Chapter 18 simple harmonic motion
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
What is said to be oscillating
Anything that vibrates back and forth about a midpoint
For an oscillating object what is the midpoint
The equilibrium position
What happens to the displacement of an object as it oscillates
Constantly changes with respect to the equilibrium position
Amplitude definition
Maximum displacement of the oscillating object from equilibrium
Free vibrations definition
If amplitude is constant and no frictional forces are present oscillations are described as free vibrations
Time period definition
T, of the oscillating motion is the time for one complete cycle (T=1/f)
frequency definition
Number of cycles per second made by an oscillating object. Hz
Angular frequency definition
2π/T = 2πf unit → rads-^1
What is phase difference
Tells us how two oscillating objects with the same speed are moving with respect to each other
For two objects oscillating at the same frequency what is their phase difference
2πΔt/T (radians)
Examples of SHM
Pendulums And mass on a spring
Simple harmonic motion definition
Oscillating motion in which the acceleration is proportional to displacement and always in the opposite direction to displacement

What is a fiducial mark
The point where you measure an oscillation from
Why is the middle used for a fiducial mark
Point where the object is moving the fastest so should give the smallest uncertainty
Equations for mass on a spring
T= 2π√m/k
Force = kΔl

Springs in parallel
Spring constant= kp + kq

Springs in series
1/k = 1/kp +1/kq

Equation for a pendulum
T = 2π√l/g
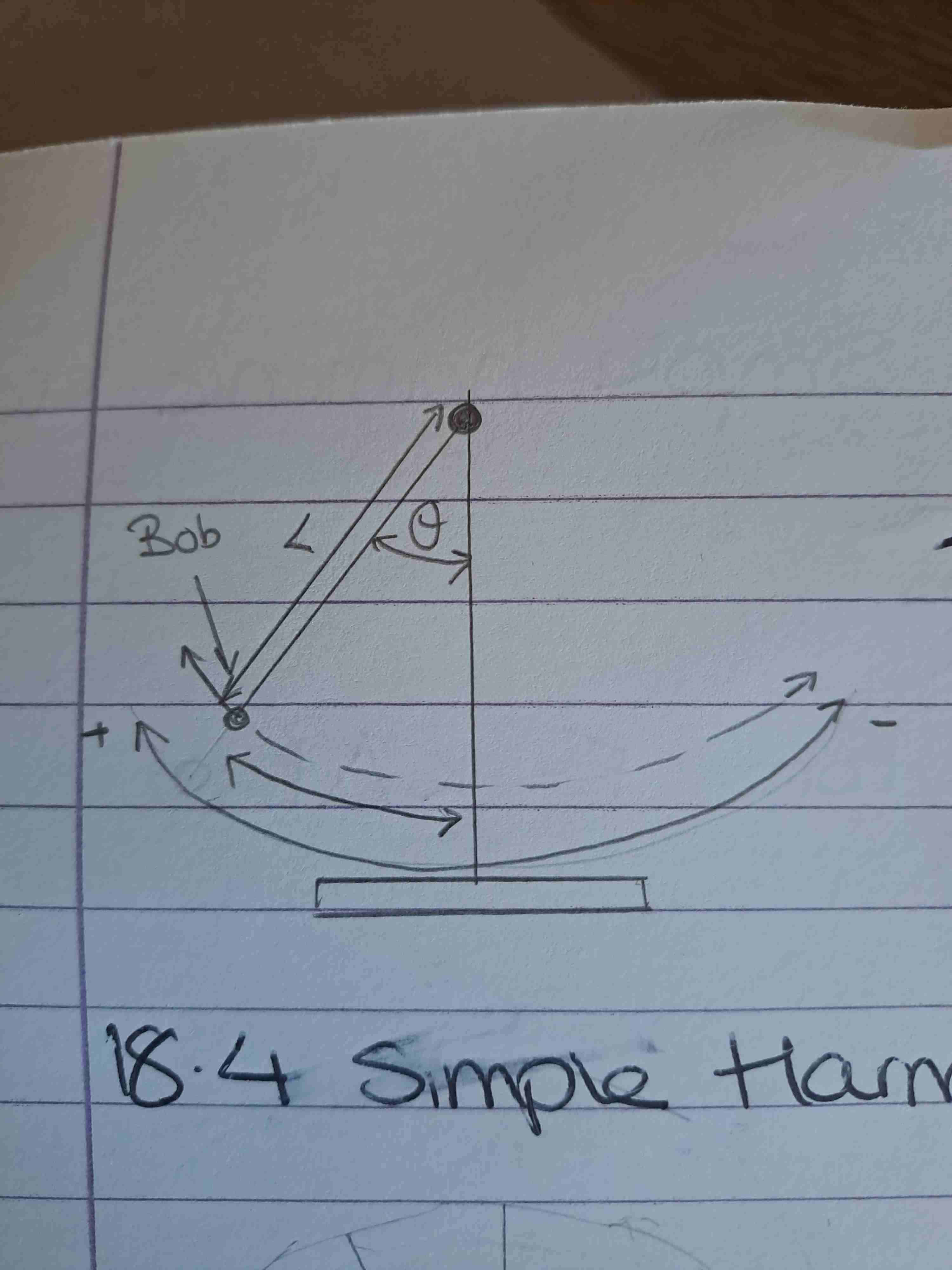
What is simple harmonic motion linked with
Circular motion
What happens to the amplitude in free oscillations
Is there is no friction the amplitude will not decrease
What happens to energy in free oscillations
Energy changes from potential to kinetic energy constantly
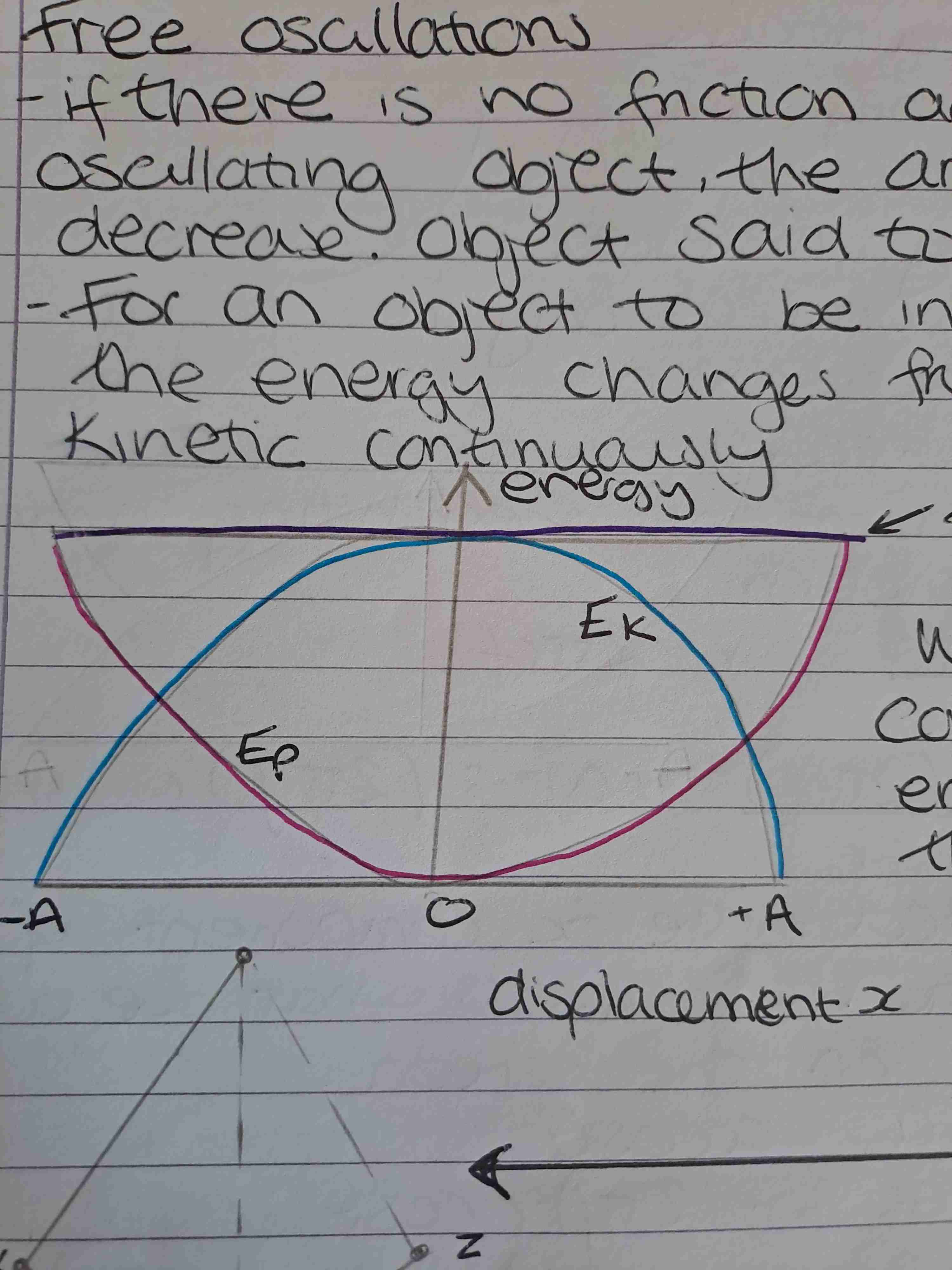
What does Etotal equal
Potential energy + kinetic energy
When a pendulum is at the midpoint what is the kinetic and potential energy
Potential energy=0
Kinetic energy= Etotal
When a pendulum is at the maximum amplitude what is the kinetic and potential energy
Potential energy = Etotal
Kinetic energy= 0
What is x
Displacement
