Lecture 21: Kidney Tumors & Lower Urinary Tract
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Renal Papillary Adenoma
Renal Papillary Adenoma
benign: < 0.5 cm & Papillary architecture
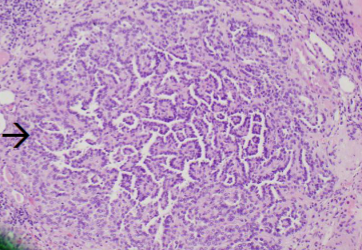
Oncocytoma
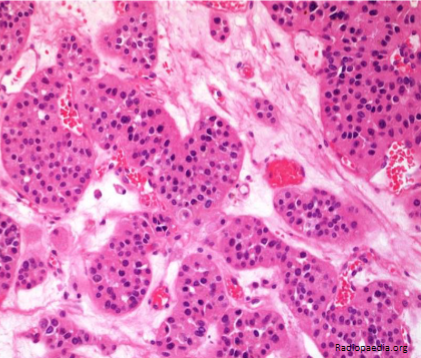
Oncocytoma
dense pink cytoplasm (eosinophilic) cell nests with bland nuclei; little mitotic activity in a paucicellular hyalinized stroma
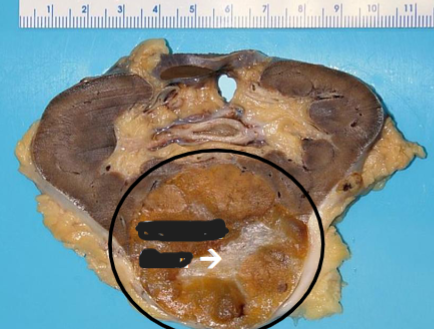
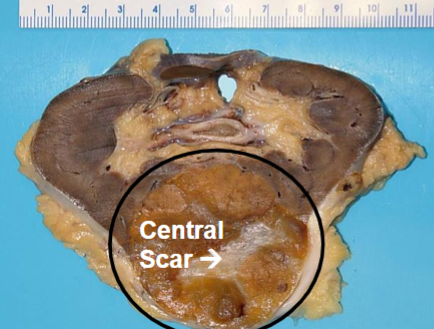
Oncocytoma
Benign
Gross: well circumscribed but unencapsulated, brown to yellow, often with central scar
Micro: dense pink cytoplasm (eosinophilic) cell nests with bland nuclei; little mitotic activity in a paucicellular hyalinized stroma
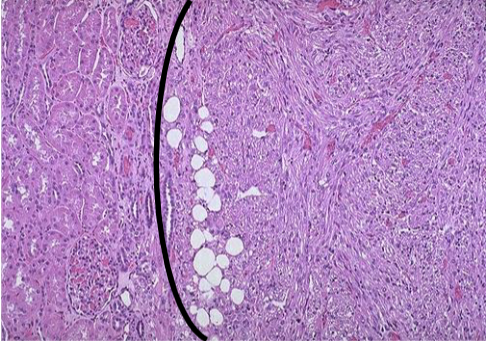
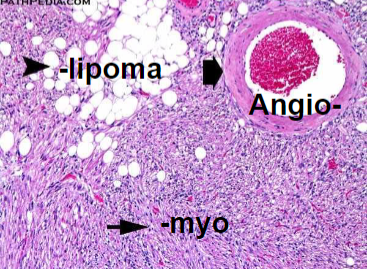
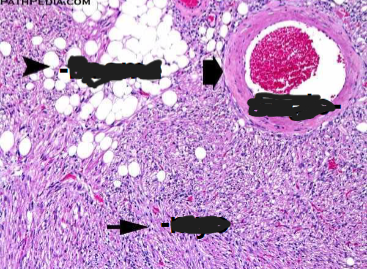
Angiomyolipoma
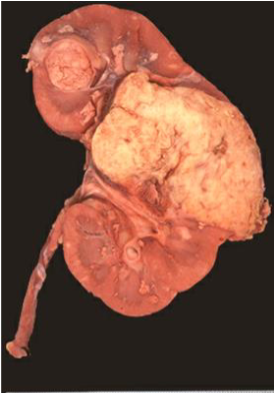
Angiomyolipoma
Angiomyolipoma
Benign, but if large may fatally hemorrhage
Neoplasm composed of: Vessels + Smooth muscle + Fat
Genetic AML: In Tuberous Sclerosis LOF mutations of Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Tumor Suppressor genes TSC1 (Hamartin) or TSC2 (Tuberin) normally inhibit mTOR (mTOR upregulates MYC → cell cycle progression).
