Cardio/Renal 19 - WBC cell counts & Disorders (Dr. Farag)
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
T/F: Dentist should identify WBC abnormalities through history, clinical examination, lab tests
Refer to a physician for further evaluation and management
True

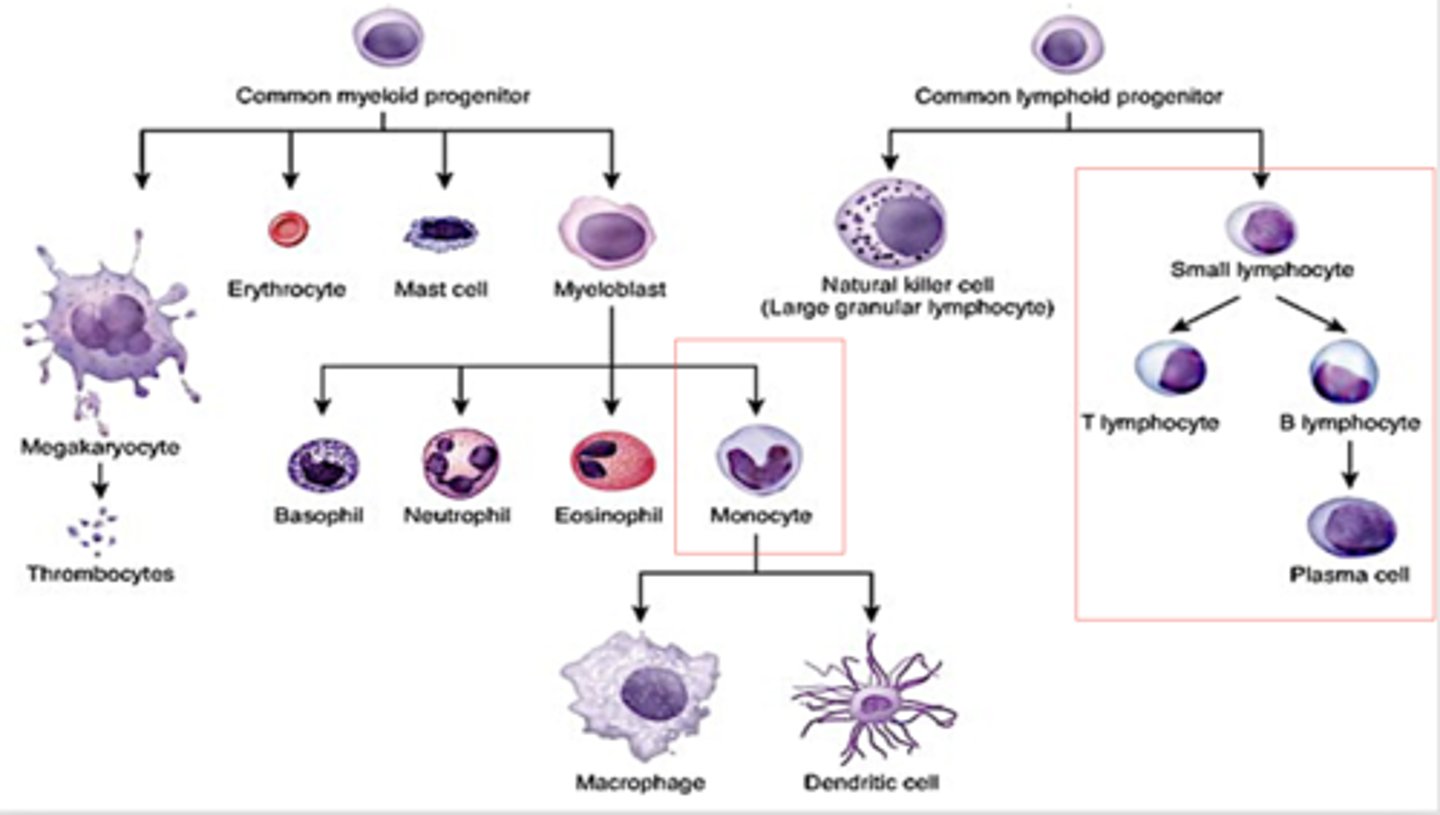
WBCs are produced by
hemapoietic stem cells in bone marrow
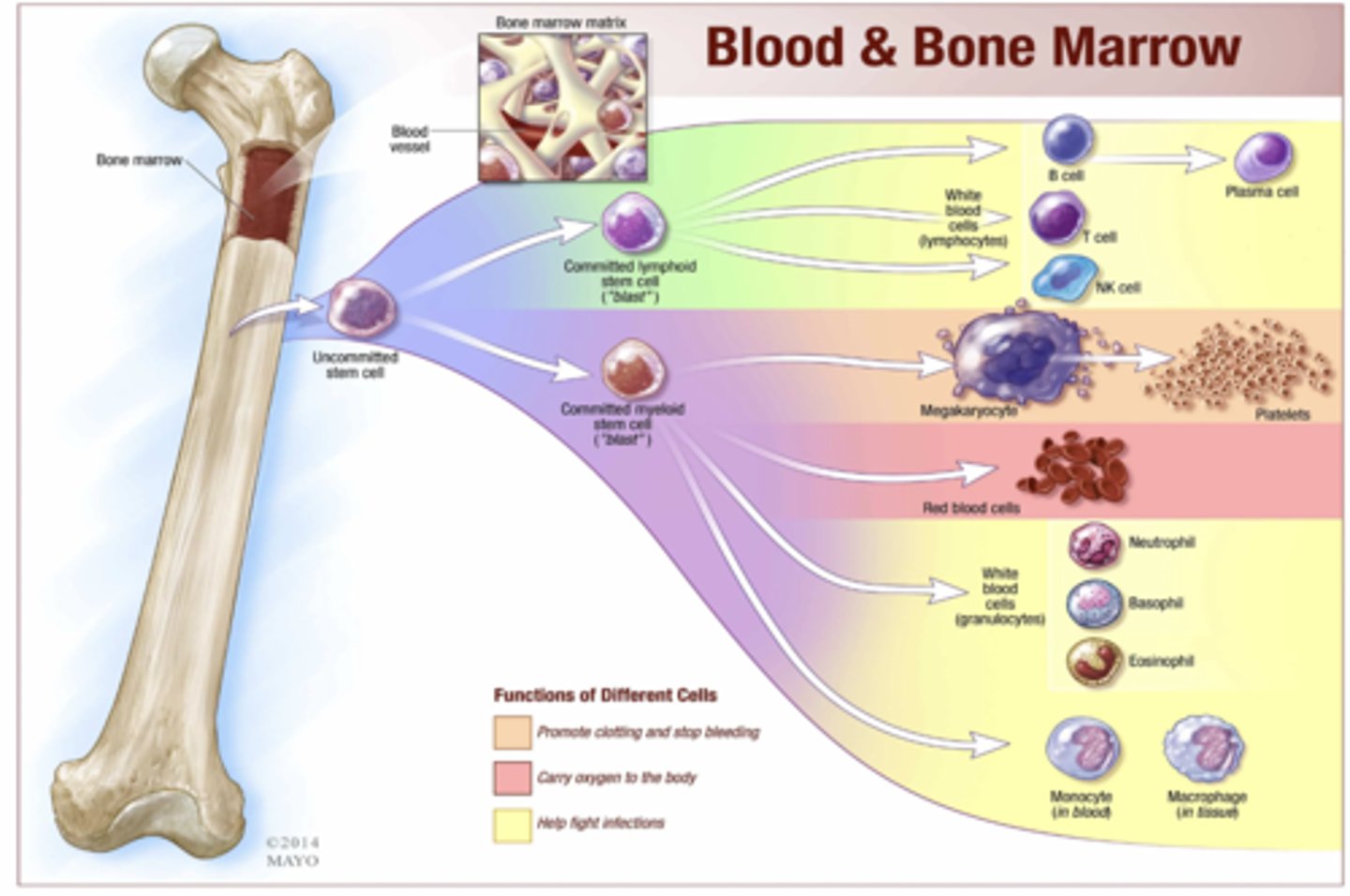
From bone marrow, an uncommitted stem cells forms into what two types of stem cells?
Committed lymphoid stem cell
Committed myeloid stem cell
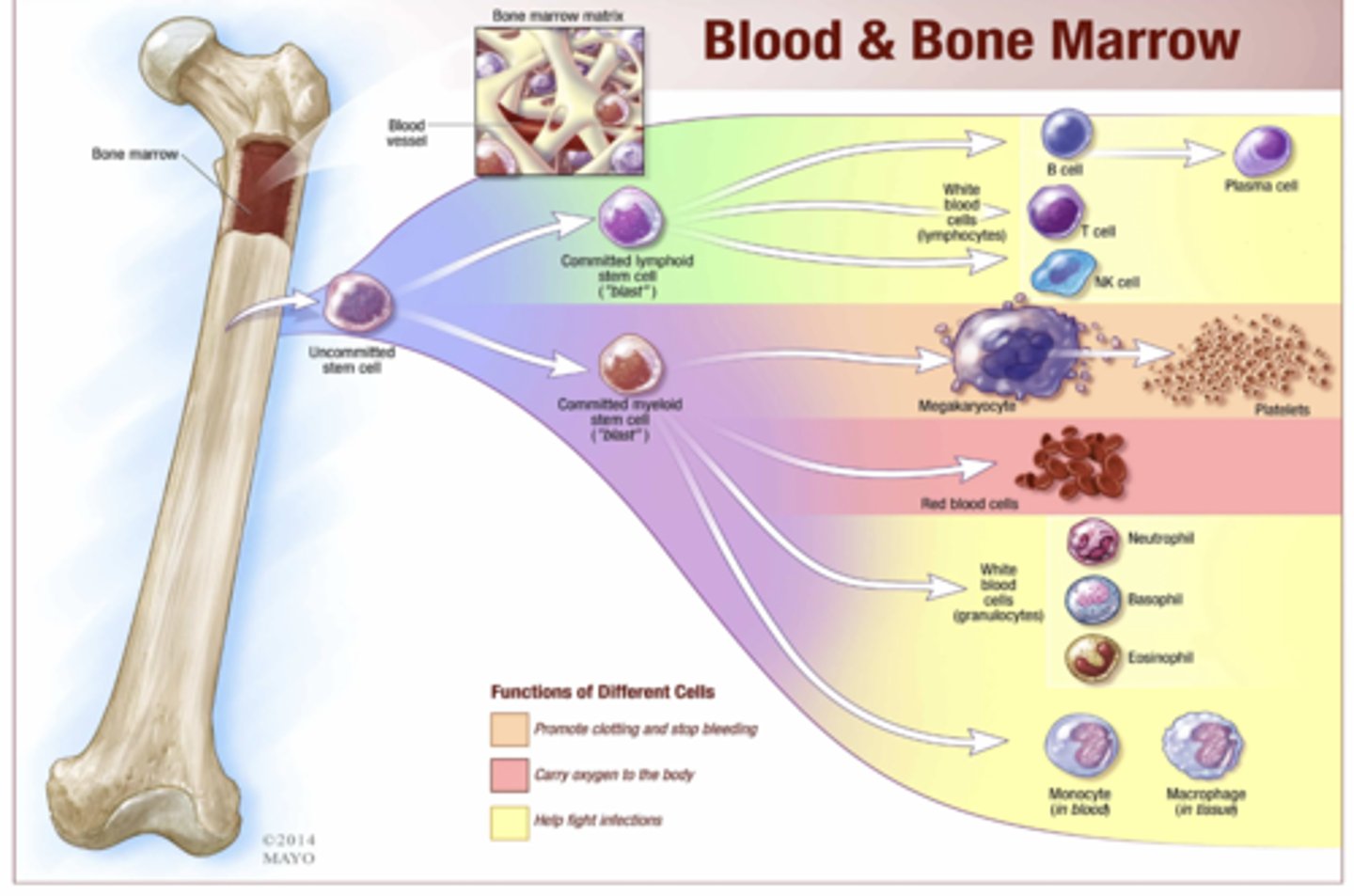
The following cells come from what stem cell lineage?
- Platelets
- RBCs
- WBCs
- Monocyte/macrophages
Committed myeloid stem cell
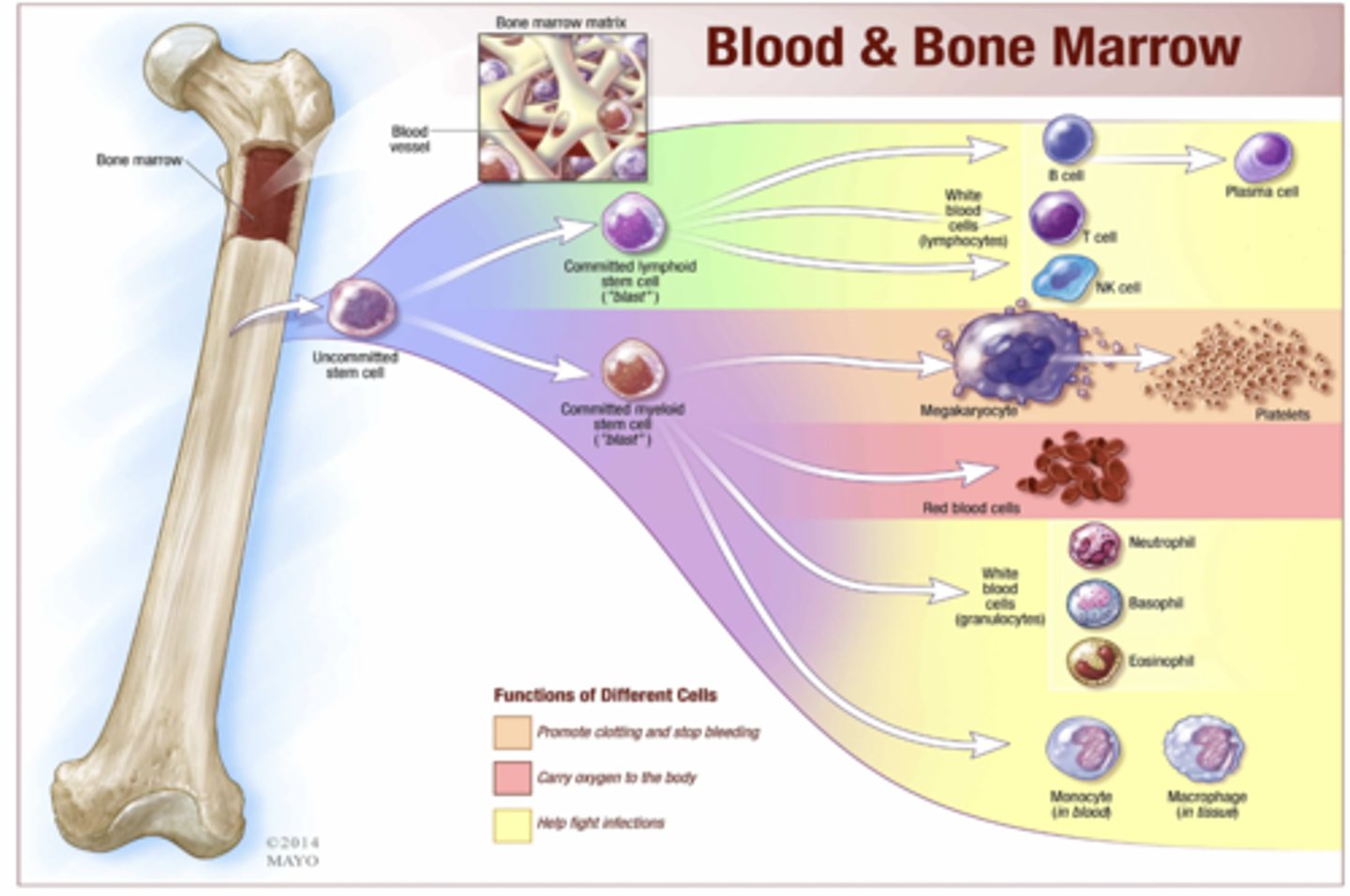
Circulating lymphocytes are what three types?
- T cells
- B cells
- Natural killer cells
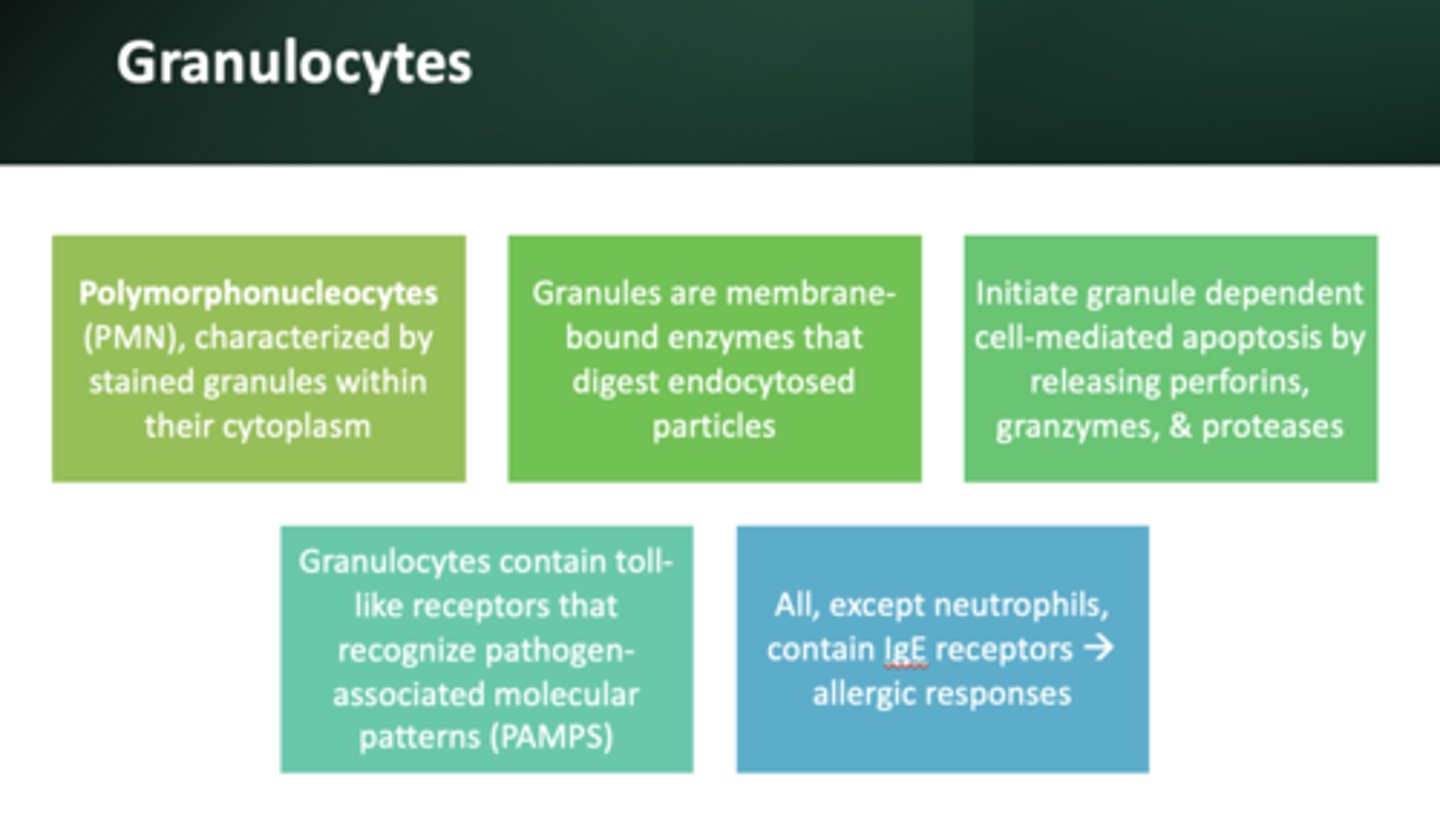
The following are all characteristics of what?
- Known as polymorphonuclear leukocytes
- Membrane bound enzymes that act primarily in the digestion of endocytosed particles
- Nucleus contains multiple lobes (polymorphonuclear)
- May cause granule dependent cell-mediated apoptosis thru release of perforins, granzymes, proteases
- Contain toll-like receptors that allow them to recognize PAMPs
Granulocytes
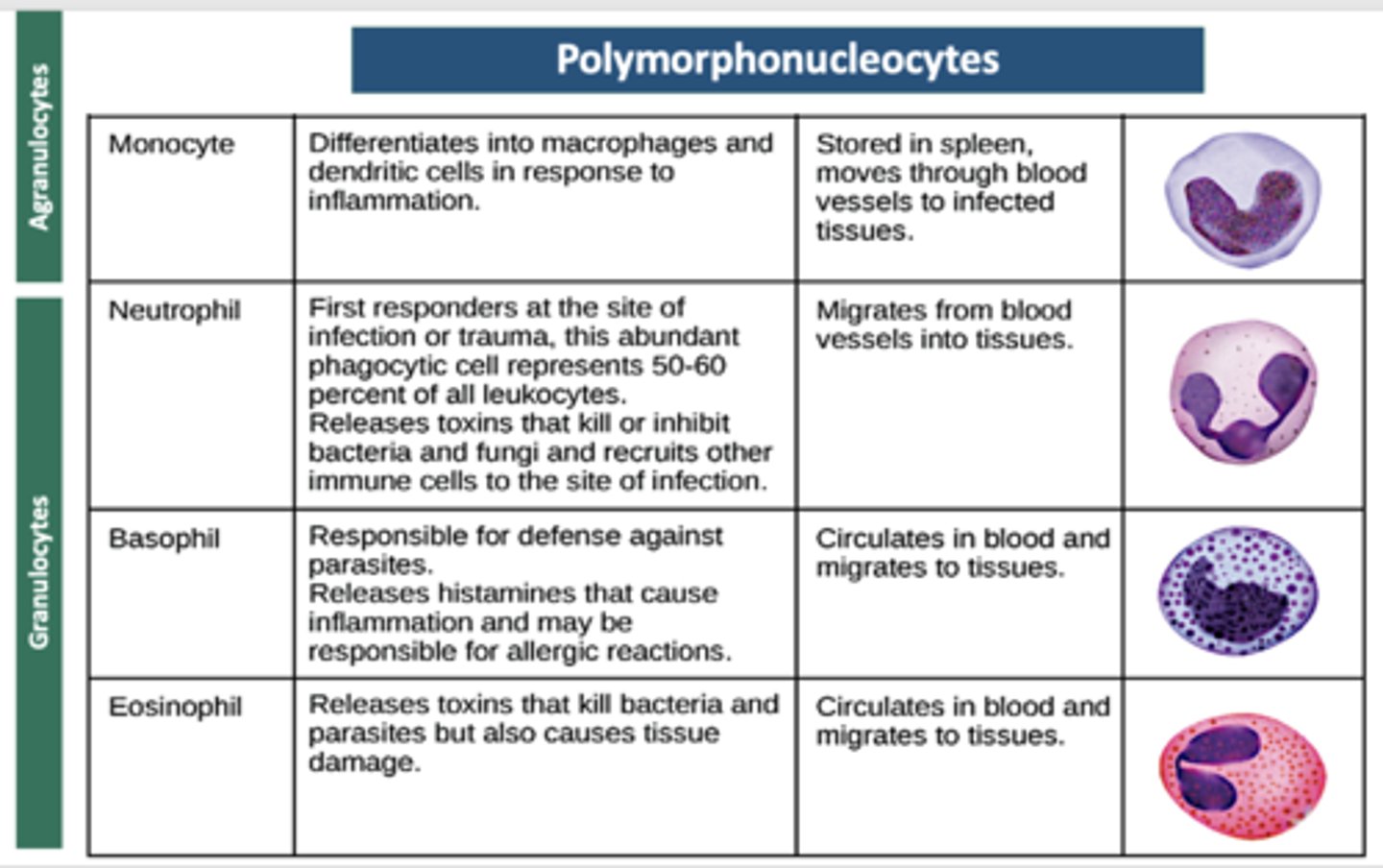
Which cell is the following:
- Differentiates into macrophages and dendritic cells in response to inflammation.
- Stored in spleen, moves through blood vessels to infected tissues.
Monocyte
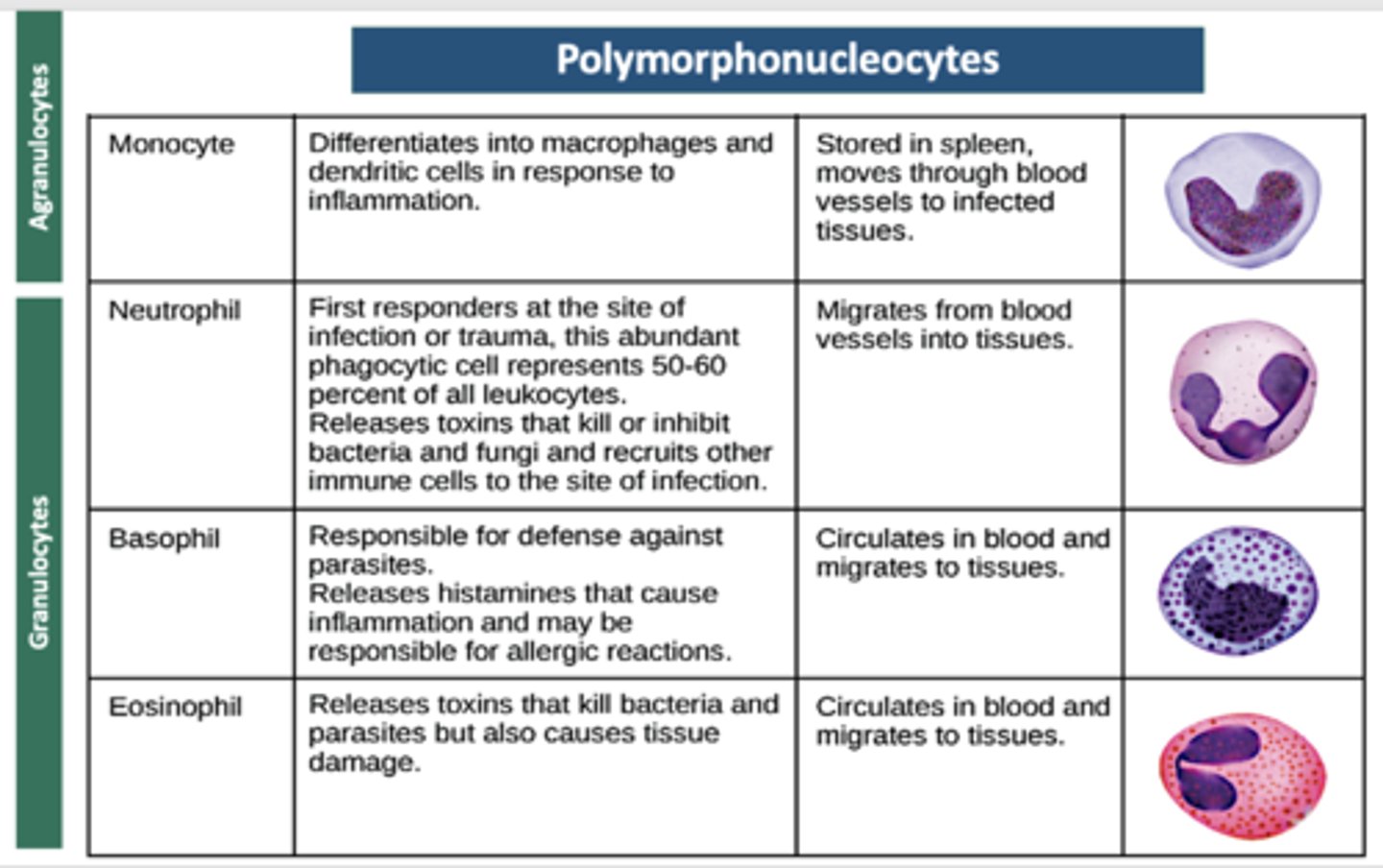
Which cell is the following:
- First responders at the site of infection or trauma, this abundant phagocytic cell represents 50-60 percent of all leukocytes.
- Releases toxins that kill or inhibit bacteria and fungi and recruits other immune cells to the site of infection.
- Migrates from blood vessels into tissues.
Neutrophil
Which cell is the following:
- Responsible for defense against parasites.
- Releases histamines that cause inflammation and may be responsible for allergic reactions.
- Circulates in blood and migrates to tissues
Basophil
Which cell is the following:
- Releases toxins that kill bacteria and parasites but also causes tissue damage.
- Circulates in blood and migrates to tissues.
Eosinophil
Which cell is the following:
- Dilates blood vessels and induces inflammation through release of histamines and heparin. Recruits macrophages and neutrophils.
Involved in wound healing and defense against pathogens but can also be responsible for allergic reactions.
