Dental Hygiene Theory 1 Midterm
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
From quizlet
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
ADHA stands for
American Dental Hygienists' Association
all of the follows are professional roles of the dental hygienist EXCEPT:
-prescribing medication
-researcher
-public health
-corporate
prescribing medication
The Act that established national privacy standards as it relates to the release of patient info in the health-care industry is called
HIPAA
The health history enables the dental hygienist to do which of the following:
-Maintain legal documentation
- identify conditions for which the patient should be referred for evaluation
-establish baseline information about the patient's health
- all of the above
all of the above
The health history form should be completed by the patient and verified by the dental hygienist at the first visit. The dental hygienist should review the history at each appointment to verify document changes
both statements are true
the standard regimen of prophylactic antibiotic medication for an adult patient who must receive it before dental treatment is...
2 grams amoxilicillin 1 hour before procedure
who was issues the first dental hygiene license in 1927?
Irene Newman
as soon as student graduates from an accredited dental hygiene school, s/he can practice as a dental hygienist
false
at regis college any YES answers written on medical history needs to be circled with students RED pencil
true
when a hygienist reviews a medical history a hygienist needs to understand the limitations on the healthy history which include the patient might not provide the correct info and the patient may not understand the importance of the history
true
Aerosols are particles that are larger than 50 microns. Aerosols are not visible to the naked eye, can remain airborne for extended time, and may be inhaled.
The first statement is false, the second statement is true
bacterial filtration efficiency determines the ability to filter out bacterial contaminants and it has been determined that a mask with a filtration level of ________ provides high level of protection for most exposures
95-98% of 3-5 micron particles
If I use a face shield as part of my PPE:
I do not need to wear protective eyewear
In what order should your PPE be put on?
Protective gown, mask, protective eyewear, gloves
Sharps containers should be no more than _________ full to avoid protrusion of sharps
3/4
the six elements in the chain of infection are...
Infectious agent, susceptible host, reservoir, portal of entry, portal of exit, transmission
Viruses are smaller than bacteria and reproduce only in living host. Viruses include Hepatitis A,B,C,D and HIV
Both statements are true
when working on your patient, your mask should be changed:
after every patient and/or whenever it becomes damp
__________ bacteria is picked up from things that are touched, and is removed through hand washing
transient
_______________________ is an approach to infection control that treats all human blood and human body fluids as if they are known to be infections for HIV, Hepatitis B, and other blood borne pathogens
standard precautions
all of the following are possible causes of carpal tunnel syndrome except:
- fever
- pregnancy
- tumor in wrist
- arthritis
fever
Bradycardia is when a patients pulse rate is below 50 beats per minute. The adult pulse rate can range from 60-100 beats per minute.
Both statements are true
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the ________ nerve becomes compressed in the carpal tunnel.
Median
Korotkoff sound is the first sound that is heard through the stethoscope which indicates diastolic pressure. The size of the blood pressure cuff should be 20% greater than the diameter of the arm, as a cuff too small will result in an artificially elevated blood pressure.
First statement is false. The second statement is true.
Korotkoff sound
sound heard during the taking of blood pressure using a sphygmomanometer and stethoscope
The respiration rate is assessed by counting the _____ of the patients chest.
Rise and fall
When taking a pulse, you use the tips of the thumb, index, and middle fingers. The fingers are placed over the ulnar pulse, located on the thumb side of the ventral side of the wrist.
Both statements are false.
When taking a temperature the clinician should ask if the patient has ingested anything that was hot/cold in the last 30 minutes. The temperature probe should be placed under the tongue.
Both statements are true
Which of the following is NOT a symptom of carpal tunnel syndrome:
- pain in hand, wrist, shoulder, neck
- pain in hands when working
- nocturnal pain in hands/forearms
- they are all symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome
they are all symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome
Which tests determine the presence of carpal tunnel syndrome
Phalen's test and tinel's sign
You take the vitals of your next patient, 41 year old Patient A, whose blood pressure is 130/85 and oral temperature is 99.9.
Patient A's blood pressure is considered stage 1 hypertension. Patient A's temperature is considered normal.
The first statement is true. The second statement is false.
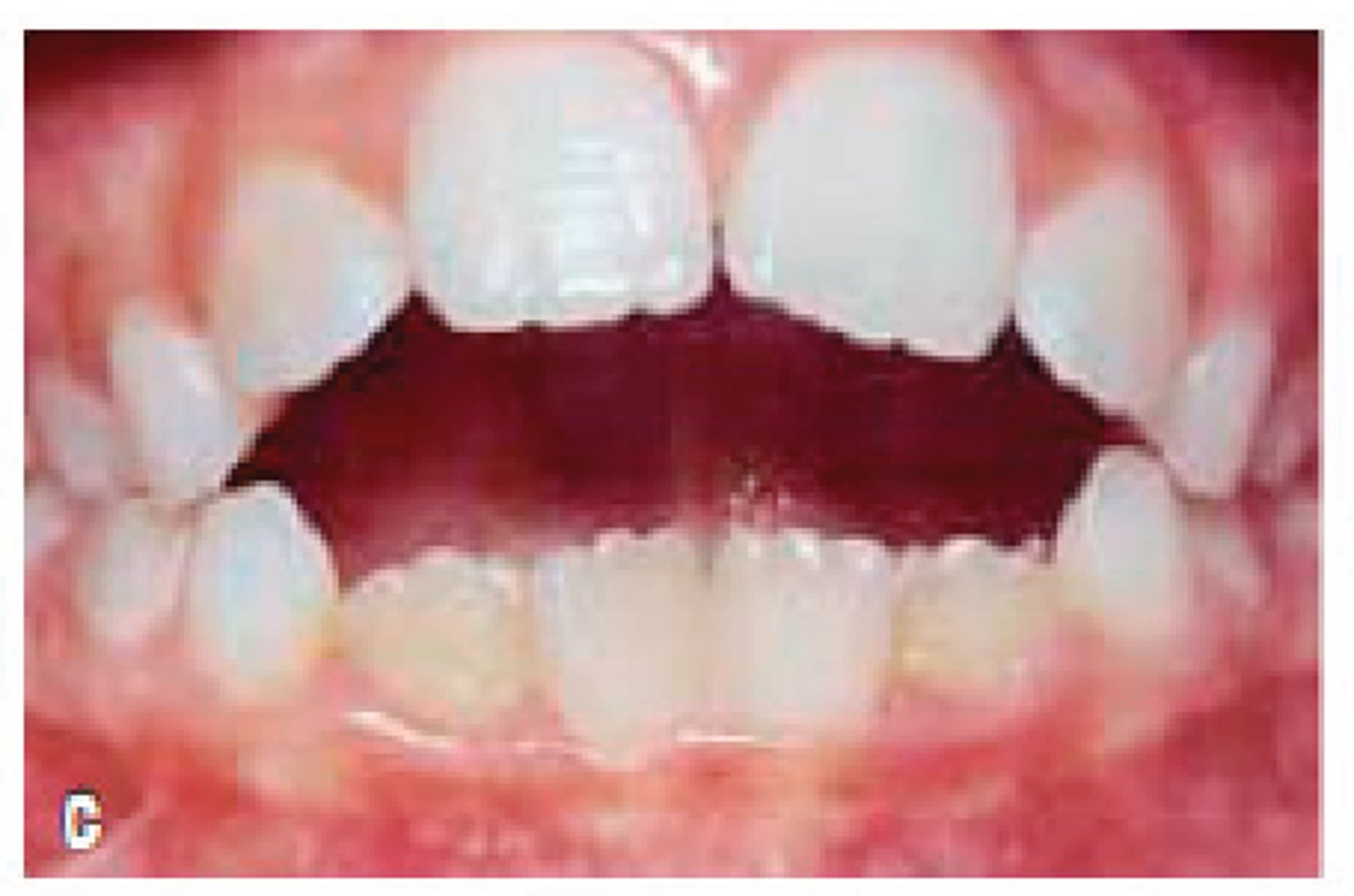
Your patients attached gingiva has an "orange peel" look to it. This is called ....
stippling
your patients gingiva is uniformly pale pink/pigmented. You would consider this color to indicate...
health
As you use your Nabors Probe (furcation probe), you notice the probe can go all the way through to the other side of the furcation, AND it is covered by soft tissue and is not visible. You would classify this furcation as:
Class 3
If your patient has inflammation in between teeth 8 and 9 and along the margins of 8 and 9, this would be considered
localized marginal gingivitis
In a healthy adult mouth, the gingival sulcus measures 0.5-3mm from the gingival margin to the base of the sulcus. In a healthy adult, the gingival margin is located against the tooth enamel 0.5-2mm coronal to the CEJ.
Both statements are true
Modifiable risk factors include all of the following EXCEPT:
- genetic disorders
- poor oral hygiene
- smoking
- stress
genetic disorders
The col is a saddle of interdental gingiva that connects the mesial and distal aspects of the interdental papilla. The center of the col is keratinized.
Both statements are false
Your patient presents with localized severe marginal inflammation with apical migration of the junctional epithelium between teeth 24 and 35. How would you clinically classify this patients oral tissues between 24 and 25?
periodontitis
your patient presents with mobility and the tooth can be moved up to 1mm in any direction. This classification of mobility is considered:
Class 1
________ is/are localized recession, V- shaped, forming a slit-like indentation in the gingiva.
Stillmans cleft
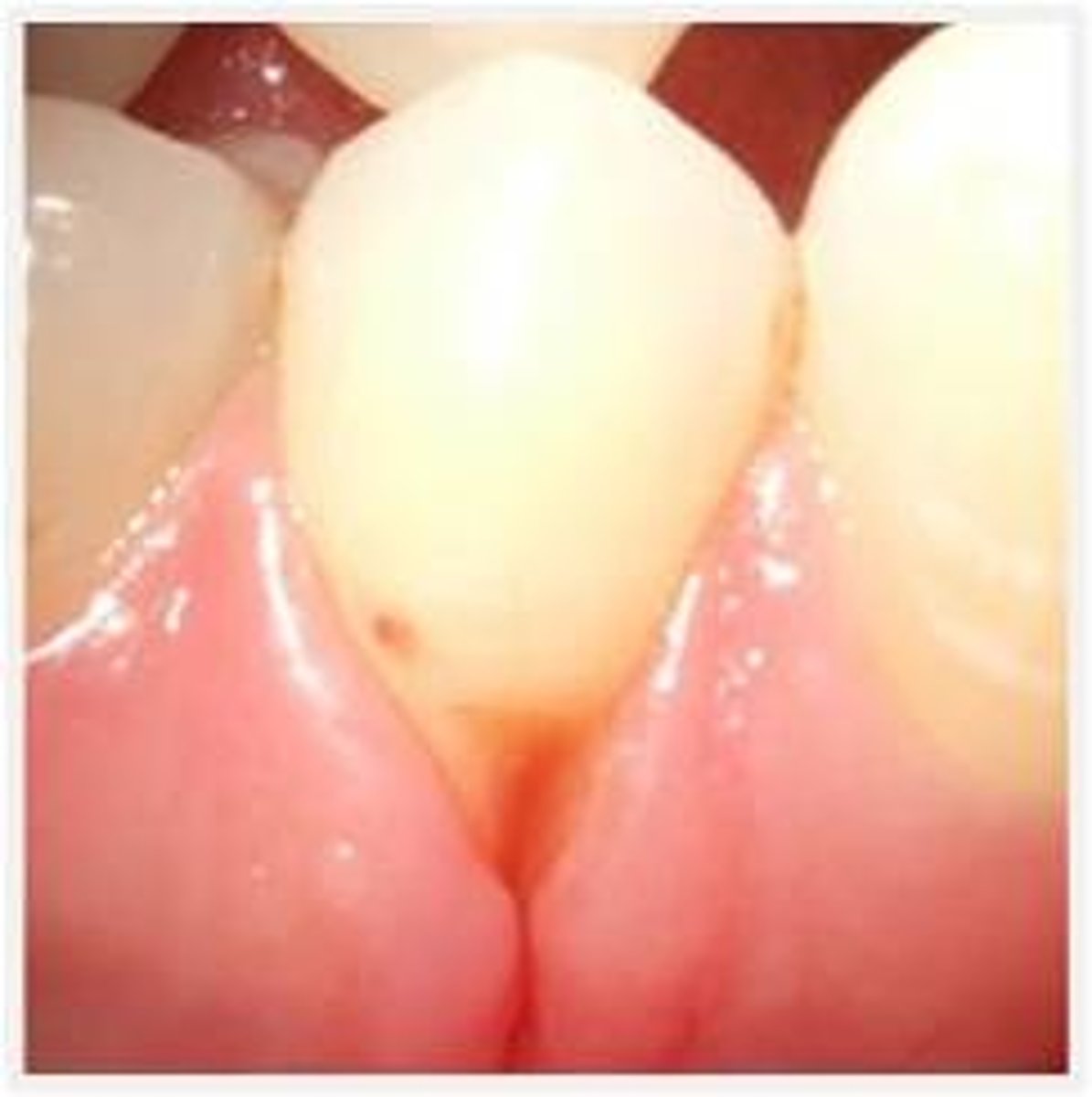
In order to examine the TMJ, during the extraoral examination, you use ________palpation
bilateral
the opening to the parotid gland is called the _____ duct. You dry the duct and try to express a drop of saliba to ____ the gland.
Stensons, Milk
the proper patient positioning for an extraoral examination is to have the patient...
in an upright position
the proper positioning for an intraoral examination is to have the patient
in a supine position
the thyroid gland...