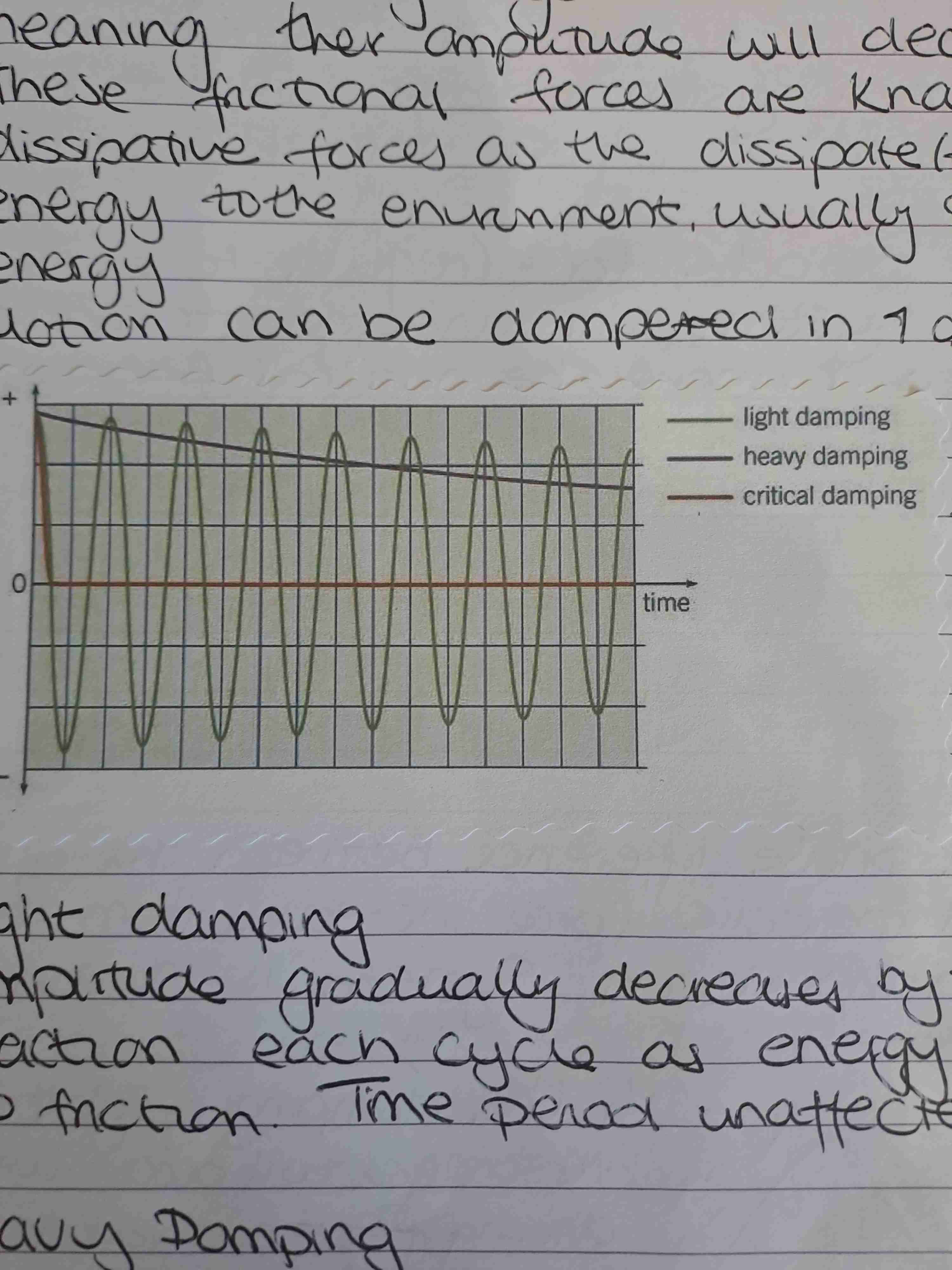
How can motion be dampened
Light, heavy and critical damping
What is light damping
Amplitude gradually decreases by the same fraction each cycle as energy lost due to friction. Time period unaffected
What is heavy damping
Friction so great no oscillations occur. The displaced object slowly returns to equilibrium
What is critical damping
Friction just enough to stop the system oscillating after it has been displaced from equilibrium. system returns to equilibrium in the shortest possible time without over shooting the equilibrium position
What type of damping do car suspension systems use
Critically damped
Damping graph
Graph
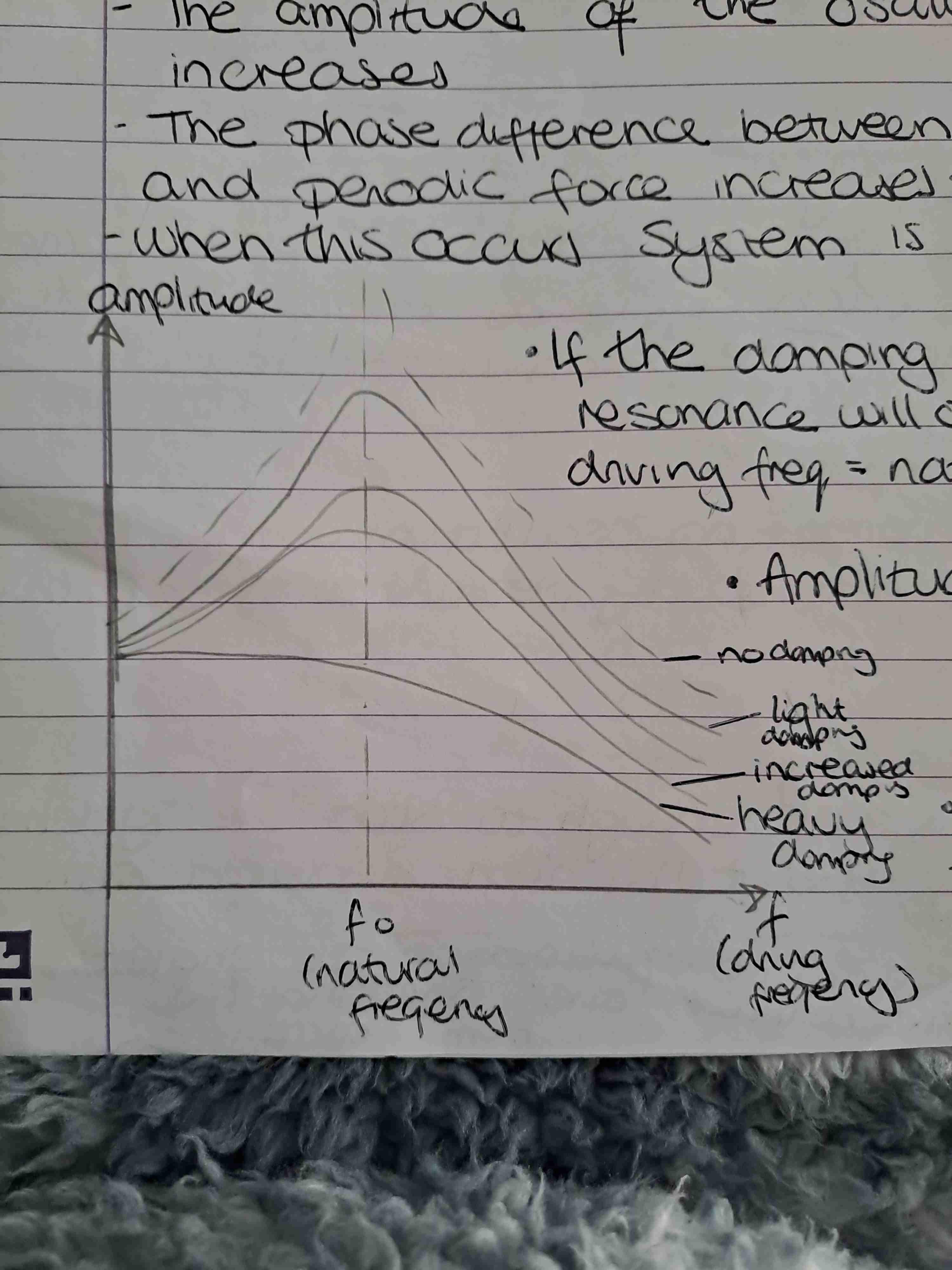
What is natural frequency
