Audio Production Ch 2
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The Science of Sound
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
sound, audio, hearing
in order to produce good quality audio, we have to understand:
sound
what is the term for: changes in air pressure cause by a vibrating object
all around; in a 3d globe shape and then bounces off flat surfaces
what direction does sound travel in
when an object making sound moves forward creating a higher air pressure
what is compression
when an object making sound moves backwards creating lower air pressure
what are rarefactions
transducer; ears, guitars, microphones
what is a device that converts one form of energy into another called; give examples
waveform
what is a graphic representation of changes in amplitude over time called
soundwaves are too complex and can’t be represented with a picture or graph
what is the difference between soundwaves and waveforms
amplitude
what is the term for how low the voltage levels of the audio signal are
distance above or below the centerline of the waveform
how is amplitude represented on a waveform graph
amount of pressure in a soundwave
what is amplitude in relation to sound
how fast pressure changes repeat in a soundwave or the number of cycles per second
what is frequency
as pitch
how is frequency perceived
Hertz (Hz) or Kilo-Hertz (KHz) when over 1,000
what is frequency measured in
20Hz to 20KHz
what frequencies can people with excellent hearing perceive
2 phases
what is one complete cycle when looking at frequency on a chart
in degrees like a circle; 360 is one complete cycle and 180 is only half of a cycle
how is frequency measured on a chart
how accurately a device will pass frequencies thorough itself; a graph
what is frequency response and what is it represented by
perfectly flat (doesn’t exist)
what does a perfectly accurate frequency response look like on a chart
how fast sound travels; 1,130ft per second/68F
what is velocity and what is sound’s velocity
the physical distance of one cycle of a wave; greek letter lambda (looks like an A with no line)
what is wavelength and what is it represented by
diving velocity of sound by the frequency
how do you calculate wavelength
the longer or more complex reflected paths of sound
what are late reflections in relation to reflection of sound
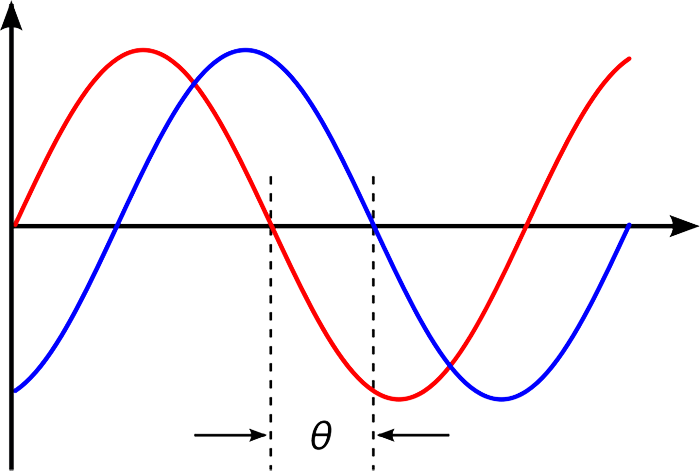
how much the elements of a wave align in time with another wave
what is phase
frequency and amplitude
what are the elements of a wave
the amount of time that one wave is ahead or behind another wave
what is phase shift
phase shift
what does the space between each wave represent
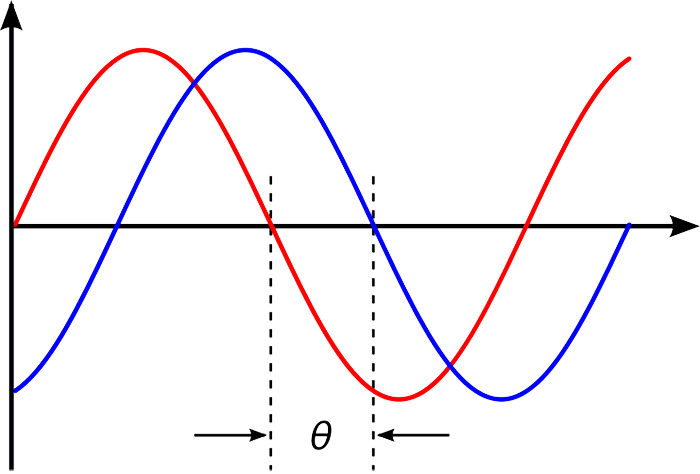
phase
what does how much the lines overlap at the same time represent
when two waves share the same features at the same time
what is in phase
the sound wave that occurs when two soundwaves are in phase and combined that is the same as the two waves but twice the amplitude
what is constructive interference
when the features of two waves are the same but the cycles occur 180 degrees different in time (opposite); phase reversal
what is out of phase and what is another name for it
phase consolation that results when two out of phase waves are combined and create a decrease in amplitude
what is destructive interference
an artificially created pure tone that consists of single frequency
what is a sine wave
natural sounds are complex waves while sine waves are only one frequency
what is the difference between natural sounds and sine waves
the presence of several different frequencies within a complex sound sound wave in addition to its fundamental frequency
what is harmonic content
the lowest frequency in a complex wave form; pitch note
what is the fundamental and what is it referred to in music
the frequencies higher than the fundamental in a complex sound
what are overtones
the harmonics and their relative levels produced by an instrument or sound source
what is timbre
by the frequency response of equipment; mic placement
how can tonal balance (timbre) be changed and what technique can you use to do so
the amplitude of the sound changes during the duration of any sound in nature
what is a sound envelope
attack, decay, sustain, release
what are the four stages of the sound envelope
the time it takes for a sound to reach its full amplitude when first sounded
what is attack
how fast the sound levels off to a sustain after the attack
what is decay
how long the sound continues after the decay
what is sustain
how long it takes to fade out at the end of the sound
what is release
dB; a unit of measurement of the amplitude of a sound wave or audio signal
what are decibels
SPL; the amount of pressure in a given area that is caused by sound
what is sound pressure level
dB SPL
what is the unit of measurement for amplitude of sound waves
the wattage or power of an audio signal
what does dBm refer to
changes the wattage or amount of power
what does moving a fader on a mixer do
volatge or pressure behind the flow
what does dBv refer to
a volume unit meter that measures the level of an audio signal
what is a VU meter
digital
what is a VU meter not commonly used for
peak program meter; purely electronic/software device that measures audio signal levels and used instead of VU meter for digital
what is PPM
the ear closest to the sound source will receive the loudest sound
what is interaural intensity differences
sound arrives at each ear at different times; the one closest hears it first
what is interaural time differences
ridges on our outer ear that create very small time differences by reflecting sound into the ear canal off these ridges; determine which direction sound is coming from
what is the effects of the pinna and what does it help us do
direct sound, early reflections, and reverberations
what 3 cues tell us how large a room is and how far away the sound is coming from
sound that travels the shortest path and reaches ear first
what is direct sound
sounds that bounce off surfaces and arrive at our ears first
what are early reflections
sound reflections that arrive at the ear more than 50 ms after the direct reflections as a continuous melded sound, even though it is many different reflections
what is reverberation