6 - Convergent Boundaries
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
three types of convergent boundaries
O-O
O-C
C-C
what are convergent boundaries driven by
heat/temp differences, motion in mantle (slab/pull, ridge/push)
why is earth a recycling medium
ocean plates are made, reworked and subducted
how long has subduction been functioning for
since the archean
what type of material gets recycled most
oceanic materials
two types of subduction
accretionary and erosive
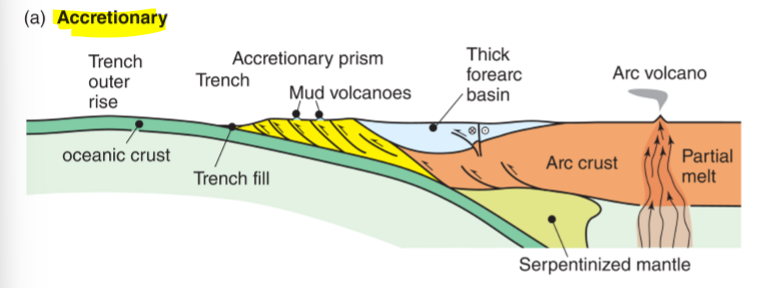
what is accretionary subduction and what are some features of it
Adding material to continent - slower, shallower angle, large accretionary wedges
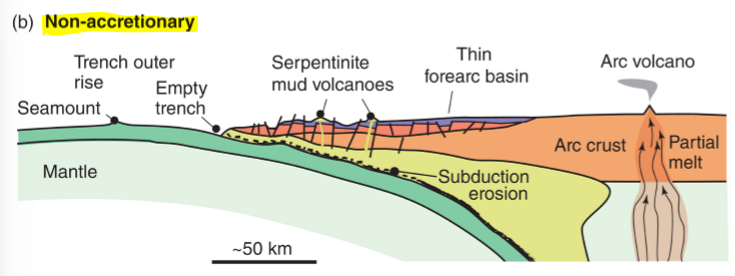
what is erosive subduction and what are the features of it
removal of material — steeper, faster subduction, thin sediments, trench rollback
which type of subduction is slower
accretionary
what kind of subduction is steeper
erosive
trench rollback is due to… s______
suction
which type of subduction creates trenched that get filled?
non accretionary (erosive)
forearc basins are thicker in which type of subduction zones
accretionary
accretionary prisms are present in what type of subduction
accretionary lol
what kind of subduction zone are we in
accretionary
what kind of crust is created from subduction and how
oceanic crust, from partial melting of the mantle
what rocks are formed from partial melting of the mantle
tholeiitic basalts
what are tholeiitic basalts made of
more Fe and les Mg and Al
what happens to the newly created oceanic crust as the plate develops
develops sediments, and becomes saturated with water, O2 and CO2
how many oceans have been carried down with subduction, where do they get trapped
like 11, trapped in mantle in hydrous reservoirs
two end members of subduction
Andean (continental)
Marianan (oceanic)
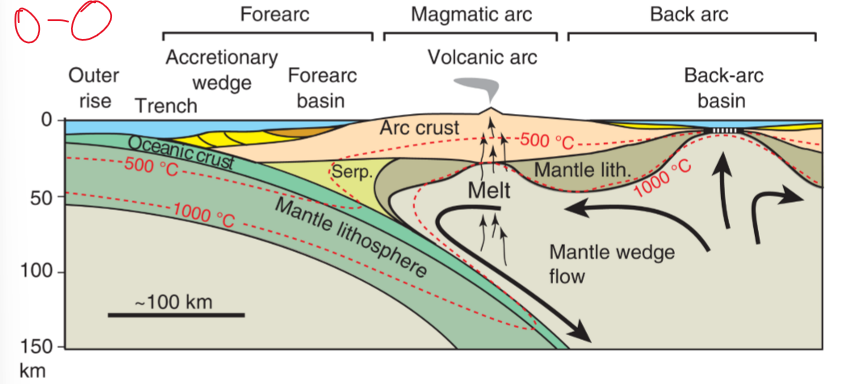
features in a O-O island arc
mafics-intermediates
from mantle
forearc, magmatic arc, back arc
accretionary wedge
trench—filled in
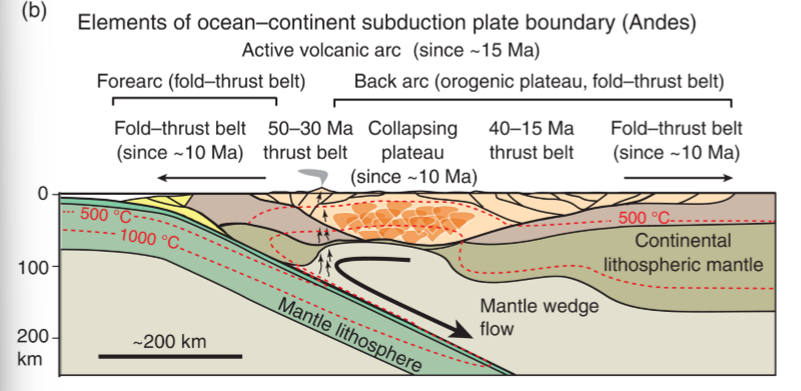
features in a O-C plate boundary
felsic-intermediates
produced at surface
forearc (fold/thrust), back arc (orogenic plateau)
no trench, no accretionary wedge
what 5 things do typical magmatic arcs have
volcanic front
forearc basin
deep sea trench
back arc basin (with or without a remnant arc)
accretionary wedge
what is the volcanic front
where the volcanoes are
