Formation of the Female Repro Sys (Fields)
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Fields
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Week 4-6 Primordial germ cells develop in the
definitive yolk sac
Primordial germ cells migrate to the genital ridge (_____ ______) where the ovaries develop
intermediate mesoderm
Intermediate mesoderm derived factors that male indifferent gonads
WT-1
SF-1
Lim-1
The _____ gene is x linked
Dax1
Thought to direct the factors below, although the ovary will still develop if the _______ gene is mutated
DAX 1
Major factors in ovary development (not located on sex chromosome)
FOXL2
WNT4
RSPO1
Sex cords are derived from
Peritoneum
Sex cords in females give rise to
Follicle/granulosa cells
Homologous to Sertoli cells in the male
Granulosa cells
Granulosa cells are derived from
peritoneum
Theca cells are derived from
mesenchyme stem cells
Homologous to Leydig cells in the male
Theca cells
Granulosa cells produce
Estrogen and Inhibin
Granulosa cells have ____ receptors
FSH
Theca cells produce
androstenedione which can be converted to testosterone
Theca cells have ____ receptors
LH
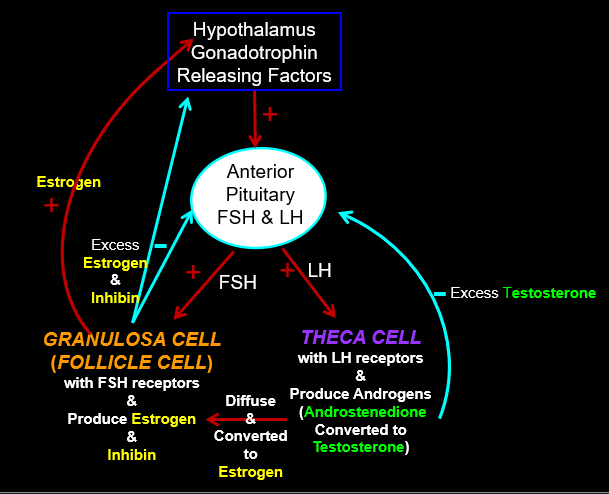
Regulation summary
Sex hormone binding globulin is produced by the
liver
Females do not produce
ABP
Increase SHBG will bind ______ and _____ making them inactive
testosterone and estrogen
Low levels of SHBG is characteristic of ______
PCOS
One of the causes of PCOS is elevated levels of androgens
Treatments for PCOS that elevate SHBG are
Oral contraceptives
Myo-inositol (produced by the kidney)
Metformin
The gubernaculum in a woman becomes the
round ligament of the ovary and the round ligament of the uterus
The suspensory ligament of the ovary is derived from
peritoneum
If the gubernaculum does not attach to the ______, an ectopic ovary can be found anywhere along the path of the gubernaculum. Even in the labia majora, the homologue to the male scrotum.
Uterus
The round ligament of the uterus can drag peritoneum (processus vaginalis) with it into the inguinal canal. Like in the male a hydrocele can result with a patent process vaginalis called the______.
Canal of Nuck
_____ cancer cells can track along the round ligament of the uterus to the superficial inguinal lymph nodes.
Uterine
and internal iliac nodes
Responsible for female reproductive organs
Paramesonephric Mullerian duct
As the mesonephric duct regresses, remnants are sits of potential ____
cysts
Gartner’s cyst
Remnant of wolffian duct
Epoophoron in mesosalpinx
Remnant of wolffian duct
Gartner’s duct
Remnant of wolffian duct
Fimbria hydatid of Morgagni develops from
Paramesonephric duct. Mullerian duct
Uterine tube develops from
Paramesonephric duct. Mullerian duct
Uterovaginal primordium which becomes Uterus, cervix, and upper 2/3 of vagina is developed from
Paramesonephric duct. Mullerian duct
Uterus, cervix, and upper 2/3 of vagina is developed from
Paramesonephric duct. Mullerian duct
Uterovaginal primordium becomes
Uterus
cervix
Upper 2/3 of vagina
Lower 1/3 of vagina develops from
Urogenital sinus
Lower 1/3 of the vagina is formed by
endoderm
Fimbriae of uterine tube, uterine tube, uterus, cervix, upper 2/3 of vagina are derived from
intermediate mesoderm
Paramesonephric duct is derived from
Intermediate mesoderm
Unicornuate
Single uterus
Unicollis
Single cervix
Unicolpus
Single vagina
Indentation in superior pole of uterus
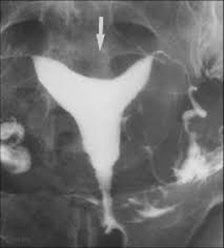
Arcuate uterus
Septation of the uterus & cervix, & unicolpus
Uterus Didelphys
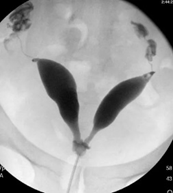
Uterus Didelphys
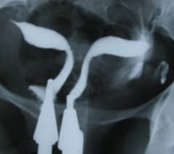
Uterus Didelphys with septated Vagina
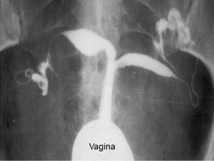
Bicornuate uterus

Atresia of the cervix
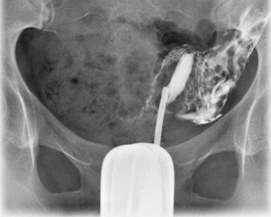
Unicornuate uterus
1 uterine horn
Typically associated with ectopic/undescended ovary.