All objects have a frequency they will vibrate at known as their natural frequency
When will a system vibrate at its natural frequency
When a system vibrates without a driving force
What happens when a periodic force is applied to a system
The system will undergo forced oscillations
What happens if the periodic force is below or above the natural frequency
The system will exhibit small amplitude oscillations at the same frequency as the driver
What happens if the frequency of the driver matches the systems natural frequency
The amplitude of the oscillations dramatically increases
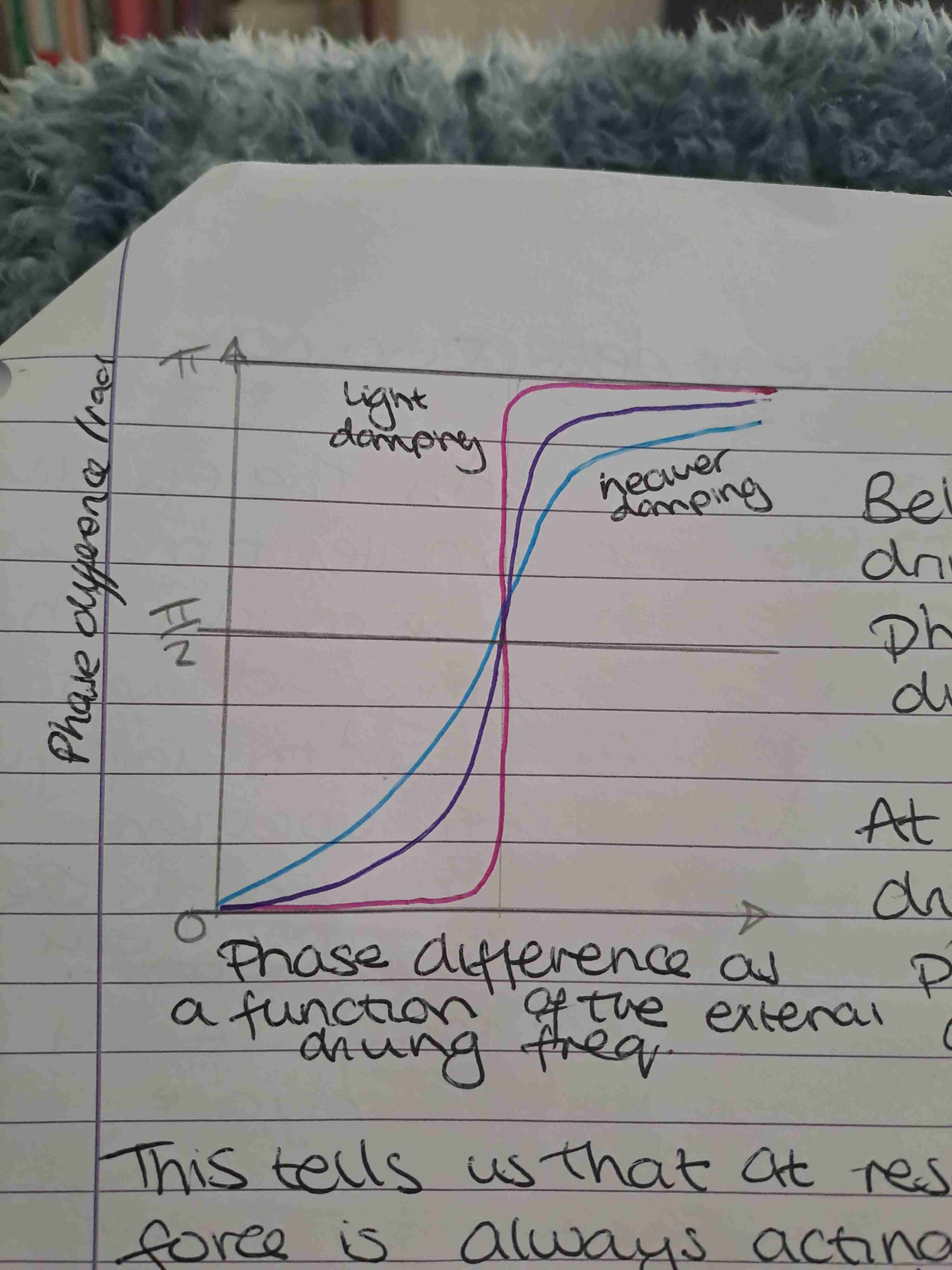
the phase difference between the displacement and periodic force increases from 0 to π/2
When this occurs the system is in resonance
If damping is light when will resonance occur