- has a bowtie shape
-is located in the middle of the lower neck
- sits below the larynx
- all of the above
all of the above
the visually inspect the tongue, a damp gauze square should be used to grasp and extend it, looking at the dorsal and ventral and lateral sides. The entire body of the tongue should be bidigitally palpated.
both statements are true
what is the proper sequence for an extraoral examination?
there is no one correct sequence as long as it is logical and efficient
when performing an extraoral oral examination the clincian must use __________ to compress tissues against the underlying bone
circular motion
you stand in front of your patient and complete a general appraisal of her face, head, and neck checking for symmetry. What skill are you using?
observation
when trying to locate the TMJ the clinician must place the index fingers just in front of the tragus of each ear and ask the patient to open and close
true
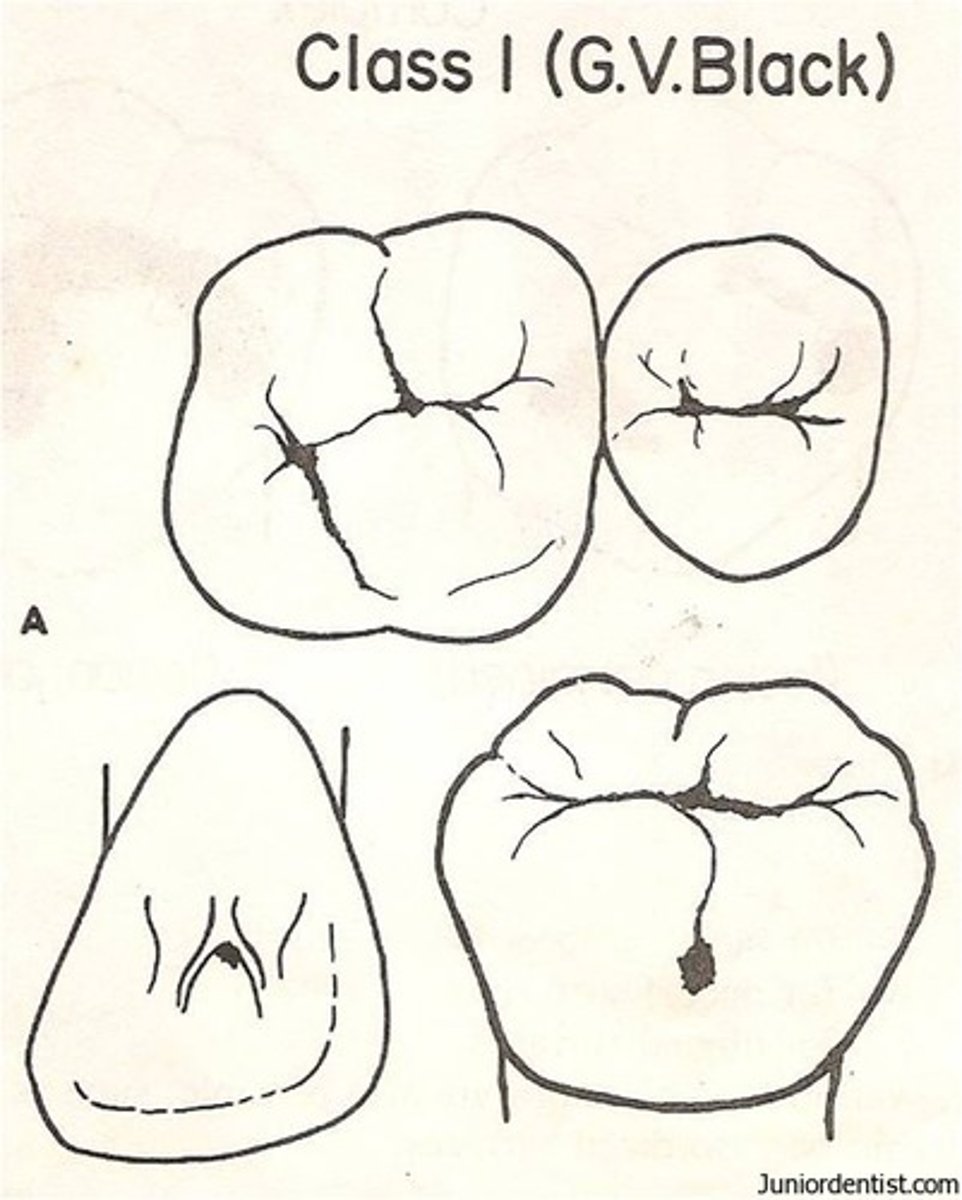
Class 1 caries
pits and fissures of posterior teeth, lingual pits of maxillary incisors
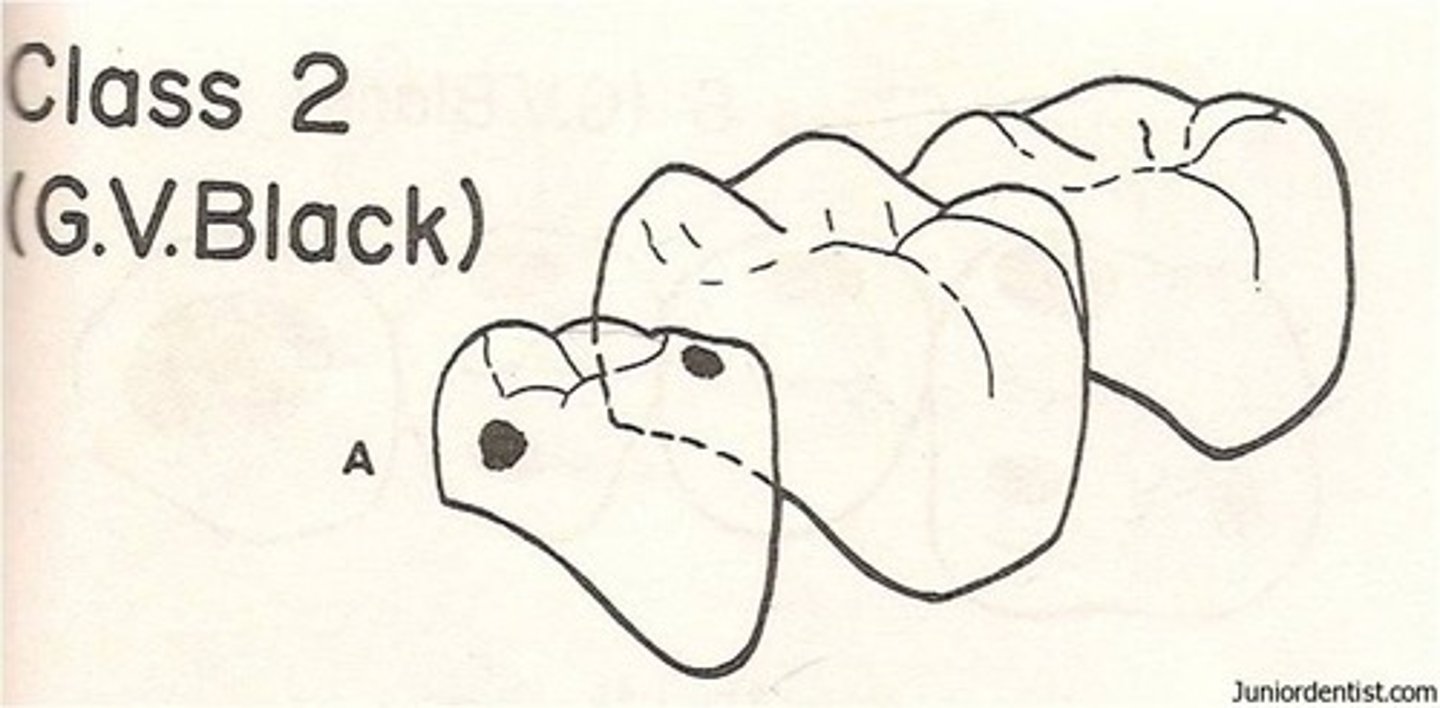
Class 2 caries
proximal, posterior teeth
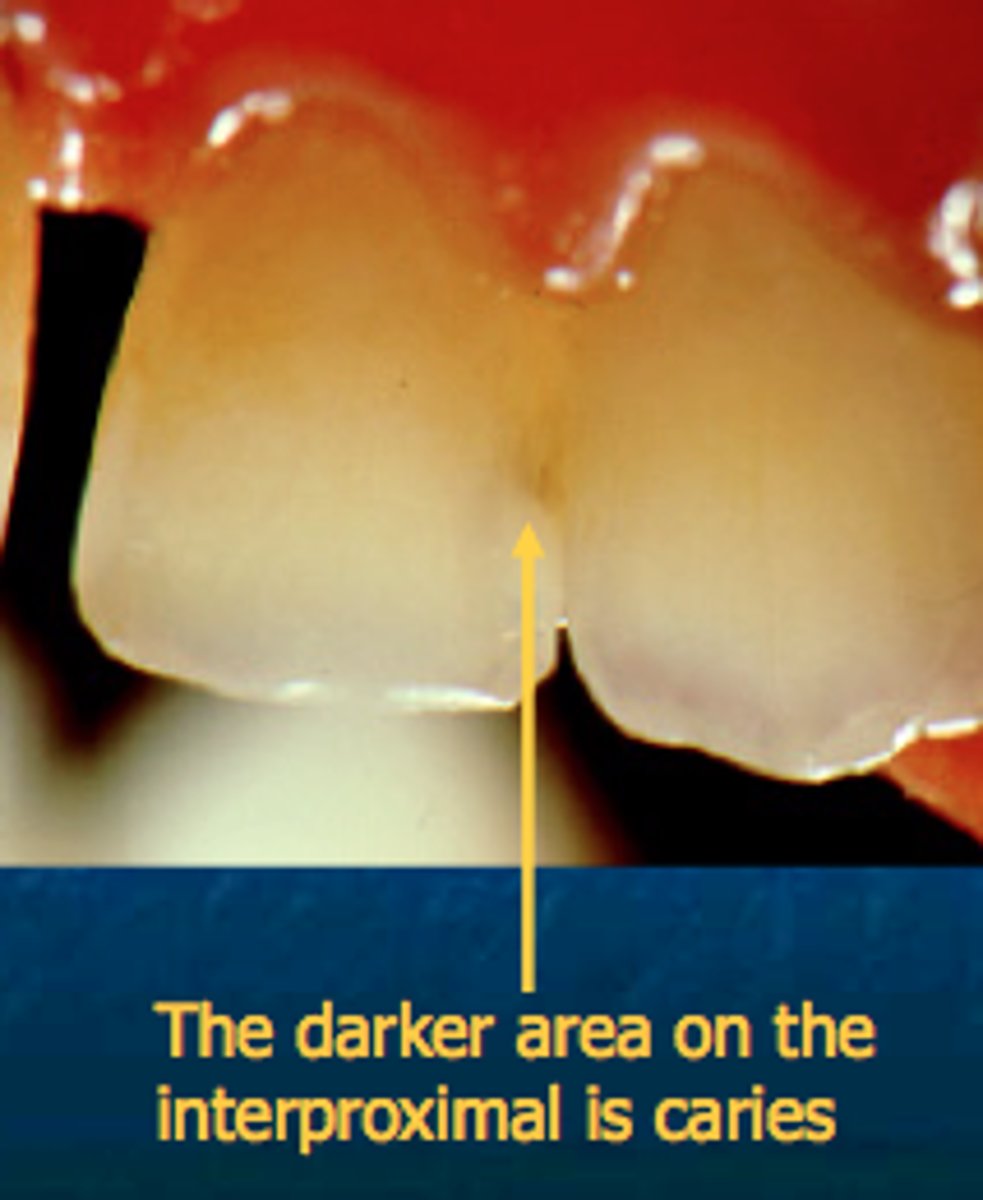
Class 3 caries
proximal, anterior teeth
Class 4 caries
proximal and incisal line angle, anterior
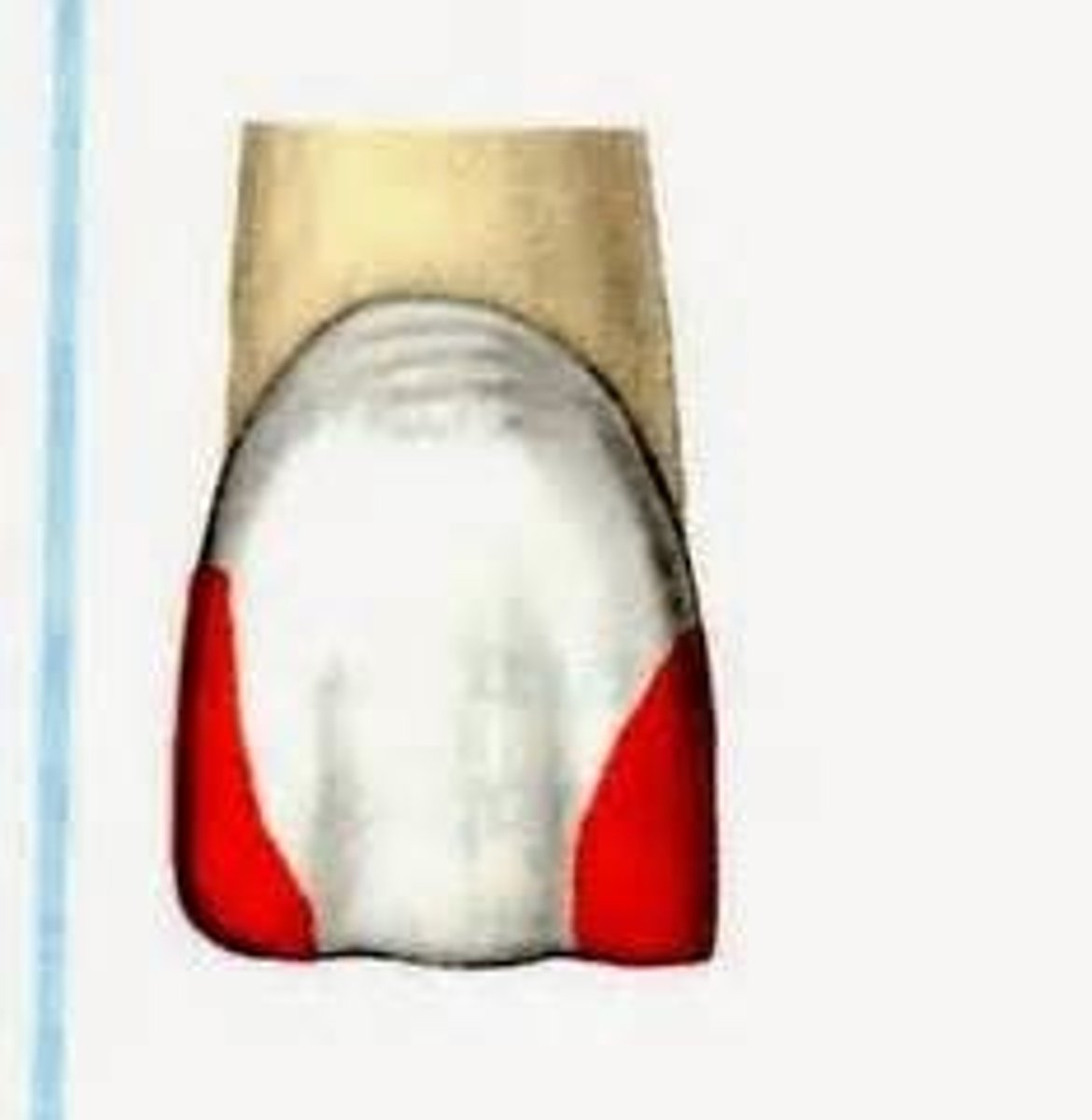
Class 5 caries
cervical 1/3 of facial or lingual
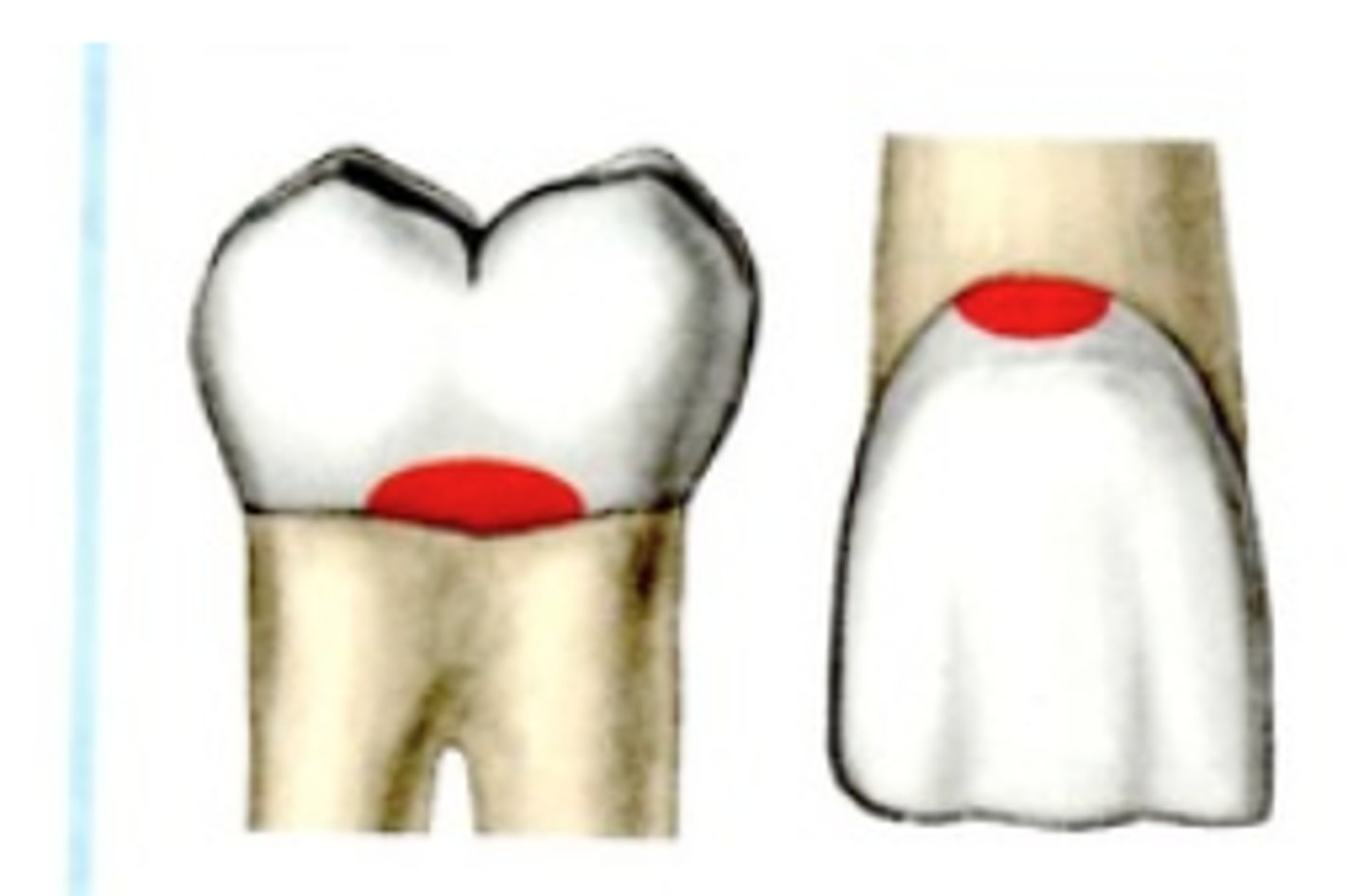
Class 6 caries
incisal edge of anterior or cusp tip of posterior
Malocclusion
any deviation from the normal positioning of the upper teeth against the lower teeth
Malocclusion Affects....
Bite
Ability to maintain adequate plaque control
Speech development
Appearance
normal occlusion
Mesiobuccal cusp of max. 1st molar occludes with buccal groove of mand. 1st molar
mesognathic
Slightly protruded jaws, facial outline is relatively flat appearance
