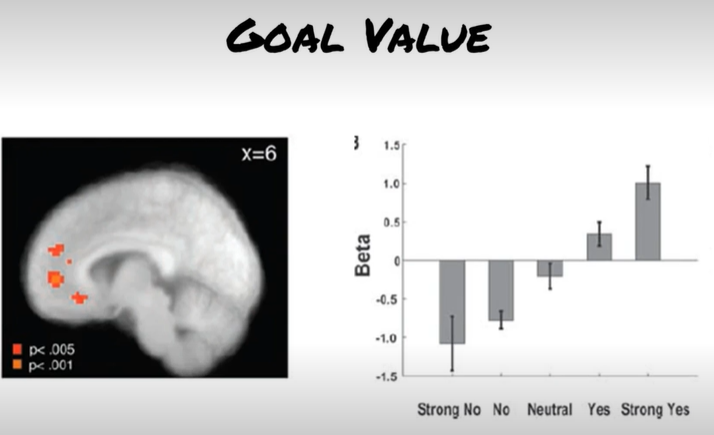
Hare et al.
Goal value data indicates..
activity in vmPFC coorelates with the subjective value fo the food item ,
strong no = weakest level of acitvity,
strong yes = highest level of activtiy
this was consistent between SC and NSC
how did vmPFC respond to taste vs health rating?
SC = signal coorelates for both for taste and health rating
NSC = signal corrolates for only taste raiting.
vmPFC reprsents subjective value of the goal itself AND value lniked to multiple dimensions of the goa
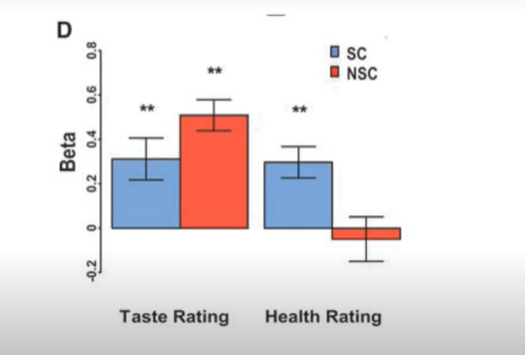
what is the pattern of activity of a brain region invovled in self-control?
on trials where subjective succesful at self control (reject liked unhealthy, or accept unliked healthy) there is more activity in DLPFC compared to trials when they dont have self control (accept liked unhealty, reject unliked healthy)
vmPFC and DLPFC interactions
DLPFC = self control signal modulates strenth of value representation in vmPFC
vmPFC = subjective value of goal information
Greater self control signal (DLPFC) correlated with decreased value signal (vmPFC) for
Liked-Unhealthy options
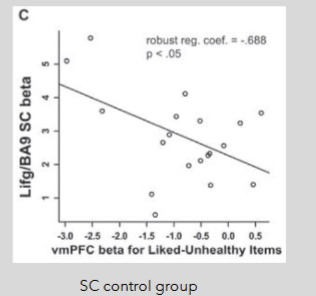
conclusions from Hare et al.
DLPFC plays a self in self-control
vmPFC represents goal value
vm PFc represnts information related to choice options (health, taste)
supports single-value system hypothesis
kind of coorborates what McClure saus about DLPFC needed in delta system for enoding value of delayed rewards!
Contrasts with McClure et al. interpretation of value encoding
◦ The delta systems might have been related to self-control
◦ Paper supports a single valuation system (vmPFC) that is modulated by self-control (DLPFC)
◦ Higher order brain systems related to self-control might have evolved to prevent
representations of short-term gains from prematurely driving actions that could prove less
valuable in the long run
Figner et al (2010)
experimental desgin
choice task
trial type: immediate/sooner smaller vs later larger
trial type: delayed sooner smaller vs later larger
varied range of differences between teh size of the reward (0.5% to 75%)
used TMS to inhibit the LPFC
Hypothesis: dual valuation mechanism
hypothesis self-control mechnism
dual valuation hypothesis > disruption of LPFC should impact valuation and choice, delta sysyem is computing the value of delayed outcomes, value computation directly influences decision process. if they disrupt the LPFC subjects should not value outcomes normally and there will be a disruption to the choice
single valuation hypothesis > LPFC does not encode value information, LPFC activity represents self-control, LPFC disruption should affect choice but not value representation
Figner et al (2010)
results
LPFC disruption increases impulsivity when immediate gains are available
Left rTMS changes behaivor, people become more impulsive by choosing the small, immediate option.
*Sham = they turned on machine noises but it wasnt actually disrupting anything.
