COMPANA LE2: Axial Skeletal System
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/216
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:33 PM on 3/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
217 Terms
1
New cards
Skeleton
Composed of rigid parts that are attached to muscles
2
New cards
Locomotion
Skeleton is powered by contractions of the muscles
3
New cards
Basic functions of the skeleton
Provision of body shape
Weight support
Facilitation of motility
Protection of soft parts (nerves, major blood vessels, viscera)
Weight support
Facilitation of motility
Protection of soft parts (nerves, major blood vessels, viscera)
4
New cards
Skeleton compoition
Mineralized connective tissue: bone, cartilage, dentin, enamel
5
New cards
Exoskeleton and Endoskeleton
Two kinds of skeleton
6
New cards
Exoskeleton
Within the integument
7
New cards
Endoskeleton
Deep, within the body
8
New cards
Keratinized exoskeleton
From the epidermis
9
New cards
Bony exoskeleton
From the dermis
10
New cards
Bony endoskeleton, cartilaginous exoskeleton, and notochord
Types of endoskeleton
11
New cards
Matrix
Protein fibers and groundsubstance
12
New cards
General connective tissues
Loose and Fibrous
13
New cards
Loose connective tissues
Mesenchyma, adipose, areolar
14
New cards
Fibrous
Dense connective tissue
15
New cards
Special connective tissues
Cartilage, bone, haemopoietic tissue, and blood
16
New cards
Cartilage
Composed of chondroitin sulfate + collagenous or elastic proteins
17
New cards
Cartilage
Hyaline, Elastic, and Fibrous
18
New cards
Hyaline cartilage
Glassy. Persists at the articular ends of long bones, at the tips of ribs, in tracheal rings, and in many parts of the skull. Collagen fibrils = not sufficient in abundance.
