Brain (help I am so tired of making quizlets bruh)
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
What are the 4 principal parts of the brain?
-Brain stem
-Diencephalon
-Cerebrum
-Cerebellum
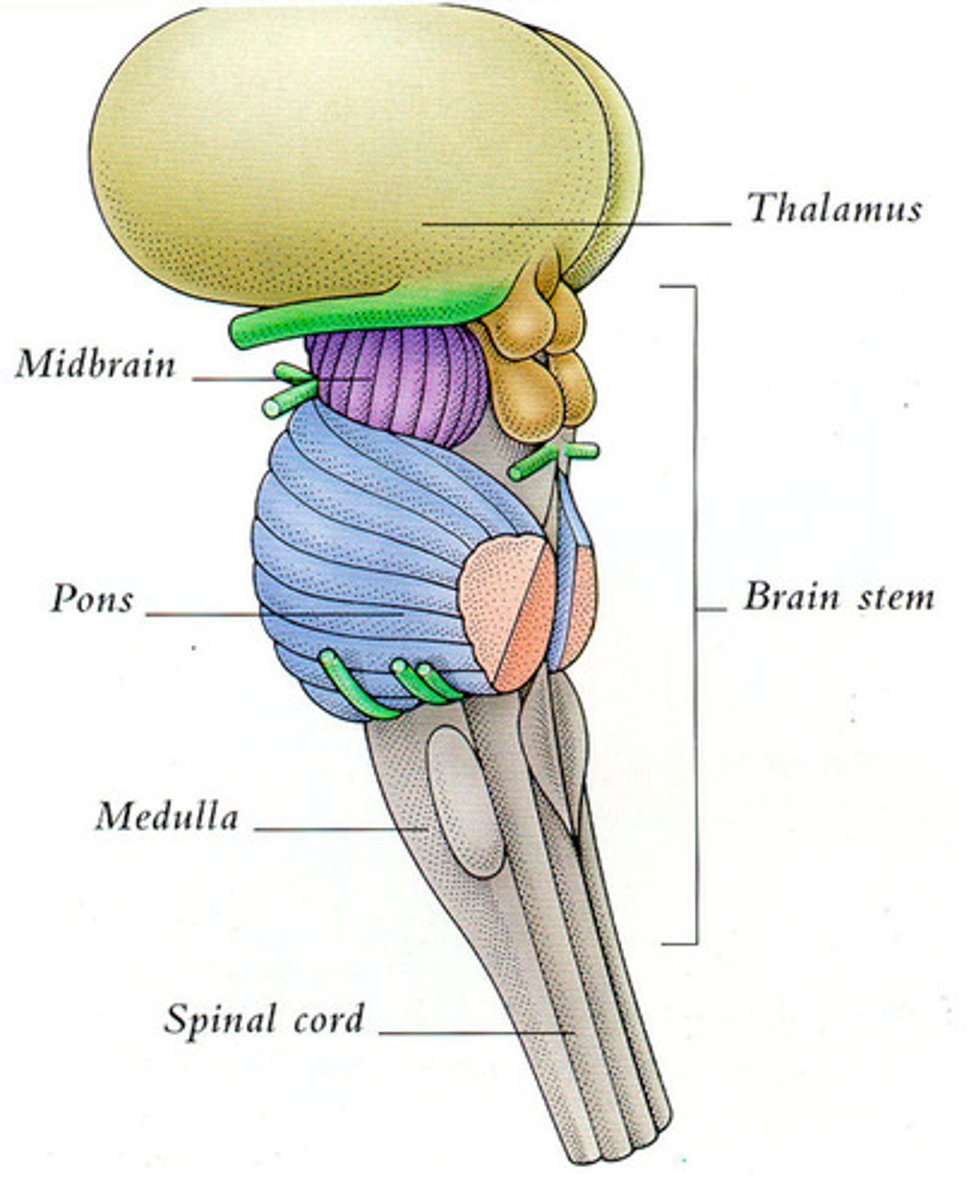
What is the brain stem comprised of?
