3 - VO2 Max
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
VO2 Max
Maximum o2 uptake
Different Aerobic Capacities
Absolute value is different to relative value (depends on muscle)
More trained skeletal muscle, better utilisation of o2
Absolute VO2 Max
the total volume of oxygen uptake (litres/min) regardless of body size.
Relative VO2 Max
millilitres of O₂ per kilogram body-weight per minute (mL·kg⁻¹·min⁻¹).
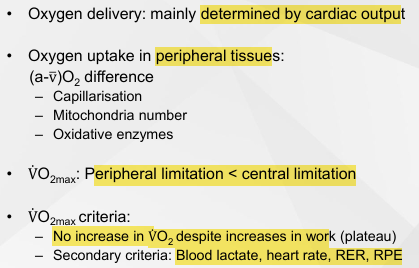
Why Use VO2 Max as a Measure For Aerobic Capacity
Sum of all these systems
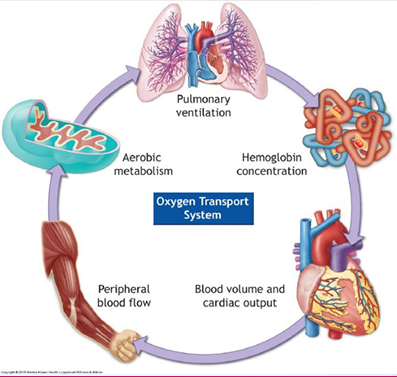
Aerobic Contribution vs Exercise Duration
ATP-PCr System - 100m, 0-10s, use exisiting ATP stores
Glycolysis - 400m
Aerobic System - 1500m
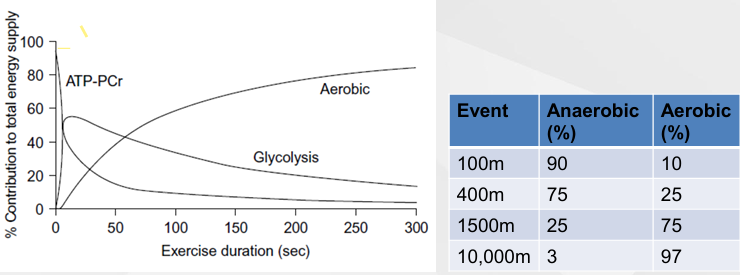
Energy Storages
Oxidation of fat - most amount of energy stored
Limited amount of energy per time (can only run so fast)
Oxidation of Carbs - Medium amount of enrgy stored
Phosphocreatine - smallest amount of energy stored
Lots of energy per time (run faster)
Only lasts a short amount of time
Anaerobic glycolysis - lactate production
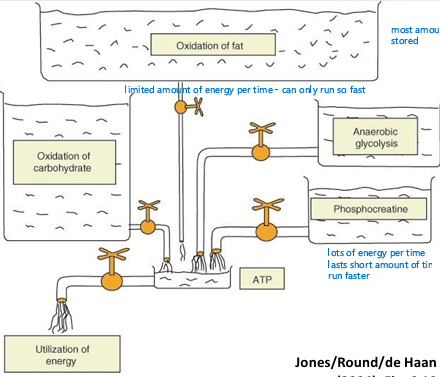
Fick Equation

VO2 Factors
Contractility - contract more vigorously
Preload - more blood returning to the heart from the peripheral
Afterload - resistance to which your heart has to contract
SNS - stress, constrict vessels to lo energy organs, dilate vessels to muscles
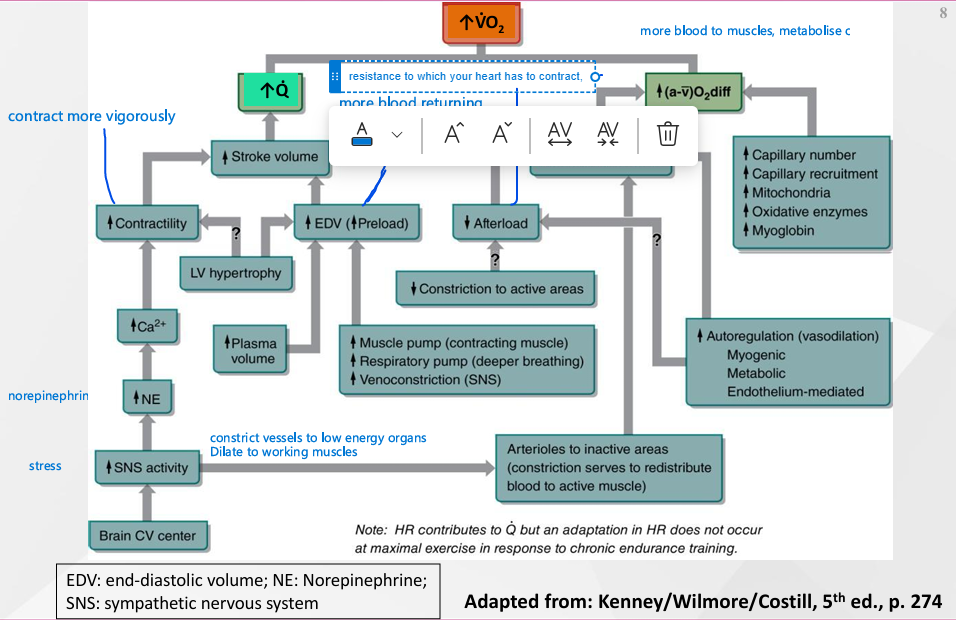
VO2 Max Depends On
Good CVS
High CO
Oxidative capacity in skeletal muscles e.g. mitochondria, oxidative enzymes
Limiting Factor - O2 Delivery vs O2 Utilisation (Basset and Howley (2000)
ACUTE EXERCISE STUDY:
Shows its a central limitation (the muscle can absorb so much o2 during single leg it absorbs less during doble leg as not enough o2 is delivered by the heart)
Extraction should be the same, so heart delivery is the issue
LONGITUDINAL TRAINING STUDIES:
2x capacity should also be 2x increase in VO2 max
Would expect individuals to have a higher VO2 Max