19
New cards
Elastic cartilage
Flexible and springy. Internal support for your ear and epiglottis.
20
New cards
Myeloid haemopoietic tissue
Inside cavities
21
New cards
Lymphoid haemopoietic tissue
In spleen, lymph nodes
22
New cards
23
New cards
24
New cards
25
New cards
Bone matrix
collagen fibers + hydroxyapatite crystals + cementing substance
26
New cards
Hydroxyapatite
3Ca3(PO4)2 Ca(OH)2
27
New cards
Water and mucopolysaccharides
Cementing substance of bone matrix
28
New cards
Osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts
Bone cells
29
New cards
Osteoblasts
Bone forming cells
30
New cards
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells
31
New cards
Osteoclasts
Resorb or break down bown
32
New cards
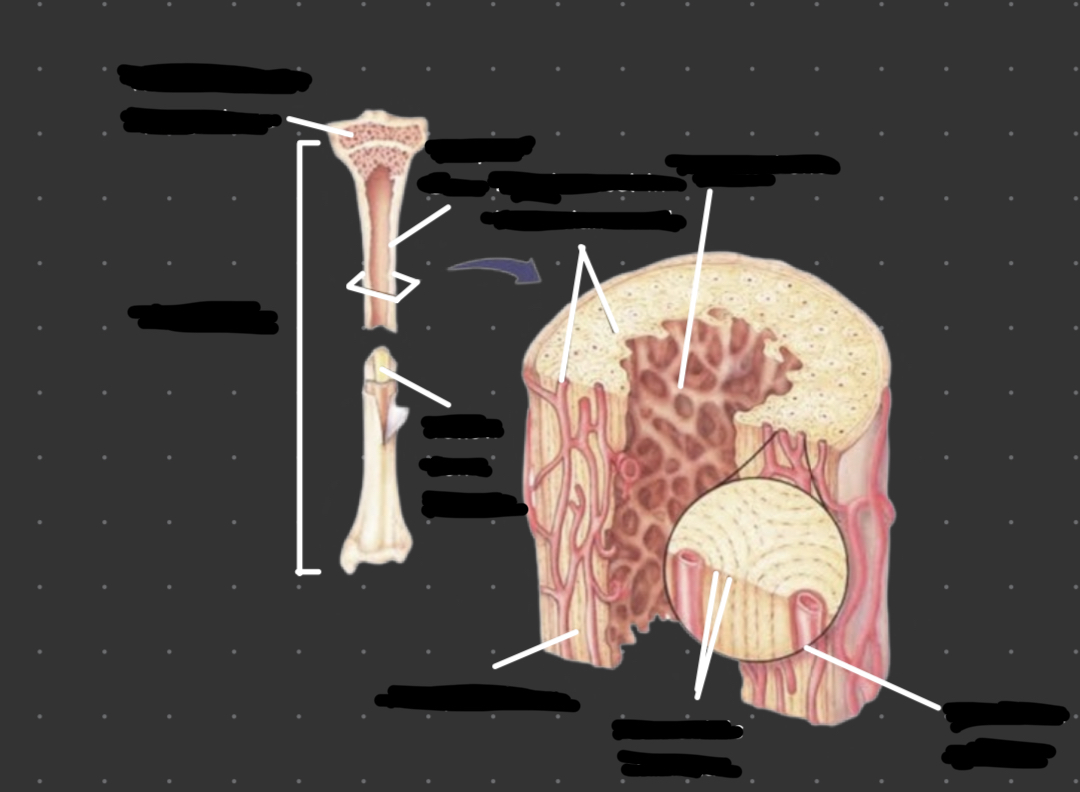
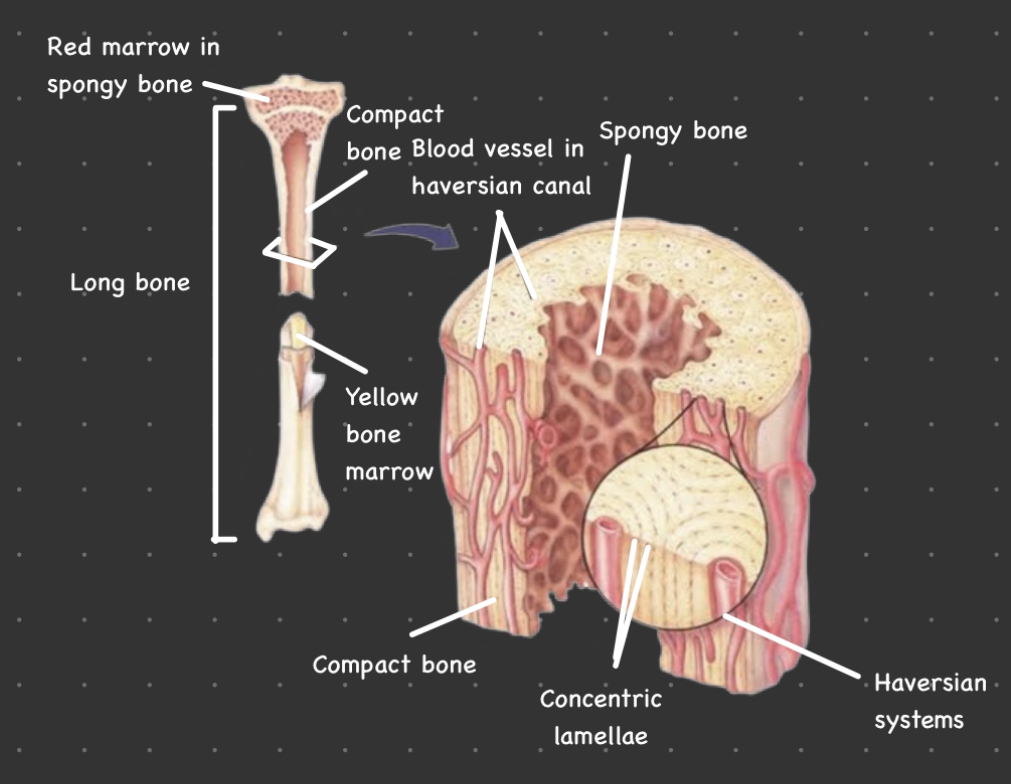
33
New cards
Calcitonin and parathyroid
Hormones in regulating bone function
34
New cards
Bone cancer
Most painful form of cancer due to pain receptors
35
New cards
Mineralization
general process wherein various inorganic ions are deposited in the organic matrix of tissues to harden them
36
New cards
Calcification
specialized type of mineralization wherein calcium carbonate (invertebrates) or calcium phosphate (vertebrates) is deposited in the organic matrix
37
New cards
Ossification
specialized type of calcification, unique to vertebrates, involving the deposition of hydroxypatite (calcium phosphate) in the organic matrix
38
New cards
Hyaline cartilage
LOCATIONS: Between tips of ribs an bones of sternum; covering bone surfaces at synovial joints; supporting larynch (voice box), trachea, and bronchi; forming part of nasal septum.
