Preparation of soap
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
oil and sodium hydroxide
Identify the reactants used in the preparation of soap
ethanol
Identify the solvent used in the preparation of soap
propan-1,2,3-triol (glycerol)
Name the co-product formed when soap is prepared.
Anti-bumping granules.
What (along with our reactants sodium hydroxide and oil, and our solvent ethanol) is added to the flask?
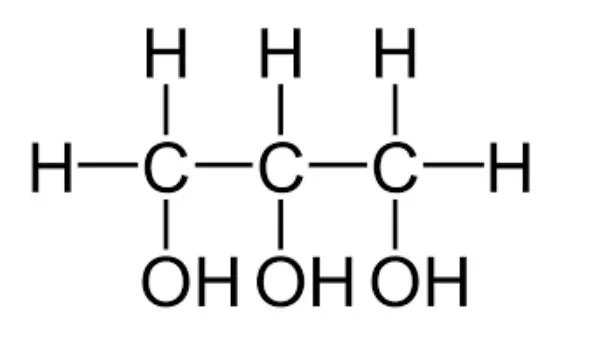
Draw the structure of the coproduct (glycerol)
Refluxing is a technique used in chemistry to keep a reaction mixture at a high temperature for a long period of time, without loss of liquid.
What is refluxing?
Refluxing speeds up the reaction time whilst also maximising the yield. (as neither solvent nor reactants are lost)
Why do we reflux in this experiment?
Heat with a hot plate.
Suggest a suitable method for refluxing the reaction mixture and then distilling off the alcohol.
A residue.
What is seen in the pear-shaped flask after refluxing?
78 degrees
What temperature does ethanol vaporise at?
To remove the ethanol.
Why do we distill the product mixture?
Ethanol is an organic solvent.
Soap is an organic solvent.
Like dissolves like. Keeping the ethanol will reduce the yield of soap.
Why do we remove the ethanol by distillation?
Removing the ethanol by distillation.
Adding the mixture to a brine solution.
How can we maximise the yield of soap in this experiment?
Brine is a saturated salt solution.
What is brine?
Safe (as there is no flame)
Convenient and easy to use
Why would you use a heat plate for refluxing and distillation?
Brine will dissolve the excess sodium hydroxide and glycerol. Soap will not dissolve in brine. The soap precipitates out of solution. This maximises the yield of soap.
What is the function of brine in this experiment?
Buchner filtration is faster than gravity filtration.
Why do we use Buchner filtration in this experiment?
One end of the soap molecule is ionic (polar).
Explain why one end of the soap molecule is described as water loving (Hydrophilic)?
Saponification
What reaction took place during the refluxing?
To remove sodium hydroxide from the soap which is corrosive.
Why do you wash the soap thoroughly?
ICE cold water which will remove the excess sodium hydroxide and brine
What do you use to wash the soap?
By leaving it to air dry overnight in the lab or by using a dessicator. We then record the mass of the soap.
How do we let the soap dry? What do we do after this?
in the brine
Where is the propan-1,2,3-triol (the coproduct) found at the end of this experiment?
A small amount of the soap is placed in the test tube of water and shaken.
The formation of a lather (suds) is proof that soap has been made.
How do you test for soap in this experiment?
C17H35COONa (sodium stearate)
What is the formula for soap?
Soap’s non-polar part (C17H35) dissolves non-polar substances on the surface of the skin (eg sebum)
Soap’s polar part (COONa) dissolves salts in sweat that sit on the surface of the skin.
Why is soap such a good cleaning agent?
Saponification is the base hydrolysis of an ester to form soap.
What is saponification?
MASS ON TOP then left Numbers of Moles and to the right Mr.
What’s that triangle for moles, mass and Mr?
The average energy required to break one mole of a substance of a particular covalent bond and to separate the neutral atoms completely from each other.
Define bond energy
If a chemical reaction takes place in a number of steps, the sum of the heat changes in the separate stages is equal to the heat change of the reaction when carried out in one stage.
Define Hess’s Law
The hot vapour rises, then condenses in the liebig condenser and then returns to the flask.
What happens to the liquid in the flask during reflux?
Refluxing heated the reaction mixture without the loss of liquid/ vapour.
How did the refluxing help bring the reaction to completion?
Animal fats are saturated (all single bonds). Vegetable fats are unsaturated (containing double or triple bonds).
What is the primary difference between animal fat and vegetable fat?
To maximise the amount of soap precipitating out
Why is a minimum of hot water used to dissolve the residue from the brine.
soap will form a lather
What will happen if the soap is added to deionised water?
soap will not easily form a lather.
what will happen if the soap is added to mineral water from a limestone region?