Biochem Recombinant DNA Technology
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Cloning Vectors
Cloning: production of an exact copy of a DNA segment.
Cloning vector: DNA molecule into which “foreign” DNA is inserted for cloning
Cloning vectors w/ inserted “foreign” DNA are introduced into host cells such as bacteria, where they multiply as the host cells multiply and produce many exact copies of the “foreign” DNA.
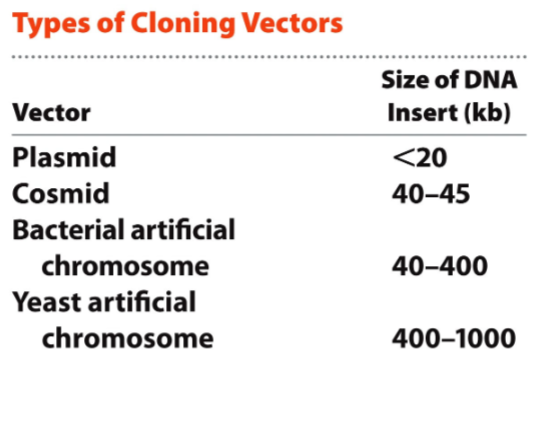
Common Cloning Vectors
1) Plasmids
2) Cosmids
3) Bacterial Artificial Chromosomes (BACs)
4) Yeast Artificial Chromosomes (YACs)
kb stands for kilobase pairs
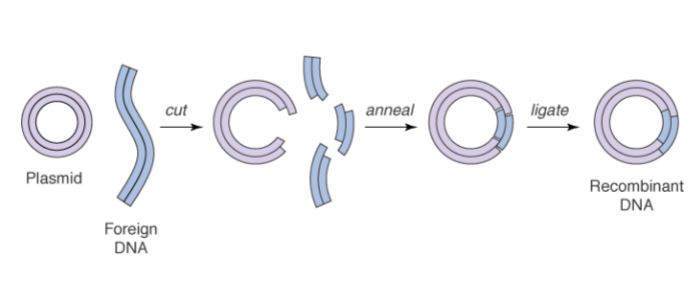
Production of a Recombinant DNA Molecule
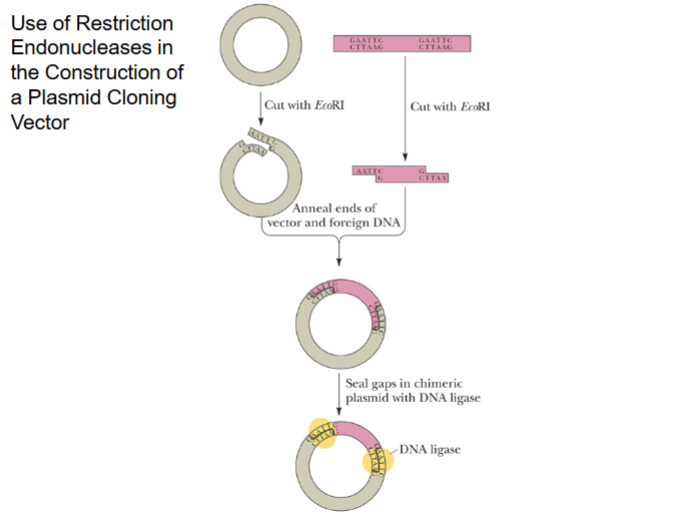
Foreign DNA fragments can be inserted into plasmid cloning vectors by cutting the plasmid and foreign DNA w/ a restriction endonuclease, and then joining the ends of the linearized plasmid and foreign DNA fragment.
Anneal means bring together, ligation completely seals backbone strand by making new phosphodiester bonds.
Use of Restriction Endonucleases in the Construction of a Plasmid Cloning Vector
DNA Libraries
Genomic Library: a set of cloned chromosomal DNA fragments representing the entire genome of an organism.
cDNA Library: a set of cloned cDNAs representing all the mRNAs (gene transcripts) synthesized by cells or tissues.
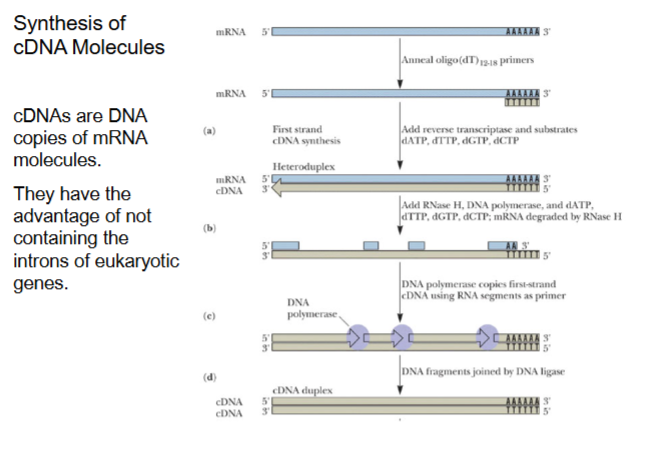
cDNAs are DNA copies of mRNA molecules.
mRNA have all had introns removed, more useful than genomic library.