39
New cards
Hyaline cartilage
FUNCTIONS: Provides stiff but somewhat flexible support; reduces friction between bone surfaces
40
New cards
Hyaline cartilage
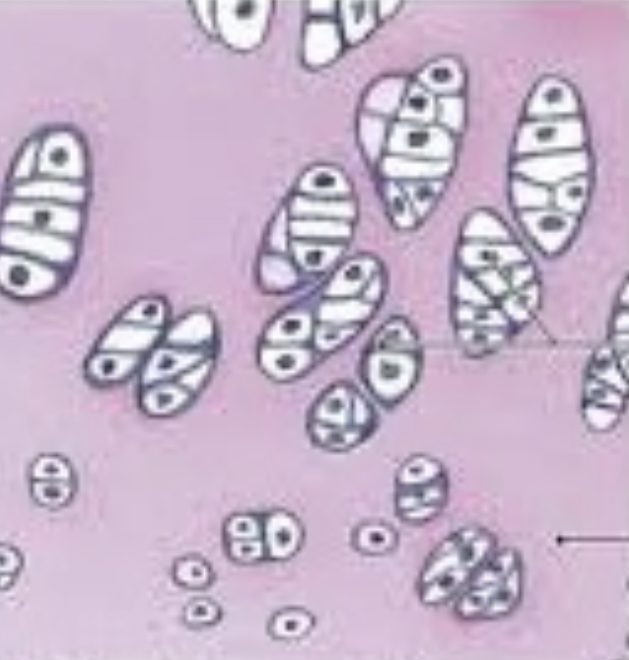
41
New cards
Elastic cartilage
LOCATIONS: Auricle of external ear; epiglottis; auditory tube; cuneiform cartilages of larynx
42
New cards
Elastic cartilage
FUNCTIONS: Provides support, but tolerates distortion without damage and returns to original shape
43
New cards
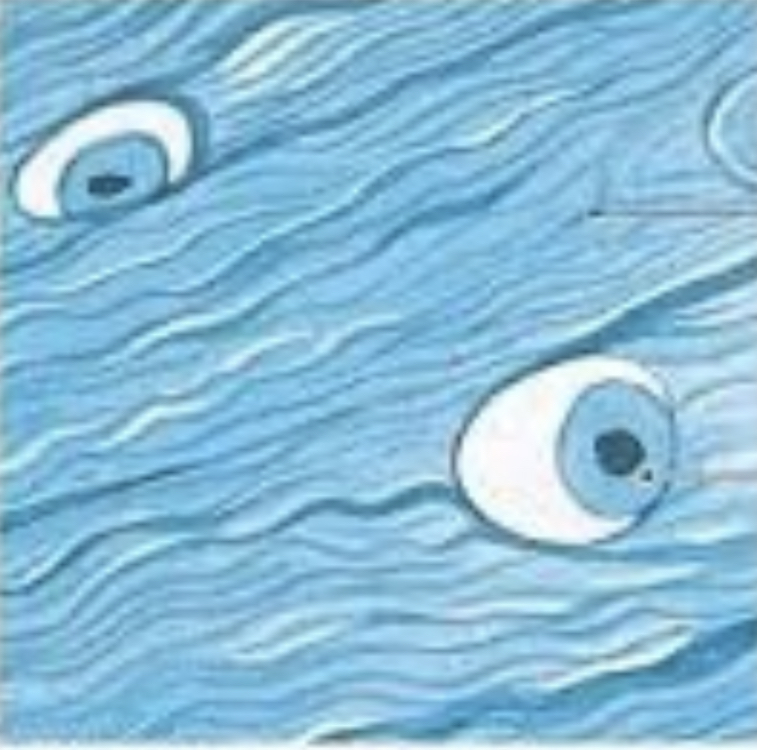
Elastic cartilage
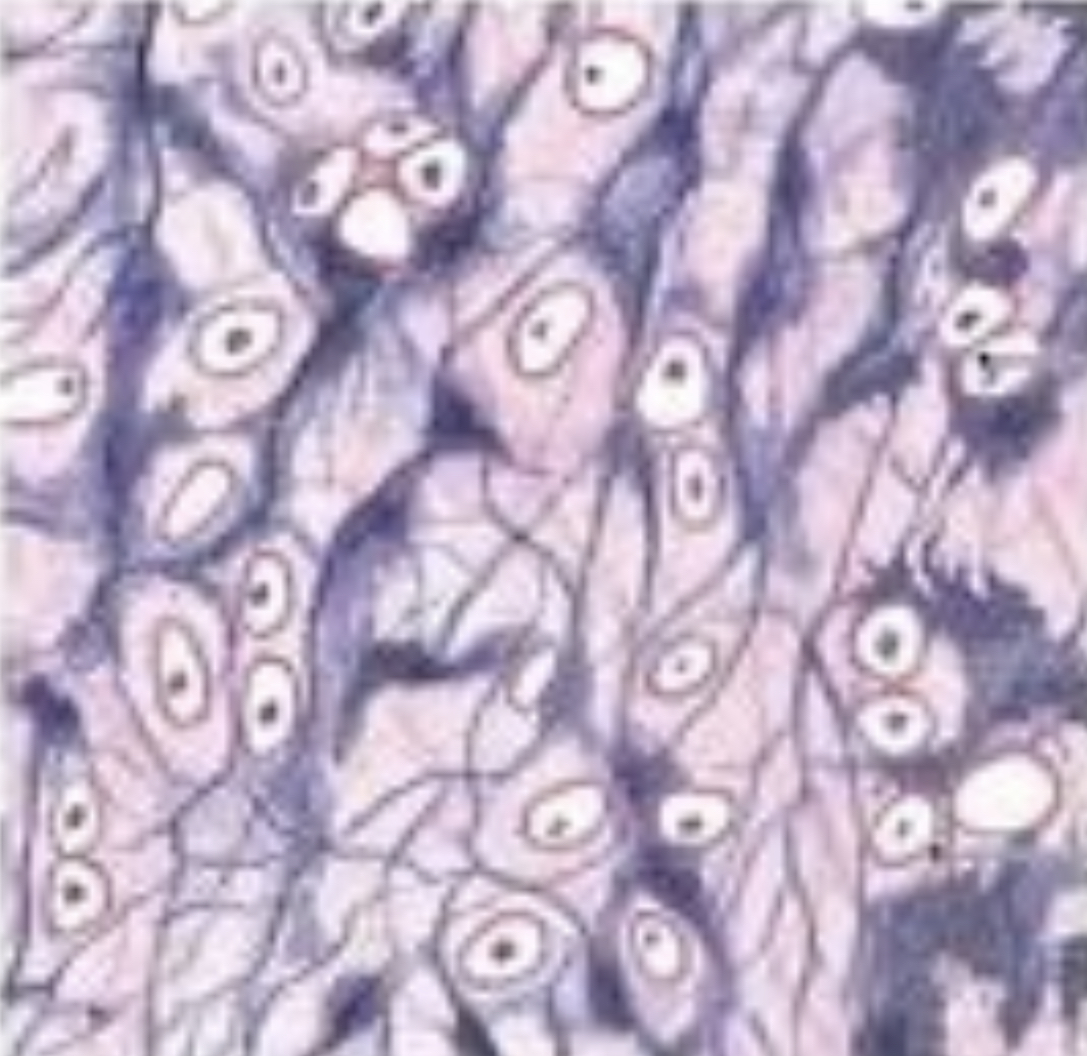
