3: Treatment of Gram Negative Infections, Anaerobic Infections, and STDs
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
What are the first line drugs of choice for uncomplicated cystitis
#1 Bactrim BID x 3 days
Nitrofurantoin 100 mg BID x 5 days
Trimethroprim 100 mg BID x 3 days
Fosfomycin 3 gm packet mixed in water x 1 dose
TMP-SMX DS is only used for uncomplicated cystitis if local resistance rates are <
20%
What are the second line drugs of choice for uncomplicated cystitis
B lactam for 3-7 days (*esp in pregnancy)
What characterizes complicated cystitis
symptoms >7 days
abn anatomy
hx of renal stones, DM, pregnancy, presence of catheter
What is the treatment for pyelonephritis
For those with high fever and flank pain, usually admit for IV Abx and once afebrile for 2 days, transition to oral
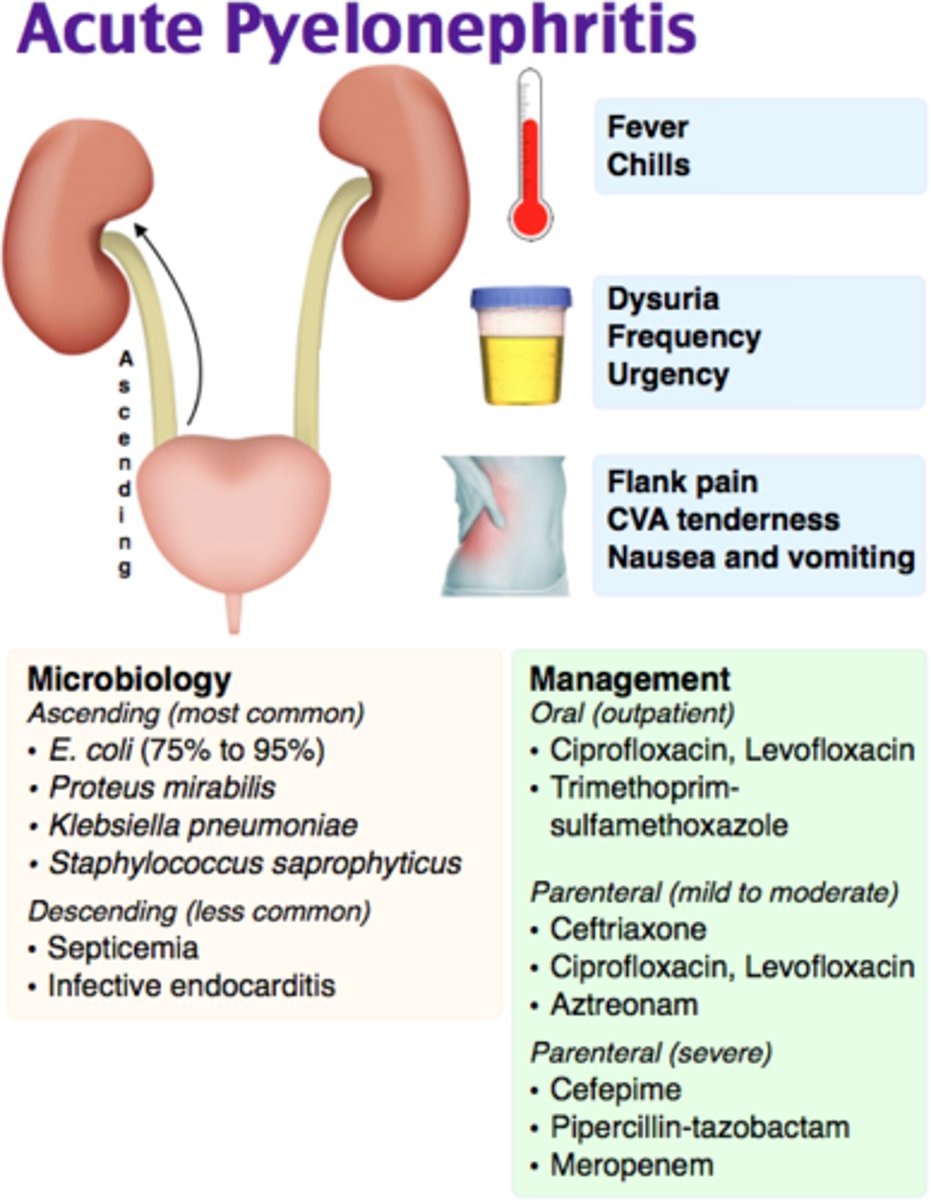
What are the drugs of choice for pyelonephritis
Ciprofloxacin 500 mg BID x 7d
Levofloxacin x 5d
TMP-SMX DS BID x14 days (if pathogen susceptible)
What IV drug can you use for pyelonephritis
Ceftriaxone followed by 7-14 days of oral abx
What characterizes a complicated UTI
Occur in patients with indwelling urinary catheters or anatomic or functional abnormalities of the urinary tract - more likely caused by antibiotic-resistant Gram negative bacilli
What are the pathogens that cause complicated UTI's most often
S. aureus
Enterococci
What is the treatment for complicated UTIs
Ciprofloxacin or levofloxacin, can be used to treat such infections in outpatients
In hospitalized patients, we can treat complicated UTIs with