Cutaneous Stigmata: Facial Angiofibromas, Periungual Fibromas, “Ash leaf” spots (hypomelanotic macules) or Shagreen patches (plaque-like skin lesions usually on nape of neck or lower back); nearly all have CNS involvement (intractable epilepsy, cognitive impairment); some develop Heart Rhabdomyoma or Pulmonary Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (proliferation in lung of smooth muscle-like cells)
Renal Cell Carcinoma
Top risk factor: Tobacco
Clear Cell (Conventional) type: most common, VHL mutations
Yellow color due to lipids in the clear cells; marked vascularity with hemorrhages (↑VEGF); multiple foci of cystic necrosis
Clear cytoplasm due to Glycogen & Lipids
Early metastasis and renal vein invasion
Papillary: GOF Germline MET Oncogene
papillae & foamy macrophages within stalks
Clinical features of Renal Cell Carcinoma
Costovertebral pain, palpable mass, hematuria
Tumor may be asymptomatic until it reaches a large size → fever, malaise, cachexia
Paraneoplastic Syndromes: Hypercalcemia (PTHrP & other cytokines), Hypertension (↑ Renin), anemia of Chronic Disease (↑ Hepcidin), Polycythemia (↑ Erythropoietin), Cushing’s disease (↑ ACTH), liver dysfunction, eosinophilia, leukemoid reactions, AA amyloidosis
Most common cause of Hydronephrosis in infants & children
Ureteropelvic Junction (UPJ) Obstruction- congenital
Most common congenital bladder abnormality
Vesicoureteral Reflux (VUR)
Reflux Nephropathy (repeated Acute or Chronic Pyelonephritis; loss of urine concentrating ability; hypertension; renal failure; high back pressure generated by bladder during micturition → hydronephrosis)
Pyelonephritic scarring
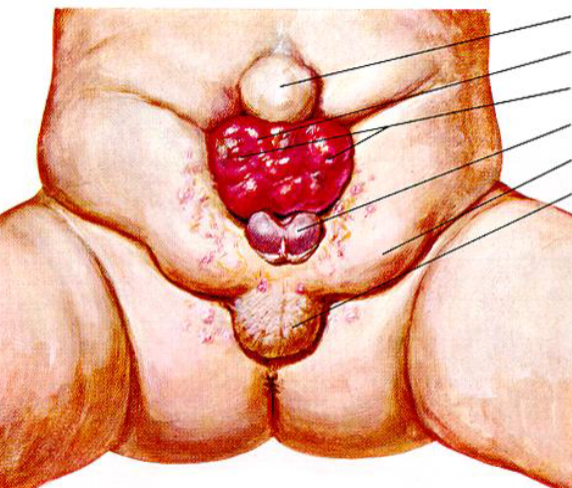
Exstrophy of the bladder
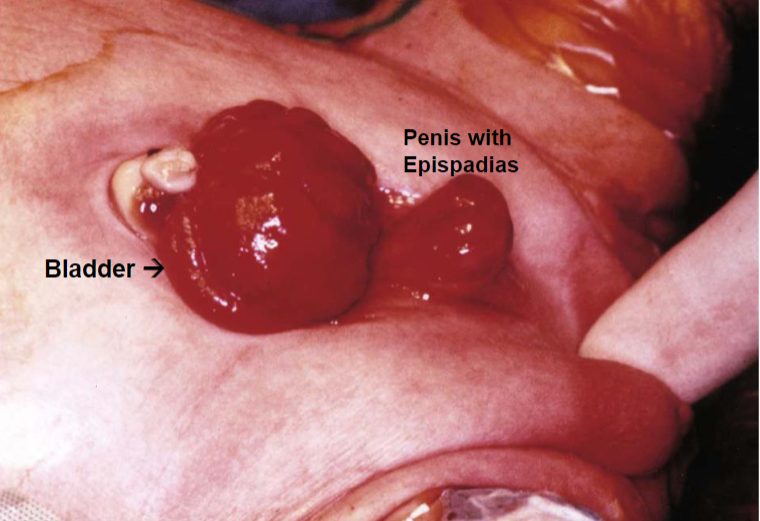
Exstrophy of the bladder
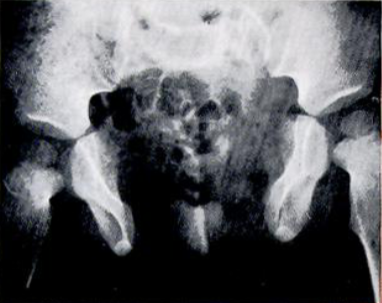
Exstrophy of the bladder