When the driving frequency equals natural frequency
What is amplitude during resonance limited by
Damping
(Heavier damping=further from natural frequency max A occurs)
Natural frequency graph
Graph
When is the driving frequency in phase with the displacement of the system
Below resonance
At resonance what is the phase difference between the driving frequency and the displacement of the system
π/2 out of phase
At resonance where does the driving force always act
At the same point in each cycle causing the amplitude to increase
Above resonance what is the phase difference between the driving frequency and the displacement of the system
π out of phase
What are the dangers of resonance and how can you remove the dangerous effects
Resonance can have dangerous effects for structures especially bridges
To avoid make structure stiffer add dampeners and change the mass
Graph of phase difference as function of the external driving frequency
Graph
What is the velocity time graph the gradient of
The displacement time graph
What is the acceleration graph the gradient of
The velocity time graph
What is the phase difference of the velocity time graph and displacement time graph
π/2
Displacement velocity acceleration time graphs
Graph
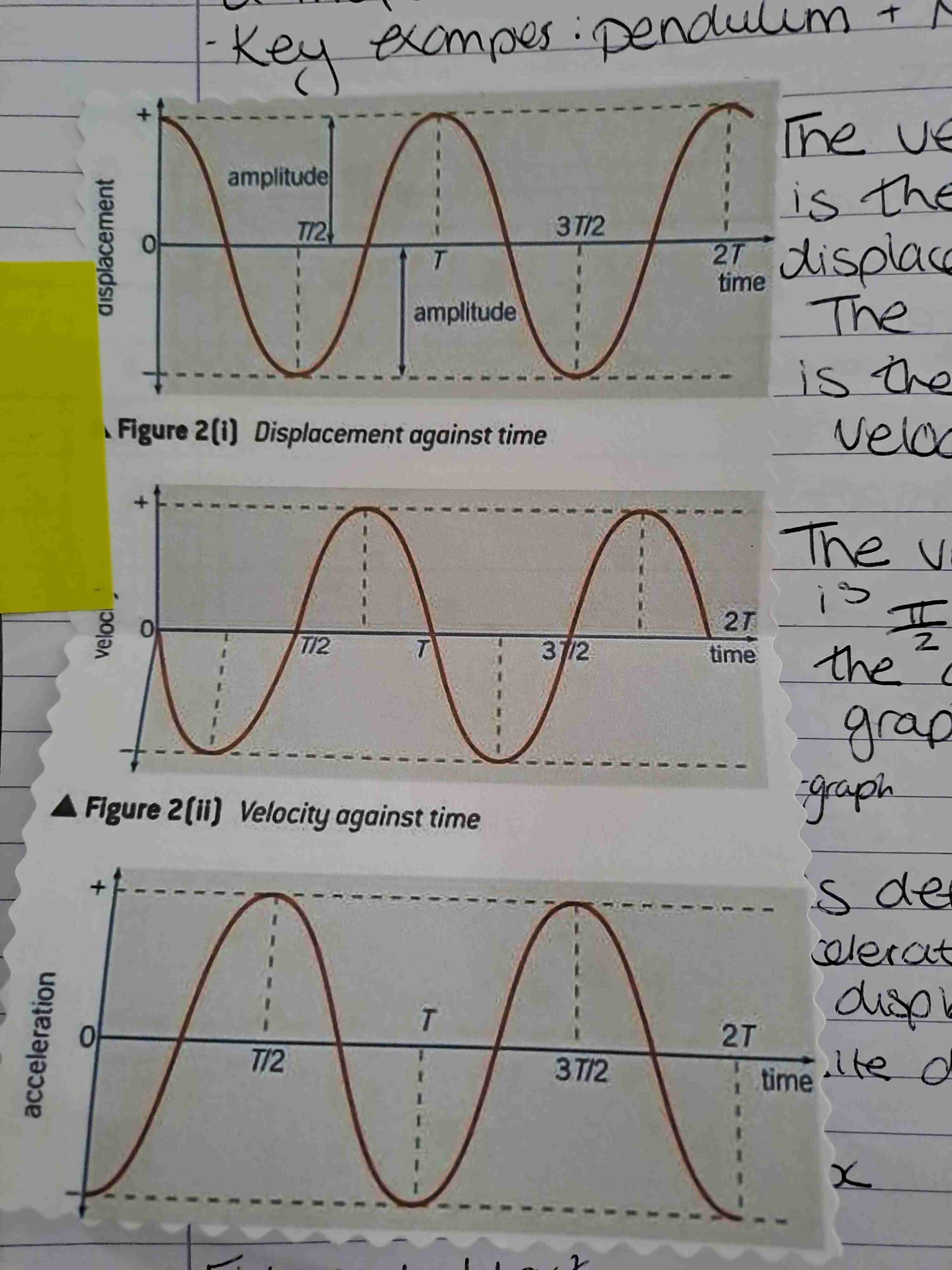
What's the phase difference of the acceleration time graph and displacement time graph
π out of phase
What is x as a trig function of t and w
x=Acos (2πft)
X=Asin(wt)
What is WT measured in
radians
Equation derivative of energies?
Equations
