3.9 enthalpy
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
what is enthalpy (H)?
a measure of the heat energy in a chemical system
chemical system referring to the atoms, molecules or ions making up the chemicals
can enthalpy be measured?
no
what can be measured if enthalpy can’t?
enthalpy changes can be measured
how do you calculate enthalpy changes?
enthalpy change= H(products) - H(reactants)
the law of conservation states that energy cannot be created or destroyed only transferred to its system and its surroundings, what are the system and the surroundings in chemistry?
the system is the chemicals, reactants and products
the surroundings is the apparatus, the laboratory, and everything that is not the chemical system
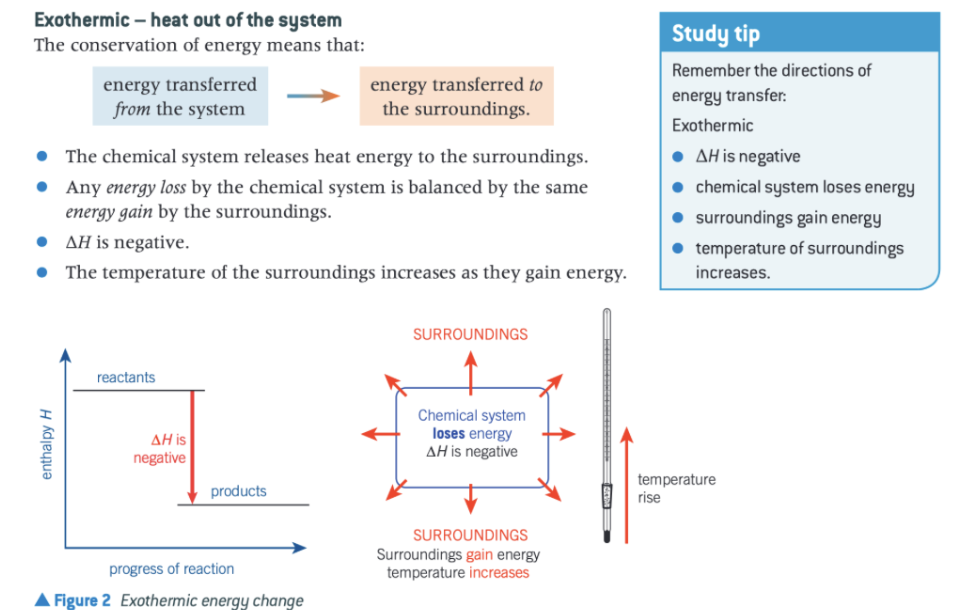
what type of change leads to energy transfer from system to surroundings?
exothermic change
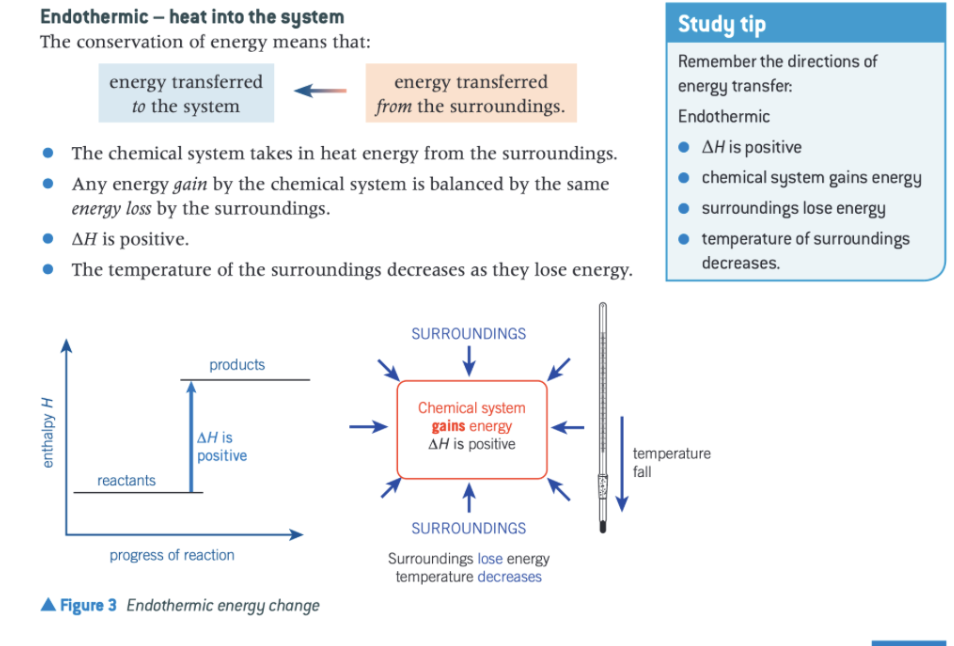
what type of change leads to energy transfer from surroundings to the system?
endothermic change
give all the features of an exothermic reaction
give all the features of an endothermic reaction
if an equation is balanced with whole numbers, the amounts are doubled, what happens to the enthalpy change?
it doubles
what are standard conditions?
a pressure of 100kPa or 1atm-1
a temperature of 298K (same as 25oc)
a concentration of 1moldm-3 (for solutions only)
all reactants and products are in their standard states, this means the physical state of a substance under standard conditions
what is the definition of the standard enthalpy change of formation?