retrognathic
Prominent maxilla and a mandible posterior to its normal relationship
prognathic
prominent protruded mandible
overbite
vertical overlap between the two arches
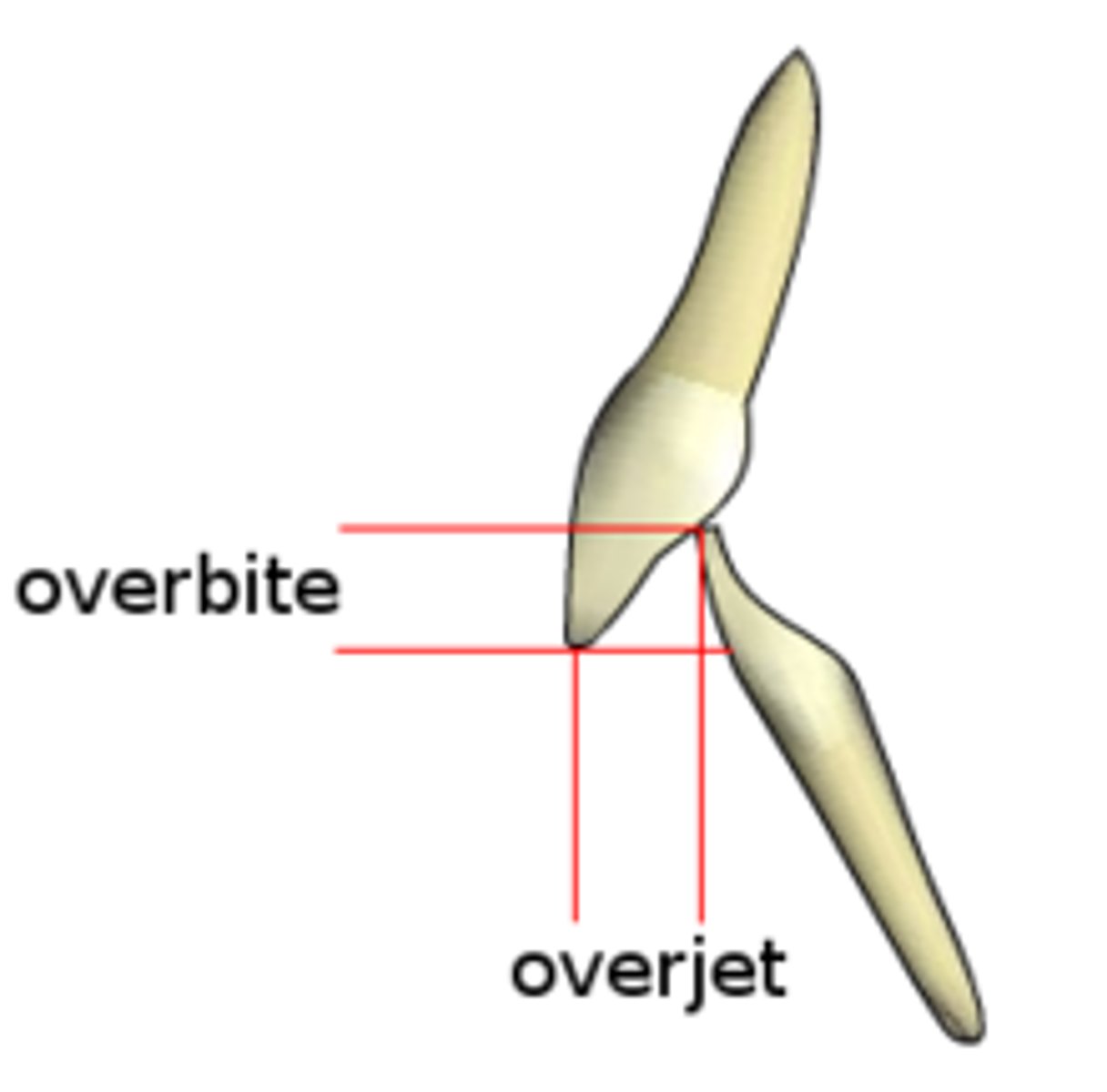
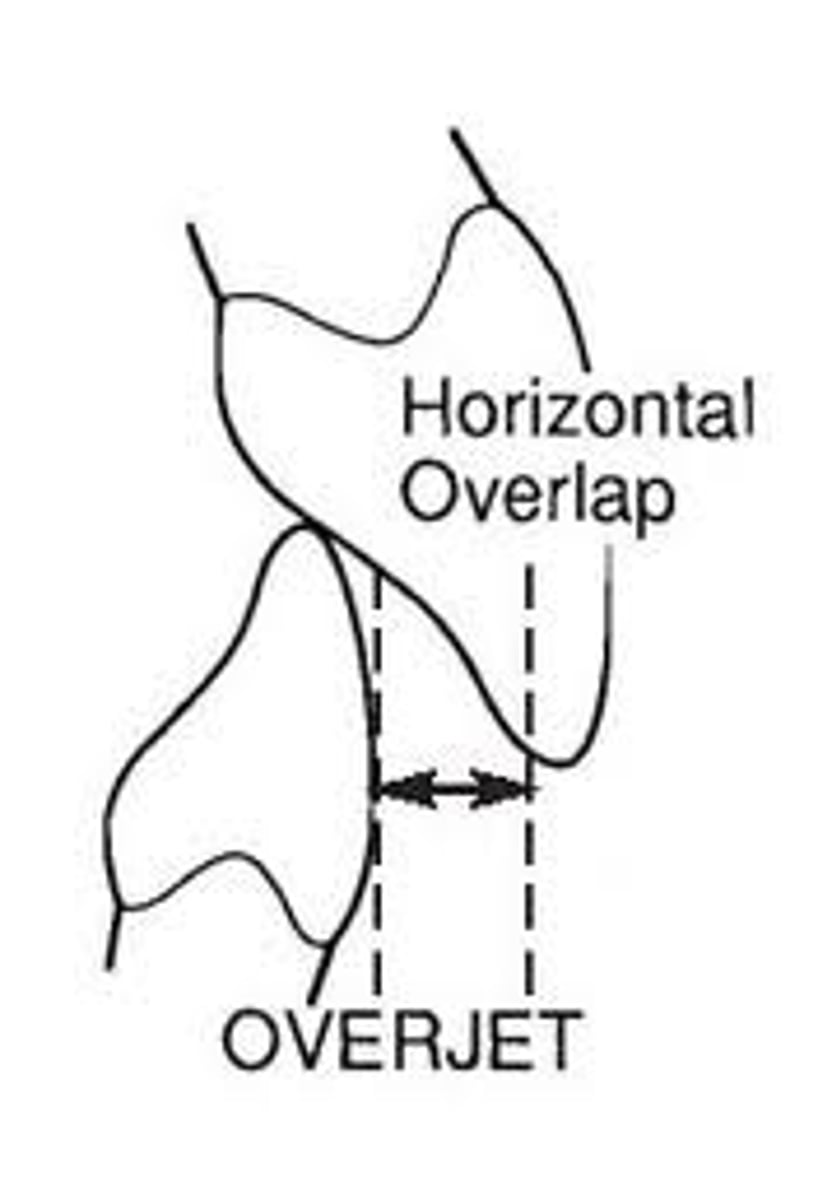
Overjet
horizontal overlap or distance between the two arches (ling of max. incisor and facial of mand. incisor)
normal overbite
incisal edges of max. teeth are within incisal 1/3 of mand. Teeth
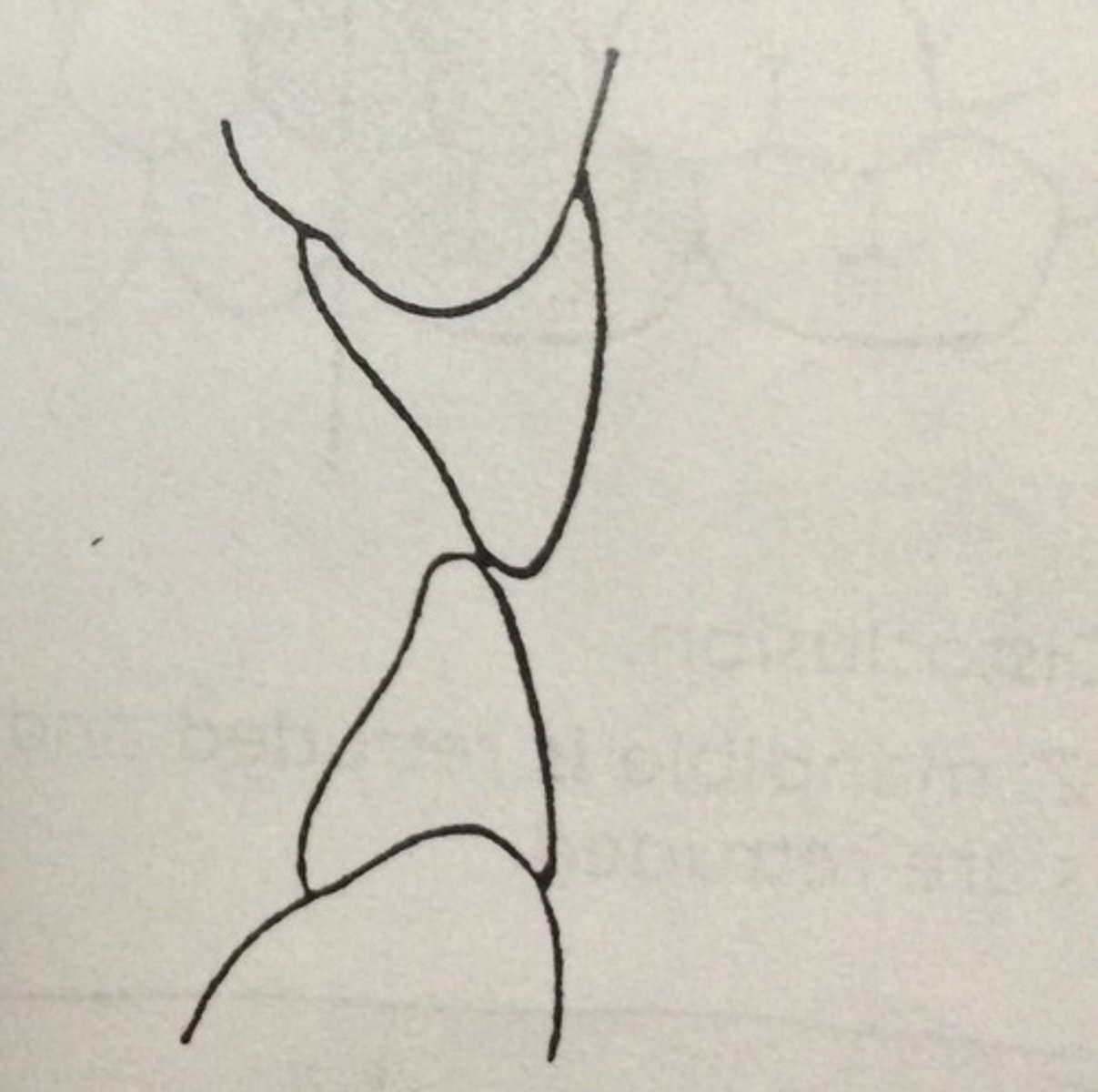

moderate overbite
incisal edges of max. teeth are within middle 1/3 of mand. Teeth

severe overbite
incisal edges of max. teeth are within the cervical 1/3 of mand. teeth

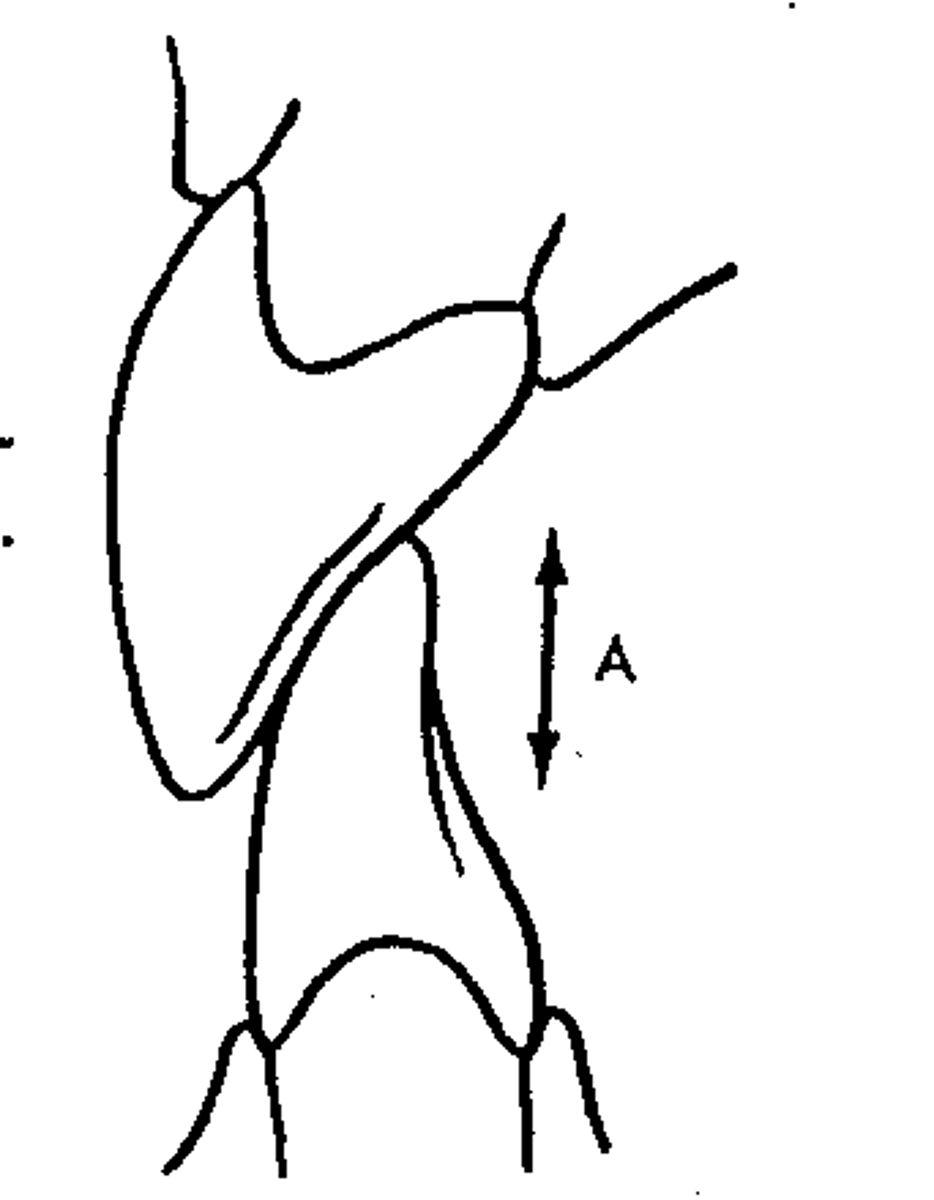
open bite
Lack of incisal contact
Posterior teeth in occlusion
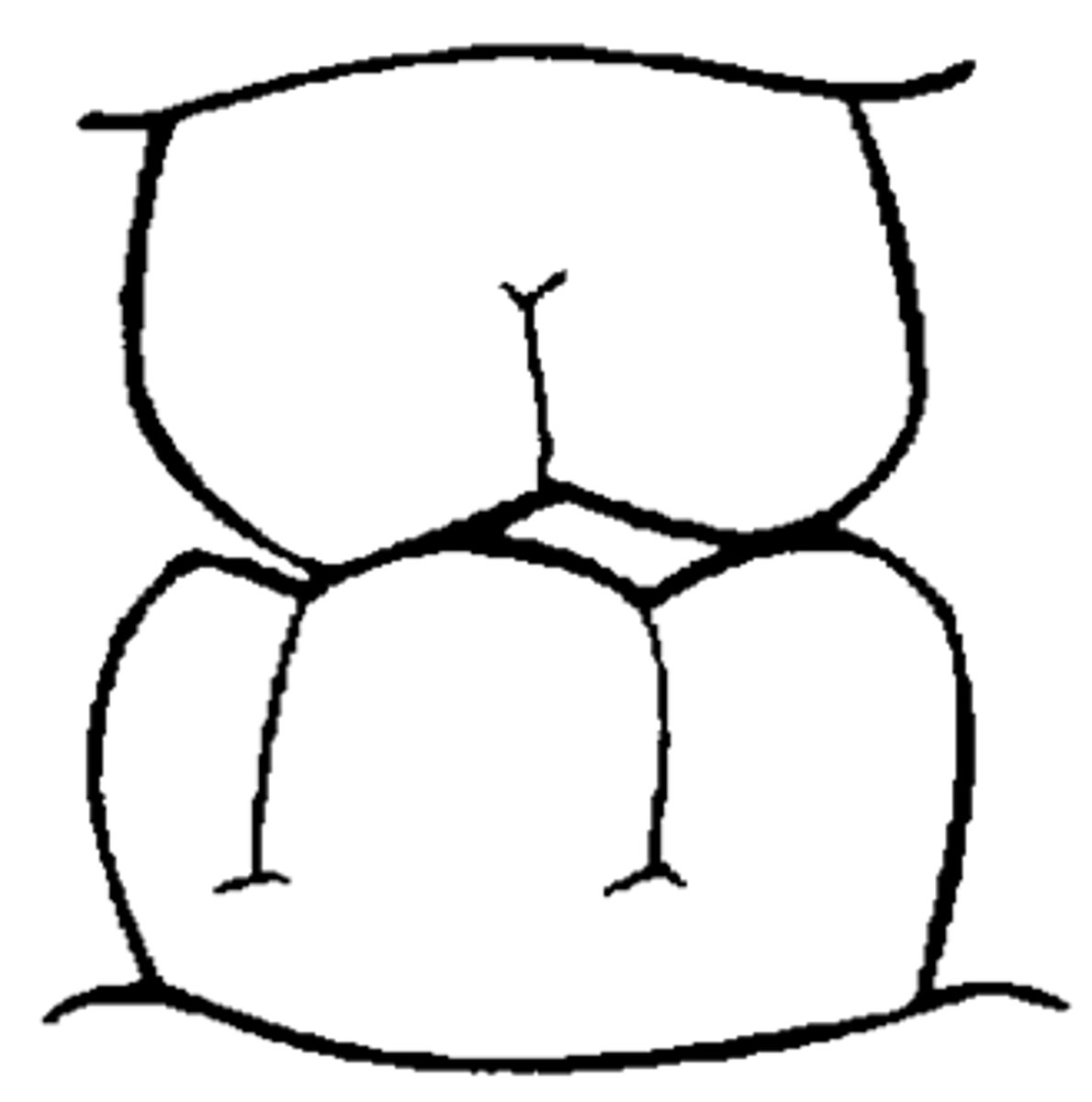
Edge-to-Edge (Incisal)
Incisal edges occlude
end-to-end
Cusp-to-cusp relationship of Posterior teeth.