Cefepime, Ceftriaxone, Fluoroquinolone, OR Piperacillin PLUS ticarcillin
What characterizes a "chronic UTI"
>3 episodes of cystitis in a year
What is the treatment for chronic UTIs
low, once daily dose of TMP-SMX for 6M-1Y
What are the alternatives to Bactrim for chronic UTI prophylaxis
TMP alone if intolerant to SMX
Fluoroquinolones if bacteria resistance to TMP-SMX
NiNitrotrofurantoin
What side effects often occur with Nitrofurantoin
nausea more common so you must take with food
Nitrofurantoin is active against _____ in urine unlike other agents
enterococcus
_______ provide symptomatic relief of pain, urgency, burning, and frequency associated with lower urinary tract mucosal inflammation from infection
urinary analgesics
What are the 2 urinary analgesics we should know
Phenazopyridine (pyridium) 200 mg PO TID and Flavoxate 100-200 mg PO TID-QID
Phenazopyridine (Pyridium) causes what strange side effect
colors urine and clothes red-orange (available OTC)
Flavoxate (Urispas) causes ______ adverse effects
anticholinergic
Pathogens causing acute prostatitis are usually similar to those causing _____. What are the pathogens?
UTIs
E. coli, Proteus spp. and Klebsiella spp
How long is the therapy for acute prostatitis
4 weeks
What is the drug of choice for acute prostatitis
TMP-SMX
What is the drug of choice for acute prostatitis when bacteria are not sensitive to TMP-SMX
Fluoroquinolones (gram - bacteria)
_____ is a common cause of recurrent UTI in men
Chronic prostatitis
Chronic prostatitis inflammation is less than acute prostatitis. Would you give the same abx as for acute? How long?