- Connective tissues, mucous membranes
Mast cell
Which cell is the following:
-Phagocytic cell that consumes foreign pathogens and cancer cells.
- Stimulates response of other immune cells.
- Migrates from blood vessels into tissues.
Macrophage
Which cell is the following:
- Kills tumor cells and virus-infected cells.
- Circulates in blood and migrates into tissues.
Natural killer cell
Which cell is the following:
- Presents antigens on its surface, thereby triggering adaptive immunity.
- Present in epithelial tissue, including skin, lung and tissues of the digestive tract.
Migrates to lymph nodes upon activation.
Dendritic cell
which granulocyte is the only one that does not have IgE receptors that implicate it in allergic responses?
neutrophils
these cells are 1st responders in a bacterial infection, defend against bacterial and fungal infections, and other very small inflammatory processes
neutrophils
these cells activity and death in large numbers from degranulations forms purulent necrosis = pus
neutrophils
these cells primarily deal with parasitic infections, predominate inflammatory cell in allergic reactions:
eosinophils
these cells are responsible for short term inflammatory responses, secrete histamine that causes vasodilation:
basophils
these cells function similarly to basophils as inflammation mediators but are more common
mast cells
these cells are involved with delayed or cellular immune function:
T lymphocytes
play an important role in the immediate, or humoral, immune system involving the production fo plasma cells and immunoglobulins (IgA, IgD, IgE, and IgM)
B lymphocytes
these cells have diverse functions that include phagocytosis, intracellular killing and mediating immune and inflammatory responses. Are also antigen presenting cells. Can be dendritic (in lymph nodes) or Langerhans cells (in skin and mucosa)
monocytes
Monocytes in tissue that phagocytose microbes are known as
macrophages
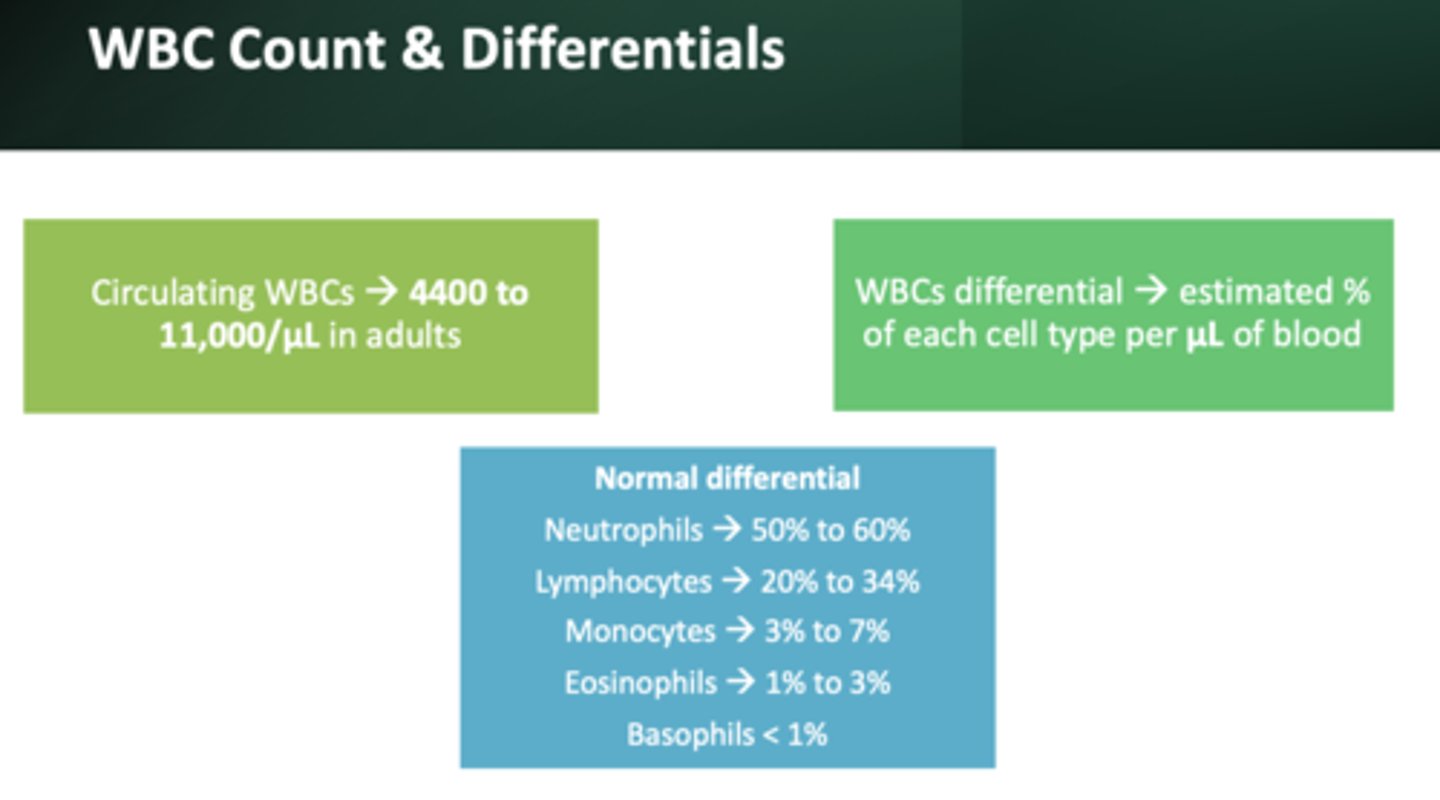
Normal WBC count:
4,400-11,00/ul
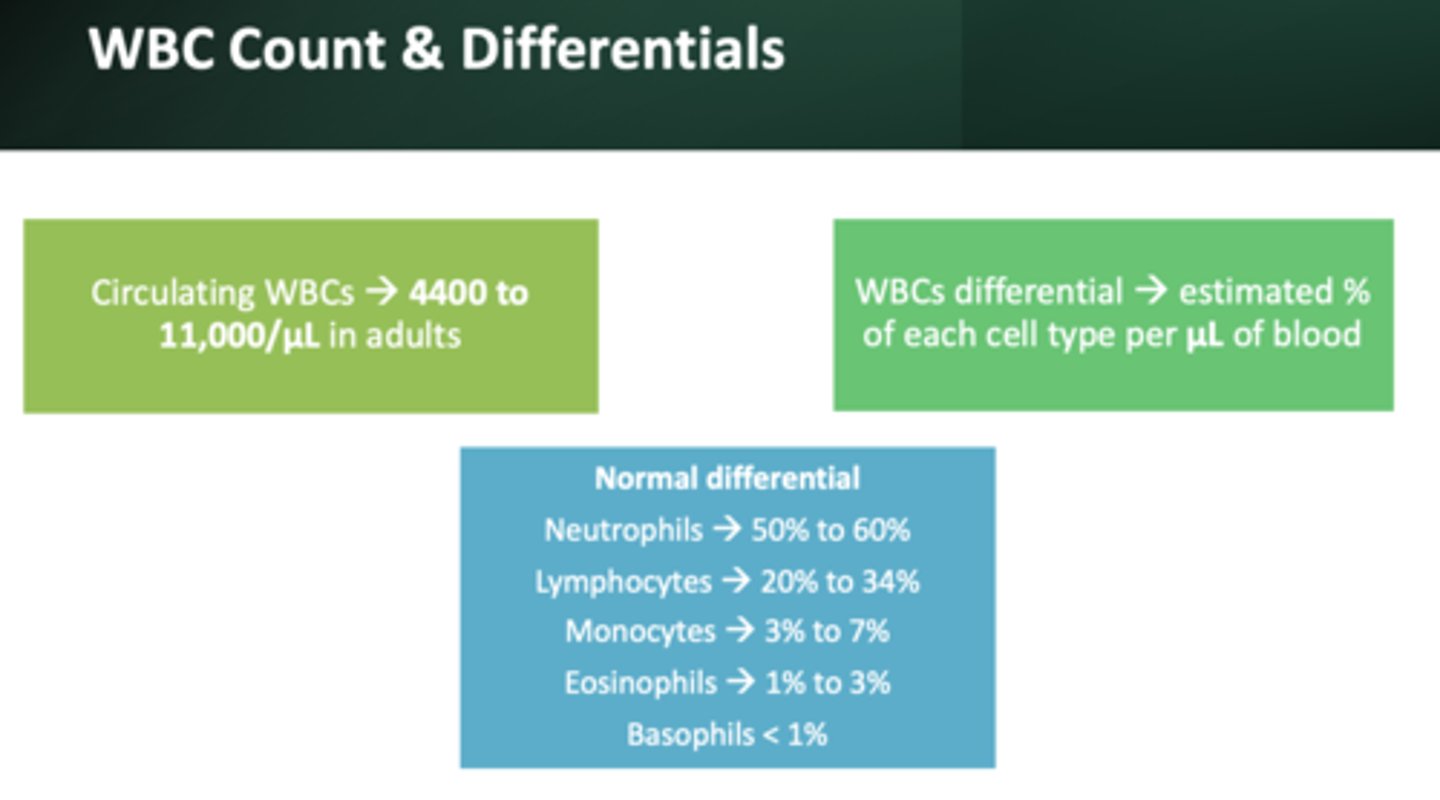
most abundant WBC:
neutrophils (50 to 60%)
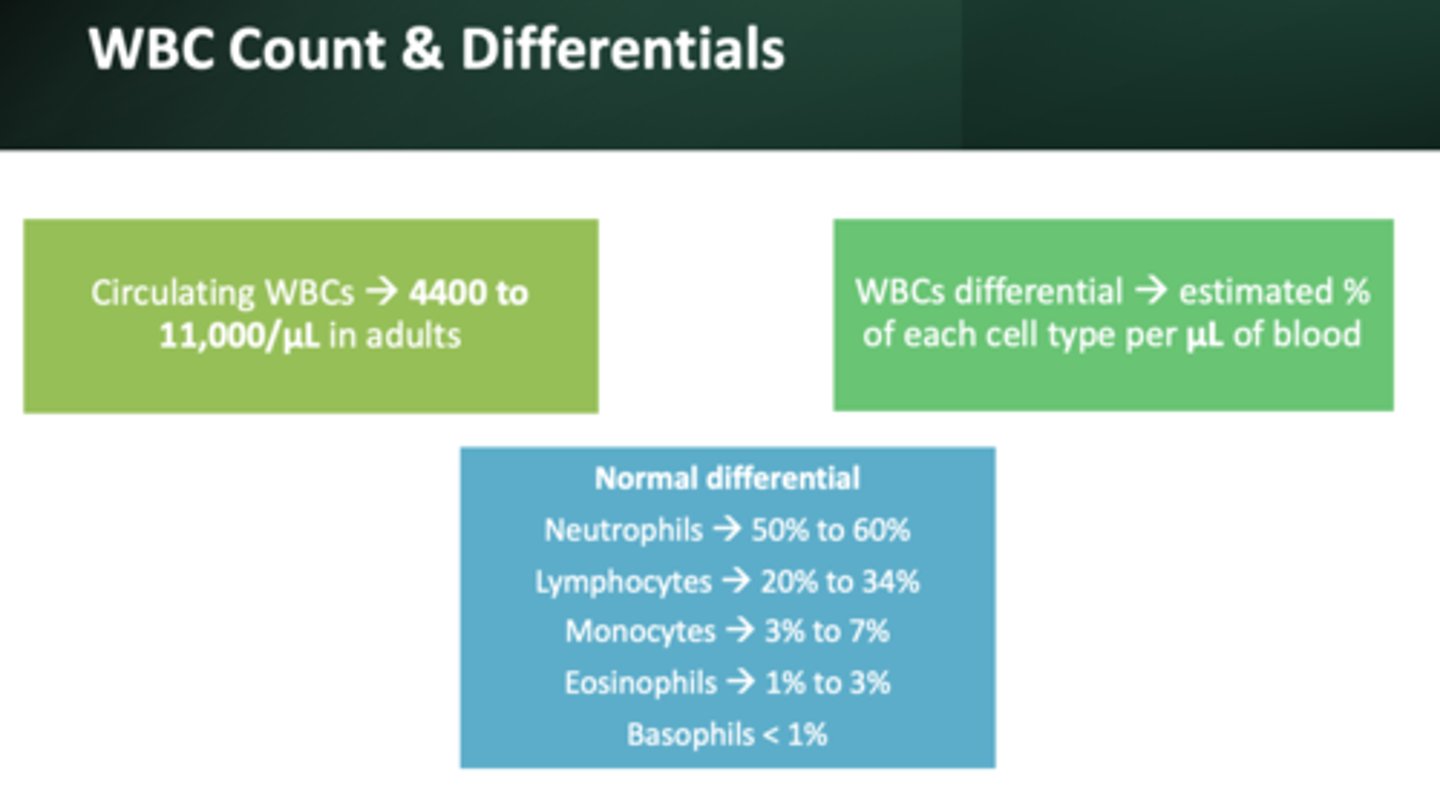
2nd most abundant WBC:
lymphocytes (20 to 34%)
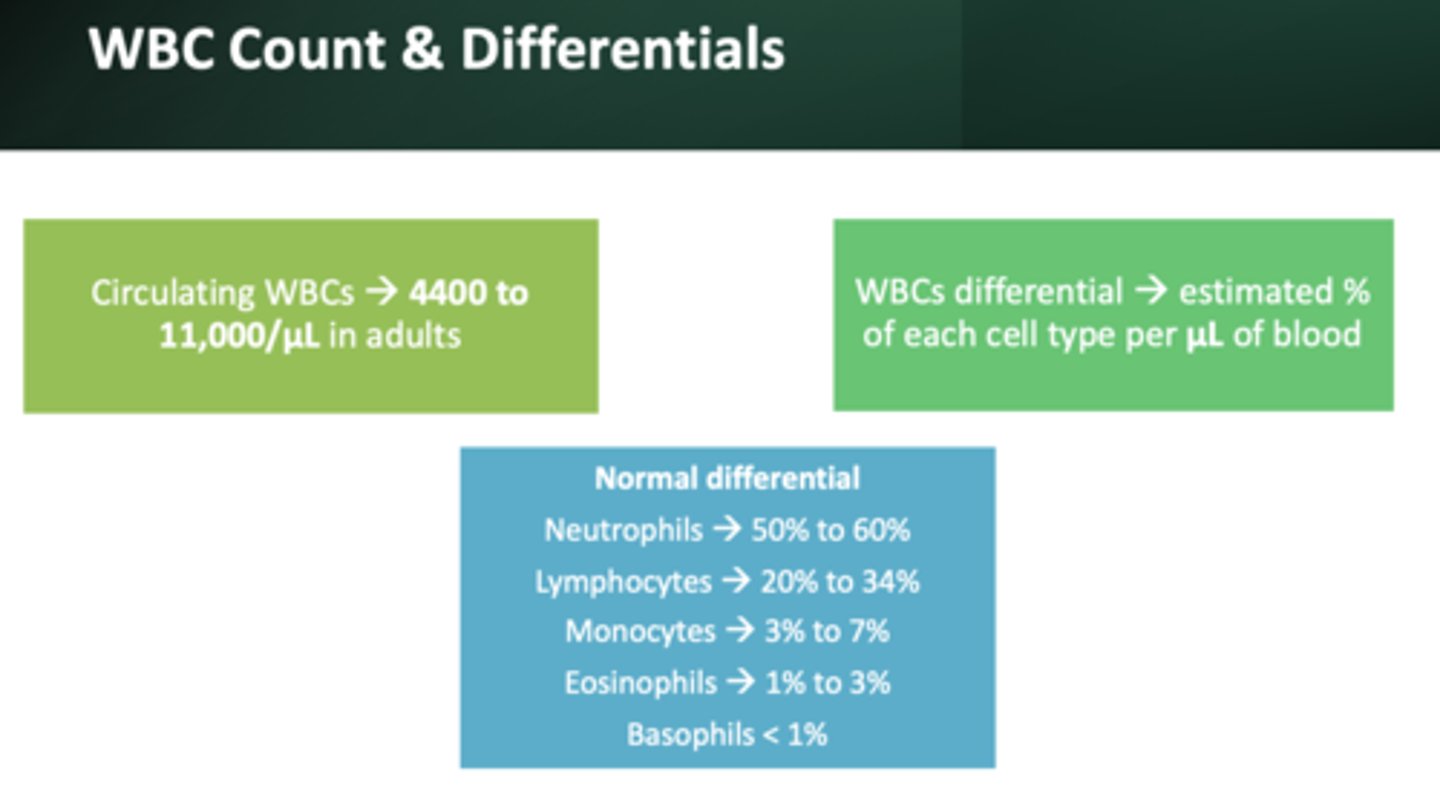
3rd most abundant WBC:
monocytes (3 to 7%)
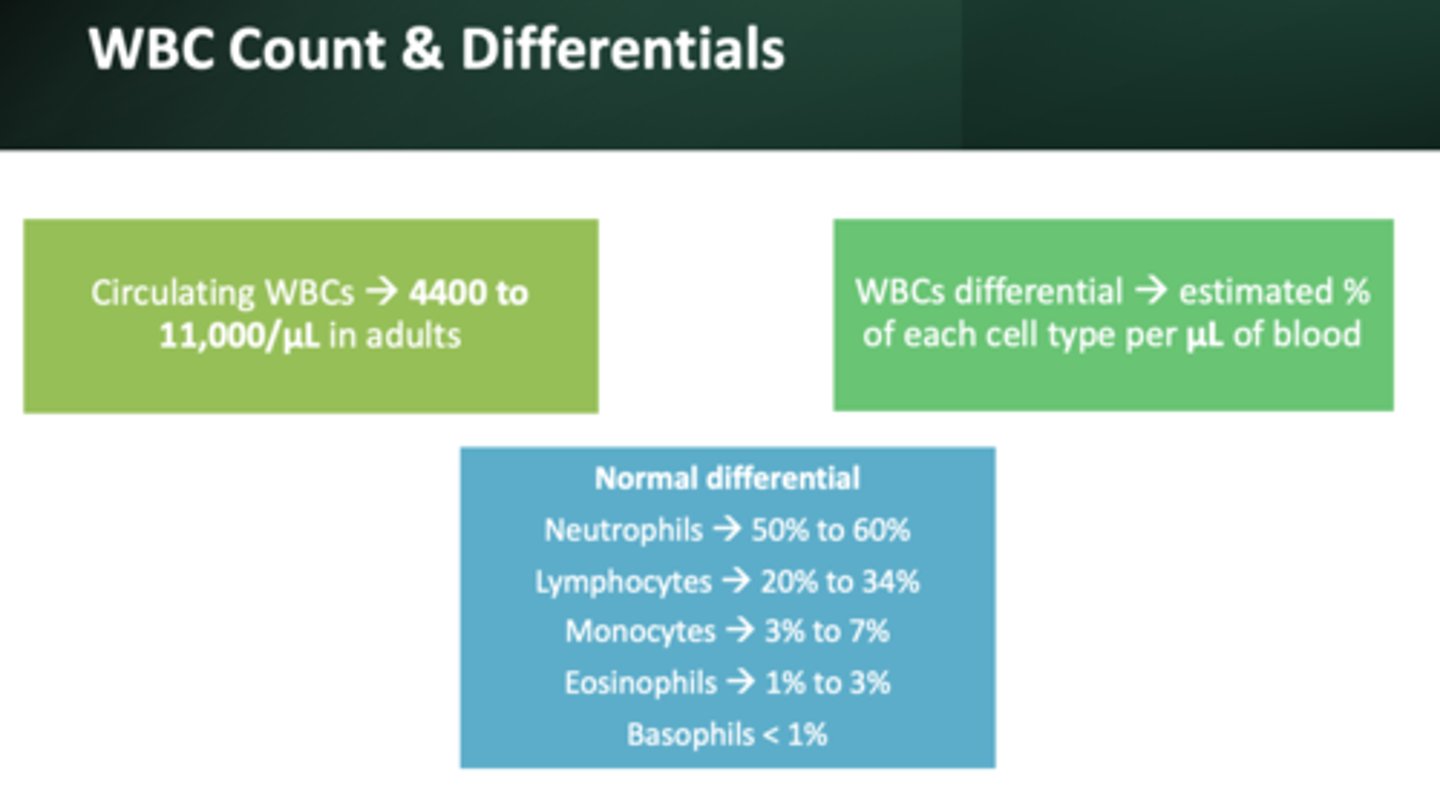
4th most abundant WBC:
eosinophils (1-3%)
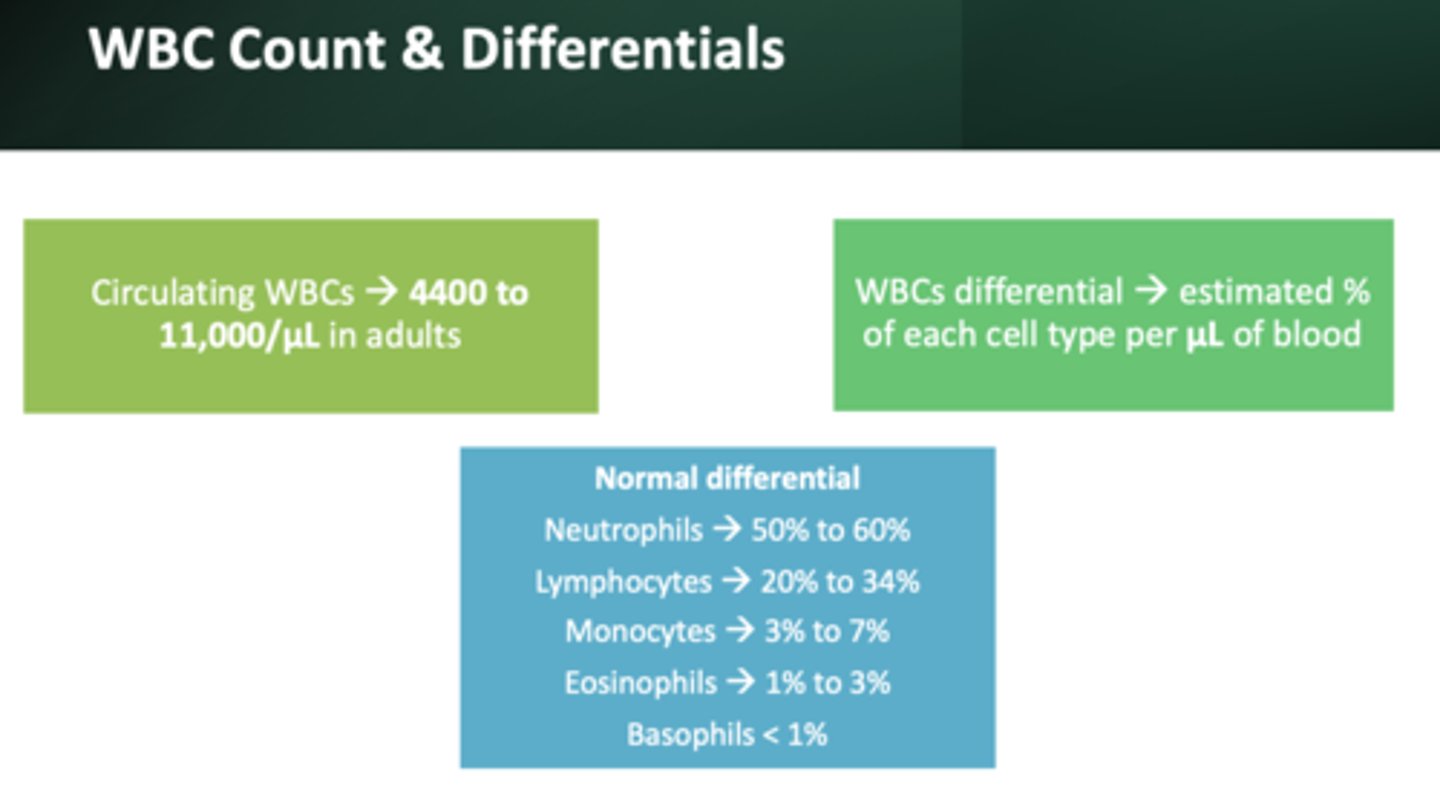
Least abundant WBC:
basophils (less than 1%)
these cells are associated with response to allergens and parasites
eosinophils