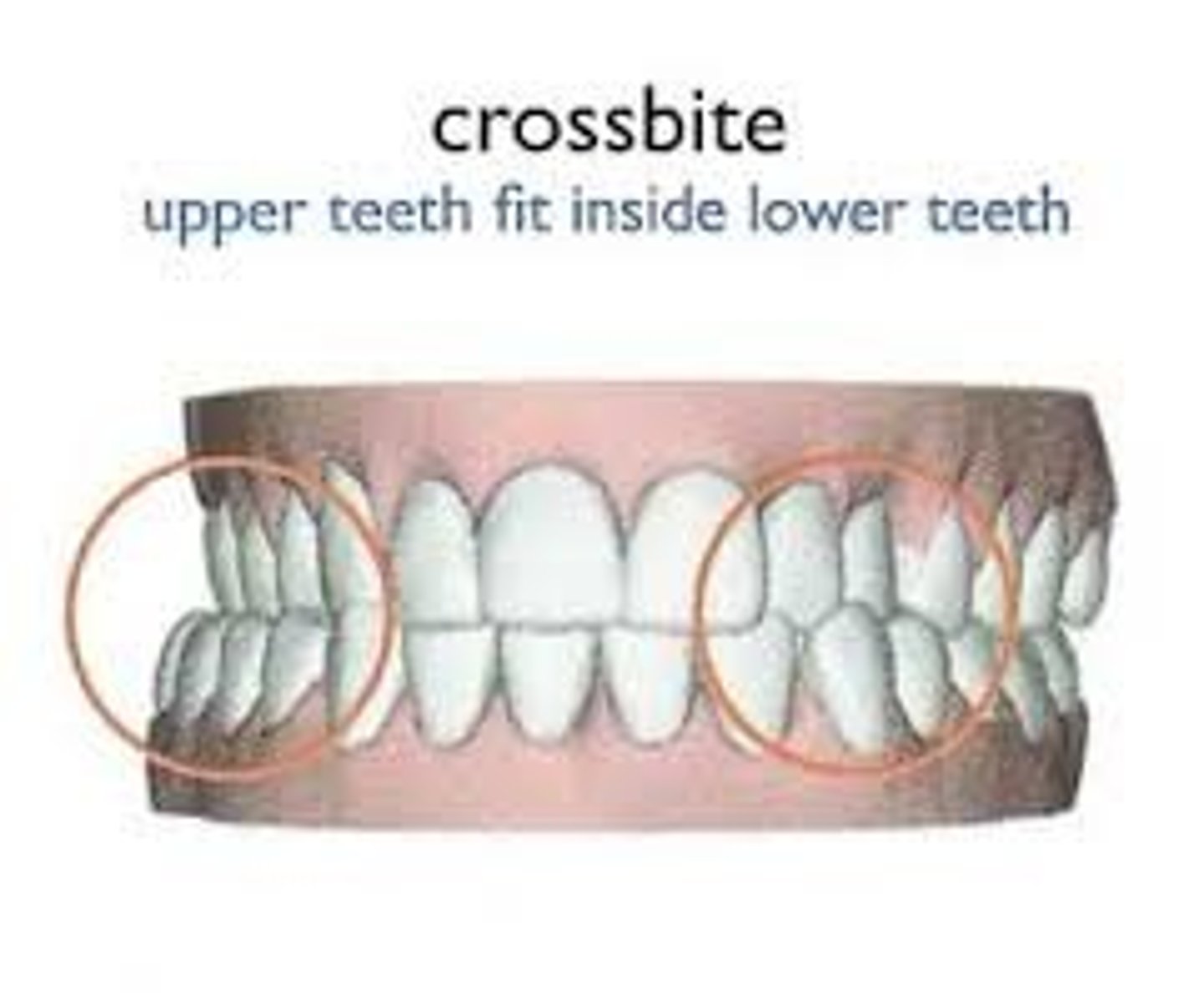
crossbite
Maxillary teeth are lingual to mandibular teeth
Tongue thrusting
The application of forceful pressure against the anterior teeth with the tongue, causing lisp
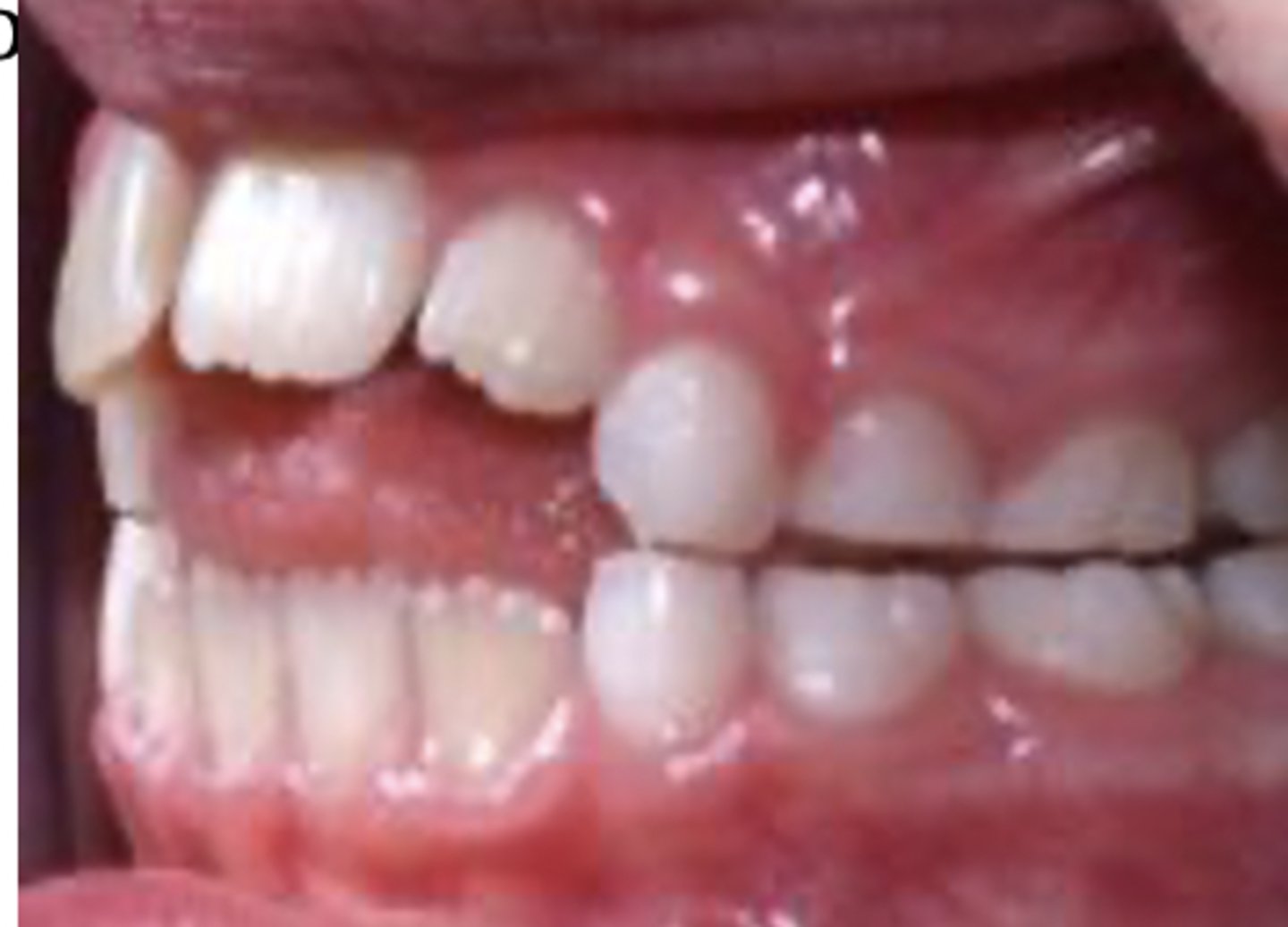
Diastma
abnormal space between teeth

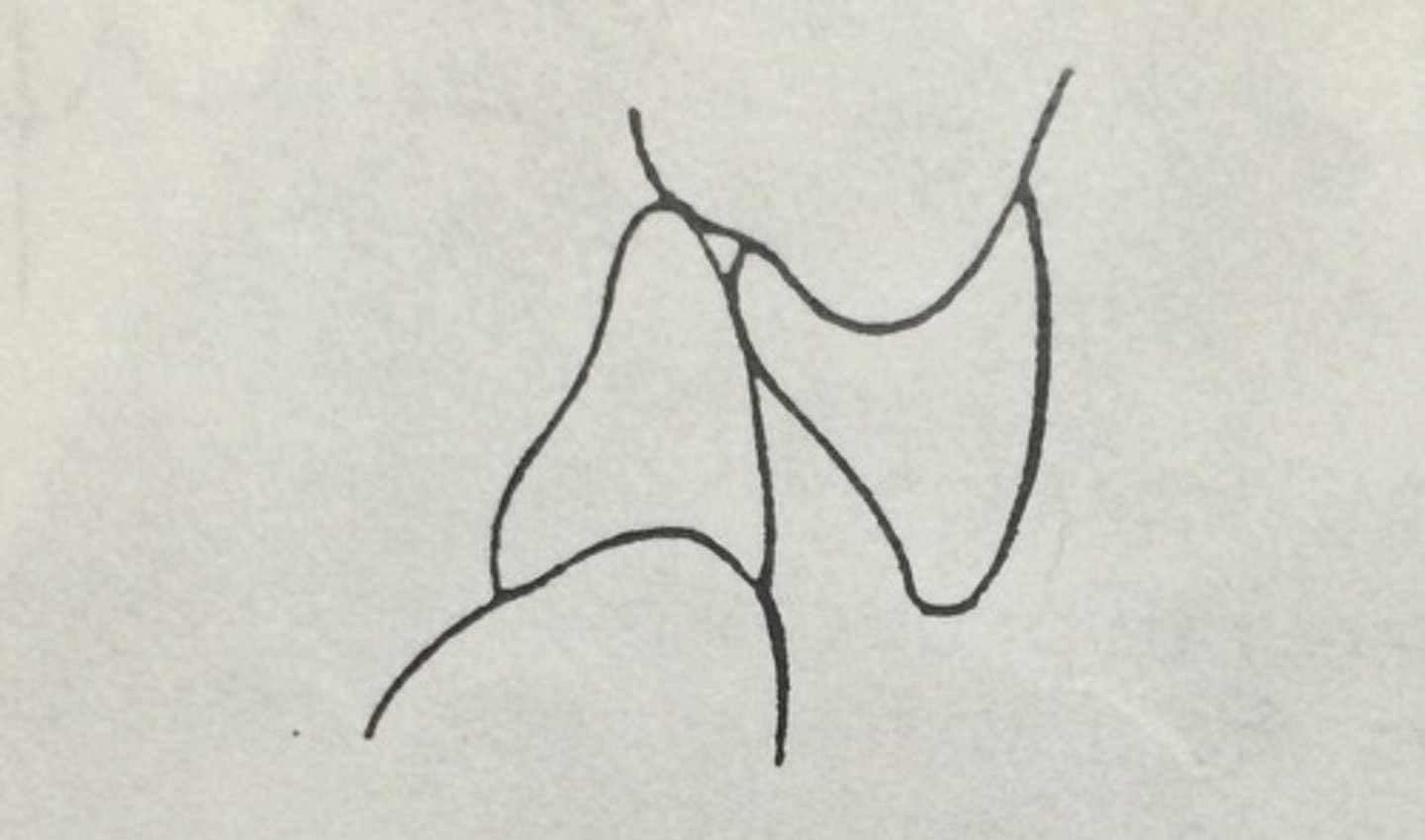
Buccoversion/Facioversion
Position buccal/facial to normal
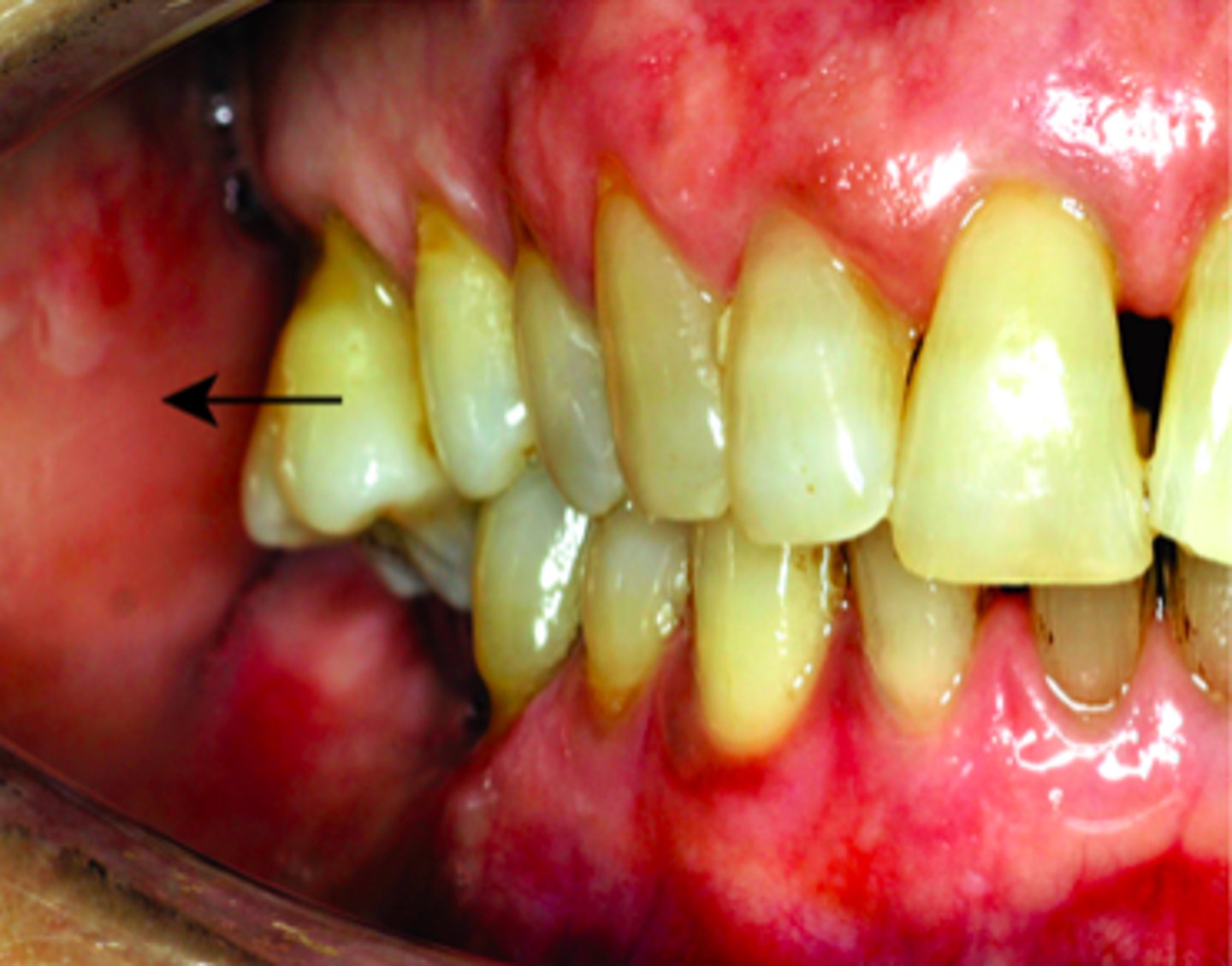
Linguoversion
Position lingual to normal
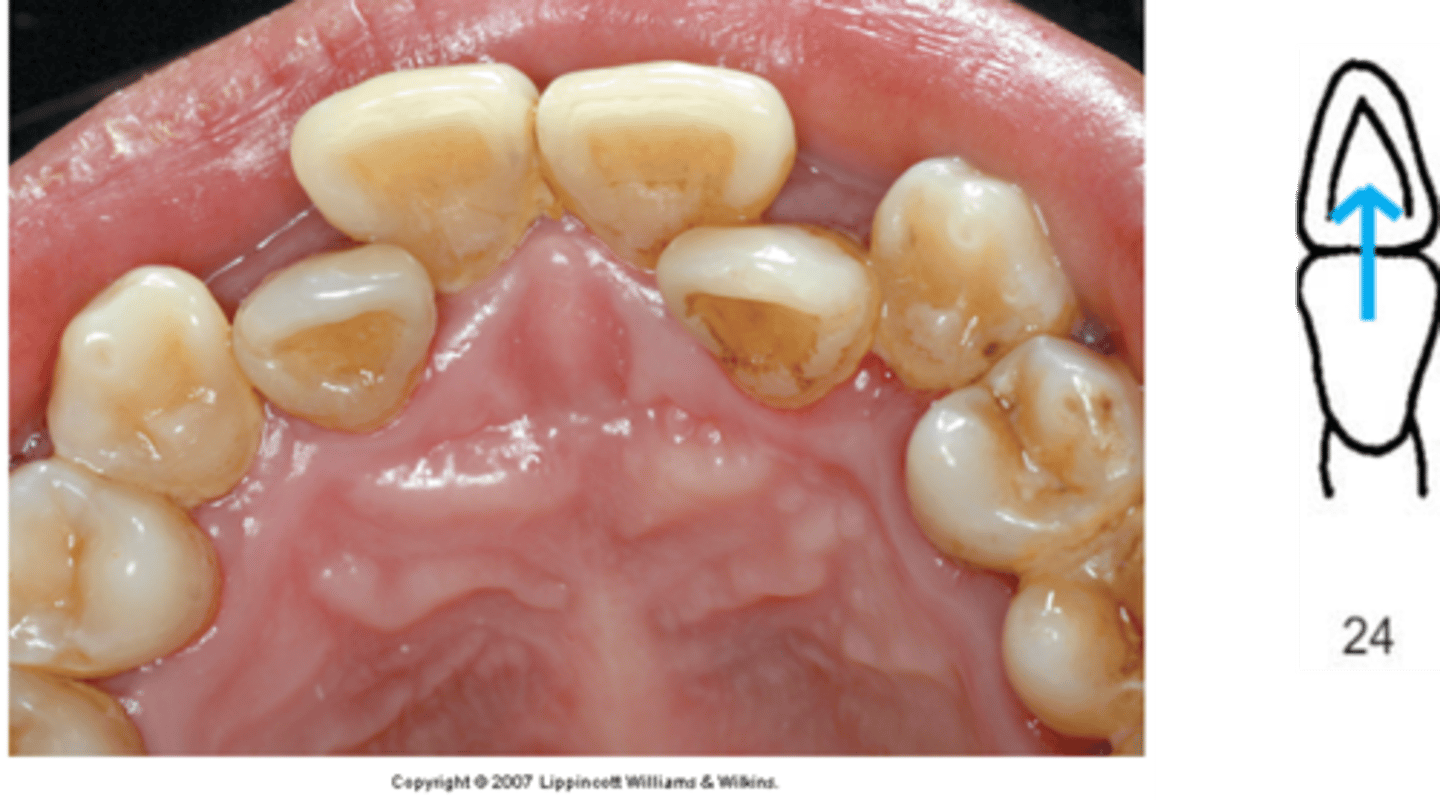
Supraversion
Elongated above the line of occlusion
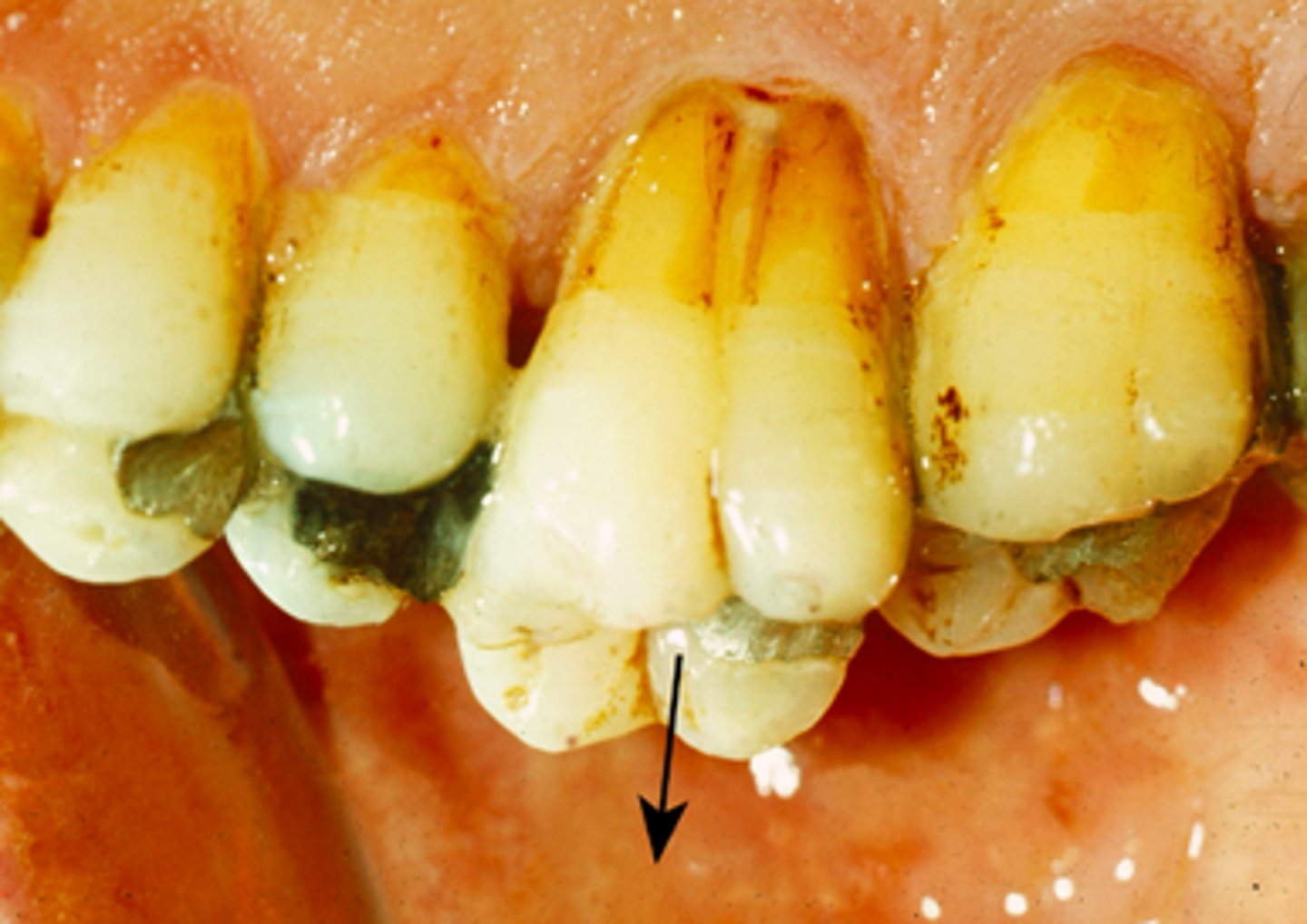
Torsiversion
Turned or rotated
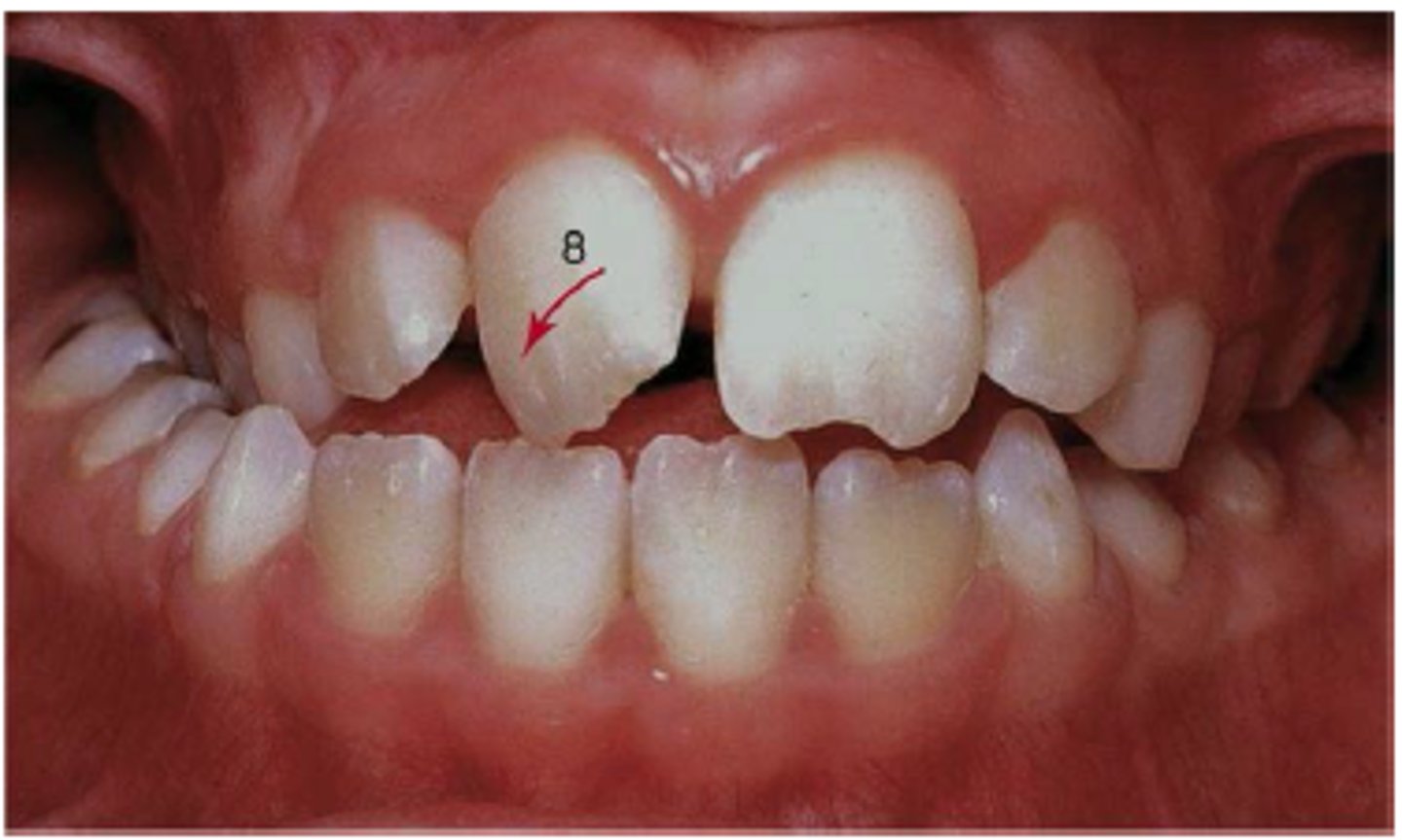
midline deviation
Interproximals of maxillary centrals do not line up with interproximals of mandibular incisors
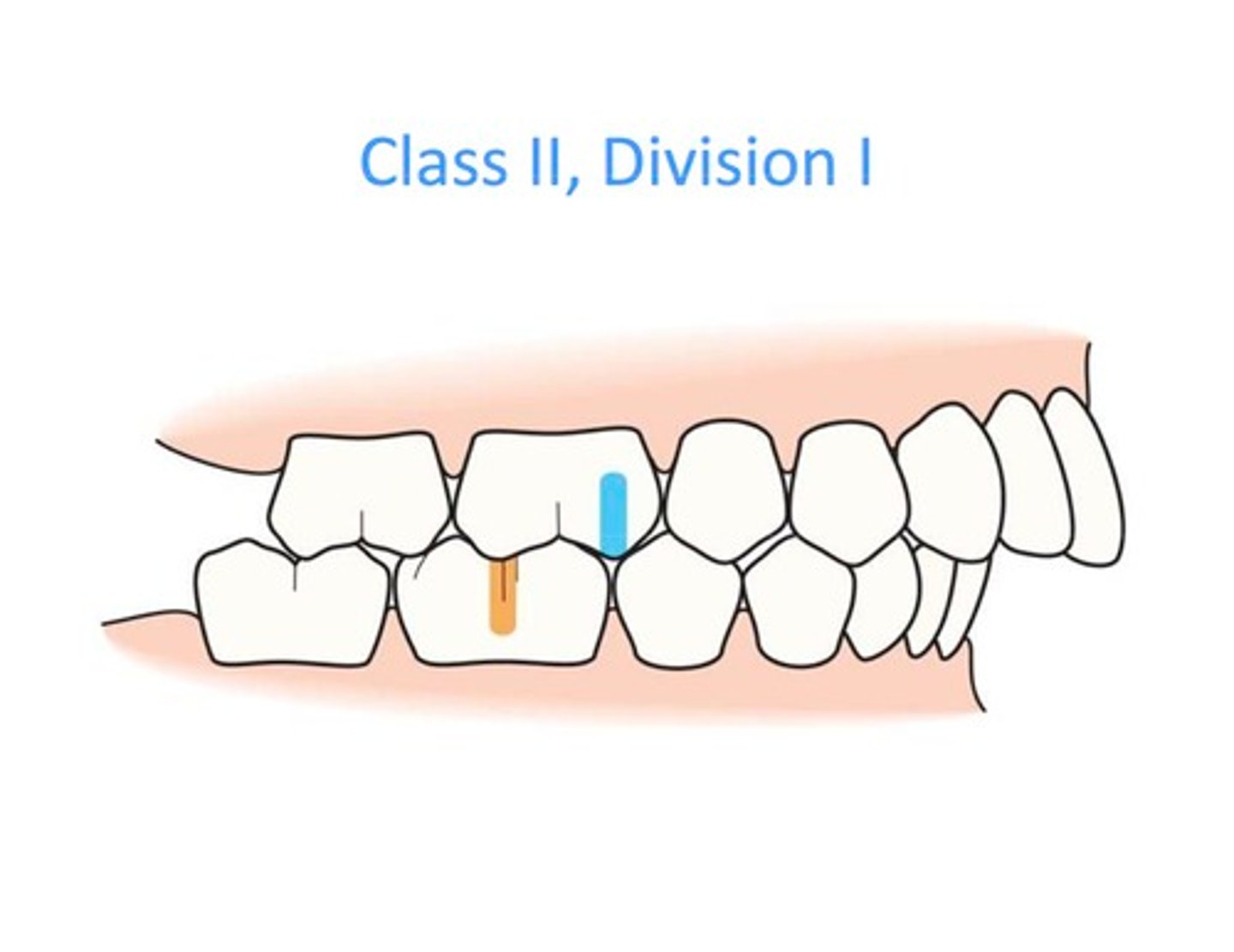
Class 2, Division 1
overbite, front teeth tilted