ctd
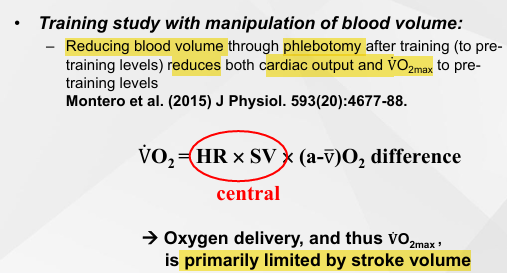
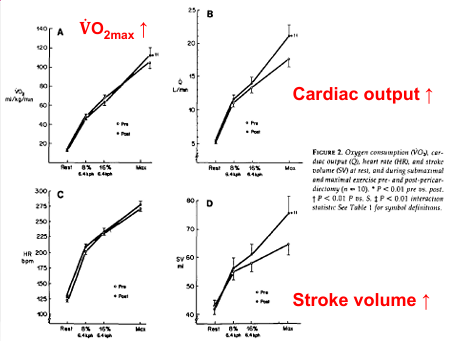
Dog Study (Stray-Gundersen et al. (1986)
Removed pericardium (lining of heart)
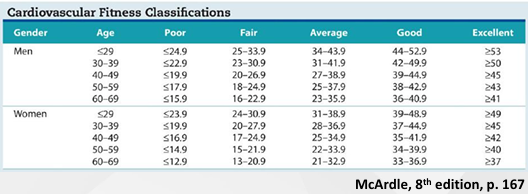
Absolute vs Relative VO2 Max Scores

Assessing fitness using VO2 Max
VO2 Max in Surgery

VO2 Max in Professional Athletes

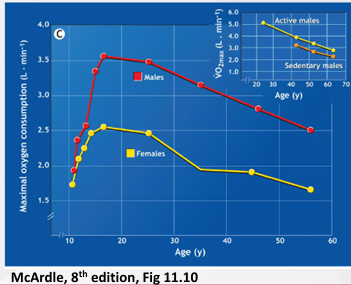
Age + Training
After 25 = decrease 1% per year
Ageing causes more rapid decline
Maybe confounded by disease
Heredity
Genetics = 25-50% variation in VO2
Elite runner - 85 ml/kg/min
Deconditioned - 65/ml/kg/min
VO2 Max Determination: Protocol Design

Incremental Exercise Test To Exhaustion
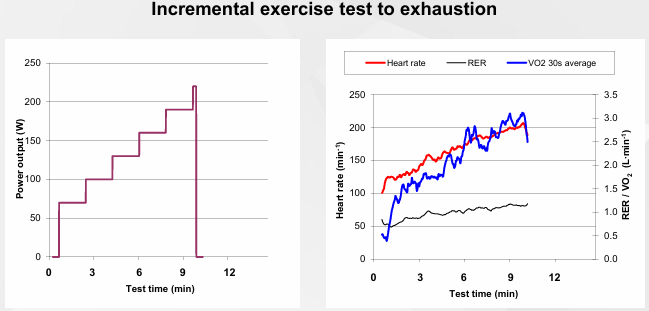
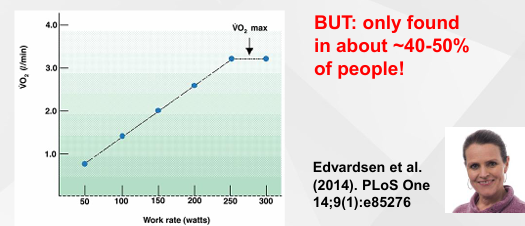
Maximal oxygen uptake: Definition (ACSM / BASES guidelines) - PRIMARY CRITERIA
Primary criterion: Plateau in VO2 despite load/speed increase to next stage (Less than 2 mL/kg/min)
When aerobic plateaus - vo2 max primer parameter if exhaustion has been reached
Energy may come from other sources e.g. anaerobic
Maximal oxygen uptake: Definition (ACSM / BASES guidelines) - SECONDARY CRITERIA
HR - within 90% of age predicted max (220-age)
Blood lactate concentration - over 8 mmol/L (indication of large contribution of anaerobic metabolism)
Respiratory exchange ratio (RER) - ( ሶVCO2/ ሶVO2) of 1.15 or above (indication of large contribution of anaerobic metabolism)#
Not all individuals show all criteria
VO2 Peak
Highest value recorded (when there’s no plataeu)
Other determinants of endurance performance

Summary