Unicornuate uterus
Paramesonephric ducts fuse to form
Uterovaginal primordium
Bulge in the posterior wall of the urogenital sinus (endoderm)
Sinus tubercle
Sinual tubercle (endoderm) induced paired
Sinovaginal bulbs
Sinovaginal bulbs (endoderm) fuse for form
Vaginal plate
Vaginal plate separates from the
urogenital sinus
Vaginal plate (endoderm) canalizes to create
vaginal canal (lower 1.3)
Failure to recanalize lower 1/3 of vagina
Imperforate vagina
Imperforate hymen is formed by _____ and _____
endoderm and ectoderm
Retained menstrual blood in the uterus (vagina).
Cyclic pelvic or abdominal pain.
Hematocolpos
Endometrial cells in the menstrual fluid can retrograde to the uterine tube and into the pouch of Douglas (peritoneal cavity). These cells can implant in the peritoneum and cause ________
endometriosis (hyperplasia and hypertrophy of endometrial cells in the peritoneum).
hyperplasia and hypertrophy of endometrial cells in the peritoneum
Endometriosis
Imperforate vagina or hymen can lead to _________ which can lead to ________
Hematocolpos
Endometriosis due to retrograde menstrual fluid in peritoneal space
Paraurethral/Skene’s gland is derived from
Endoderm/ urogenital sinus
Homologue to prostate gland
Skene’s gland
Greater vestibular/ Bartholin’s glands are derived from
Endoderm/ urogenital sinus
Homologue to bulbourethral/ Cowper’s glands
Greater vestibular/ Bartholin’s glands
Vaginal vestibule (vagina opening, membranous urethra), skene’s gland opening, greater vestibule gland opening) is derived from
Endoderm/ urogenital sinus
Genital tubercle is derived from
Mesoderm
Genital urogenital fold is derived from
Mesoderm
Genital swelling is derived from
Mesoderm
Genital tubercle in female forms the
clitoris and bulbs of vestibule
Clitoris and bulbs of vestibule are derived from
mesoderm
Crus of clitoris is derived from
mesoderm
skeletal muscle is derived from
myotome
paraxial mesoderm
In females, the genital fold forms the
Labina minora
mesenchyme of Labia minora is derived from
Mesoderm
In females, genital swelling/ labioscrotal swelling makes the
Labia majora
The mesenchyme of labia majora is formed from
Mesoderm
streak ovaries (dysgenesis) but normal female genitalia. There is no male chromosome, so not issue with male androgens. “Ovarian failure is a typical feature.” hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is necessary to achieve the development of normal female sexual characteristics and to prevent cardiovascular complications and osteoporosis.
Turner Syndrome XO
Genetically female. (46 XX); external genitalia masculinized; scrotal fusion; persistent urogenital sinus. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia or giving androgens during pregnancy.
Female Pseudohermaphroditism
group of conditions in which there is a discrepancy between the external genitals and the internal genitals (testes and ovaries).
Intersex
The person has chromosomes of a woman, the ovaries of a woman, but external genitals that appear male.
exposed to excess male hormones before birth.
46, XX INTERSEX
The person has the chromosomes of a man, but the external genitals are incompletely formed, ambiguous, or clearly female.
androgen insensitivity syndrome (AIS) common cause
46, XY INTERSEX
The person has both ovarian and testicular tissue.
TRUE GONADAL INTERSEX
Which of the following is derived from the urogenital sinus?
A.uterus
B.uterine tubes
C.cervix
D.Vagina (lower 1/3)
D.Vagina (lower 1/3)
A 25 year old woman is diagnosed with a bicornuate uterus. This is the result of a failure of the caudal fusion of the:
A.Paramesonephric ducts
B.Urogenital sinus
C.Mesonephric ducts
D.Cloaca
E.Sinovaginal bulbs
A.Paramesonephric ducts
Epoophoron cysts will be found in the:
A.Mesometrium
B.Mesovarium
C.Mesosalpinx
D.Paramesonephric duct
E.Vaginal plate
C.Mesosalpinx
The bulbourethral gland in the male is homologous to the ___________ in the female.
A.greater vestibular
B.Skeen's glands
C.prostate
D.seminal vesicle
A.greater vestibular
There was a failure of the urorectal septum to divide the cloaca into the urogenital sinus and rectum. The structure most likely to develop normally is the:
A.Rectum
B.Vagina (lower 1/3rd )
C.Uterus
D.Bladder
C.Uterus
A neonate has an abnormal fusion of her two labia minora. This structure forms from the:
A.genital tubercle
B.genital folds
C.genital swellings
D.Ectoderm
B.genital folds