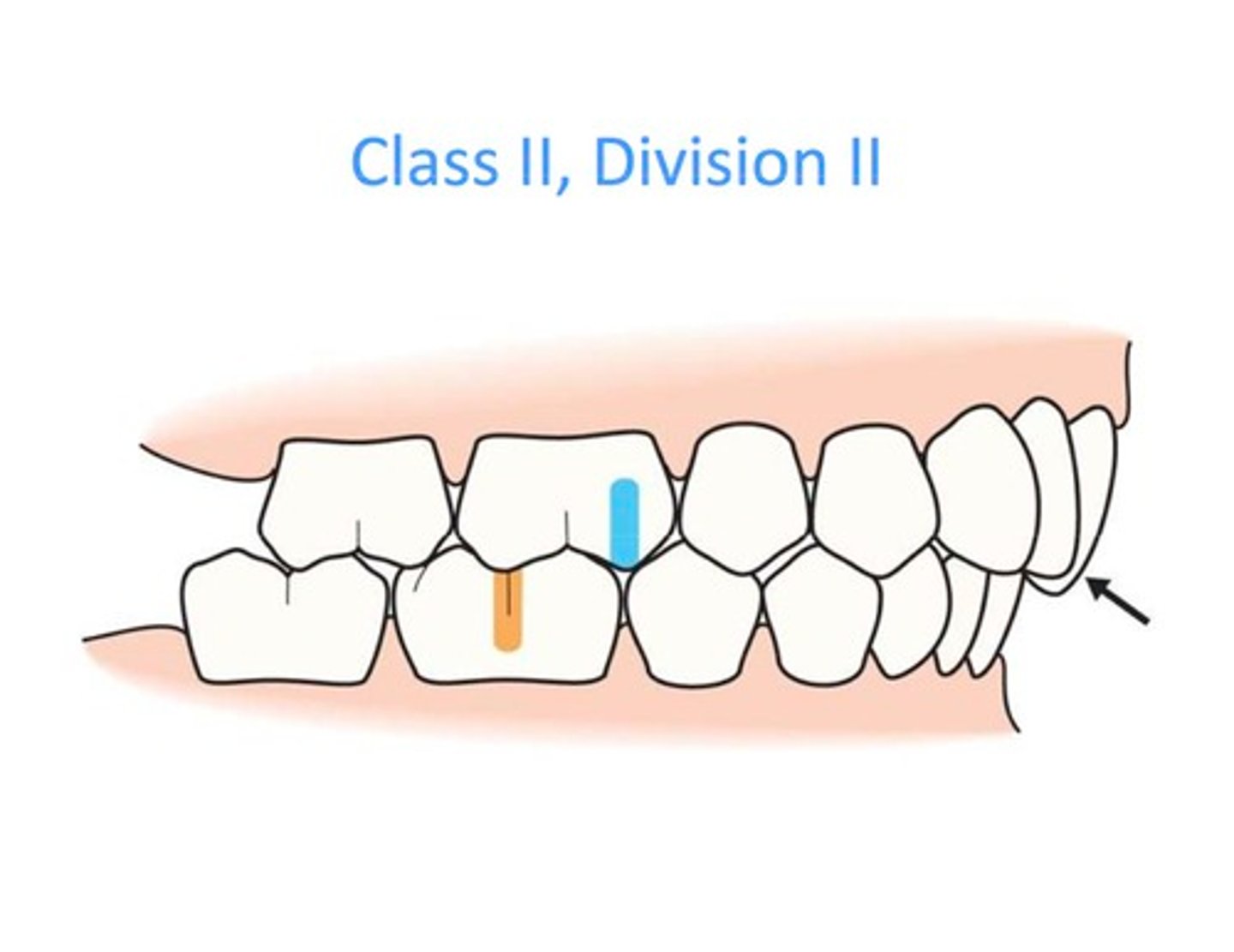
Class 2, Division 2
overbite
class 3 malocclusion
underbite
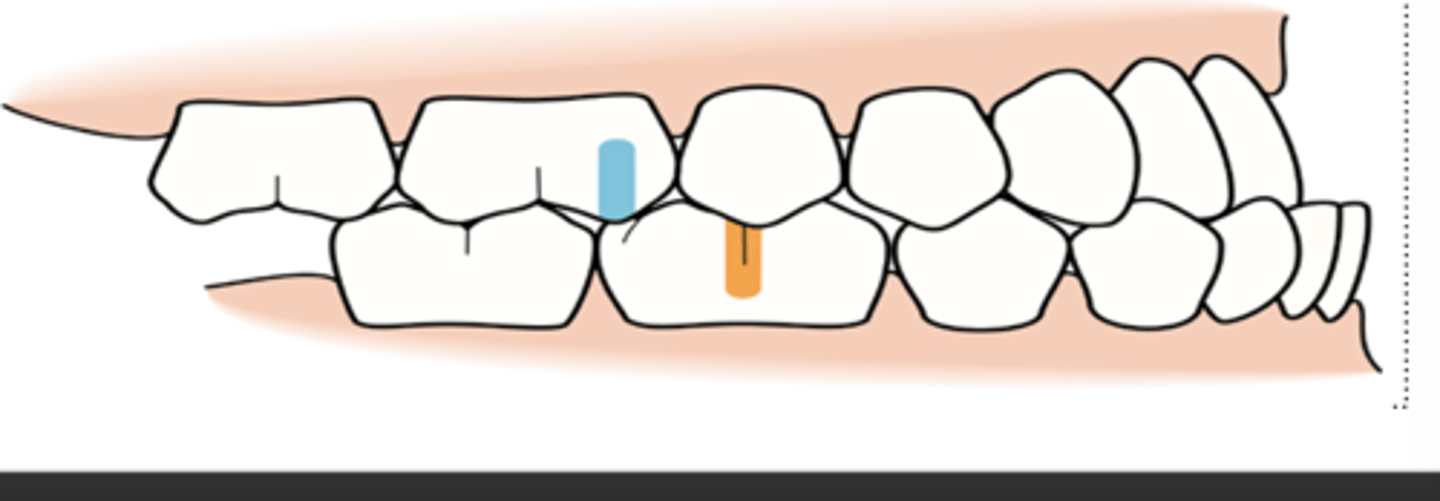
caries development
-Starts with acidogenic and aciduric bacteria in biofilm
-Biofilm acting to metabolize the fermentable carbohydrates ingested by the patient
-Acid formation demineralize the enamel, cementum and/or dentin and lead to cavity formation
-Continues process of demineralization and remineralization is happening throughout life of the tooth
Are caries an infectious transmissible disease?
YES
Remineralization
Occurs when the minerals are replaced in the tooth, calcium, phosphate, and flouride ions
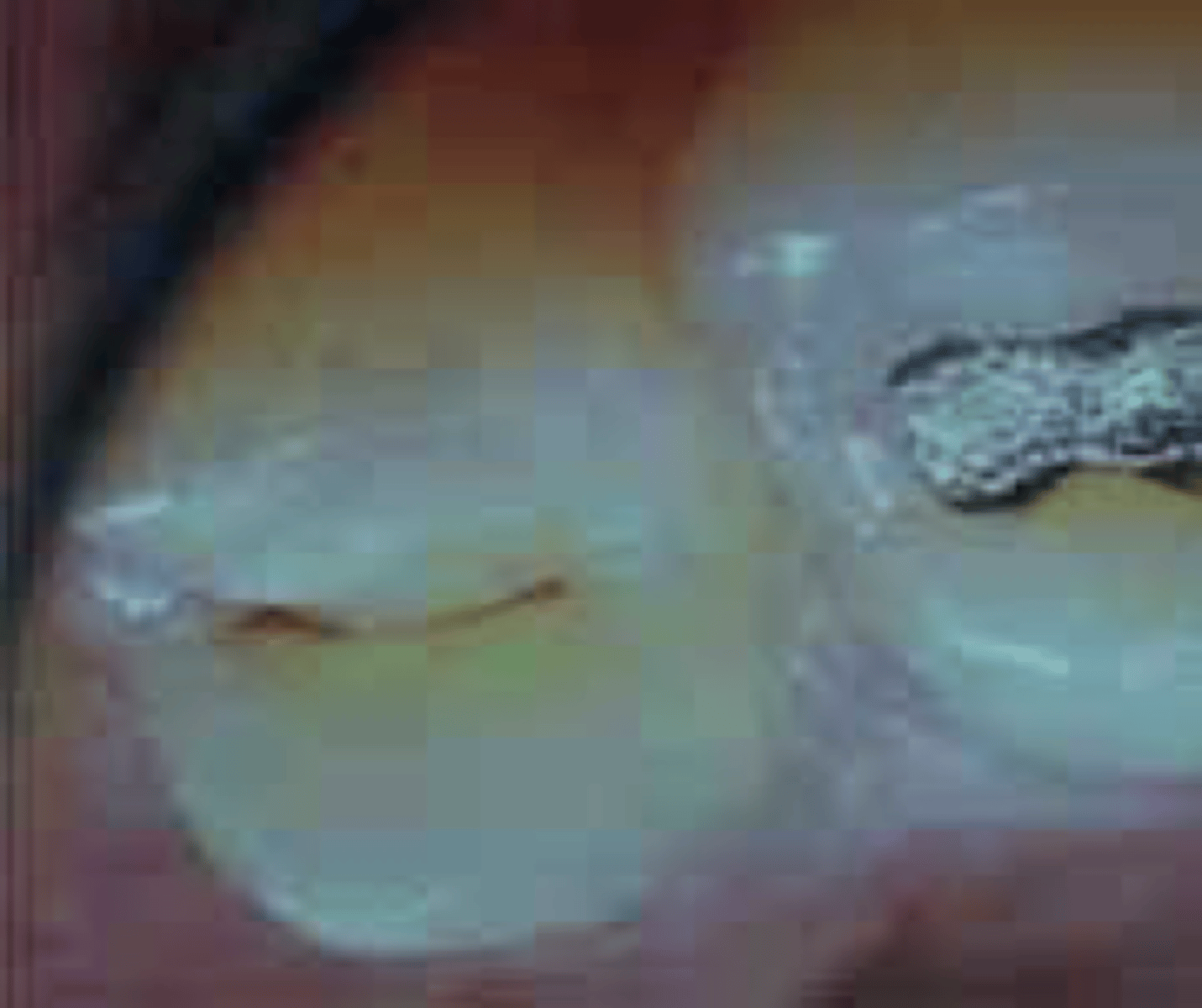
smooth surface caries
Begins in smooth surfaces where there are no pits, grooves, biofilm collects proximal surfaces, cerical 1/3, harder to clean areas
pit and fissure carries