-Medulla oblongata
-Pons
-Midbrain
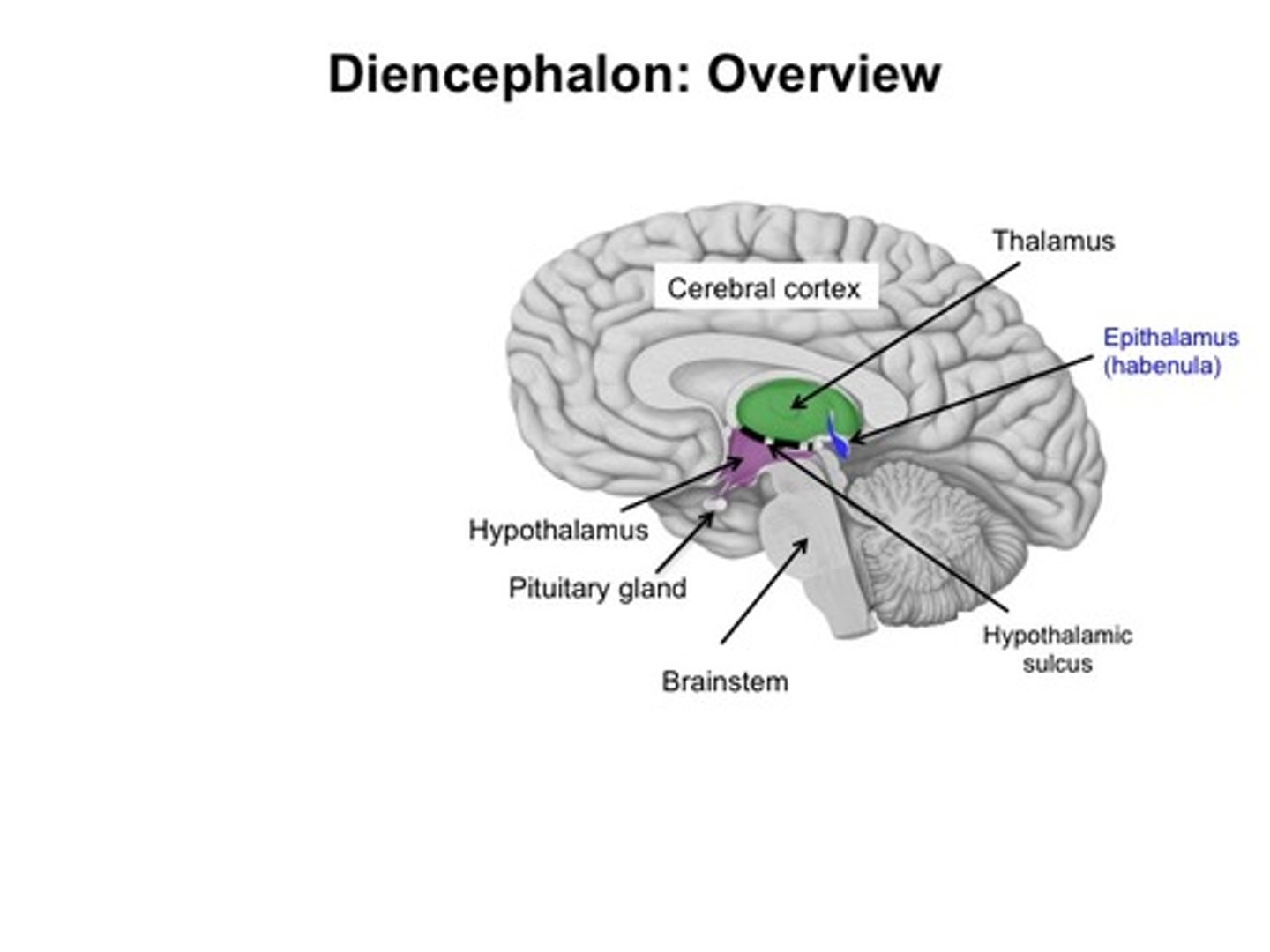
What is the diencephalon comprised of?
-Thalamus
-Hypothalamus
-Epithalamus (pineal gland)
-Subthalamus (mamillary bodies)
Another term for cerebrum
Telencephalon
Cerebellum + pons = ?
Metencephalon
What is the prosencephalon?
Cerebrum + diencephalon
What is the mesencephalon?
Mid brain
What is the rhombencephalon?