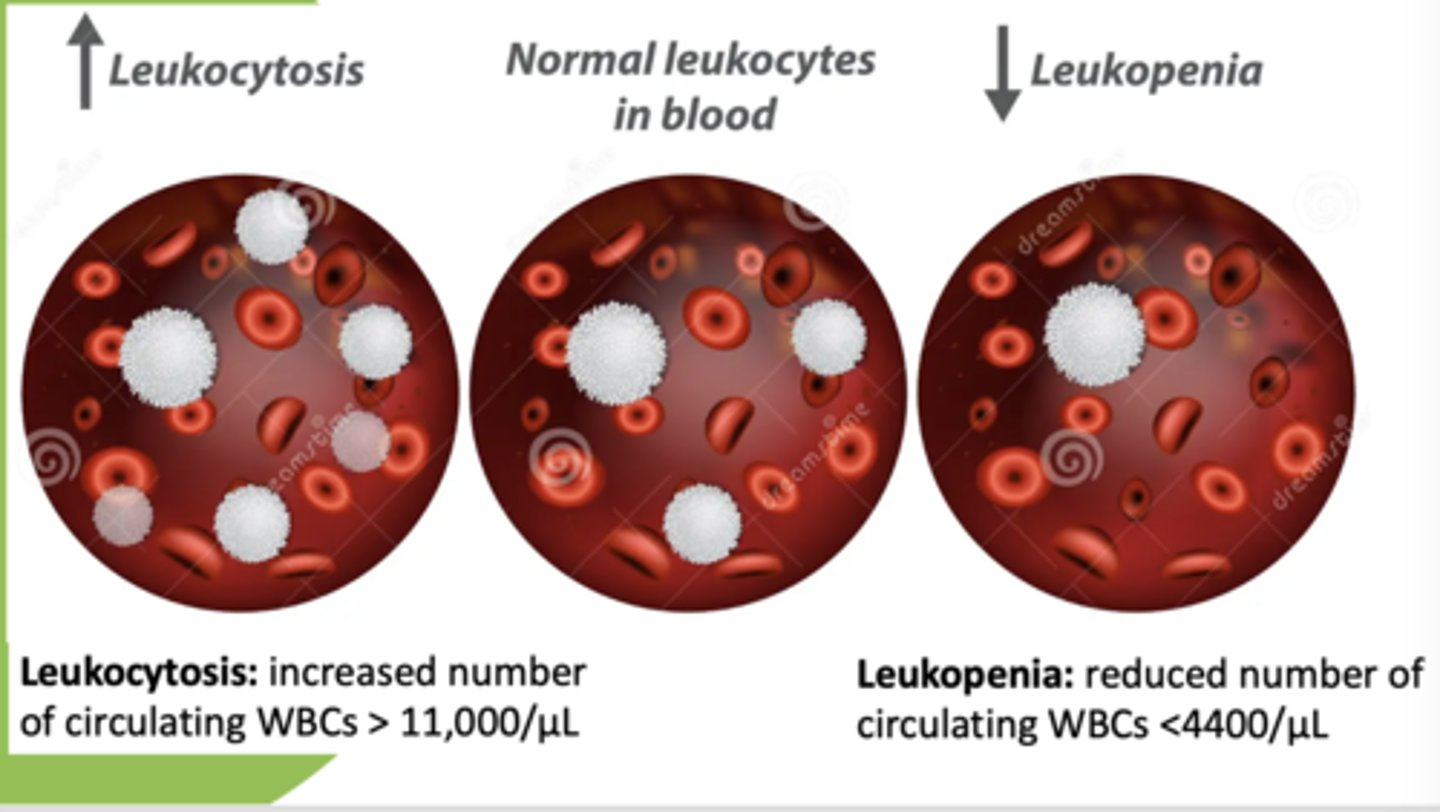
increased WBC count/circulating WBCs (greater than 11,000/ul):
leukocytosis
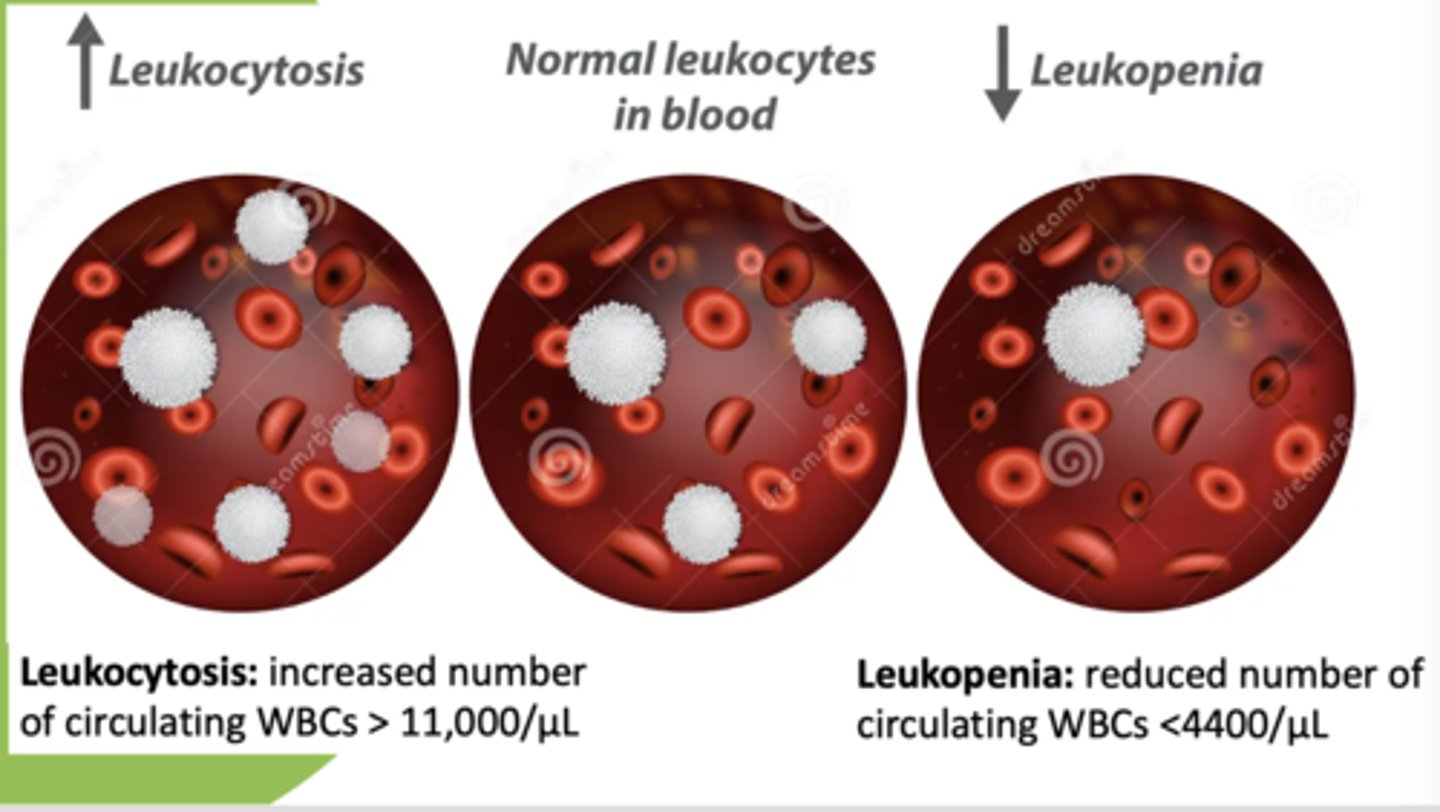
decreased WBC count/circulating WBCs (less than 4,400/ul):
leukopenia
immature neoplastic malignancy of myeloid cells:
acute myeloid leukemia
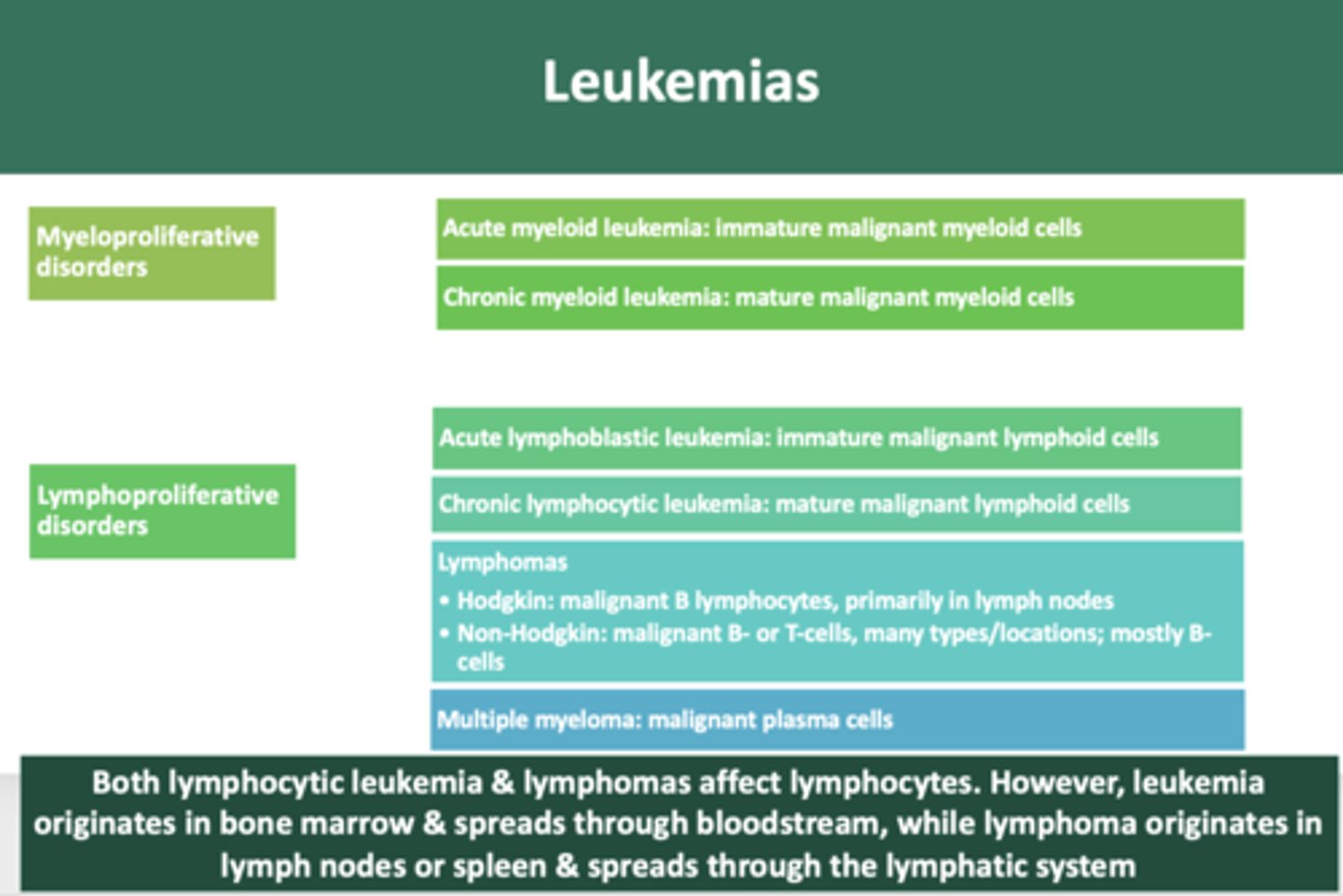
mature neoplastic malignancy of myeloid cells:
chronic myeloid leukemia
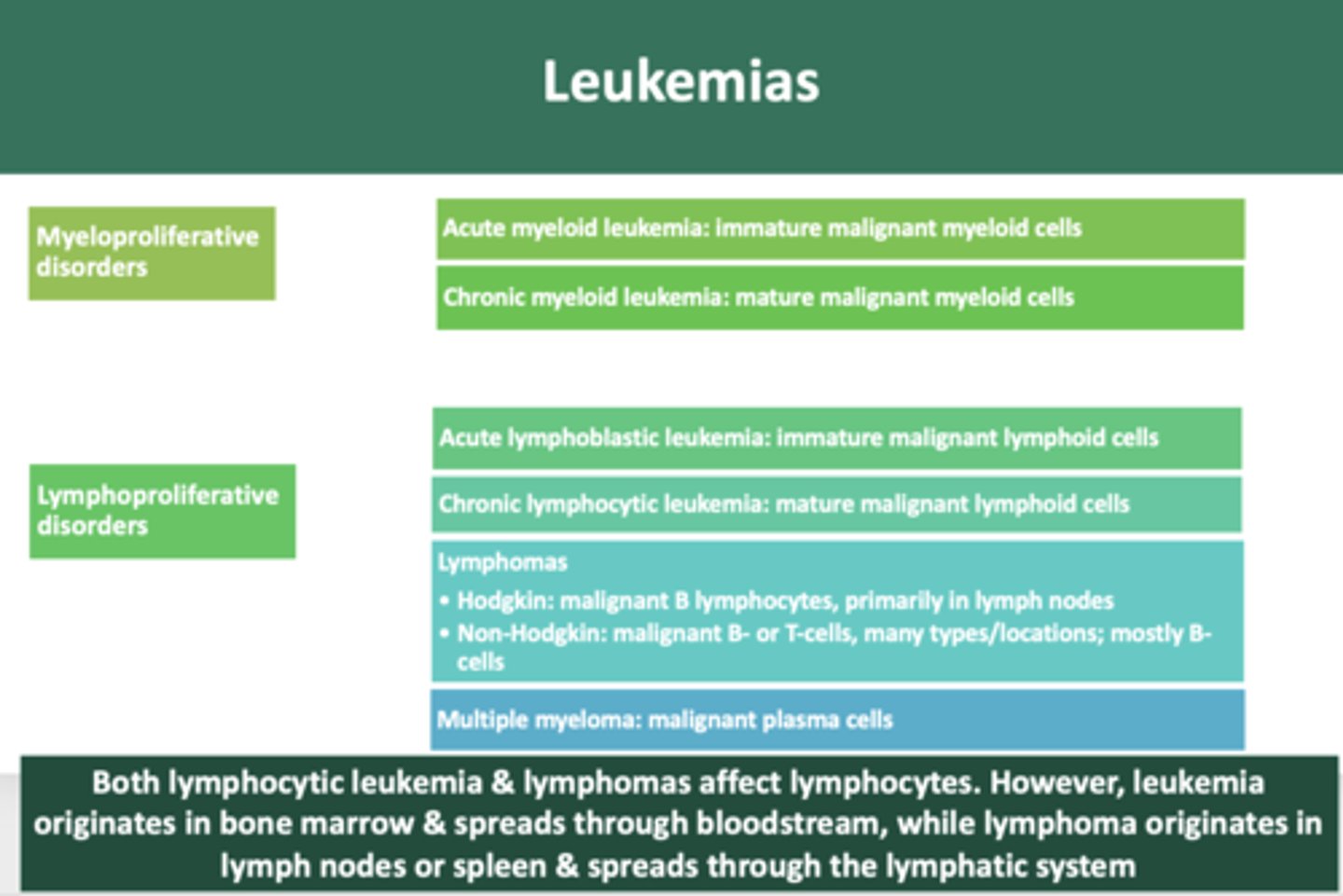
immature neoplastic malignancy of lymphoid cells
acute lymphoblastic leukemia
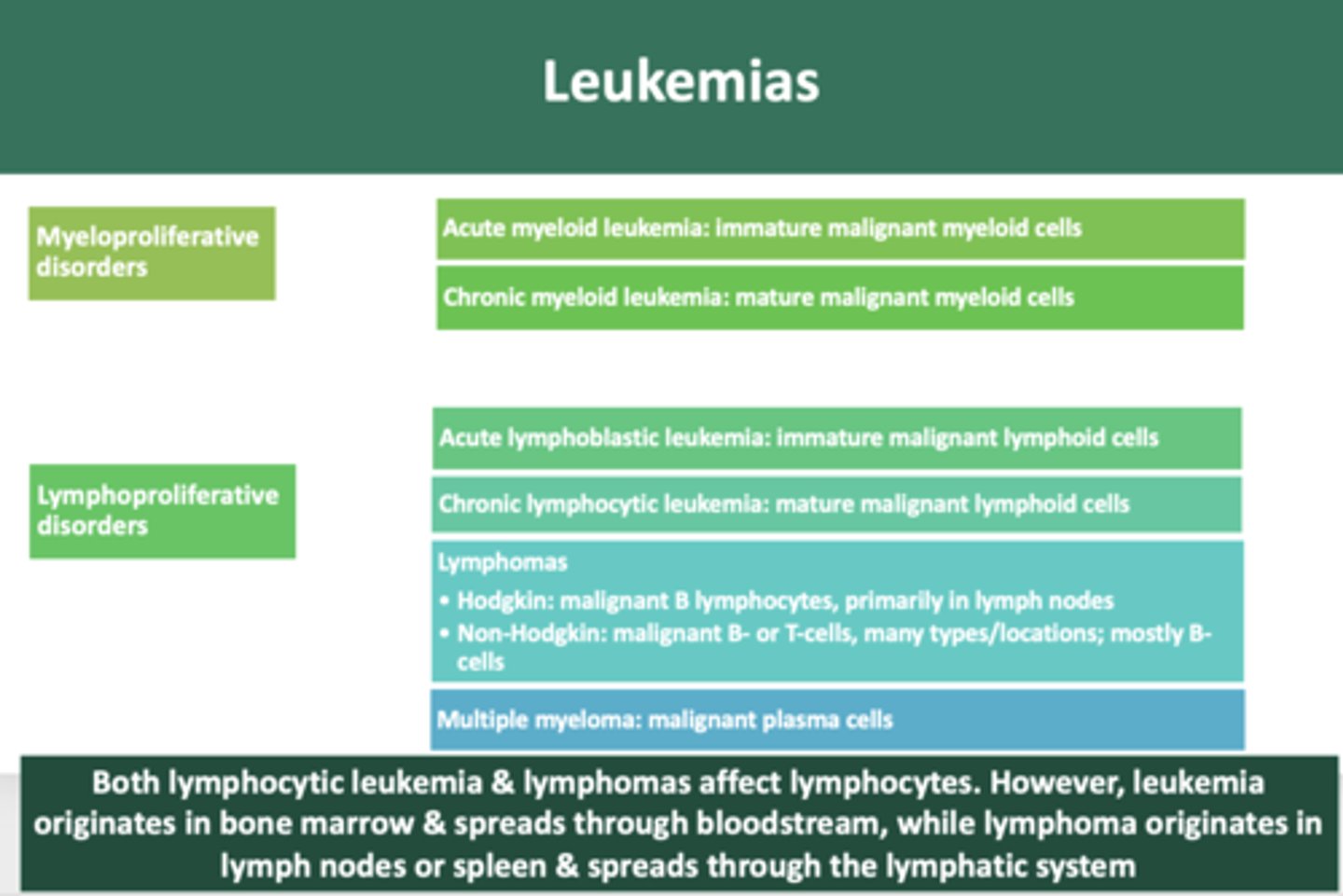
mature neoplastic malignancy of lymphoid cells
chronic lymphocytic leukemia
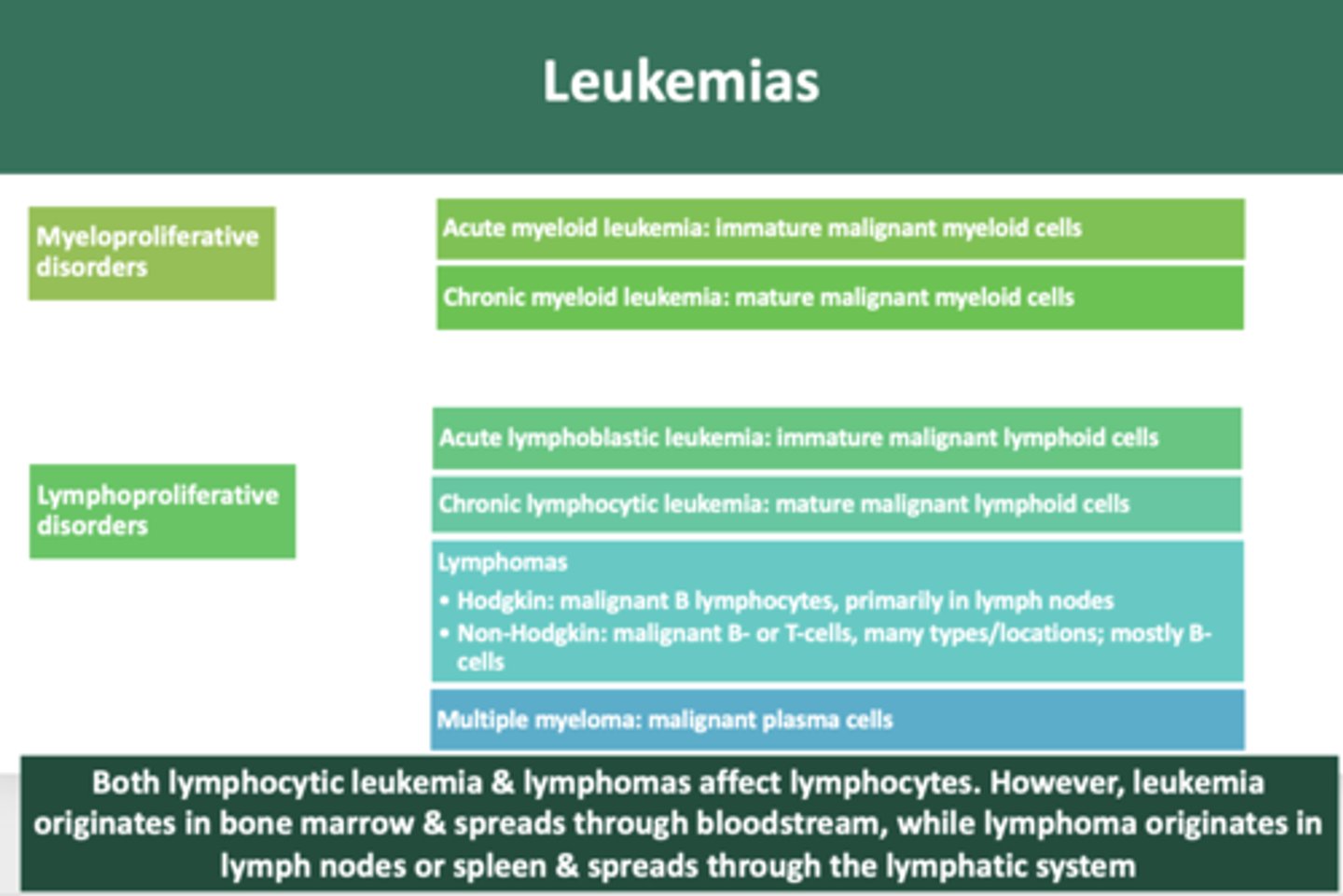
overproduction of malignant plasma cells involving bone
multiple myeloma
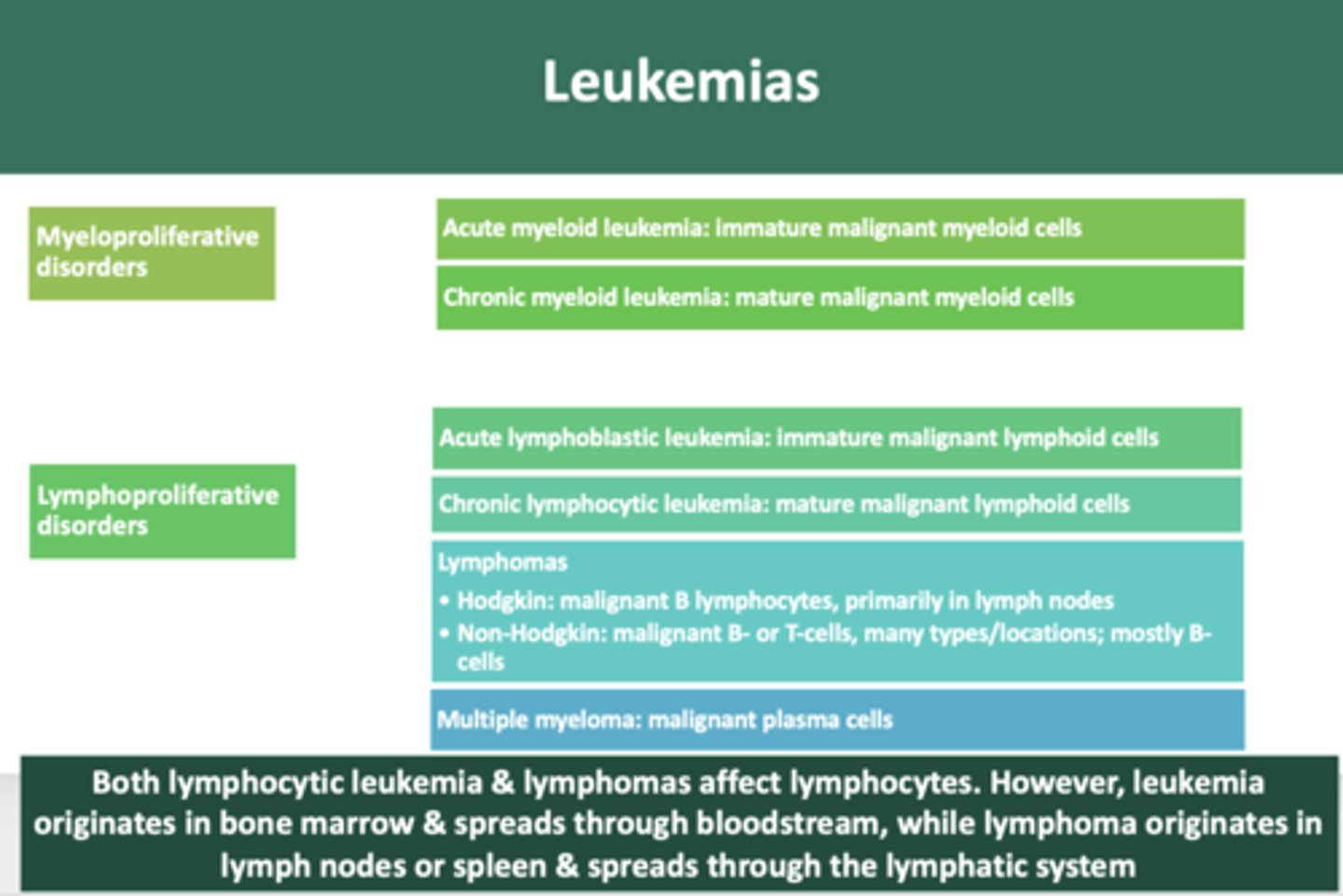
malignant growth of B lymphocytes, primarily in lymph nodes