Occurs in endings of grooves of teeth (buccal groove of mand. molars; occlusal pits molars/premolars)
Minute faults in enamel
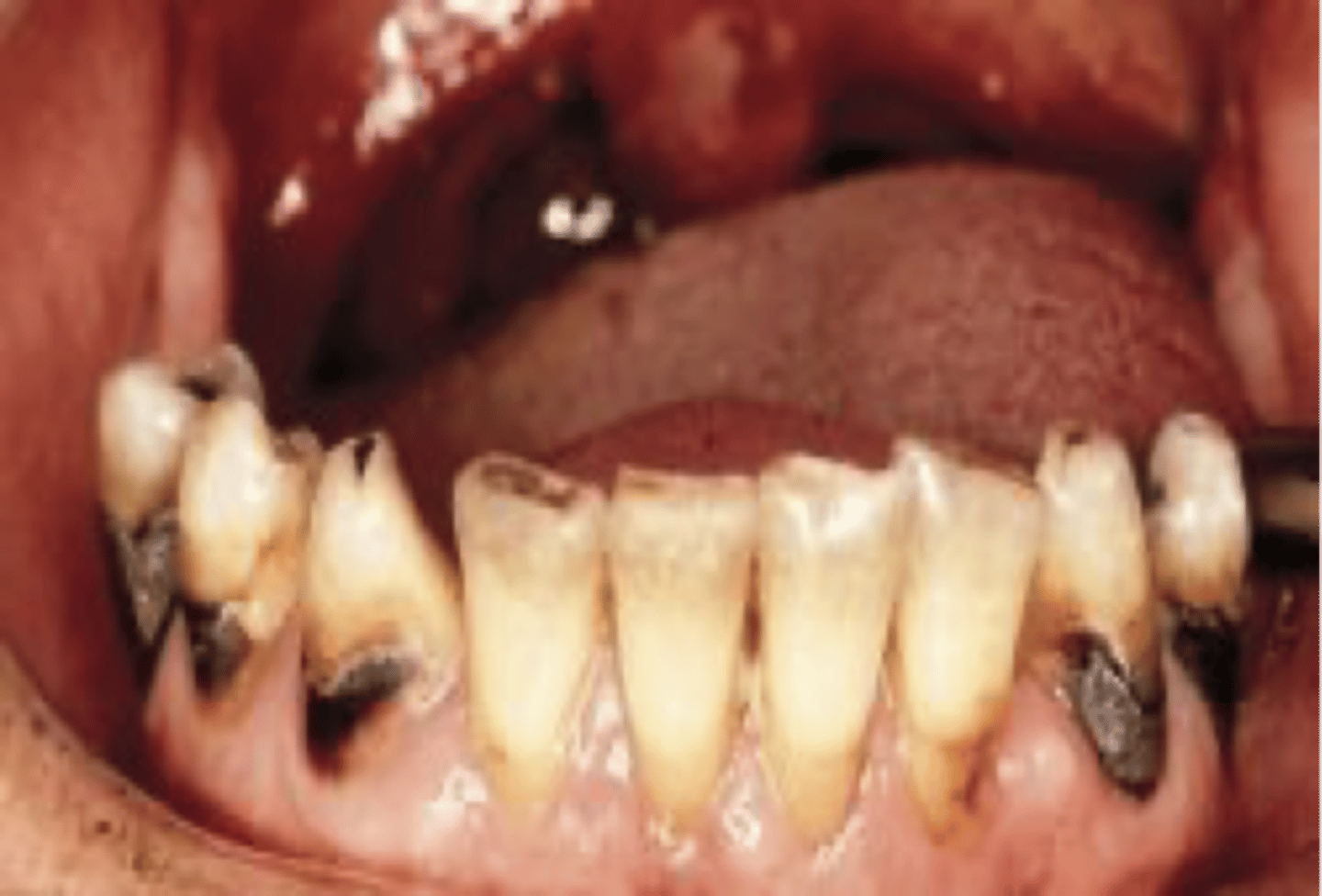
root caries
Soft progressive lesion of cementum and dentin
Gingival recession
Strength of CEJ
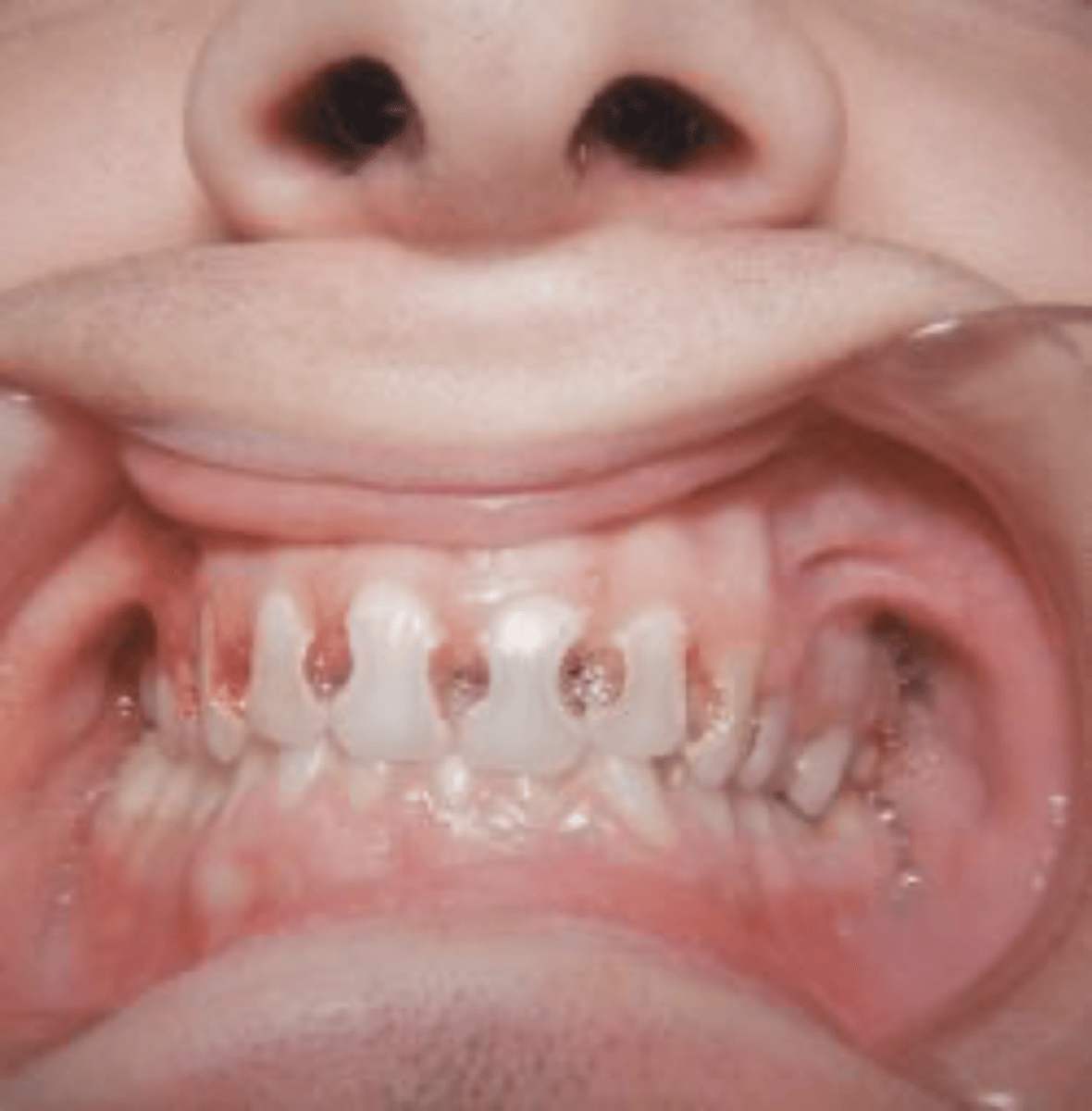
early child caries
Any dental caries in first 3 years
Nursing bottle syndrome
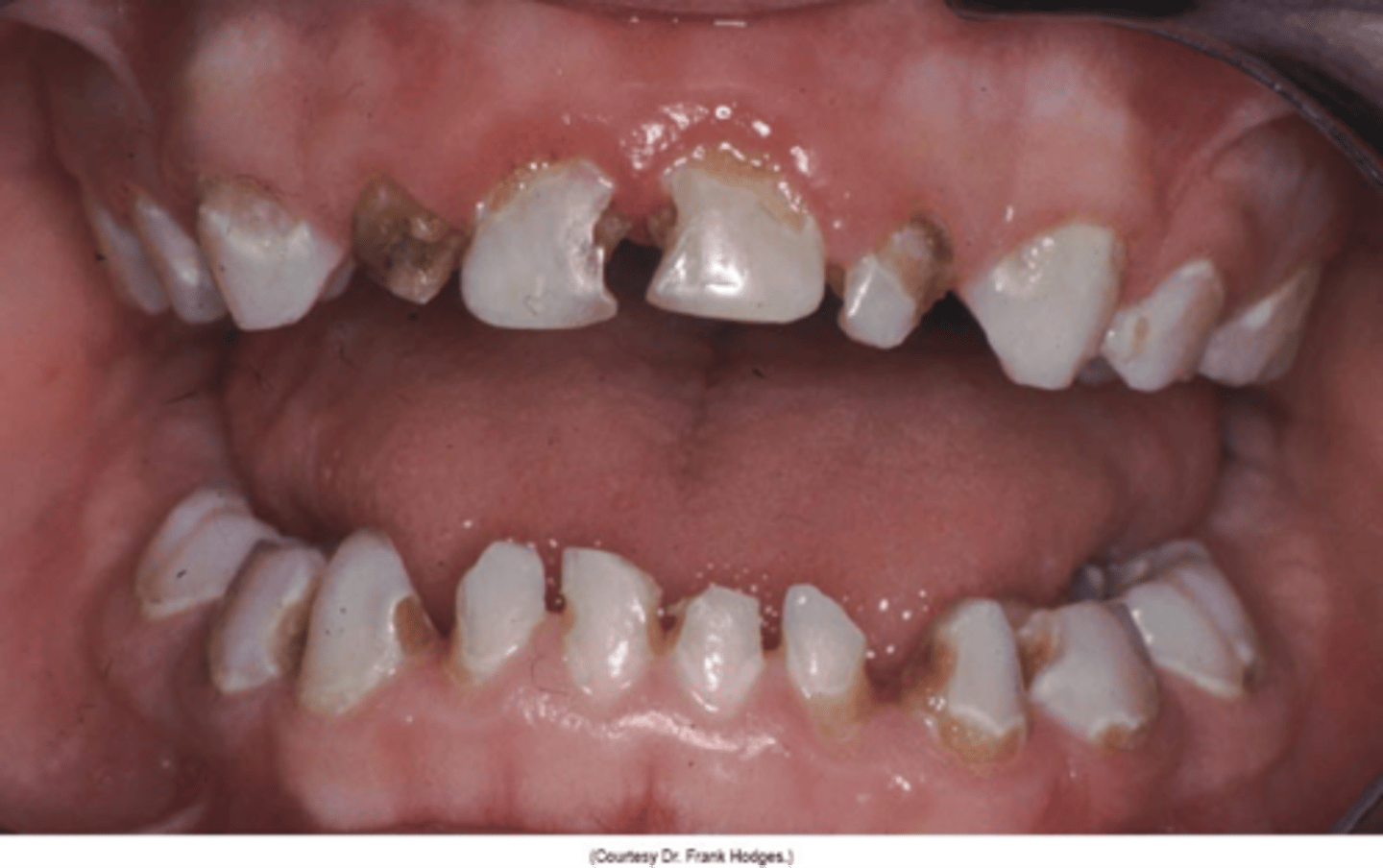
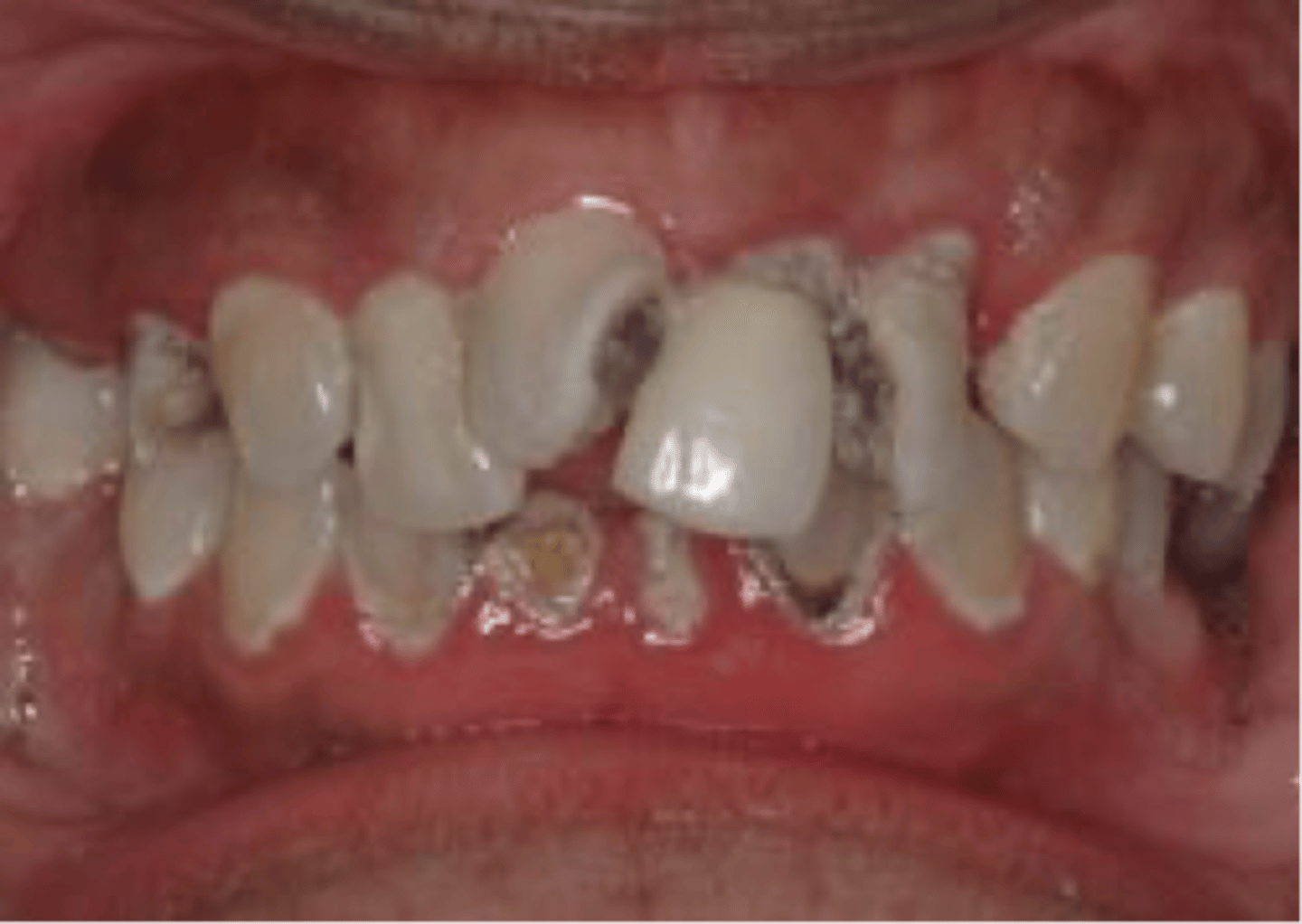
Rampant Caries
Rapidly progressive
Urgent intervention
CAMBRA
Caries Management by Risk Assessment
Caries risk factors
-Medium or high streptococci mutans and lactobacilli counts
-Visible heavy plaque biofilm on teeth
-Frequent snacking between meals
-Deep pits and fissures
Recreational drug use
-Inadequate salivary flow
-Saliva-reducing factors
-Exposed roots
Orthodontic appliances
Caries Protective Factors
-Lives, works, attends school in fluoridated community
-Uses fluoride toothpaste at least once daily
-Uses fluoride toothpaste at least two times/day
-Uses fluoride mouth rinse daily
-Uses 5000 ppm fluoride toothpaste daily
- Adequate salivary flow
normal PH range prior to eating
6.2 - 7.0
PH is caries susceptible patient is _____
Lower side (more acidic)
PH in caries resistant patient
Higher side (more basic)
Mutans Streptococci
-colonize the teeth and help form the biofilm because they create a sticky environment for survival multiplication
-most active during initial stages of demineralization/cavity formation
Lactobacilli
most active during the progression of the cavity
acidogenic and aciduric bacteria
produce acids as a result of metabolizing fermentable carbohydrate, increases risk for caries when present in the flora
critical PH for demineralization
4.5-5.5