1.2.6 - price determination
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
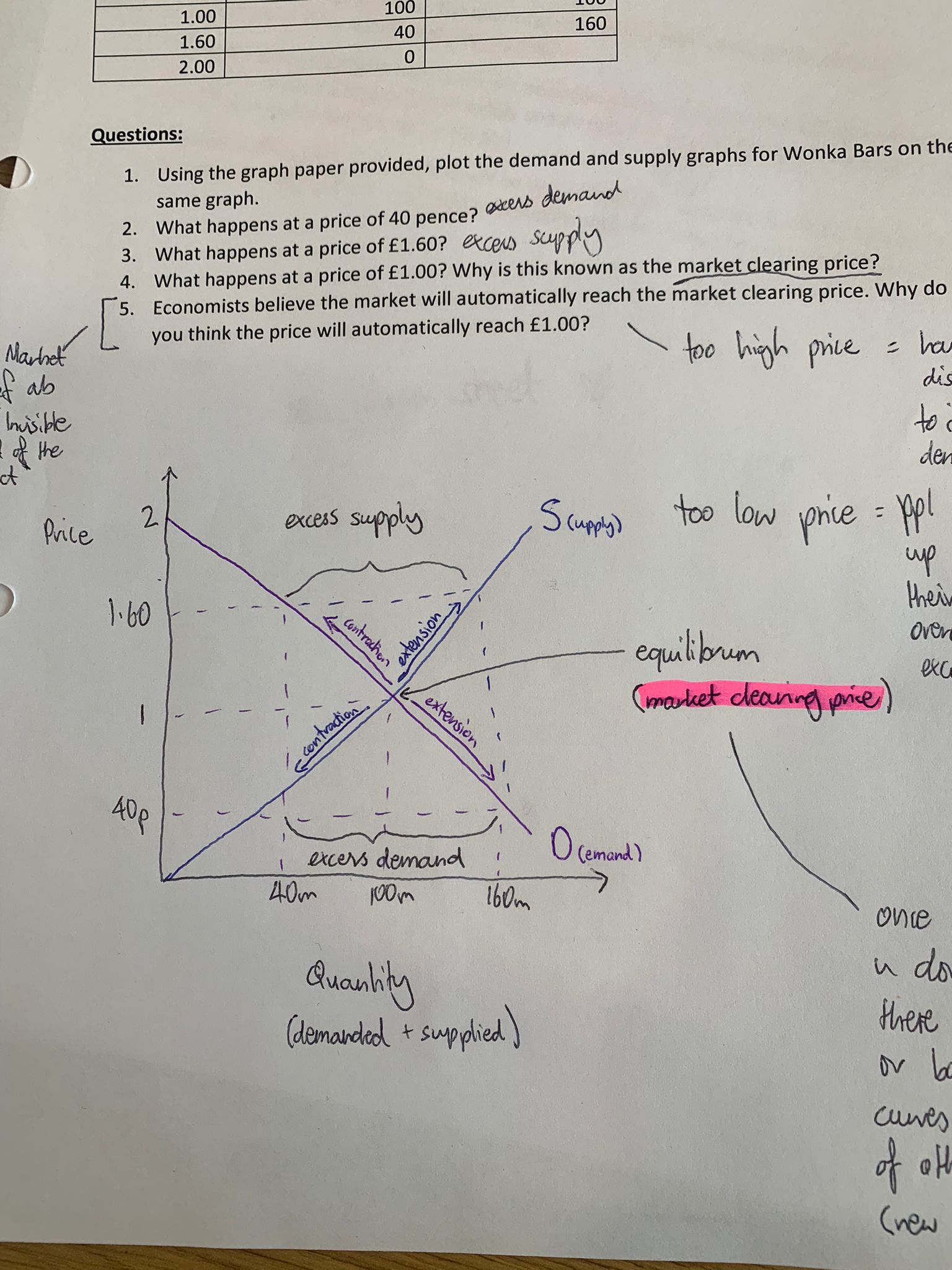
how many times does quantity demanded equal quantity supplied
ONCE (where the curves intersect)
what is the price at which demand = supply known as
market clearing price/equilibrium price
what happens if price is too high
excess supply compared to quantity demanded
how does the price too high situation rectify itself
stocks build up
firms cut prices
causes contraction in supply, and extension in demand
market reaches equilibrium and clears (demand = supply)
what happens if price is too low
excess demand for the supply available
how does the price too low situation rectify itself
not enough stock for customers who want it
customers bid up prices
causes contraction in supply and extension in demand
market reaches equilibrium and clears (demand = supply)
draw/picture a supply demand graph
.
what happens if there is an increase in demand (due to another factor)
shift in demand curve to the right
if the price remains as it was, there would be excess demand
then the excess demand process occurs, causing the market to reach a new equilibrium
what happens if there is a decrease in demand (due to another factor)
shift in demand curve to the left
if price remains as it was, there would be excess supply
then the excess supply process occurs, causing the market to reach a new equilibrium
what happens if there is an increase or decrease in supply
increase supply (shift right) = excess supply
decrease supply (shift left) = excess demand
relative processes occur to reach new equilibrium