Synthesis of cDNA molecules
2 steps: 1) reverse transcriptase to make cDNA copy.
2) Remove mRNA and use DNA polymerase to reform RNA strand as cDNA
*Note RNase H cuts RNA but not DNA
RNA and Protein Expression
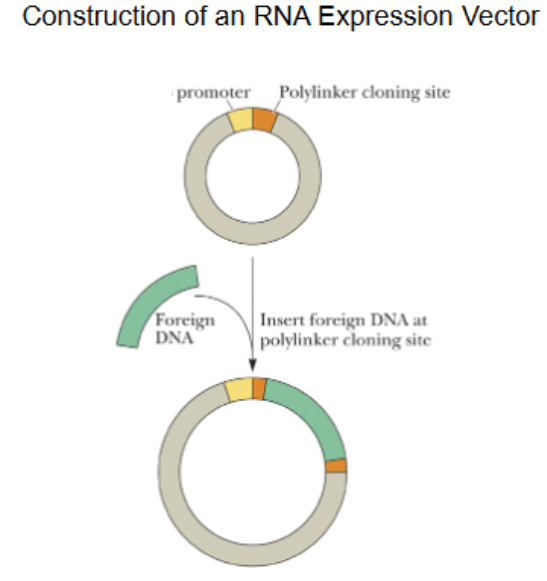
RNA Expression: a vector for in vitro (in lab) expression of a cDNA molecule or other foreign DNA can be constructed by placing a promoter sequence (site of RNA polymerase binding) next to the inserted DNA.
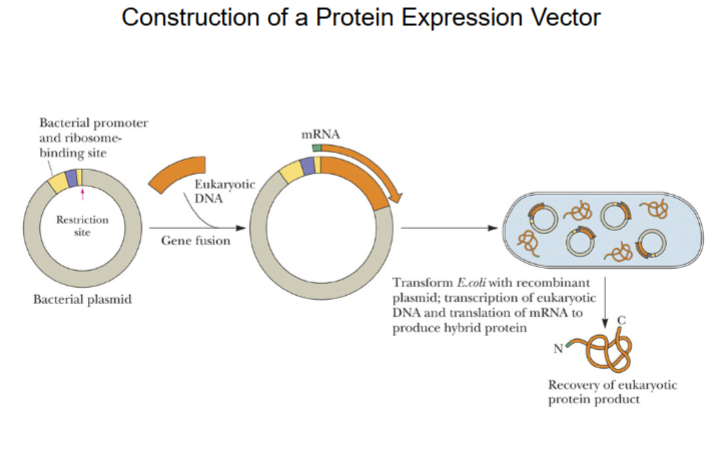
Protein Expression: to express a protein in E. coli or other host cells, a cDNA molecule is inserted next to (1) a promoter sequence and (2) a ribosome-binding site sequence.
Constructing an RNA expression vector
A plasmid cloning vector, foreign DNA often human cDNA. Cut at polylinker cloning site w/ restriction endonuclease (EcoRI), add foreign DNA, anneal shut, seal w/ DNA ligase enzyme.
Construction of a protein expression vector
Bacterial plasmid w/ human cDNA, mRNA created in cell, which creates protein.
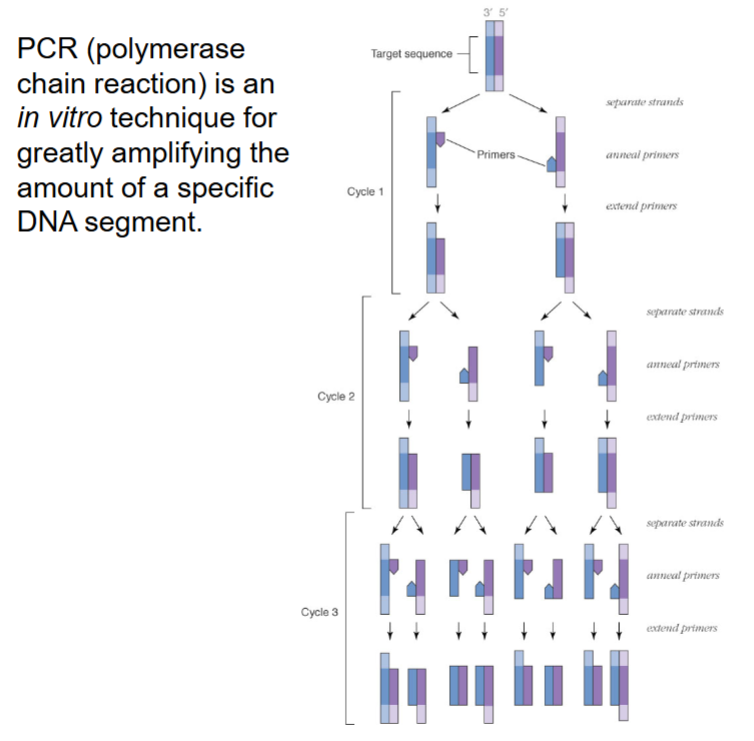
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) process.