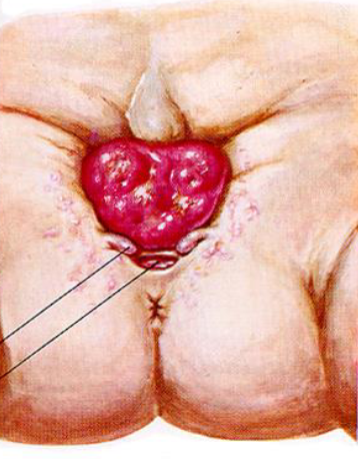
Exstrophy of the bladder
Urachus
Urachus (median umbilical ligament) is a fibrous remnant of embryonic Allantois that runs that from bladder dome to umbilicus
Urachal Fistula: urine passed via belly button
Bacterial Cystitis
Predisposing factors: obstruction, women, long-term catheterization
Complication: Pyelonephritis → leukocyte casts in urine
Hemorrhagic cystitis
cytotoxic chemotherapy (Cyclophosphamide) or Adenovirus infection
Interstitial Cystitis (Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome)
fissures, punctate hemorrhages, ulceration (Hunner Ulcers)
middle-aged women
may ultimately progress to a scarred contracted bladder
path → minimal changes, few Mast cells in mucosa
Polypoid Cystitis
due to marked submucosal edema from irritation
most often seen with indwelling catheters
Malakoplakia
usually in context of chronic bacterial infection or immunosuppressed transplant patients
Path → sheets of macrophages with abundant granular cytoplasm (Phagolysosomes with bacterial fragments) & mineralized inclusions (Michaelis-Gutmann bodies)
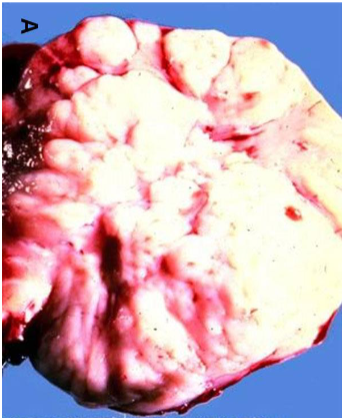
Malakoplakia
Soft, yellowish plaques
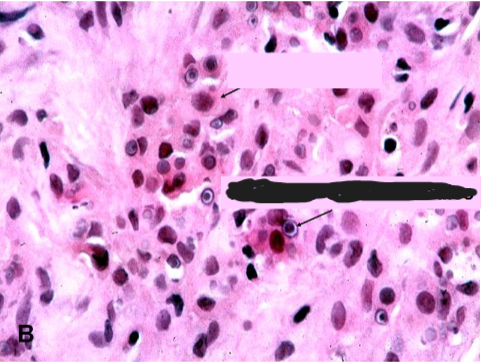
Malakoplakia
concentrically layered Michaelis-Guttman bodies
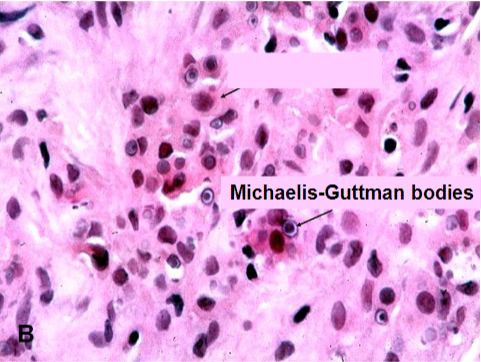
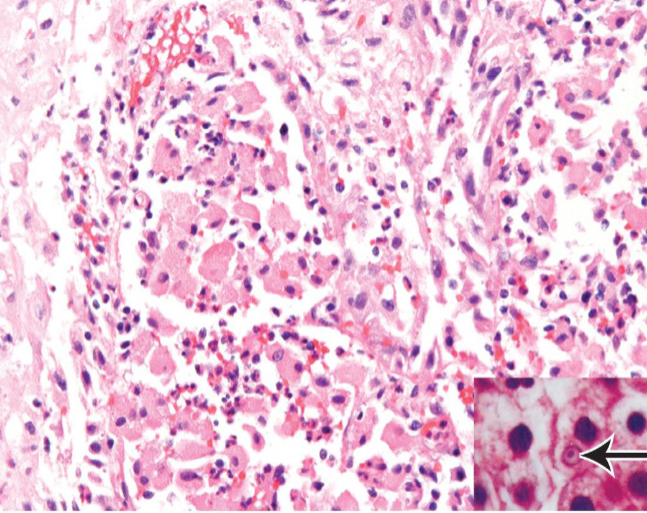
Malakoplakia
Macrophages with abundant eosinophilic granular cytoplasm
Michaelis-Gutmann body
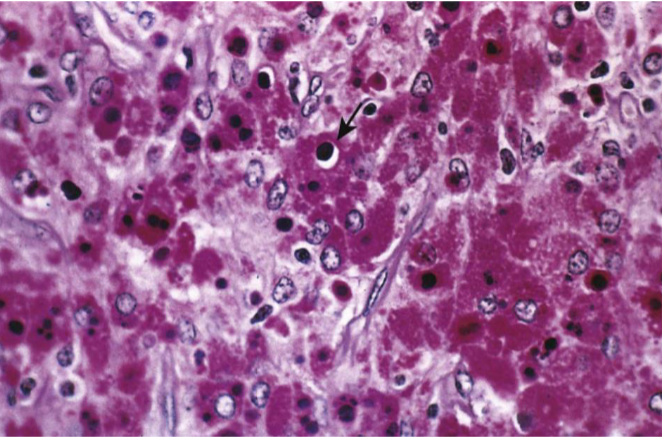
Malakoplakia
Michaelis-Gutmann bodies containing Iron & Calcium
Cystitis Cystica et Glandularis
Chronic Cystitis or mucosal irritation
Extensive intestinal type metaplasia is a risk factor for adenocarcinoma
Squamous Metaplasia
in response to chronic injury, urinary tract infections, irritation or inflammation
Risk factor for squamous cell carcinoma