LPFC disruption does not impact choices that dont require self-control (easy choices)
LPFC disruption did not impact choices that invovled only delayed outcomes
LPFC disruption decreases self-control when immediate outcomes are available
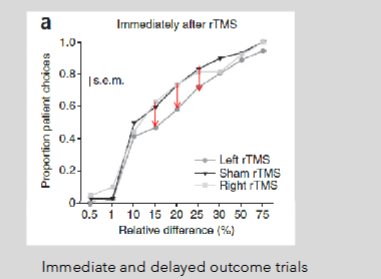
Figner et al (2010)
valuation task results
disrupting LPFC does not interfere with valuation of individual outcomes
LPFC might be like a brake pedal that stops valuation signals from directly driving choice
(self-control)
◦ Another hypothesis: LPFC could alter attention to dimensions of choice options
(attentional modulation)
◦ Gives choice mechanism more time to receive additional information regarding the value of delayed outcome
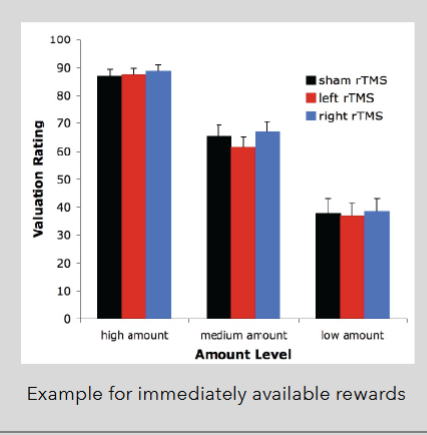
Figner et al (2010)
conclusion
LPFC might be like a brake pedal that stops valuation signals from directly driving choice
(self-control)
◦ Another hypothesis: LPFC could alter attention to dimensions of choice options
(attentional modulation)
◦ Gives choice mechanism more time to receive additional information regarding the value of delayed outcome
Trust & Cooperaton
Rilling et al. (2002) - neural basis for social cooperation
what is prisoners dilemma?
two suspected crimnals are arrested
if neither rats each other out = both 1 year in jail
if one rats the other out = 10 years in jail for quiet one, 0 years for one who rats
if both rat each other out = both 5 years in jail
Trust & Cooperaton
Rilling et al. (2002) - neural basis for social cooperation
what is prisoners dilemma assumptions?
criminals act out of self interest
they dont want to go to jail
they dont have a binding contract with each other (loyalty not obligbated)
they will never meed again (no fear of revenge)
game theory central assumption?
subjects are rational who will make the decision that will maximize utility. so players always do whats in their own interest, they both tell on each other would be the most rational outcome. and both get 5 years
What is nash equilibirum of prisoners dilemma?
unconstrained partner
CC leads to positive or negative PDE? CD?
nash equil is where both players deter (tell on the oter) because neither player can improve their outcome by changing strategy. - strategy pair for which there is no better strategy for each player given the other players strategy.
unconstrained partner = do whatever they want
cc= positive PD yay
CD = negative PD traitor!
summary on antVS
signal is observed during decision-making and feedback
during decision, may be action-value encoding
during feedback, may reflect an error signal
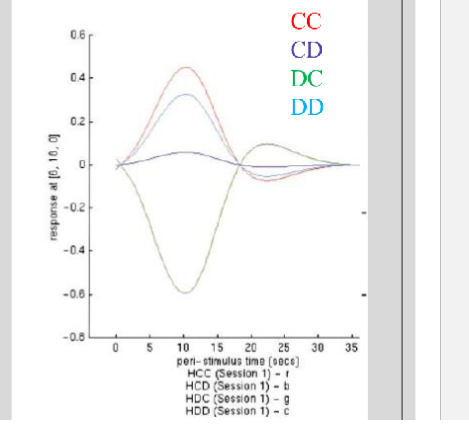
true or false, more antVS activity while observing CC outcome predicts subsequent CC trial?
true, prob of CC after CC increass as more trial outcomes are CC. correlation betwen neural activity and behavior
brain regions are sensitive to social interaction (HH vs HC)
when engaging in strategic interactions, you need to learn about your partner
trustworthiness/ willingness
Learning is supported by brain regiosn involved in representing reward/ value and linking action to these representations (antVS)
signals are consistent with prediction errors signals at time of outcome
Haroush & Williams (2015) - neuronal prediction of opponent behavior during cooperative social interchange in primate
experimental design
prisioners dilemma experiment in monkeys; cant see each others answers until end.
1) CC = 4 juice each
2) DC = 7 juice, 1 juice
3) DD= 2 juice each
Haroush & Williams (2015)
neuron response
population 1 neurons encode the monkeys decision not info about other monkey. activity is before the monkeys action, 24% of neurons encoded the monkeys choice on the current trial, 16% resposne differently to choosing cooperatoin vs denial and accurate 66% time
population 2 neurosn encode a representation of what the monkey thinks the other monkey is planning to do. activity predicted other monkey action 80% time
Haroush & Williams (2015)
impact of ACC disruption
stimulating ACC when picture presented makes monkey cooperate less.
when other monkey cooperates on a previous trials, experimental monkey more likely to choose cooperate but disrupting ACC makes experimental monkey show lower prob of cooperation.
In contrast, when other monkey denied previous trial, experimental monkey choose defect but disrupting ACC make the experimental monkeyy no change in their overall probabiltiy of cooperation/denial because prevents integration fo previous positive information
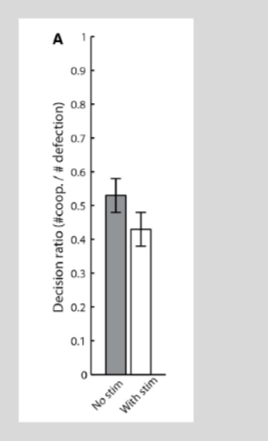
Haroush & Williams (2015)
summary
dACC may encode model of the environment
This may include explicit representation of another’s unknown behavior
two distinct groups of neurons found in dACC > one encode self and the other encodes other peoples decisions >