In vitro (in lab) technique to clone DNA. Doubles DNA every cycle:
1) Melt DNA strands apart.
2) Apply primers to separated strands.
3) Add building blocks (dNTPs) to primers w/ heat stable Taq DNA polymerase.
4) Repeat.
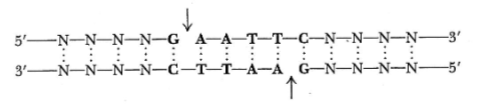
Restriction endonucleases
Widely applied in cloning and sequencing of DNA molecules.
Useful because they cut DNA at specific sequences, typically 4-6 nucleotides in length.
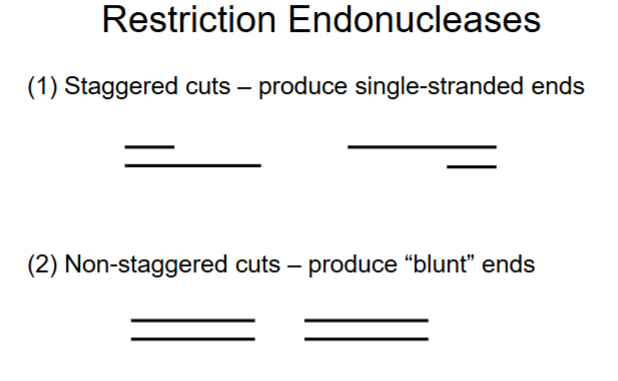
Ex: restriction enzyme EcoRI, makes staggered cuts.
Staggered vs blunt ends
Southern Blotting
FOR DNA!
DNA fragments are separated by gel electrophoresis (neg. charged backbone), transferred to a sheet of membrane (blotted), and detected w/ a DNA probe.
Northern Blotting
FOR RNA!
RNA molecules such as mRNAs are separated in a gel, transferred to a sheet of membrane, and detected w/ a probe.
Western Blotting
FOR PROTEINS!
Proteins are separated in a gel, transferred to a sheet of membrane, and detected w/ antibodies.
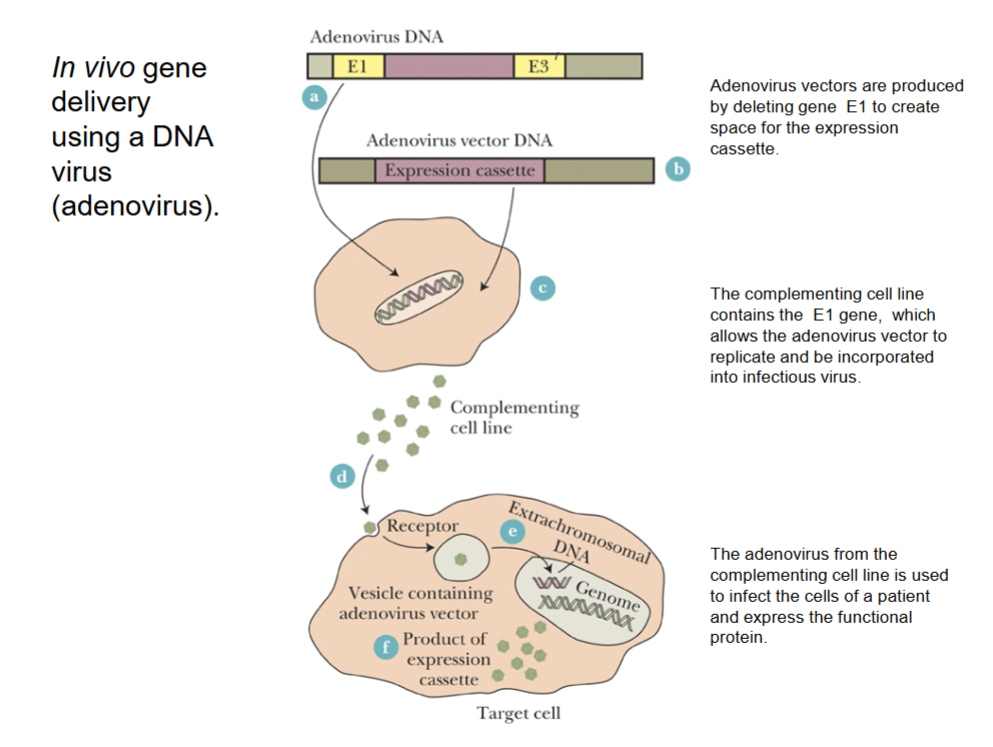
Human Gene Therapy
Introduction of a functional gene into cells of human tissues and organs to correct damage caused by a mutant gene.
Expression cassette
Consists of (1) a cDNA version of the gene, along with (2) a promoter (site of RNA polymerase binding)
Virus-mediated gene delivery
The expression cassette is incorporated into a virus which can infect human cells.
Viral vectors include:
DNA virus vectors
Retrovirus (RNA) vectors