Cerebellum + pons + medulla oblongata
CSF functions
-Protection
-Provides support
-Transports nutrients to CNS tissue
-Transports waste away from CNS tissue
Choroid plexus
Ependymal cells with blood supply
-Produces and maintains CSF
-Transports nutrients, vitamins, and ions to CSF
-Removes wastes from CSF
Circulation of CSF
CSF from the choroid plexus of the lateral ventricles -> interventricular foramen -> third ventricle -> aqueduct of the midbrain -> fourth ventricle -> lateral aperture and median aperture -> most into subarachnoid space, some into central canal of spinal cord -> around the brain and spinal cord, eventually enters circulation via arachnoid granulations
Blood supply to brain
Internal carotid arteries + basilar artery -> cerebral arterial circle
Brain stem: Medulla oblongata
-Relays info to the thalamus and brain stem
-Regulates heart rate, blood pressure, digestion
-Initiates breathing
-Continuation of spinal cord above foramen magnum
-Pyramidal decussation
-All communication between brain and spinal cord passes thru MO
Brain stem: Pons
-Relays info to the cerebellum and thalamus
-Regulates somatic and visceral motor centers
-Modulates the output of medulla oblongata (increasing the rate and depth of breathing
-Connects spinal cord to brain and links parts of the brain together
Brain stem: Midbrain/Mesencephalon
-Processes visual and auditory data (corpora quadrigemina)
-Maintains consciousnesses and alertness
-Involved with reflexive somatic motor response
-Cerebral peduncles
Parts of corpora quadrigemina
-Superior colliculus (visual reflex center)
-Inferior colliculus (auditory reflex center)
Diencephalon: Thalamus
-Relays info to the cerebrum
-Processes sensory info
-Thalamic nuclei joined by intermediate mass
-Main sensory switchboard that has motor synapses
Diencephalon: Hypothalamus
-Connected to pituitary gland via infundibulum
-Consists of mamillary body and numerous nuclei
-Homeostasis related functions, including:
-> Integration of ANS from visceral stimuli
-> Physical and functional connection between nervous and endocrine systems
-> Hormone production
-> Hunger, thirst, temp regulation
-> etc
Diencephalon: Epithalamus
-Contains pineal gland
-Melatonin production
-Regulates day-night cycles
Diencephalon: Subthalamus
Contains mammillary bodies (reflex centers associated with eating and smell)
Limbic system location
Located between the cerebrum and the diencephalon just superior to the corpus callosum
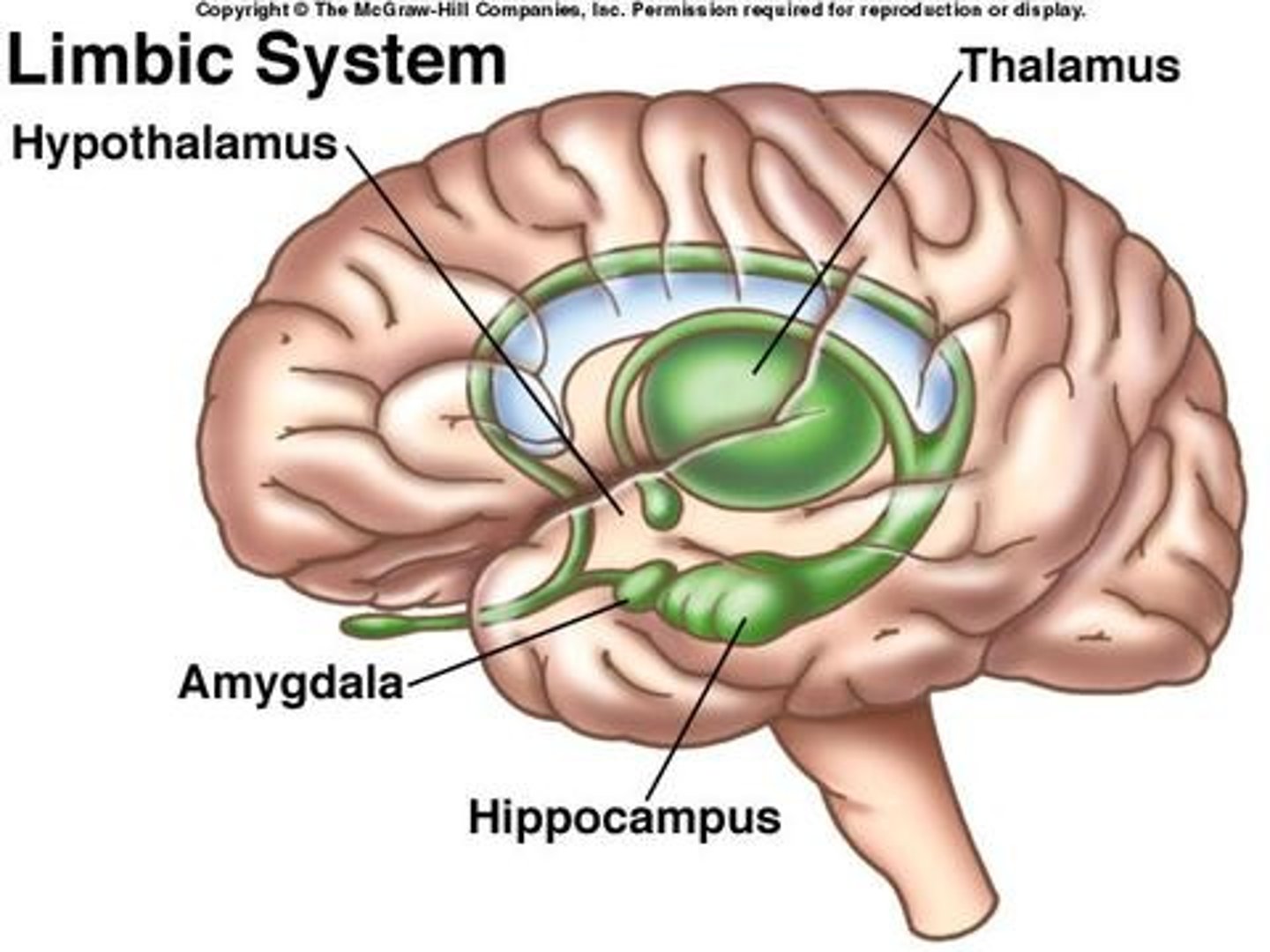
Limbic system functions
-Establishes emotional states
-Links conscious functions with the unconscious autonomic functions
-Facilitates memory storage and retrieval
The limbic system: the fornix
-Tract of white matter connecting the hippocampus with the hypothalamus