what is the definition of the standard enthalpy change of combustion?

what is the definition of standard enthalpy change of neutralisation?

what is standard enthalpy change of a reaction?

when carrying out reactions is the thermometer part of surroundings or the experiment?
the surroundings
what do we measure temperature in which is 273+ for celsius degrees?
kelvin
what three quantities are needed to calculate energy change of surroundings?
mass
specific heat capacity
temperature change
what is specific heat capacity meaning? ( c )
energy required to raise the temperature of 1g of a substance by 1K
do good conductors have a high specific capacity or low?
small values
do insulators have high specific capacity or low?
large values
how is temperature change of surroundings calculated? (triangle T)
thermometer readings of final temp-initial temp
how do u measure mass of the surroundings? (m)
using scales
how do you calculate energy change in joules?
q=m c triangleT
energy = mass x specific heat capacity of surroundings x temperature change of surroundings
how would you simplified work out the standard enthalpy change of combustion?
combust the fuel and use the thermal energy released to heat a known mass of water by measuring the temperature change of water, we can determine the standard enthalpy change of combustion
explain step by step how would you work out the standard enthalpy change of combustion?
use balance to measure starting mass of the spurt burner and the fuel then measure the mass of water
use thermometer to measure the starting temperature of the water
remove cap from spirit burner and immediately light the wick
thermal energy released causes water temperature to increase, so stir using thermometer to make sure all the thermal energy is distributed
after several minutes, extinguish the flame by placing the cap on the burner
use thermometer to read the temperature of the water
use balance to measure the mass of the spirit burner and the fuel to calculate mass of the fuel combusted
why do you have to like the wick of spirit burner immediately?
or else fuel will evaporate and make our final results less accurate
how would you calculate the mass of the fuel combusted?
starting mass - final mass
how would you work out standard enthalpy change of combustion mathematically after receiving all values?
use equation
energy change of water = mass of water (g) x specific heat capacity of water x temperature change of water (oc)
divide this value by 1000 to get value into kJ mol-1, so now have value of energy change of water
work out number of moles by dividing mass of fuel/ mr of fuel
work out standard enthalpy change of combustion by thermal energy (kJ) / number of moles
why would published values of standard enthalpy change of combustion be higher?
if we leave unlit spirit burner uncapped fuel will evaporate, so look like we burned more fuel then we actually did, so reaction show less exothermic then actually is
lots of heat energy doesn’t go into water some goes to metal calorimeter and great deal transferred to the air
not all fuel underwent complete combustion, and incomplete combustion releases less thermal energy
experiment may not of been in standard conditions
what is the definition for average bond enthalpy?
energy needed to break one mole of a specific bond in a molecule in the gaseous state
why is it called AVERAGE bond enthalpy?
different bond energy depending on molecule we find the bond in so scientists take an average value
for enthalpy reaction of neutralisation what do you assume the specific heat capacity is and why?
4.18 because if its aqueous we assume it’s the same as water
how do you work out the weight of something that is given in volume
use density of water which is 1g/cm3 to work out the weight once again assuming its similar to water if its aqueous
what is Hess’s law?
if a reaction can be carried out by two different pathways then the total enthalpy change for these two pathways will be the same provided that the starting and final conditions are the same for both pathways
in hess’s cycle when using combustion data do arrows point down or up?
points down
in hess’s cycle when using formation data do arrows point down or up?
up
what is a short way you can get answer for a question without doing the whole Hess’s cycle? But what is exception?
reactants-products
can’t do it if the products aren’t gas