Hodgkin's lymphoma
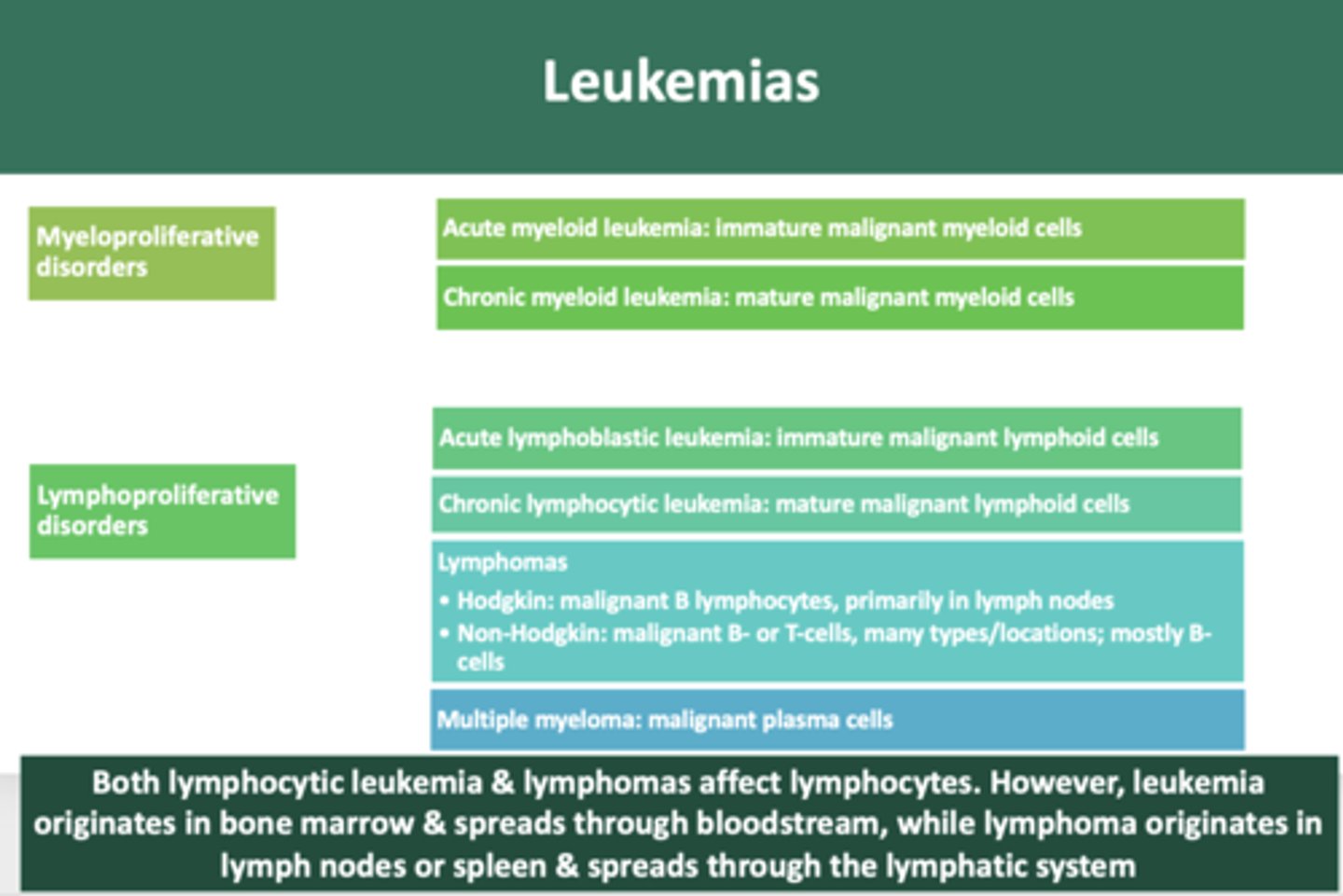
B-cell or T-cell malignant neoplasms, many types and locations, most are of B-cell lineage
Non-hodgkin Lymphoma
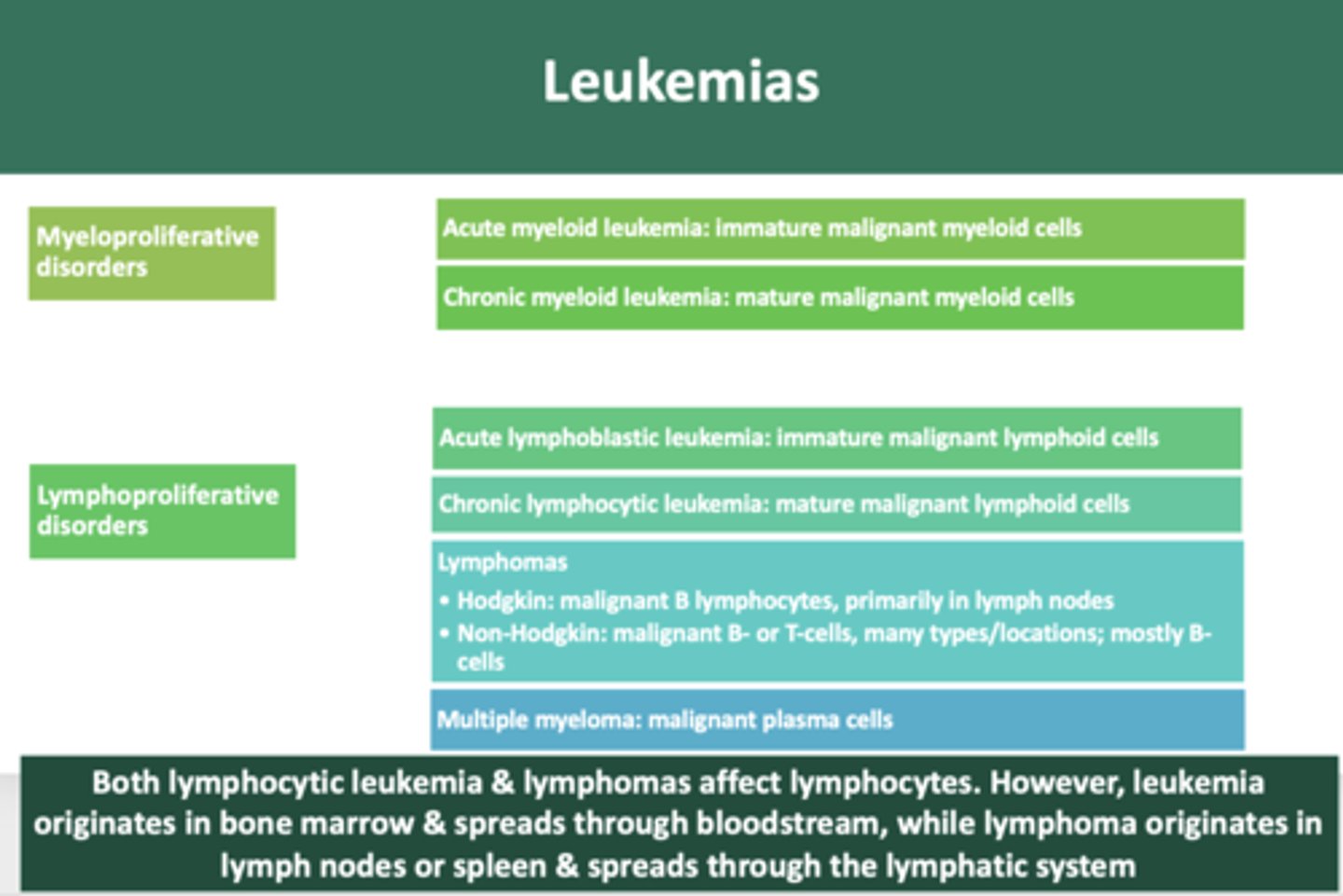
Both lymphocytic leukemia & lymphomas affect lymphocytes. However, leukemia originates in __________ & spreads through bloodstream, while lymphoma originates in __________ or spleen & spreads through the lymphatic system
bone marrow, lymph nodes
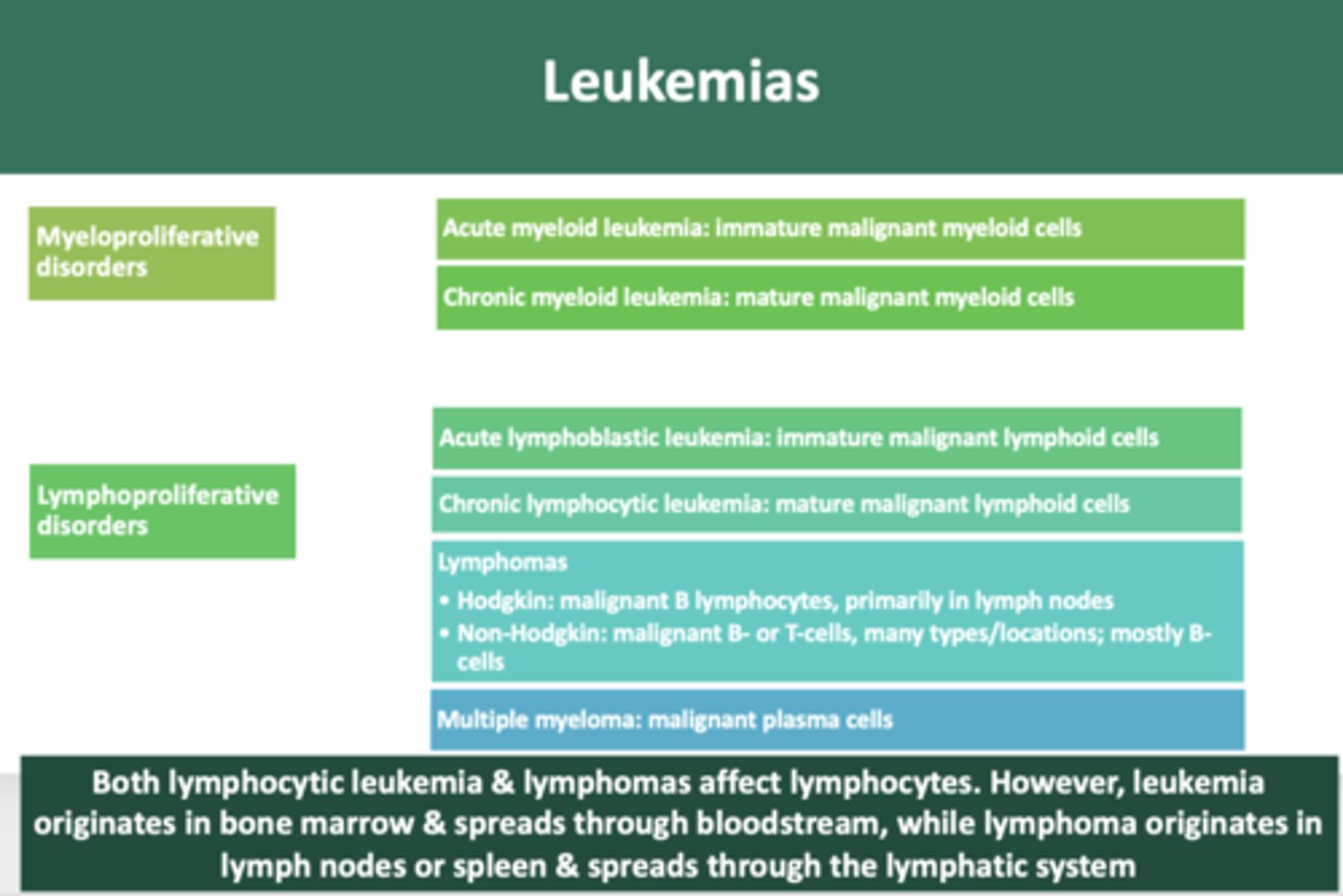
non Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma involving bone and lymph nodes
Burkitt lymphoma
leukocytosis resulting from exercise, pregnancy, and emotional stress:
physiologic leukocytosis
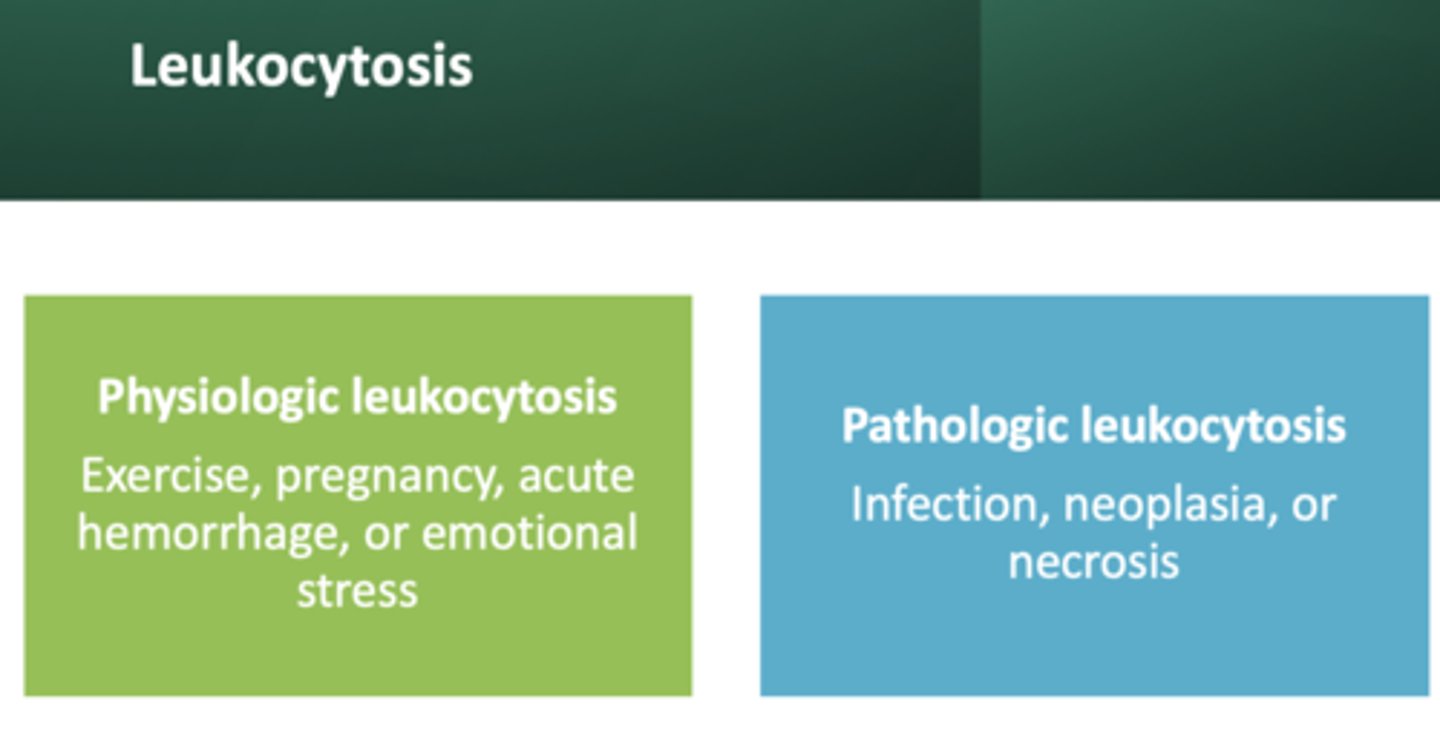
leukocytosis resulting from infection, neoplasia, or necrosis:
pathologic leukocytosis