-Many of the fibers extend into the mamillary bodies
->Mamillary bodies control reflex movements associated with eating
What is included in the limbic system?
-Nuclei of the thalamus and hypothalamus
-Cingulate gyrus
-Dentate gyrus
-Parahippocampal gyrus
-Hippocampus
-Amygdala
What separates the 2 hemispheres of the cerebrum?
Longitudinal fissure
Falx cerebri
-Fold of dura mater in longitudinal fissure
-Encloses superior sagittal sinus and inferior saggital sunus
Wha type of matter comprises the cerebral cortex?
Gray matter
What is the name of the raised "wrinkles" on the cerebrum?
Gyrus singular, gyri plural
Where is white matter found?
Deep to gray matter
What is white matter comprised of?
-Myelinated axons connecting areas
White matter of cerebrum: Association fibers
-Tracts that connect gyri within hemispheres (Acruate fibers and longitudinal fasciculi)
White matter of cerebrum: Commisural fibers
-Tracts that connect 2 hemispheres (anterior commissure and corpus callosum)
White matter of cerebrum: Projection fibers
-Tracts that connect the cerebrum with other parts of the brain and spinal cord
Lobes of the cerebral hemispheres
-Frontal lobe
-Parietal lobe
-Temporal lobe
-Occipital lobe
Frontal lobe separations
-Separated from parietal by CENTRAL sulcus
-Separated from temporal by LATERAL sulcus
Parietal lobe separations
-Separated from frontal by CENTRAL sulcus
-Separated from occipital by PARIETO-OCCIPITAL sulcus
Temporal lobe separations
-Separated from frontal by LATERAL sulcus
-Insula lies deep to lateral sulcus
Occipital lobe separations
-Separated from parietal by PARIETO-OCCIPITAL sulcus
Frontal lobe
-Conscious control of skeletal muscles
-Last lobe of brain to develop
Occipital lobe
-Perception of visual stimuli
Parietal lobe
-Conscious perception of touch, pressure, vibration, pain, temp, taste
Temporal lobe
-Conscious perception of auditory and olfactory stimuli
Frontal lobe: Primary motor cortex
-Anterior to central sulcus
-Neurons direct voluntary movements by controlling somatic motor neurons in the brain stem and spinal cord
-Also known as precentral gyrus
Frontal lobe: Broca's area
-Motor speech center
-Motor center that regulates patterns of breathing and vocalization for speech
Frontal lobe: Prefrontal cortex
-Performs complicated learning and reasoning functions
-Understanding consequences of actions
-Emotional context and motivation
-Last brain region to fully develop
Wernicke's area
-Speech interpretation center
Parietal lobe: Primary sensory cortex
-Posterior to central sulcus
-Neurons receive somatic sensory info for touch, pressure, pain, taste, and temp
-Also called postcentral gyrus
Cerebellum functions
-Control of subconscious skeletal muscle movement necessary for balance, coordination and posture
What separates the cerebellum from the cerebrum?