what is the forearc basin
head of arc, has sediments shredding off mountains produced by the arc
what is a remnant arc
from extension from trench suction
whats an example of a backarc basin
sea of japan
what is slab rollback
slab subducts, pulls down, and rolls back
what does trench suction cause and create
causes extension, creates rifting with a backarc spreading region
what are the phase changes that subducting slabs go through
“wet” mafic crust to anhydrous eclogite
“Wet” serpentinized mantle dehydrates
released fluids = hydraulic fracturing and other failures
Triggers earthquakes = Benioff zone
what is the benioff zone
pattern of earthquakes we see in subducting zones
what causes shallow and deep earthquakes on cold, old, deeply hydrated subducting slabs
phase changes
adding or taking away water
volume changes
fracturing
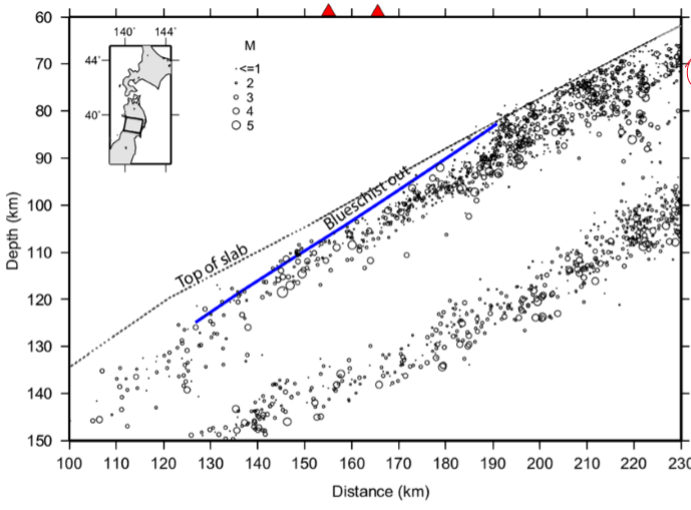
what inferences can you make about why this diagram of arc volcanoes has two different sets of point
deep vs shallow earthquakes, due to a “double layer” of subducting slabs
what is slab bending
the degree angle to which a slab subducts, which impacts geology
do strongly bent slabs experience compression or extension, and what happens as a result of the steep angle
extension, creates normal faulting and fractures, which brings in more water
do steep or shallow angled slabs bring in more water
steep
what does the presence of alot of water mean for the subducting slab
the water has to exit somewhere from the slab, more intermediate depth seismicity
why does a steeper subduction angle mean its more active
more water needs to escape the slab, quicker phase changes
can a single zone see different degrees of subduction angles
yuppers
is buoyancy positive or negative as slabs subduct
negative, cuz density increases
do slabs continue to subduct forever
no they stall
at what depth does the mantle undergo a fundamental change
660 km
why do some slabs bend or even break
due to subduction angles
4 types of fractures that occur in subducting slabs
propagating tear - just a simple tear
fracture in between a steep slab and a shallow slab
slab window in between a steep slab and a shallow slab
slab window creating a spreading ridge in between a steep slab and a shallow slab
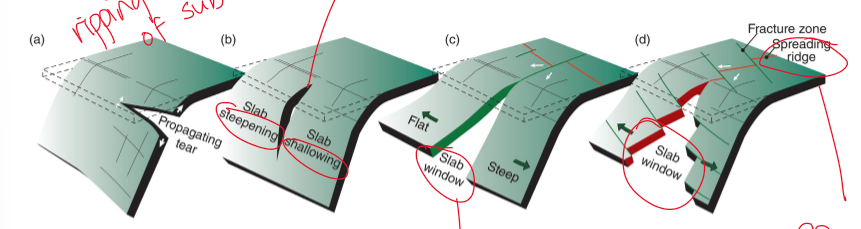
what are the A and B types of subduction
A: ampferer/alpine
B: benioff/pacifc
what is ampferer/alpine subduction
continental crust or fragments being forced into the zone
