mechanisms of evolution: drift & draft
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
Drift (+ forms)
Selectively neutral allele frequences drift by random change
selective neutrality
no differential reproduction or natural selection when different alleles of a certain gene confer equal fitness benefits or do not affect fitness
→ random reproduction of alleles
eg. human eye color
Drift halts when an allele eventually becomes fixed, either by disappearing from the population or replacing the other alleles entirely
2 forms: founder effect & bottleneck
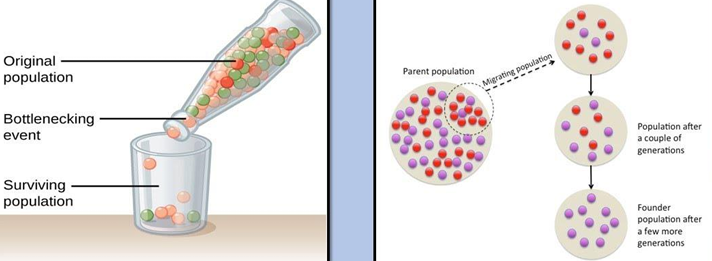
founder effect (form of genetic drift)
high frequencies of specific genetic traits inherited from the few common ancestors who first had them
affects especially small populations with few founding members
effects of recessive alleles on phenotype
eg. Ellis-Van Creveld Syndrome in Amish people
eg. Salla disease in Finland/Sweden
Ellis–van Creveld syndrome in Amish people
polydactyly: extra finger/toe
Amish people = religious group from Dutch ancestors who migratede to US
religious beliefs: stay & marry in own group → little gene pool → If there are some carriers of a recessive allele in that limited group, the chance increases that children inherit the allele from both parents and thus become homozygous → disease then manifests
bottleneck (form of genetic drift)
Rapid dramatic changes cause most individuals to die without passing on their genes → The few survivors of these evolutionary "bottlenecks" then are reproductively very successful → large populations in subsequent generations
extraordinary reduction in genetic diversity of a species since most variability is lost at the time of the bottleneck
Low genetic variation among modern humans implies bottleneck(s) in our evolutionary past
we descend from a small number of humans who survived an evolutionary bottleneck
examples: drought in Africa & Toba supervolcano eruption
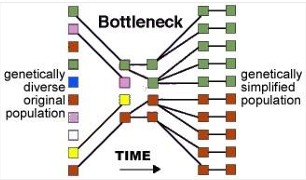
differences & similiarities between bottle neck effect & founder’s effect
They both lead to loss of genetic diversity but they have very different mechanisms
bottleneck: original population is reduced bcs the majority of the individuals died in some sort of bottleneck event => surviving population has much lower degree in genetic diversity → all those alleles that went extinct with the indiviudals that died remain extinct
founder: from the current population there is a smaller migrating population were the allele frequencies might not be representative for the original parent population => in successive generations those alleles that are carried by the original founders can become much higher in frequency
Draft (=hitch hiking)
linkage: genes that are located close together in a chromosome tend to be inherited together
hitch-hiking: a netral polymorphism is linked to alleles that are undergoing a selective sweep
fitness benefits → neutral allele increases (until it become fixed)
non-advantage → neutral allele decrease (to extinction)
drift & draft are both used for…
maintenance of genetic variation