-Transverse fissure
Tentorium cerebelli
-"Tent over the cerebellum"
-Fold of dura mater in transverse fissure
-Encloses transverse sinus
What separates the cerebellar hemispheres?
-Vermis
Lobes of the cerebral hemispheres
-Anterior
-Posterior
-Flocculonodular
What is the name of the gray and white matter in the cerebellum?
-Gray matter = Folia
-White matter = Arbor vitae
-Folia surrounds arbor vitae
How does the cerebellum attach to the brainstem?
-Via cerebellar penduncles
What does the inferior cerebellar penduncle attach to?
-Medulla oblongata
What does the middle cerebellar penduncle attach to?
-Pons
What does the superior cerebellar penduncle attach to?
-Midbrain (mesencephalon), diencephalon, cerebrum
Ventricular system of the brain
-Ventricles 1 and 2 (called lateral ventricles) located in cerebral hemispheres, separated by septum pellucidum
-Ventricle 3 in the diencephalon
-Ventricle 4 between pons and cerebellum
What do the cerebrum consist of?
-Gyri (raised areas)
-Sulci (gaps)
-Central sulcus
-Longitudinal fissure
-Cerebral lobes
-Lateral fissure/sulcus
-Corpus callosum
-Basal nuclei
-Limbic system
Motor association area
-In front of the primary motor cortex
-Motor memories and patterns
Sensory association area
-Behind primary sensory cortex
-Sensory memories
High order functions
-Pons and above
-Cerebral cortex
-Conscious and unconscious info processing
What is the primitive brain
The medulla
Insula
-Lies deep to lateral sulcus
-Olfactory cortex and gustatory (taste) cortex
Hemispheric specialization
-Left hemisphere = speech center, writing, language, math (memorization)
-Right hemisphere = analysis by touch, spatial visualization (creativity)
Lateral ventricles
-Main portion in parietal lobes
-Anterior horns extending into frontal lobe
-Posterior horns extending into occipital lobe
-Inferior horn extending into temporal lobe
-Communicate with 3rd ventricle thru interventricular foramen
Third ventricle
-Communicates with 4th ventricle thru aqueduct in midbrain
Fourth ventricle
-Communicates with central canal of spinal cord
Protection of the brain
-Bones of skull
-Cranial meninges
-CSF
-Blood-brain barrier
Cranial meninges
-Dura mater (outermost)
-Arachnoid mater (middle)
-Pia mater (innermost)
2 layers of dura mater
1) Endosteal layer
-Outermost layer
-Fused to periosteum of cranial bones
2) Meningeal layer
-Innermost layer
What is in between the 2 layers of the dura mater?
-Superior sagittal sinus
-Inferior sagittal sinus
The meningeal layer of cranial dura mater forms folds called:
-Falx cerebri
-Tentorium cerebelli
-Falx cerebelli
-Diaphragma sellae
Arachnoid mater
-Consists of projections called arachnoid granulations (drain CSF from CNS)
-Weblike material underlying arachnoid layer (anchors cerebral blood vessels)
Pia mater
-Attached to surface of brain (follows sulci and gyri)
Basal nuclei
-Masses of gray matter embedded in white matter inferior to lateral ventricles... (Gray matter in the center of the brain)
Functions of basal nuclei
-SMOOTHS movements out... doesn't initiate
-Involvement in subconscious control and integration of skeletal muscle tone
-Involvement with coordination of learned movement patterns
-Involvement in processing, integration, and relay of info in cerebral cortex
Cerebral penduncles
-Have ascending fibers that synapse in the thalamus and descending fibers pf the corticospinal pathway
Medulla oblongata contains the nuclei of which cranial nerves?
VIII, IX, X, XI, XII
Medulla oblongata major reflex centers
-Cardiovascular center (cardiac and vasomotor)
-Respiratory center (rhythmic breathing)
The pons contains the nuclei of which cranial nerves?
V, VI, VII, VIII
Nuclei in the pons that relay cerebellar commands consists of:
Cerebellar penduncles
Where do the arachnoid granulations exit out into?
The superior sagittal sinus
New visual pathway
Receptor -> thalamus -> primary visual cortex
-Conscious
Old visual pathway
Receptor -> superior colliculus
-Unconscious