pyogenic infections induce leukocytosis that is characterized by an increase # of:
neutrophils
tuberculosis, syphilis and viral infections cause an increase in which cell?
lymphocytes
protozoal infections cause an increase in which cell?
monocytes

allergies and parasitic infections cause an increase in which cell?
eosinophils

cellular necrosis causes an increase in which cell?
neutrophils
leukemia cause an increase in which cell?
immature leukocytes

carcinoma of glandular tissue cause an increase in which cell?
neutrophils

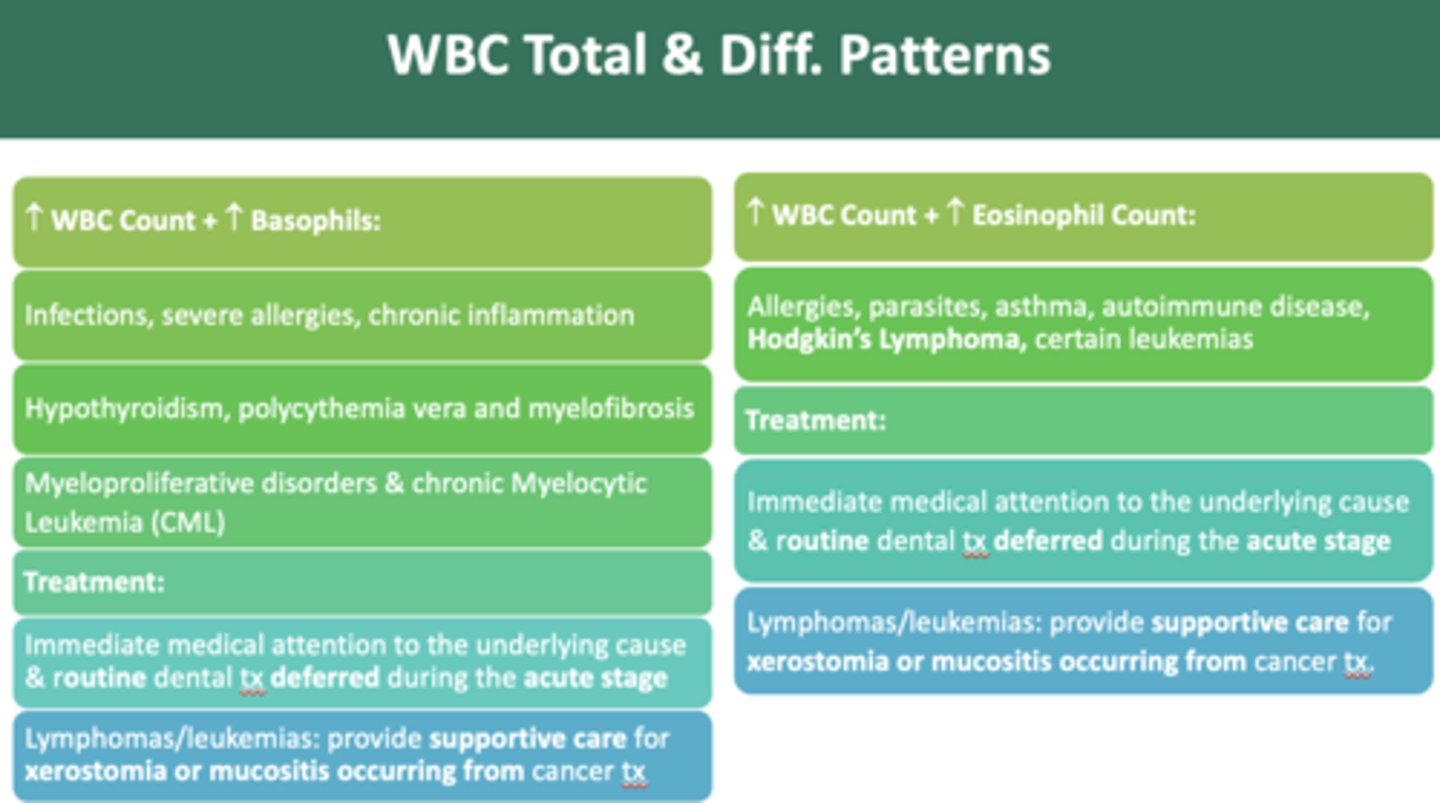
allergies, parasites, asthma, autoimmune disease, and Hodgkin’s Lymphoma cause an increase in which cell?
eosinophils
t/f: acute bleeding can also result in leukocytosis
true
an acute influx of immature cells in the circulation can be from bone marrow in response to
severe infection & inflammation

if excess # of immature granulocytes are in circulation from a bacterial infection response, a shift to the ______ has occurred
left
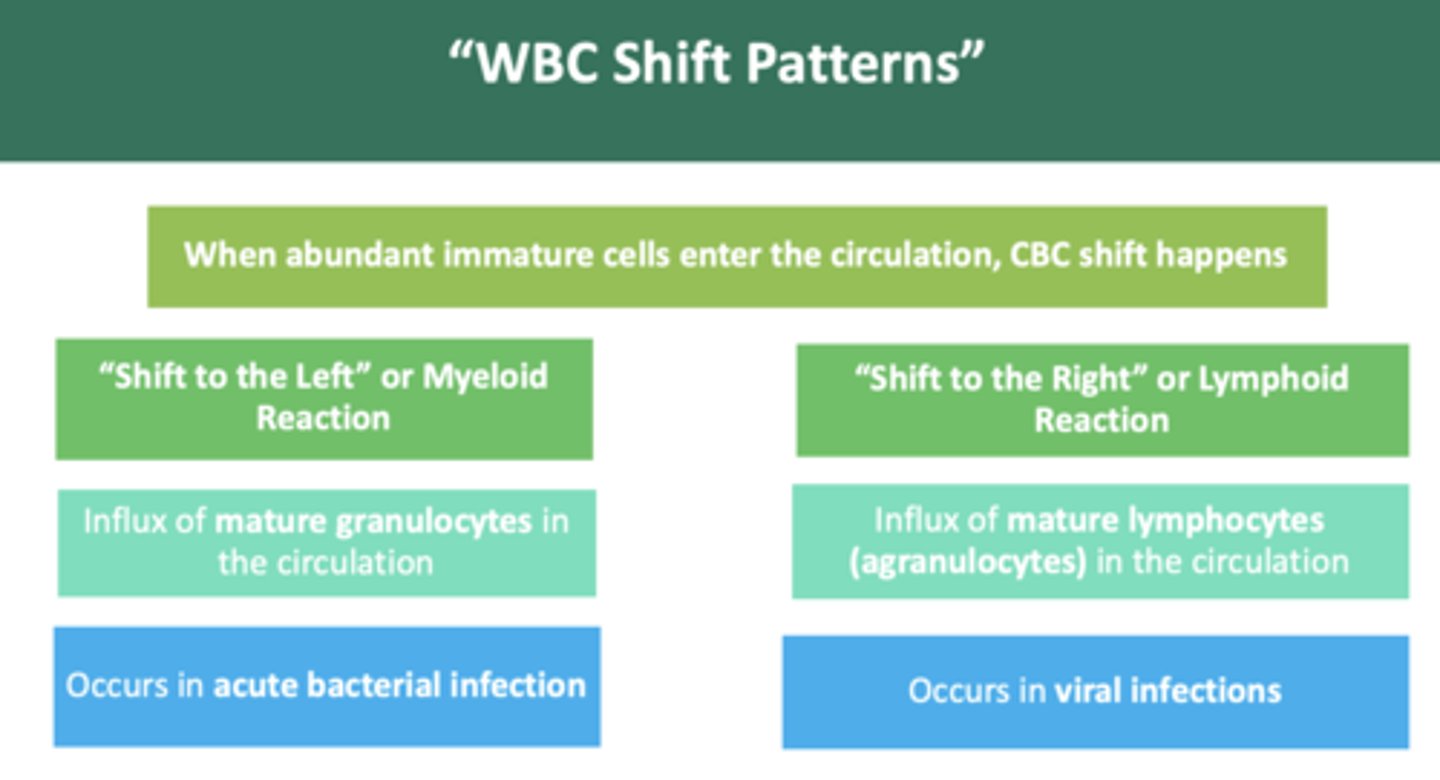
if excess # of immature lymphocytes are in circulation from a viral infection response, a shift to the ______ has occurred
right
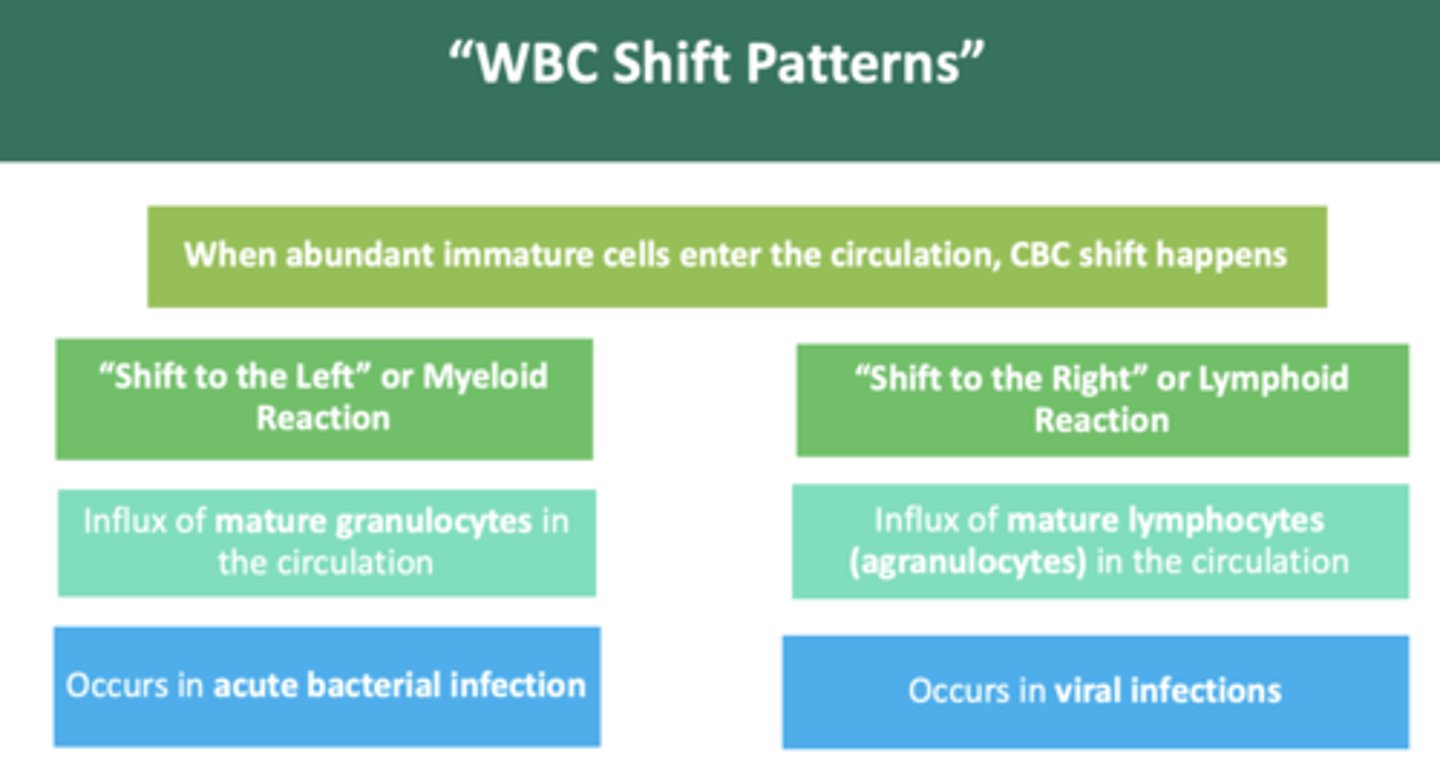
a "shift to the left" indicates a:
myeloid reaction

