D.1.2 - Protein Synthesis
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What does DNA have to do with protein synthesis?
Organic bases in DNA code for the sequence of amino acids produced in the ribosomes to create proteins. (transcription and translation)
Transcription
RNA is synthesised using the base sequence in one strand of DNA as a template
What makes up genes?
A sequence of nitrogenous bases at a given point in the DNA sequence
Transcription process
An area of the DNA for one gene becomes unzipped, and one of the two strands (template strand) will be used as a template to create the mRNA molecule. RNA polymerase (enzyme) binds to a promoter sequence at the beginning of the gene code.
RNA polymerase functions
Breaks hydrogen bonds, separates DNA strands
Links RNA nucleotides to form the RNA strand as complementary base pairing occurs
RNA complementary base pairing
Free RNA nucleotides in the nucleus join onto their complementary base in the template strand. Hydrogen bonds form between the base pairs - the location of the hydrogen bonds and the chemical structure of the bases make sure that only complementary bases bind.
Why is RNA always shorter than DNA?
RNA strands only contain information for a single gene.
Where is the molecular stability of DNA important?
In the somatic (body) cells that don’t undergo cell division (such as nerve cells) but still need to produce RNA.
Mutation def.
Permanent changes to DNA
Which direction does RNA polymerase synthesise in?
5’ to 3’ end
Which strand is used to synthesise RNA and why?
The antisense strand (strand that starts from 3’ end), because the new antiparallel RNA strand will then start at the 5’ end. The sense strand will be nearly identical to the new RNA strand, except for the switch between T-U.
Compare and contrast DNA and RNA polymerase
Compare:
They both move in the same direction - 5’ to 3’
Contrast:
DNA needs a primer whereas RNA doesn’t
DNA needs helicose, RNA can break hydrogen bonds itself
Transcription is the first step of _?
Gene expression
Translation
Process of directing protein synthesis by information encoded in mRNA
Main RNA types involved in translation
mRNA
tRNA
rRNA
mRNA functions
Carries DNA from the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm
tRNA function
Carries amino acids to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm
rRNA function
Combines with ribosomal proteins to create ribosomes
Ribosome structure
Comprised of two subunits made of rRNA: one large, one small
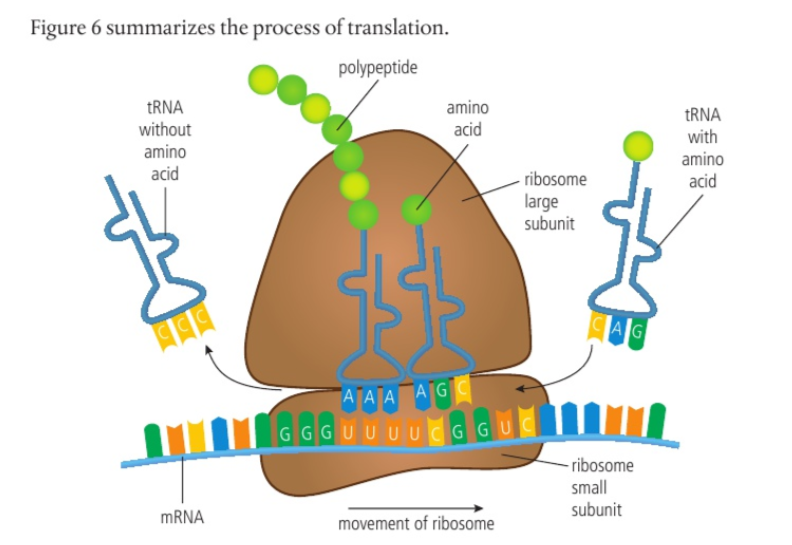
Translation process:
mRNA bonds with small subunit of the ribsosome at the initiation site
tRNA with an amino acid attatched bonds with the large subunit
A second tRNA molecule binds to the subunit and forms complementary base pairs with the mRNA. Two tRNAs can simultaneously bond to the large subunit.
An enzyme catalyses a condensation reaction between between the two amino acids, forming a peptide bond
The first tRNA molecule detatches from the amino acid and floats into the cytoplasm, the ribosome moves down the mRNA strand
A new tRNA molecule attatches, pairing an amino acid with the next base sequence
The process continues until a protein has been formed
DNA triplet in transcription
mRNA codon
How does translation work (tRNA and mRNA)
Reliant on complementary base pairing between mRNA codons and tRNA anticodons. tRNA anticodons determine which amino acid will be attatched to that molecule.
tRNA variations
20, one per amino acid. They are differentiated by the anitcodon.
Genetic code two characteristics
Degeneracy
Universailty
Genetic code degeneracy
There is more than one codon for each amino acid (there are 20 amino acids and 64 codon combinations)
Genetic code universality
With few exceptions, all living organisms have the same genetic code
Stop codons
UAA, UGA, UAG - signal the end of a polypeptide chain
Single point mutuation
A change in one of the bases of a sequence. This can affect protein structure - one example is sickle cell disease.
Ribosome two areas
Small subunit (40S) and large subunit (60S)
Start codon
AUG