Nephrogenic metaplasia/adenoma
Chronic Cystitis or mucosal irritation
No malignant potential
Bladder Cancer
Urothelial derived Transitional Cell Carcinoma (TCC)
Risk factors:
Cigarettes
male & Older age
industrial exposure to Aromatic amines (Aniline dyes)
Schistosoma haematobium infection → squamous carcinoma
Therapeutic irradiation or cyclophosphamide
Phenacetin
Bladder Cancer Clinical and Diagnosis
usually presents with PAINLESS HEMATURIA
may present with symptoms from obstruction (hydronephrosis) or pyelonephritis
Diagnosis: Cystoscopy
BIG PICTURE for Urothelial tumors
Low grade, Noninvasive tumors with papillary growth are not going to kill you
High grade, Noninvasive, papillary or flat (Carcinoma in situ) might very well kill you
Urothelial cancer is often Multifocal and often recurs at a different site
Precursor lesions to invasive Urothelial cancer
Low Grade: Papillary urothelial carcinoma, Low Grade, Noninvasive
High Grade:
Papillary urothelial carcinoma, High Grade, noninvasive
Flat noninvasive urothelial carcinoma (Carcinoma in situ)- most invasive cancers arise from CIS
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Bladder
Schistosomiasis (aka Bilharzia)
Arises from squamous metaplasia
Treatment of Bladder Cancer
Transurethral resection for localized, noninvasive, low-grade tumors
BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guerin) intravesical instillation of attenuated M. bovis for high risk of progression lesions
Radical Cystectomy for tumors invading detrusor muscle, for CIS refractory to treatment or extending into prostatic Urethra or urethral ducts
Most common cause of bladder outlet obstruction
Men: Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Women: Cystocele (Bladder Prolapse)
May cause:
Urinary incontinence
Bladder neck obstruction
Angiomyolipoma