a "shift to the right" indicates a:
lymphoid reaction
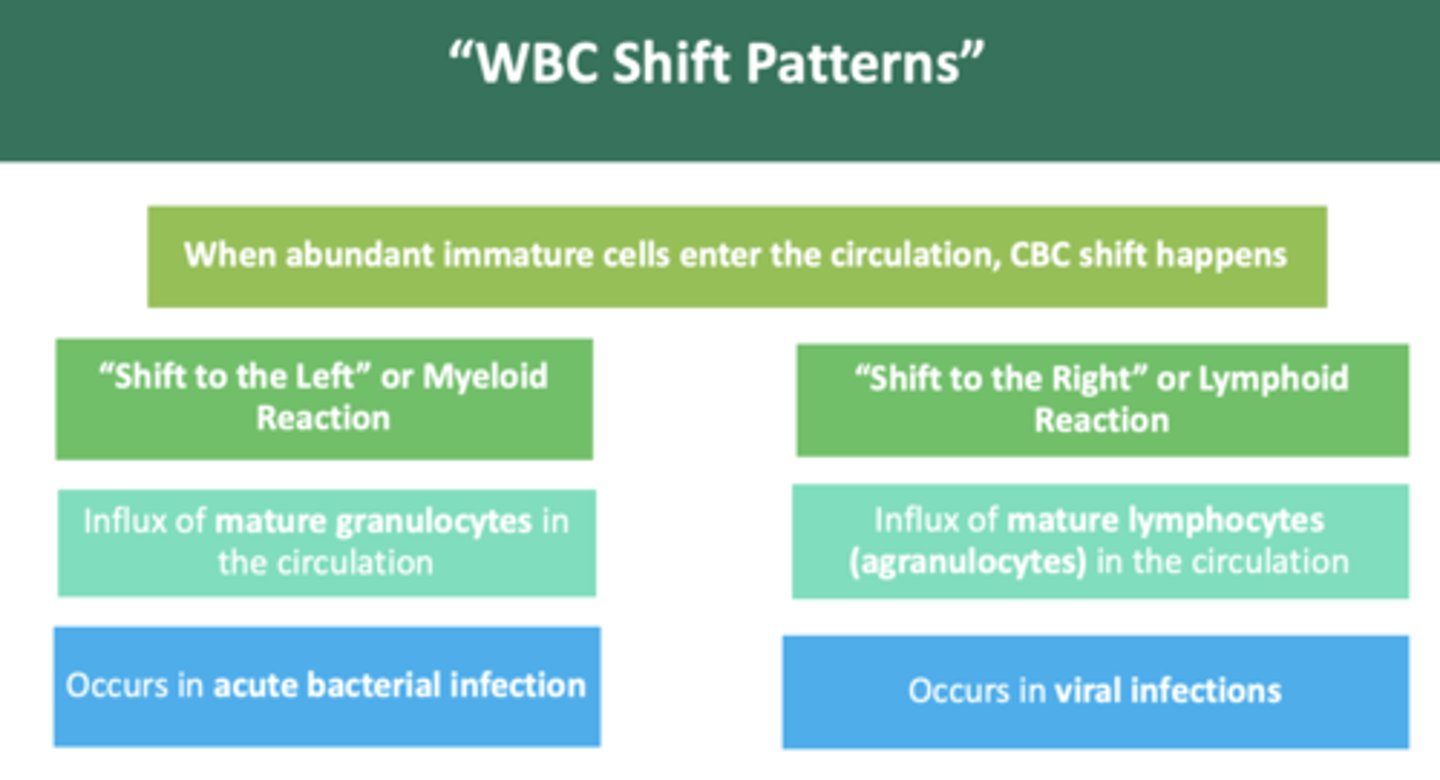
during a blood work up, you notice an increase in WBC count + increase in neutrophil count patter. What type of infection might have occurred?
bacterial infection
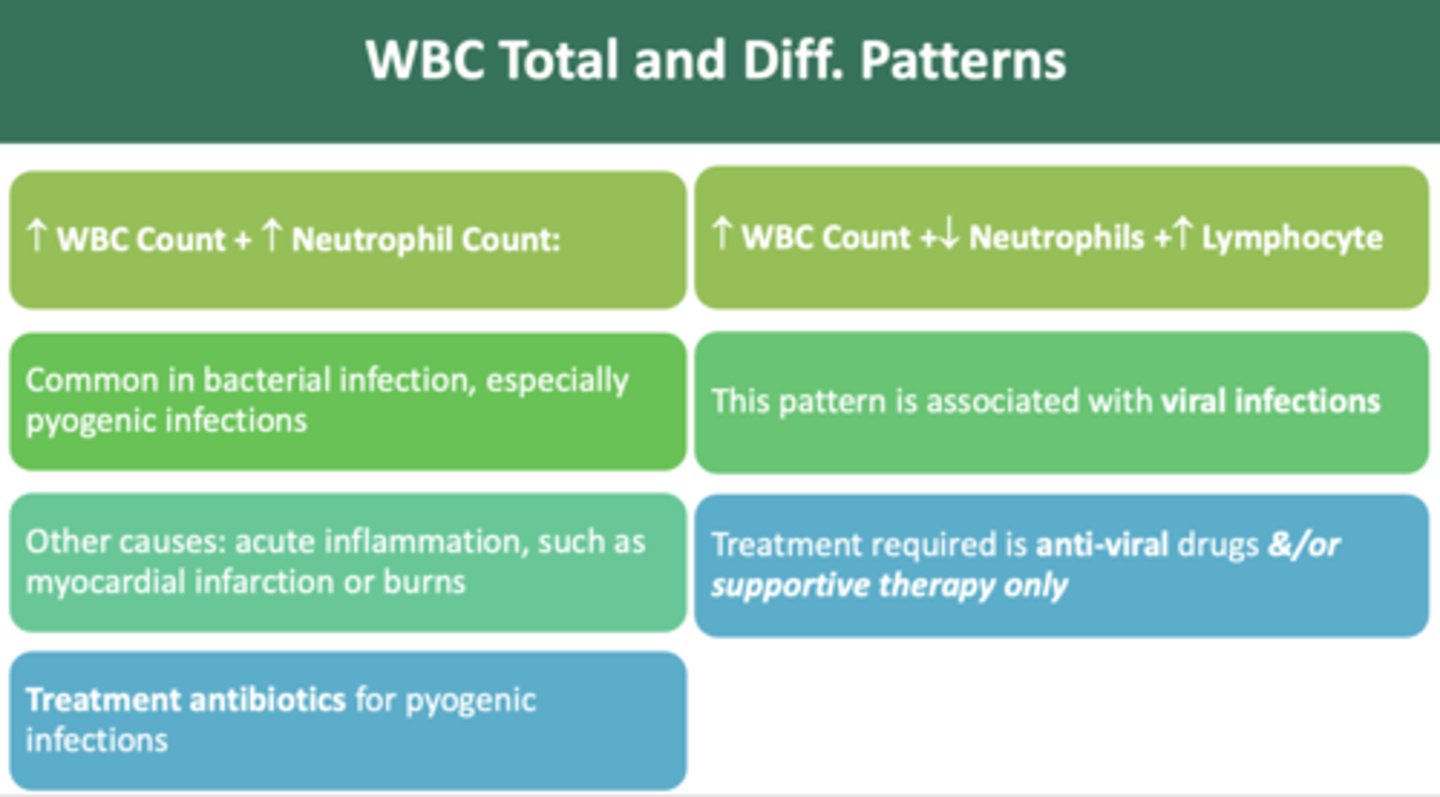
during a blood work up, you notice an increase in WBC count + decrease in neutrophil + increase in lymphocyte pattern. What type of infection might have occurred?
viral infection
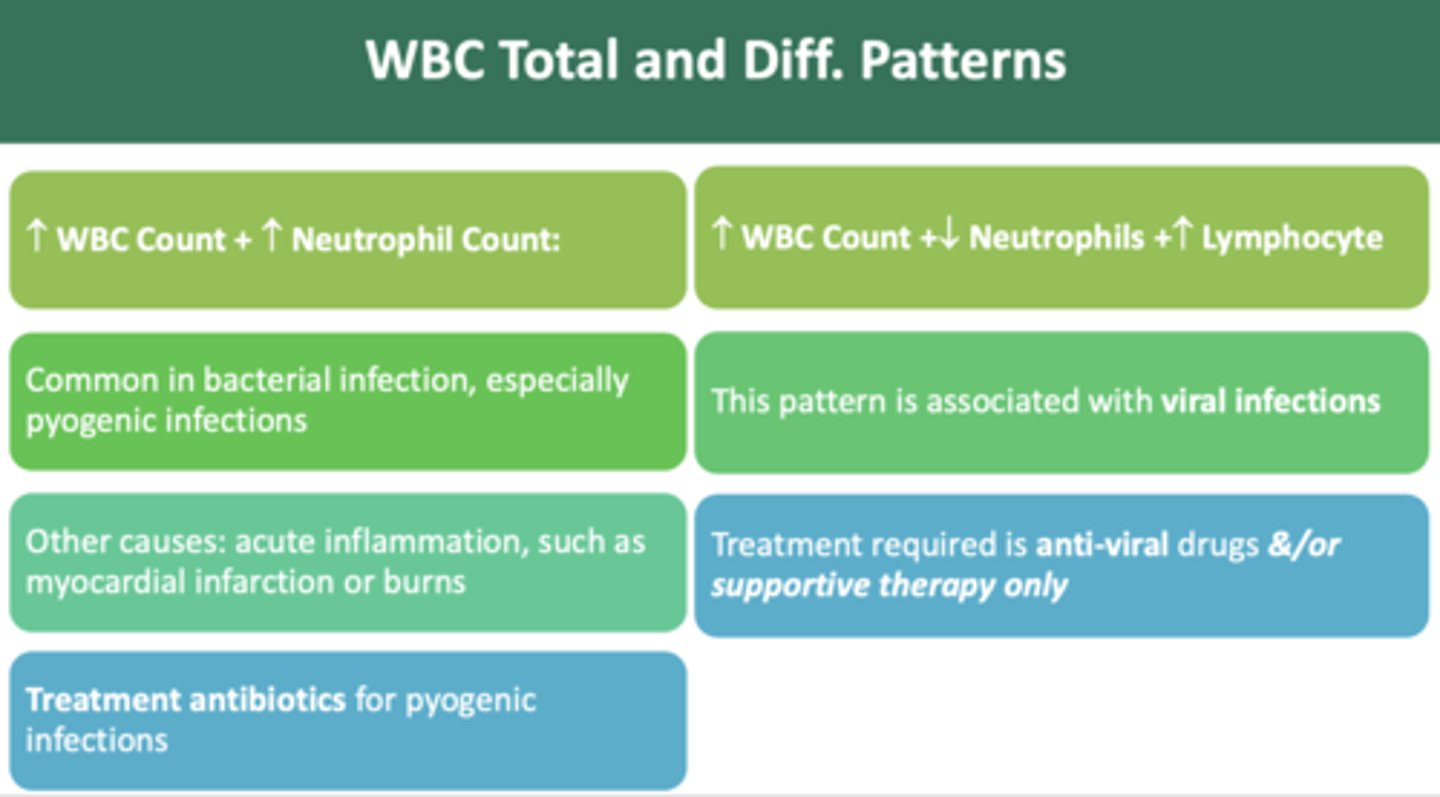
as a dentist, if you observe an increase in WBC count + increase in monocyte count pattern, which indicate a chronic infection/inflammation, you should:
defer routine treatment for 4-6 weeks
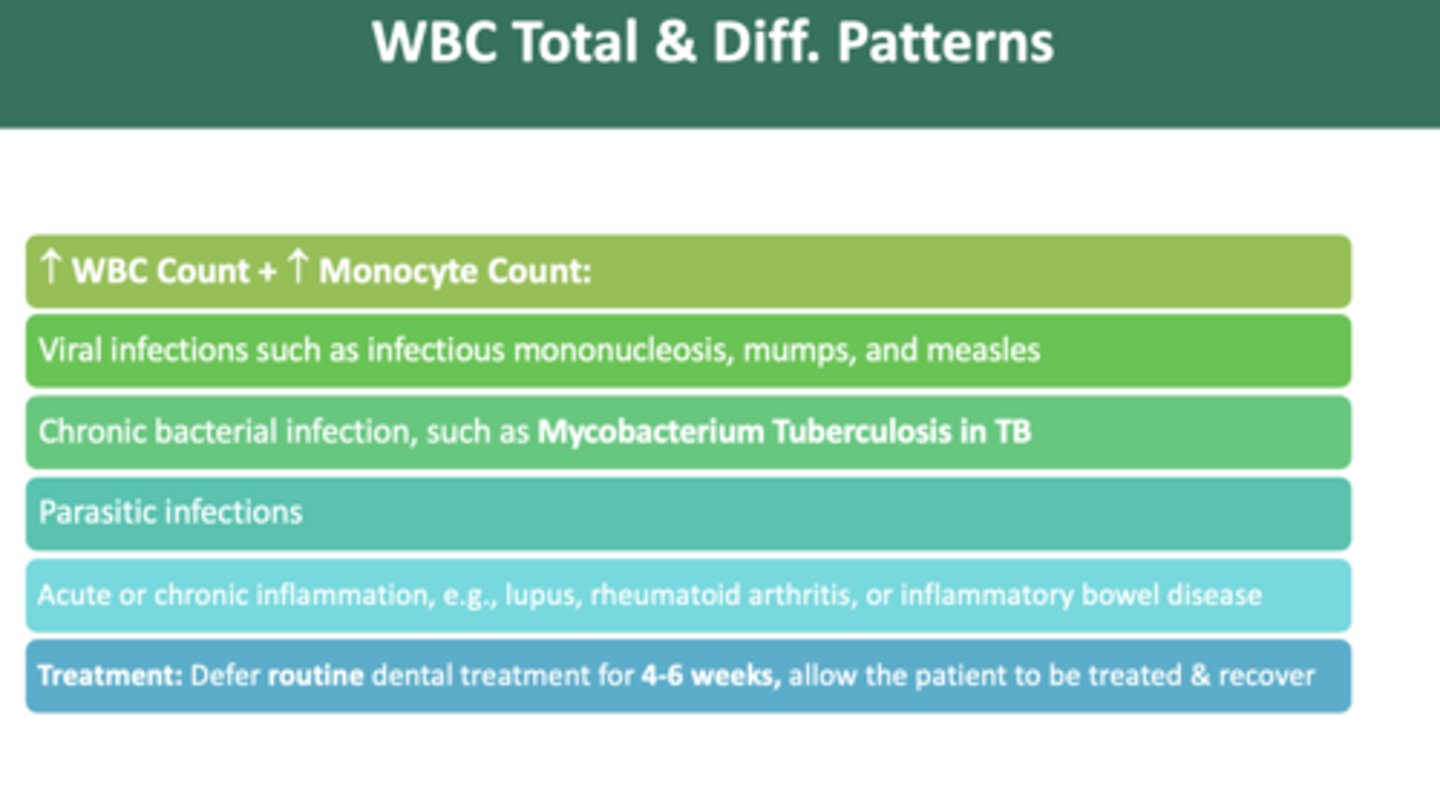
as a dentist, if you observe an increase in WBC count + increase in monocyte count pattern, which could indicate which viral infections?
Mononucleosis, mumps, and measles
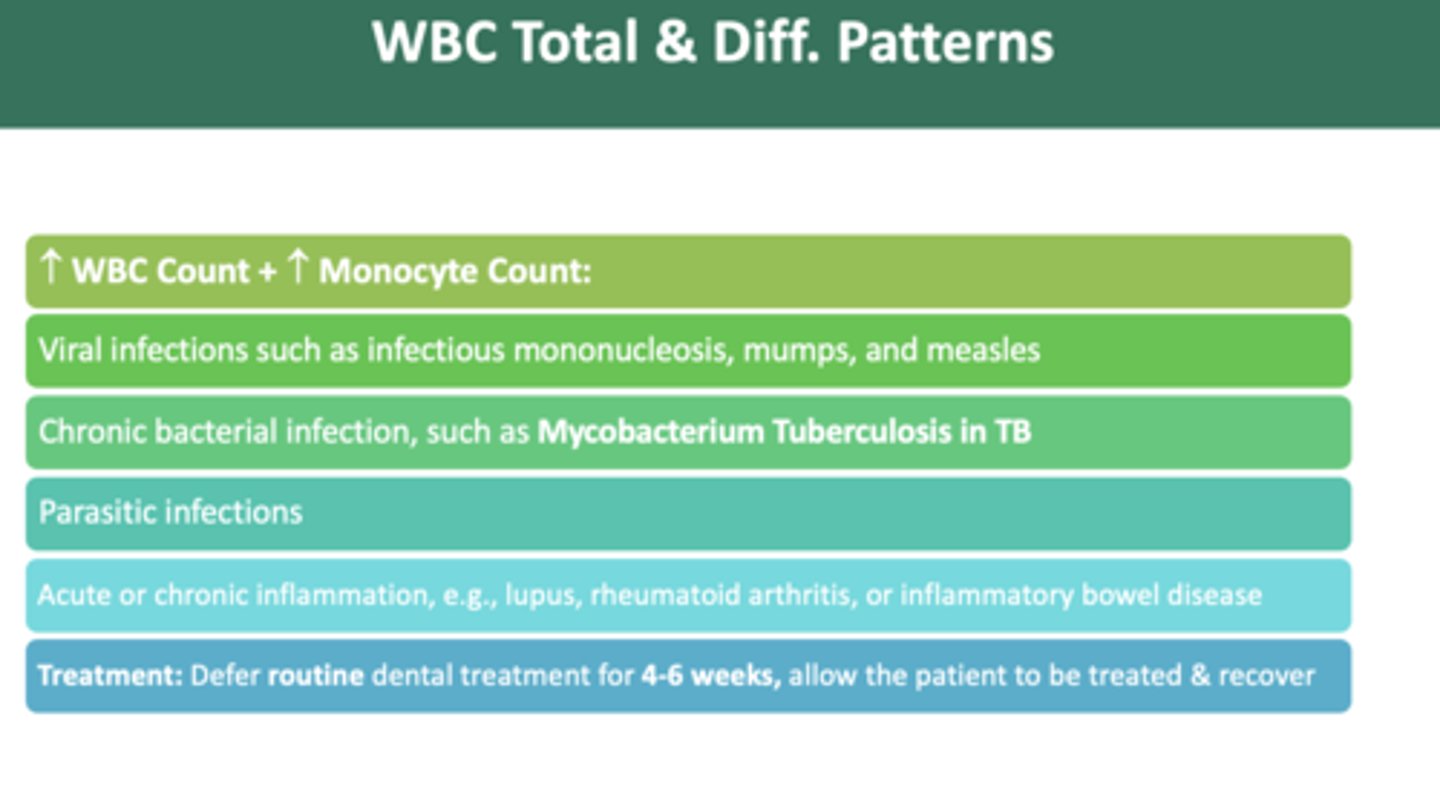
as a dentist, if you observe an increase in WBC count + increase in monocyte count pattern, which could indicate which bacterial infection?
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis in TB