Yes, use the same abx as for acute but must give for 6-12 weeks
What antibiotic would you use for chronic prostatitis
TMP-SMX first
Then fluoroquinolones
What are the typical gram negative bacteria that cause intra-abdominal infections
•Esherichia coli
•Klebsiella spp
•Proteus spp
•Also Pseudomonas aeruginosa if hospital-acquired
What type of bacteria typically causes intrabd infections
gram negative
What is the gram-positive bacteria that causes intra-abdominal infections
Enterococcus
_______ bacteria typically is what causes intra-abdominal abscess formation and outnumber gram-negative bacteria by ______ in the colon
Anaerobic
1000:1
What is a single agent with gram-positive/negative and anaerobic coverage (including enterococcus)
Piperacillin-tazobactam (Zosyn)
What is a single agent with gram-positive/negative and anaerobic coverage (not including enterococcus)
Doripenem
Doripenem is an imipenem derivative with longer _____
T 1/2
Doripenem is most resistant to ______ to _______
B-lactams to extended spectrum B lactamasese
What is a common anaerobic GI infection
Bacteroides fragilis (common bacterium in distal small bowel and colon)
What is a common anaerobic respiratory infection
Peptostreptococcus (can cause aspiration pneumonia from inhalation of upper GI bacterial flora)
What is a common anaerobic skin and soft tissue infection
C. perfringes (causative agent of gas gangrene)
What abx increase the risk for C. diff
clindamycin, tetracyclines and cephalosporins
For mild-moderate C. diff infection use
Oral metronidazole 500mg TID x 10-14 days (absorbed, but high concentrations reach colon)
For severe C. diff infection use
Oral vancomycin 125mg QID x 10-14 days (not absorbed, high concentrations in the colon)
For life threatening C. diff infection use
Oral vancomycin 500mg QID plus IV metronidazole 500mg TID x 10-14 days
What is the BEST agent for anaerobic infections
metronidazole
Metronidazole has excellent ____ penetration, esp CNS. It is rapidly bacterio____. It has local antiinflammatory activity in GI tract.
tissue
bacteriocidal
What are the other antibiotic agents to use for anaerobic infections
Clindamycin and Penicillin/B-lactamase inhibitor combos
What is used for Pseudomonas aeruginosa UTI
Cipro
What is used for Pseudomonas aeruginosa systemic infections
•Piperacillin/tazobactam +/- tobramycin
•Ceftazidime or cefepime +/- tobramycin
•Meropenem or doripenem +/- tobramycin
What is used for Pseudomonas aeruginosa pulmonary infections
•Same as above but add aminoglycoside
•Inhaled tobramycin also available for cystic fibrosis patients
Hospital acquired pneumonia is defined as
pneumonia that occurs 48 hrs or more after hosp admission or endotracheal intubation
**slide 19-22
rewatch this section
What are the two main treatments for Chlamydia
Azithromycin 1 gm x 1 dose or
Doxycycline 100mg PO bid x 7 days
What are alternative treatments for Chlamydia
•Erythromycin 500mg PO qid x 7 days
•Levofloxacin 500mg PO qd x 7 days
If you treat for gonorrhea, you don't even have to test for ____ because you are treating it anyways
chlamydia
What is the treatment for gonorrhea
Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM x 1 dose PLUS Azithromycin 1gm x 1 dose
OR Doxycycline 100mg BID x 7d
_______ or _____ are no longer recommended for gonorrhea due to high resistance rates
Fluoroquinolones or oral cephalosporins
PID is a polymicrobial infection possibly involving
Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, anaerobic bacteria, and gram negative bacteria
What is the outpatient treatment for PID
•Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM x 1 dose plus
•Doxycycline 100 mg bid x 14 days with or without
•Metronidazole 500 mg bid x 14 days
What is the intpatient treatment for PID
•Give IV until able to tolerate oral antibiotics
•Cefotetan 2 gm IV q12 hrs plus
•Doxycycline 100 mg IV q12 hrs
What are the pathogens causing nongonococcal urethritis
Ureaplasma urealyticum or Mycoplasma genitalium
What is the treatment for nongonococcal urethritis? what is the same as
Usually responds to azithromycin or doxycycline at same doses as for Chlamydia trachomatis
What is the treatment for trichomoniasis
Metronidazole 2 gm orally x 1 dose
What is the treatment for BV
•Metronidazole 500mg PO bid x 7 days
•Metronidazole gel 0.75% intravaginally qd x 5 days
What is the treatment for primary and secondary syphilis
Penicillin G benzathine 2.4 million units IM x 1 dose
What is the alternative for primary secondary syphilis if there is an allergy to penicillin
doxycycline 100 mg PO BID x 14 days
What is the treatment for tertiary syphillis
Penicillin G benzathine 2.4 million units IM weekly x 3 doses for tertiary infections
What is the treatment for neurosyphillis
High dose Penicillin G IV x 10-14 days