stalling things out, slow subduction, reorganizing forces
what is benioff/pacific subduction
classic oceanic subduction,
plate goes down, nothing gets caught in it
what does the mafic crust turn into in high P and low T regimes, mention hydration
first into blueschist (hydrated) — then eclogite (less hydrated)
how often are eclogites exhumed at the surface, and how
rarely, theyre underplated then exhumed
if we see eclogite then theres likely lots of _____
garnet
why is eclogite a “messenger”
we can use thermobarometry to calculate geotherms (temp/depth) = history/time data of subduction
in eclogite, when the mineral assemblage changes, does the whole crystal crystallize
no, it produces zoning
do andean or marianan collisions cause jamming of continents, therefore stopping the subduction
andean causes jamming, stops subduction
how does more continent form at margins
during C-C collisions, crust being stuffed up onto side, major reorientation of forces
which plates collided to form himalayas
india and asia
effects of slab pull during C-C collisions
gets weaker as continent subducts slightly, ultimately breaks off = transitions to collision margin from subduction margin
what is the hinterland block and what are some features of it
it is lifted as lower density material is thrust under (underthrusting)
high elevations, uplift + erosion
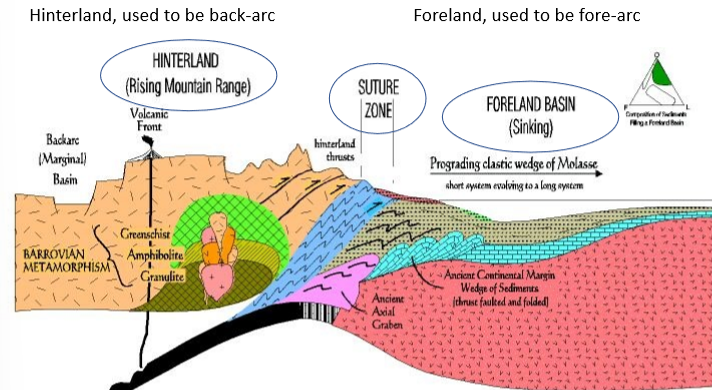
what did the hinterland block used to be
the back arc/magmatic arc, was uplifted and eroded away
are there volcanic rocks in the himalayas
only the roots of them because they have been uplifted and eroded
what is the suture zone and what types of rock are found there
contact between hinterland and foreland blocks, represents a closed ocean basin
scraps of ocean crust or accretionary complex
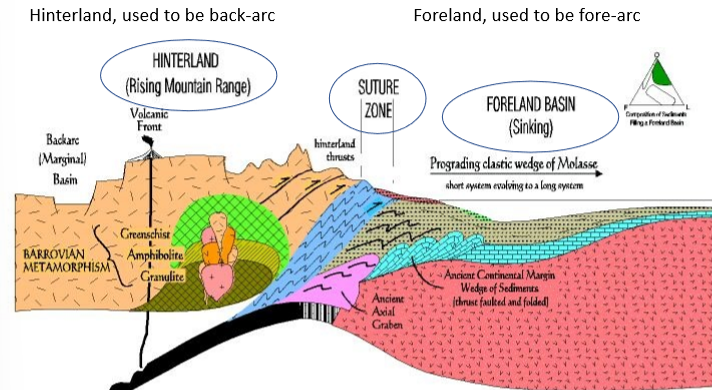
what is the foreland block and what does it form as collision progresses
it is pushed down by the overthrust block, forms a foreland basin and a large clastic wedge
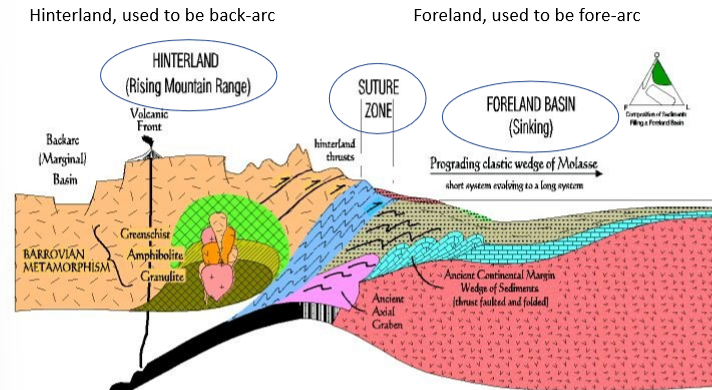
why does a foreland basin form
cuz theres so much erosion and uplist on the hinterland block that the sediment has to go somewhere
what is an arc-continent
where subduction slows but doesnt stop, forms volcanic island arcs or continental fragments
what are “cookie bites”
when the slab takes a part of the continent down with subduction
example of a large fold and thrust belt
the rockies