as a dentist, if you observe an increase in WBC count + increase in basophil count pattern, you should:
defer routine treatment until medically cleared
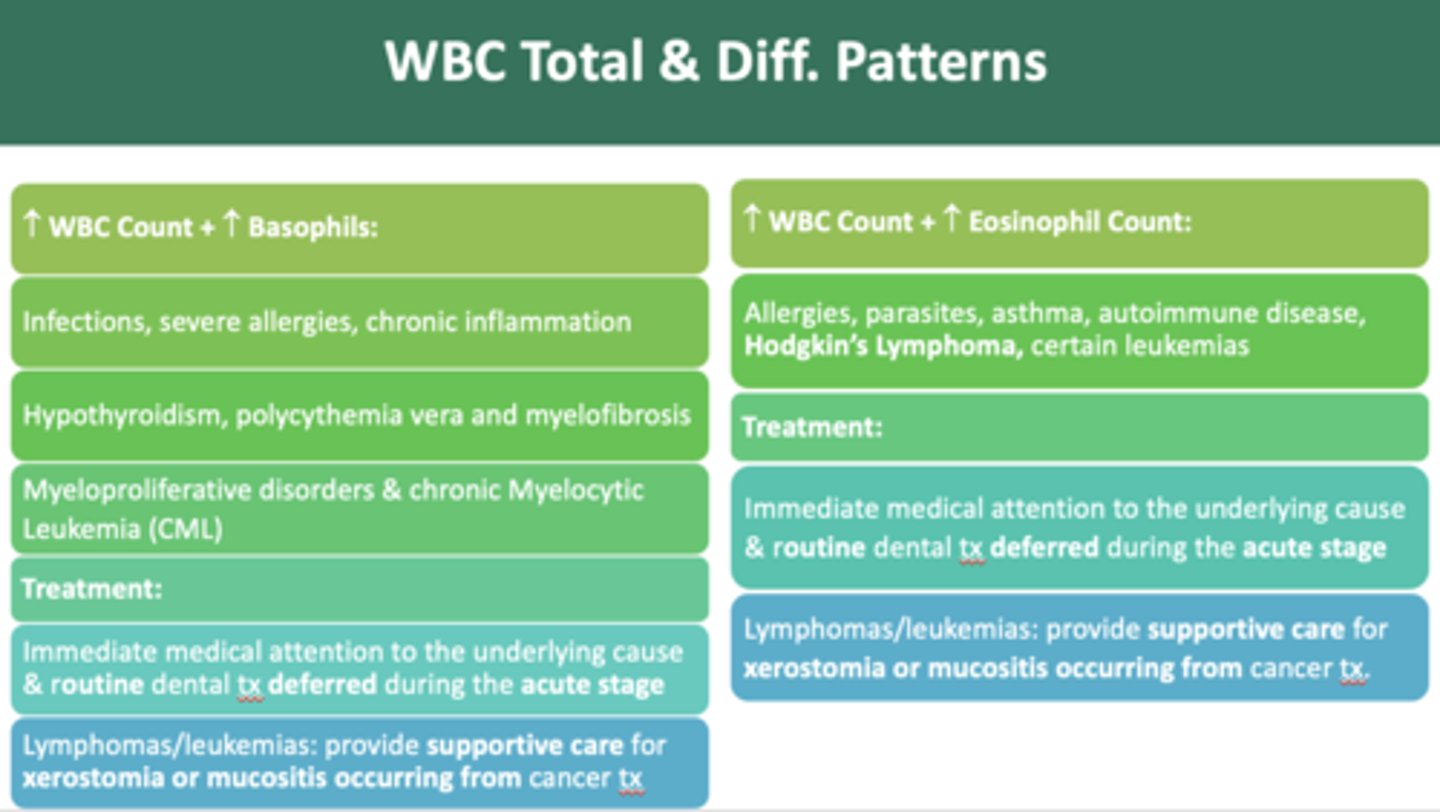
The following have an increase in WBC count and which cell?
- Infections
- Severe allergies
- Chronic inflammation
- Hypothyroidism
- Polycythemia vera
- Myelofibrosis
- Myeloproliferative disorders
- Chronic Myelocytic Leukemia (CML)
Basophils
helps assess the gravity of the leukopenia:
absolute neutrophil count (ANC)
as a dentist, if you observe an increase in WBC count + increase in eosinophil count pattern, you should:
defer routine treatment until medically cleared
Normal ANC Count:
1,500-7,200 cells/mm3
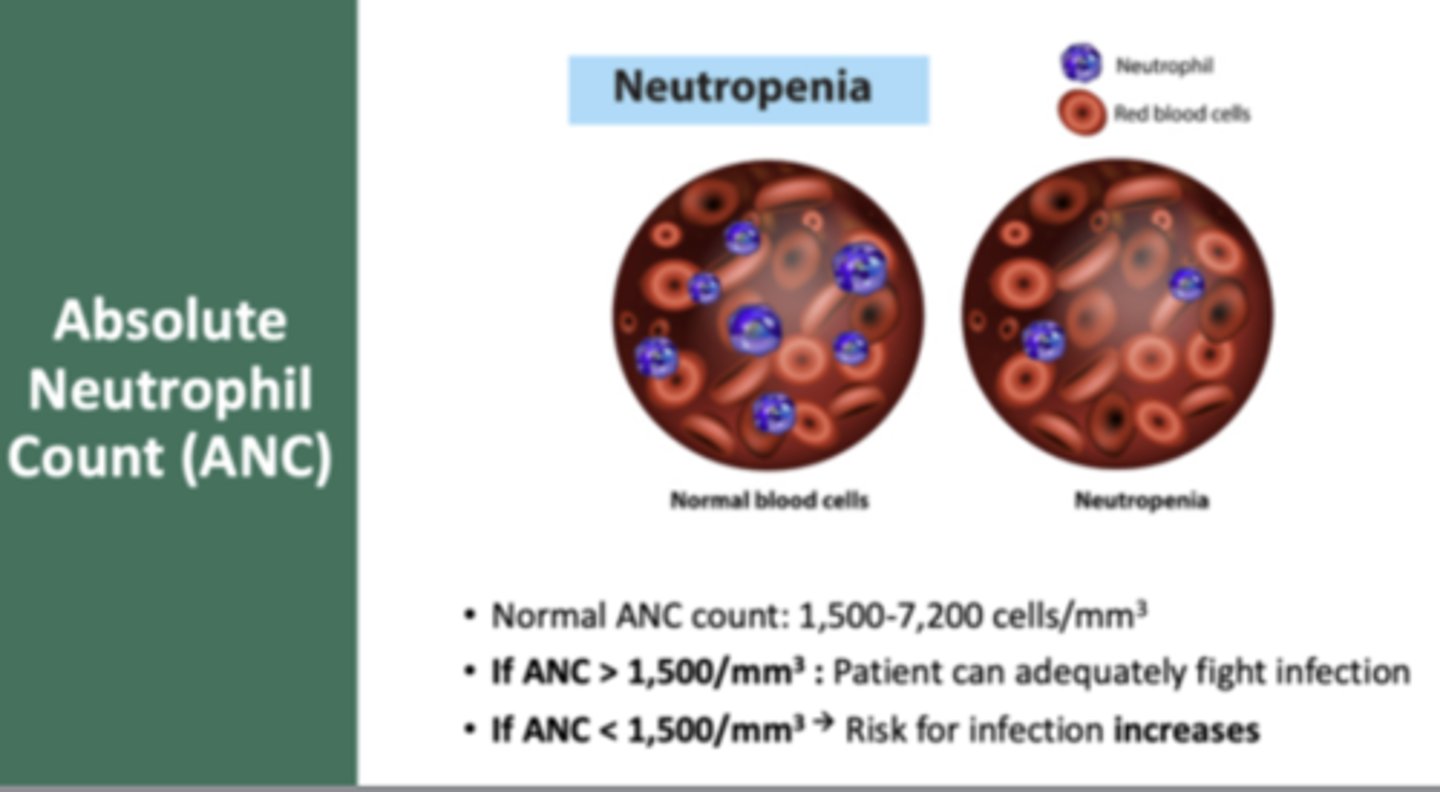
if ANC ___________ patient can adequately fight off infection
> 1,500/mm
a patient with MILD neutropenia will have an ANC range of:
1000-1,500 Neutrophils/mm3

a patient with MODERATE neutropenia will have an ANC range of:
500-1,000 Neutrophils/mm3

a patient with SEVERE neutropenia will have an ANC range of:
0-500 Neutrophils/mm3 (do NOT perform dental treatment)

the only difference between dental guidelines for patients with MILD vs MODERATE neutropenia is:
use premedication for all procedures (moderate neutropenia) vs just major (mild neutropenia)

T/F: You can only perform minor dental procedures when a patient has moderate neutropenia
False; major and minor can be performed w/ non-alcohol mouth rinse before and antibiotics for 3-5 days after major procedures

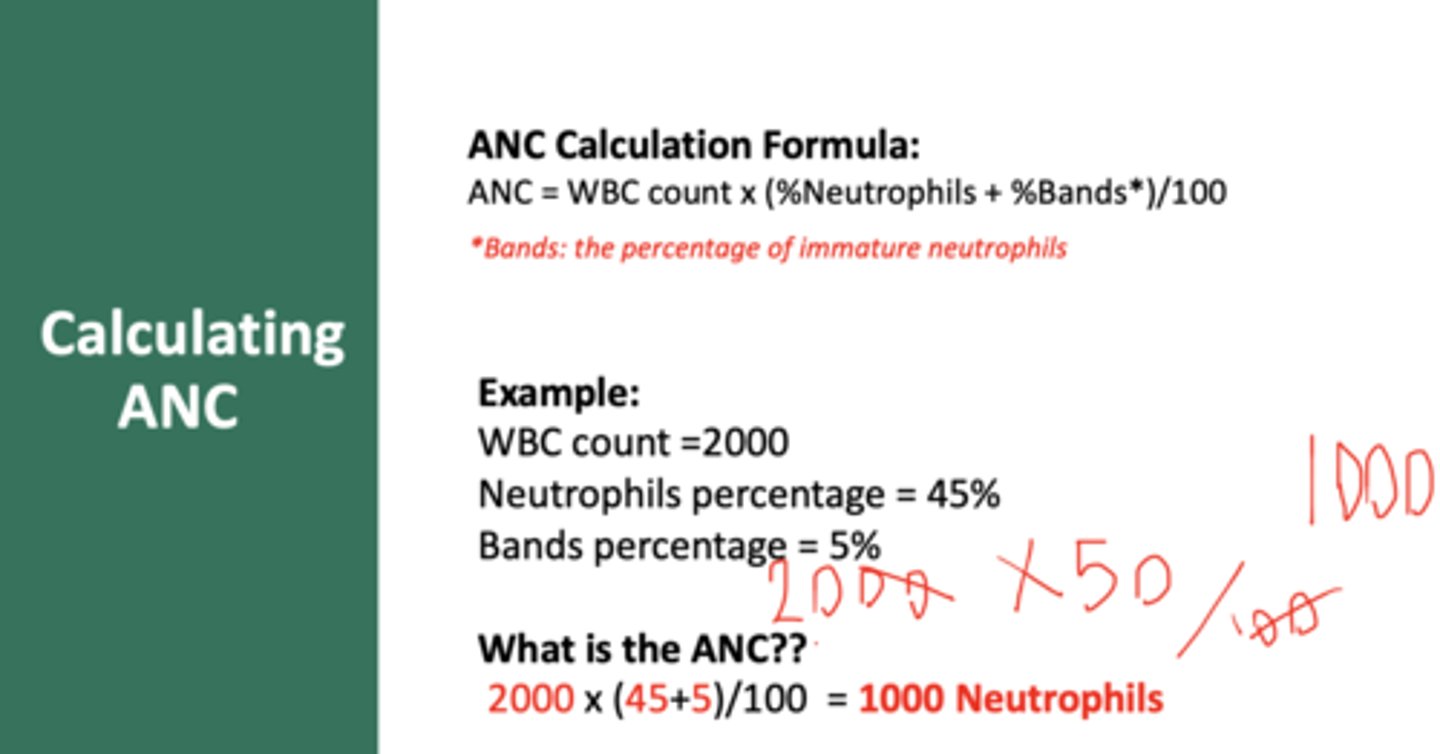
How to calculate an ANC (absolute neutrophil count)
(Segmented neutrophils + bands/100) x WBC count
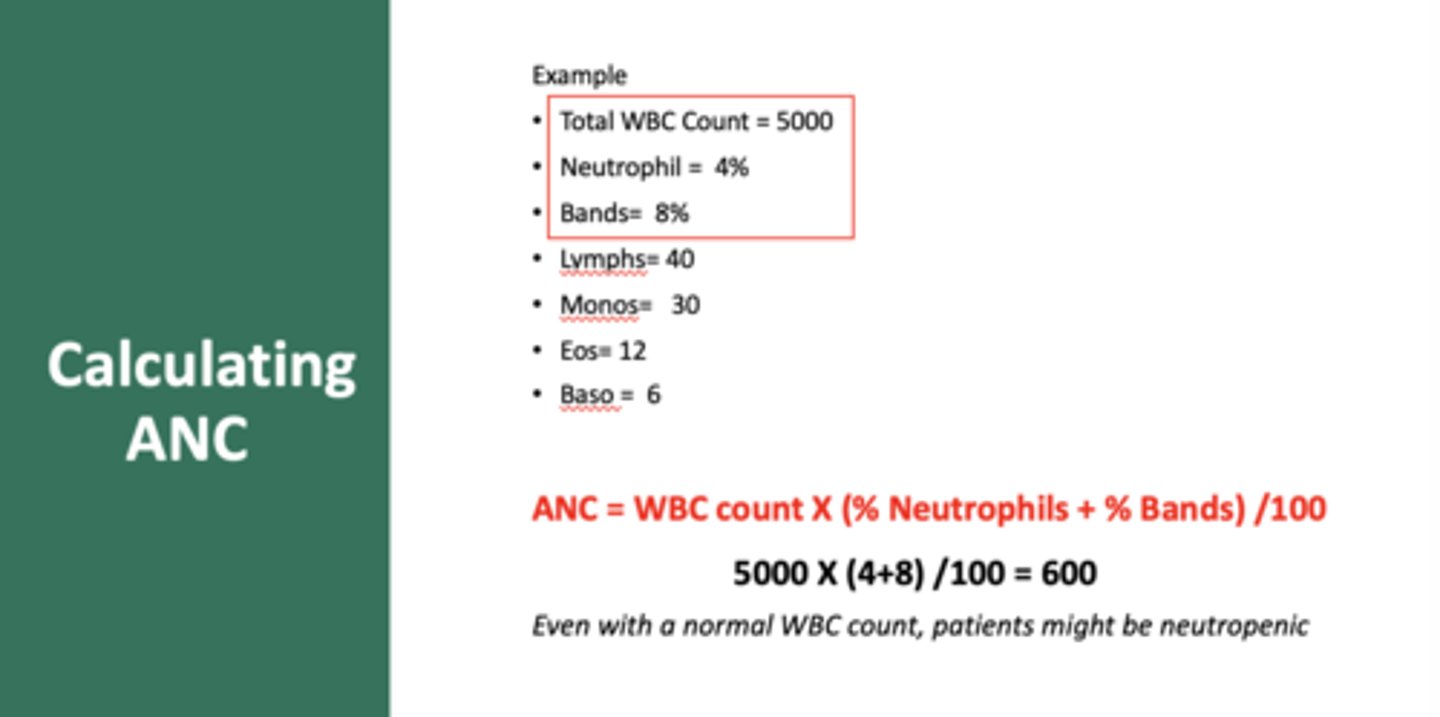
Calculate the ANC based on:
- Total WBC count = 5000
- Neutrophil = 4%
- Bands=8%
600
patients with neutropenia who are also febrile need:
hospitalization, medical emergency!!

what is usually the only symptom of severe neutropenia?
fever

what is usually the only sign of infection of severe neutropenia?
Pain and erythema

T/F: No fluctuation or exudates/pus with any oral abscess in severe neutropenia
True

for patients with severe neutropenia, what medication can increase WBC production?
neupogen
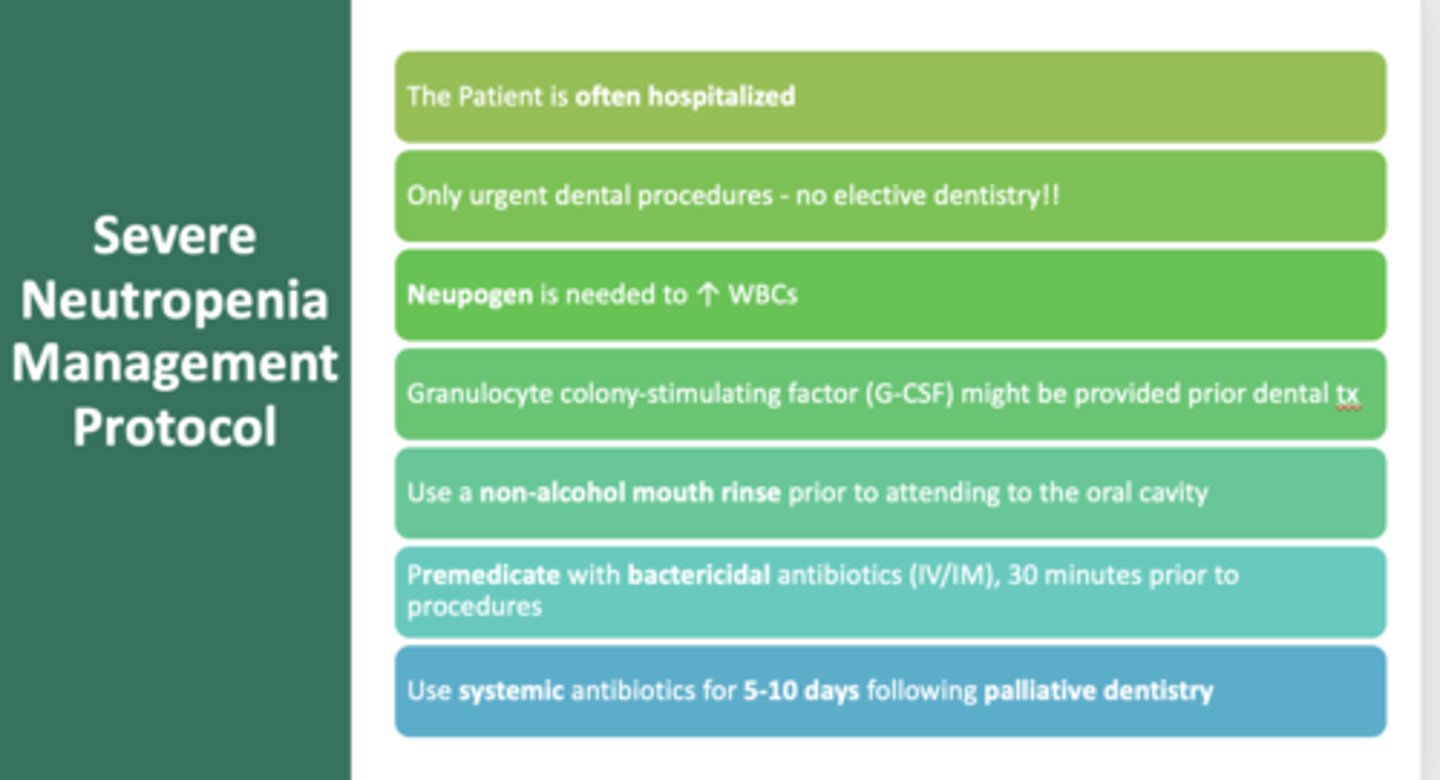
What should you have a patient with severe neutropenia do before attending to the oral cavity and after?
- Non-alcohol mouth rinse
- Premedicate with bactericidal antibiotics (IV/IM), 30 minutes prior to procedures
- Use systemic antibiotics for 5-10 days following palliative dentistry

Rare genetic disorder, regular periodic reduction of neutrophils, occurs in 21-day cycles
cyclic neutropenia

a heterogeneous group of malignant disorders of the blood-forming tissues, characterized by defects in the maturation and proliferation of leukocytes
leukemia
Oral manifestation of cyclic neutropenia
Painful ulcer covered by whitish membrane & erythematous halo
what is the most common type of leukemia and primarily affects older adults?
chronic lymphocytic leukemia

ulcerations
gingival hemorrhages
petechiae
ecchymoses
tooth loosening
delayed wound healing
common oral manifestations of leukemia

Occurs predominately in child and represents one of the more common childhood malignances
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia

This type of leukemia shows peak prevalence during the third and fourth decades of life
Chronic myeloid leukemia

This type of leukemia affects a broader range, including children
Acute myeloid leukemia

this is a cancer of the lymph organs and tissues that presents as discrete tissue masses:
lymphoma
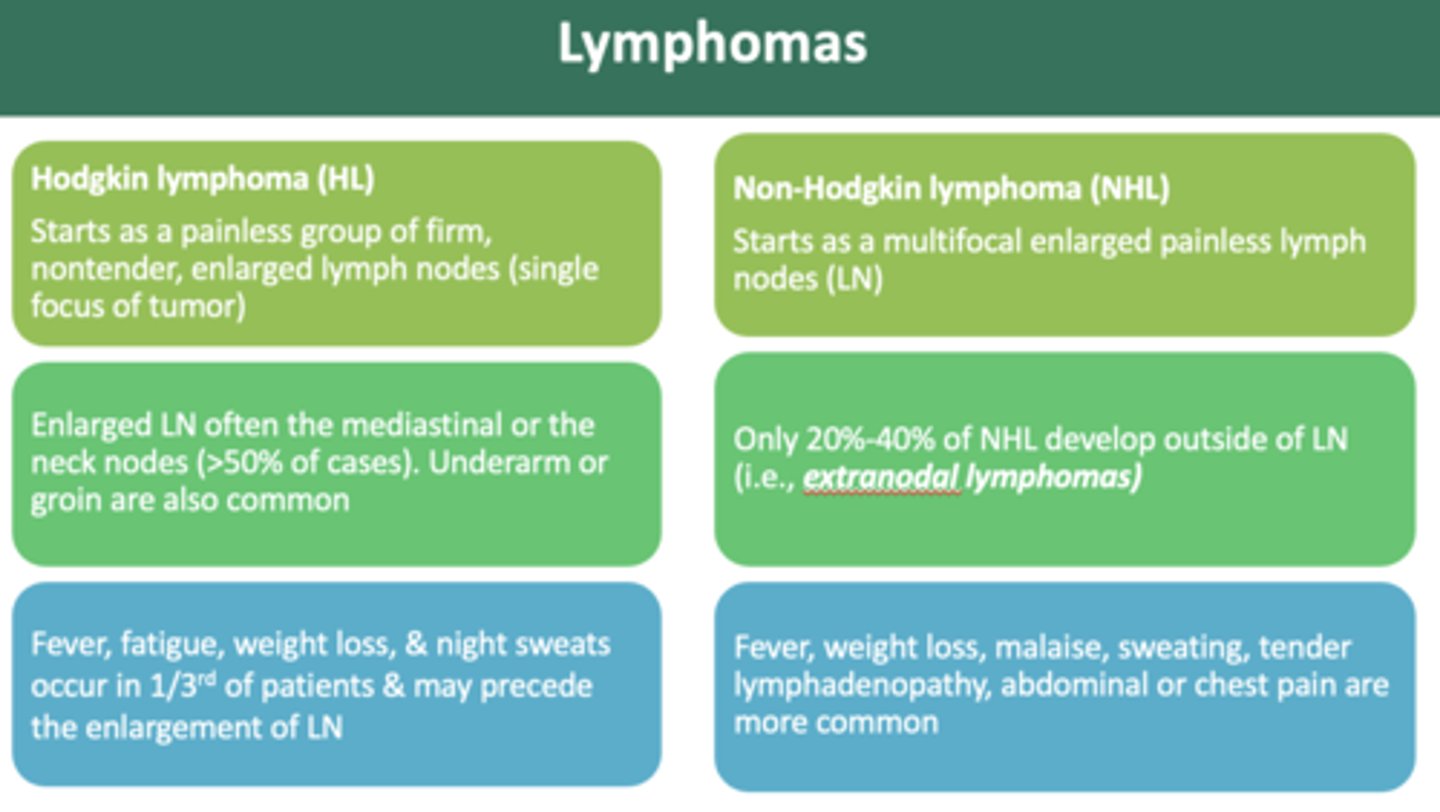
Patient presents with painless mass, non-tender, enlarged lymph nodes. Patient also has recent weight loss, and night sweats. When palpates, the lymph nodes are a rubbery consistency. What is the diagnosis?
Hodgkin lymphoma
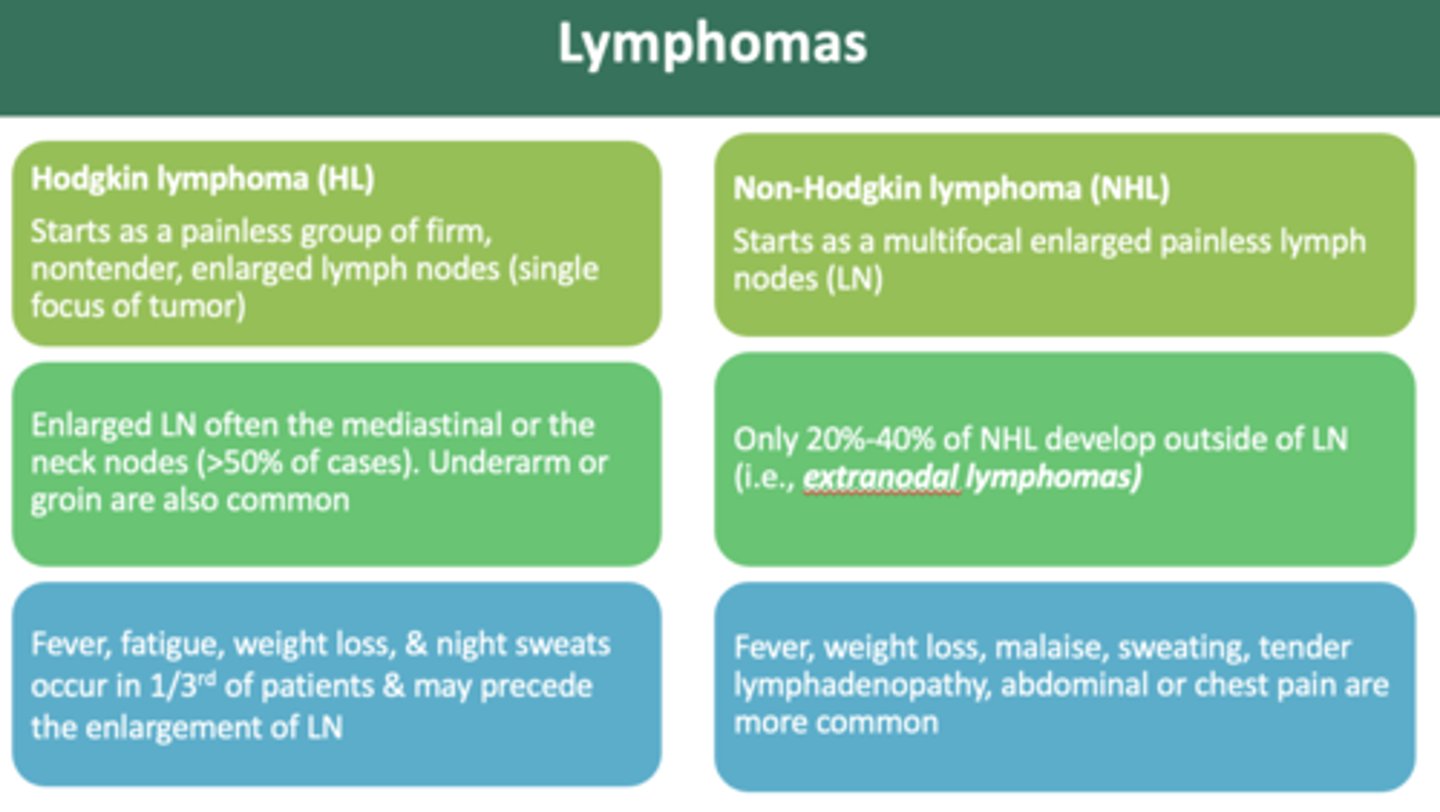
the difference between Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin lymphomas is:
- multifocal tumors (non hodgkin)
- single focal (hodgkin)
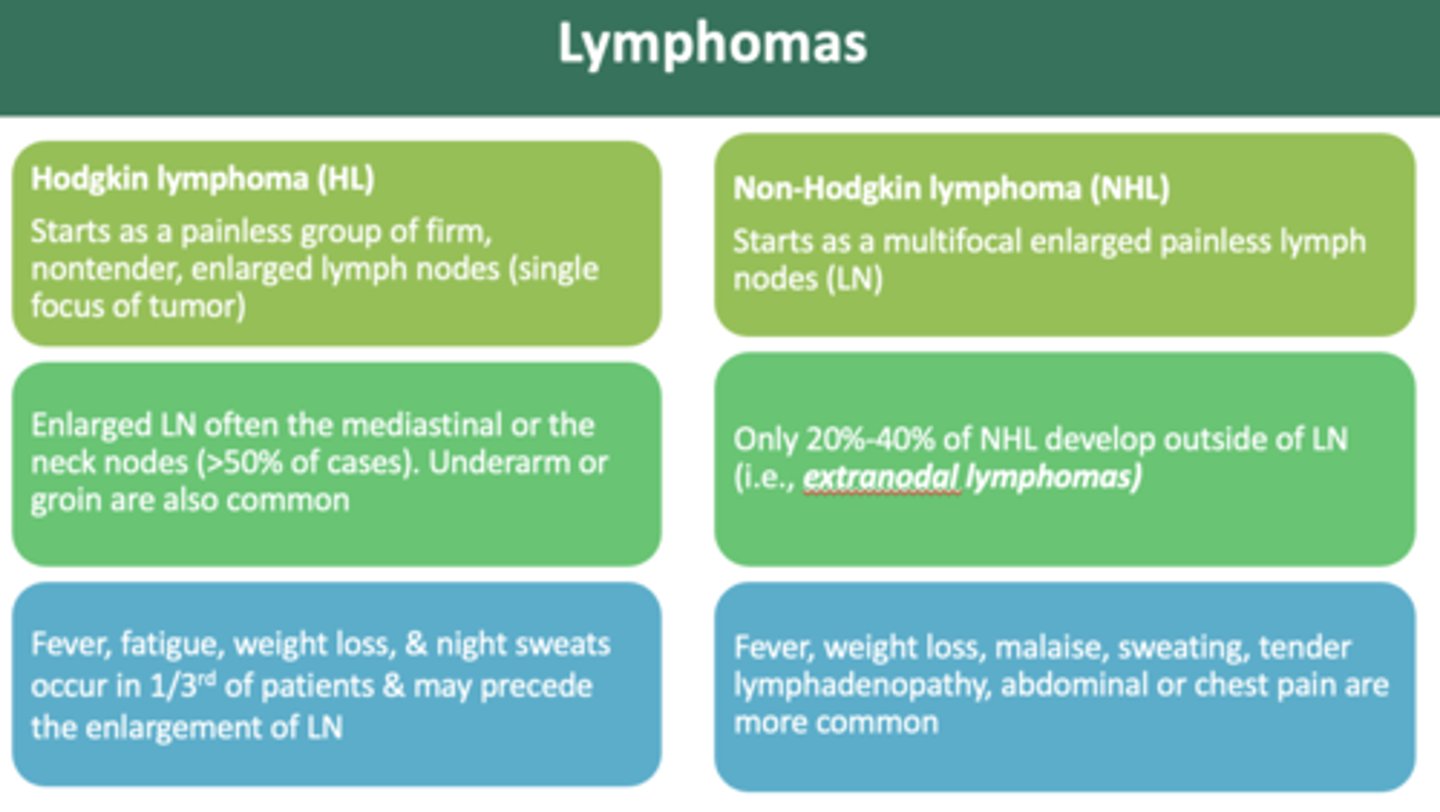
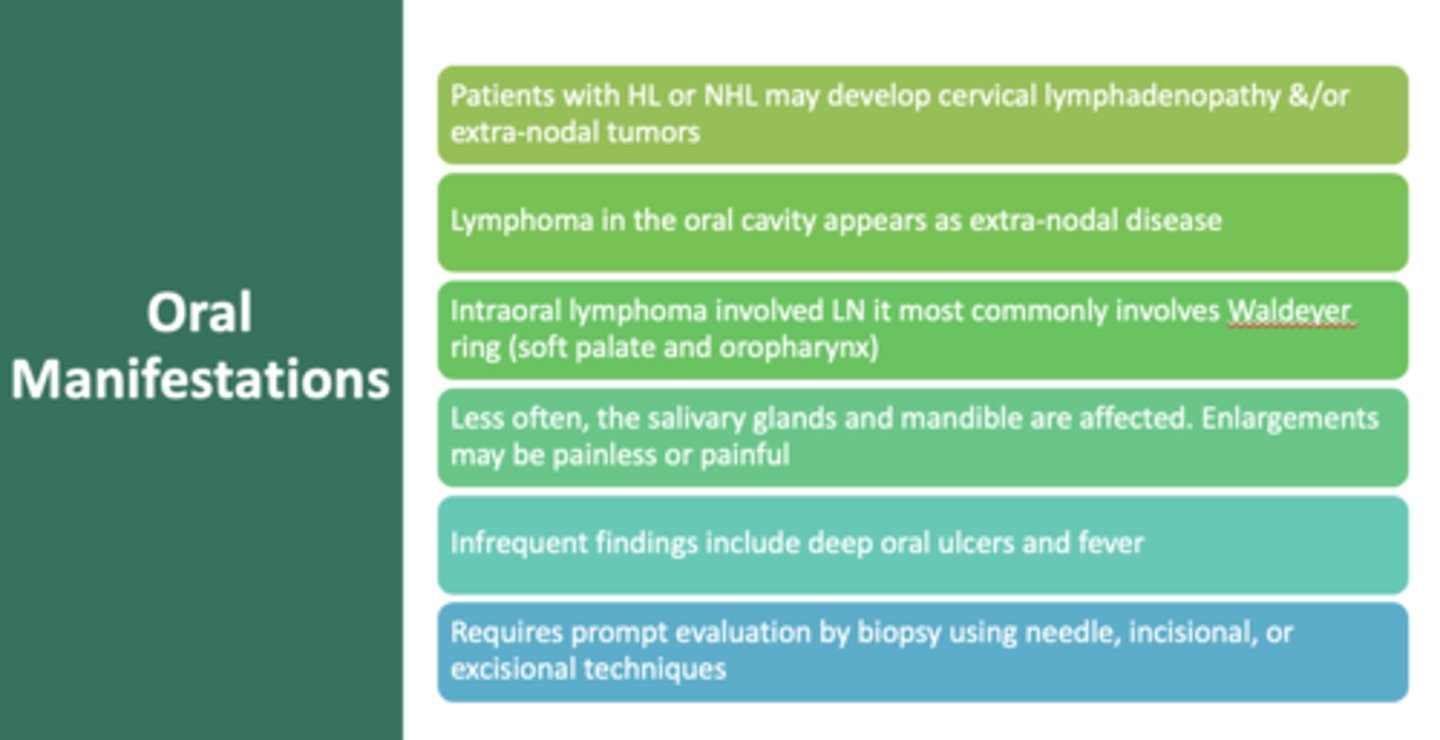
Lymphoma in the oral cavity appears as ______-nodal disease
extra
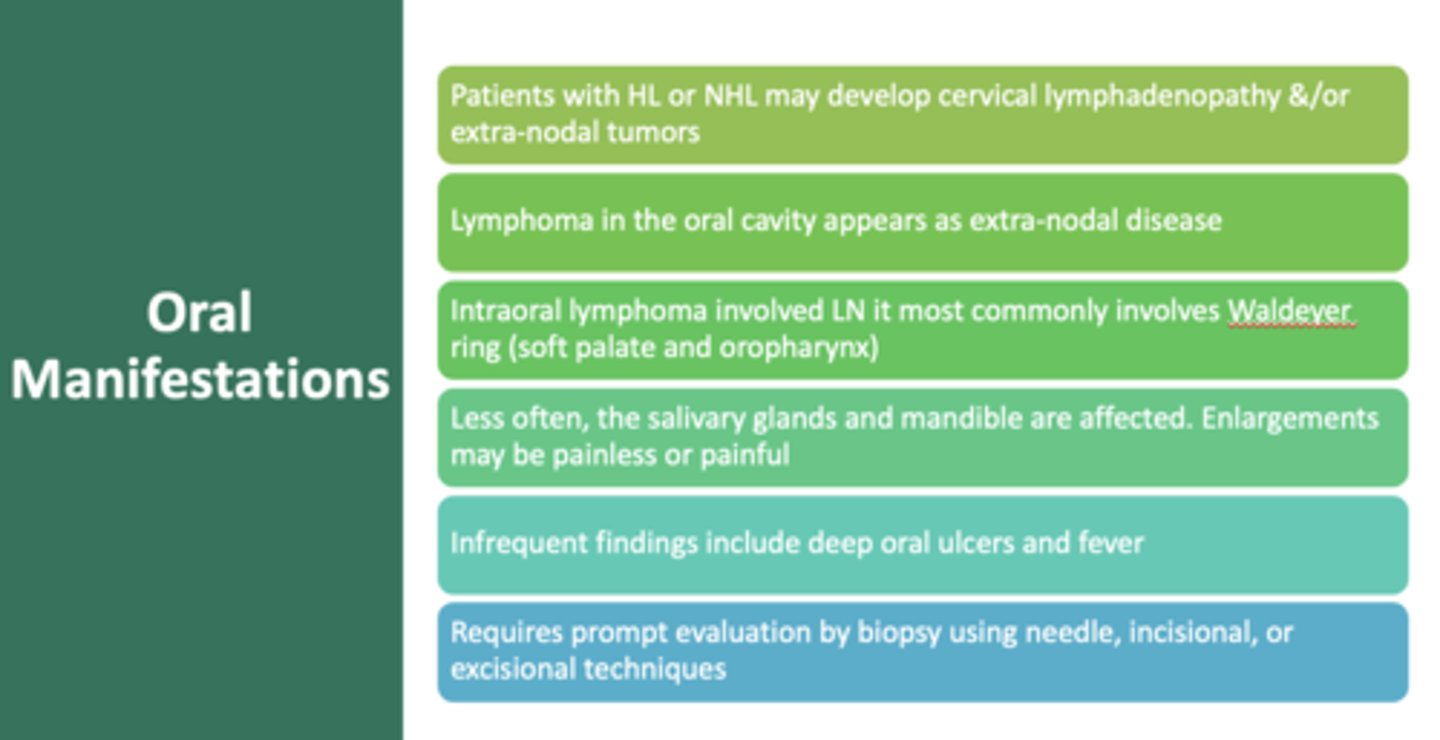
intraoral lymphoma most commonly involve:
Waldeyer's ring (soft palate and oropharynx)
Patient presents with multifocal tumor, enlarged lymph nodes, fever and weight loss. The patient experiences painless lymph node swelling for longer than 2 weeks. What is the diagnosis?
Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
this type of B cell lymphoma mostly arises at extranodal sites with predilection for tumors of the jaw and involvement of abdominal organs ( kidneys, ovaries, adrenal glands), rapid growth displaces adjacent teeth, pain and paresthesia accompany, can double in size every 3 days:
Burkitt lymphoma

what is the most common lymphoma of childhood?
Burkitt lymphoma

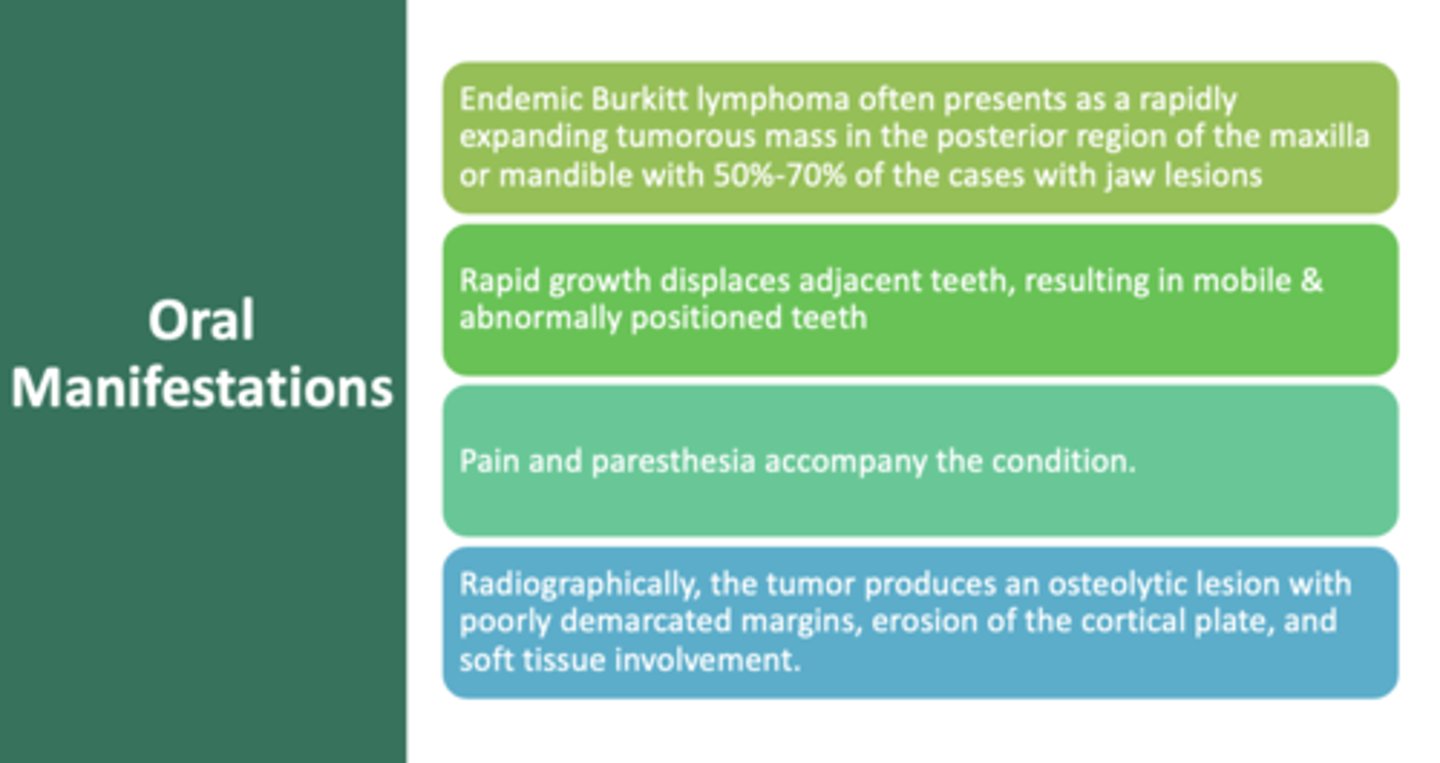
An aggressive B-cell (non hodgkin lymphoma) that often presents as rapidly expanding tumorous mass in the posterior region of the maxilla or mandible
Burkitt lymphoma

What type of Burkitt lymphoma often presents as a rapidly expanding tumorous mass in the posterior region of the maxilla or mandible with 50%-70% of the cases with jaw lesions?
Endemic