44
New cards
Fibrous cartilage
LOCATIONS: Pads within knee joint; between pubic bones of pelvis; intervertebral discs
45
New cards
Fibrous cartilage
FUNCTIONS: Resists compression; prevents bone-to-bone contact; limits relative movement
46
New cards
Fibrous cartilage

47
New cards
Cartilage matrix
collagen fibers + sulfated mucopolysaccharide (e.g. chondroitin sulfate)
48
New cards
Chondroblasts and chondrocytes
Cartilage cells
49
New cards
Cartilage
Avascular: diffusion-mediated gas and nutrient exchange
50
New cards
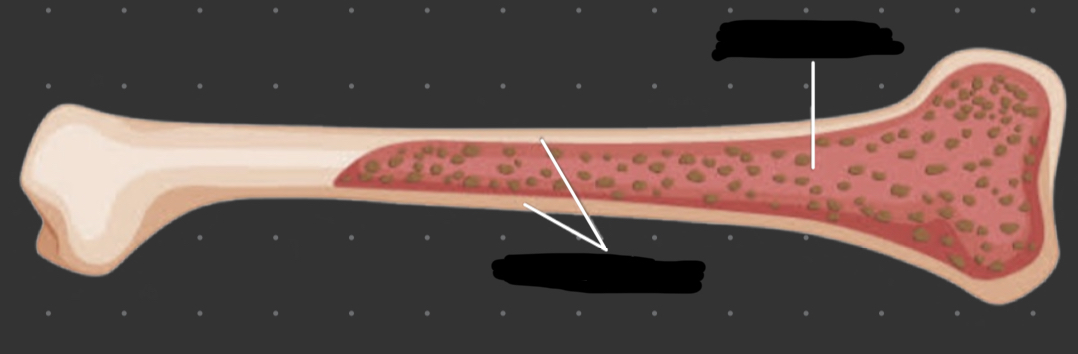
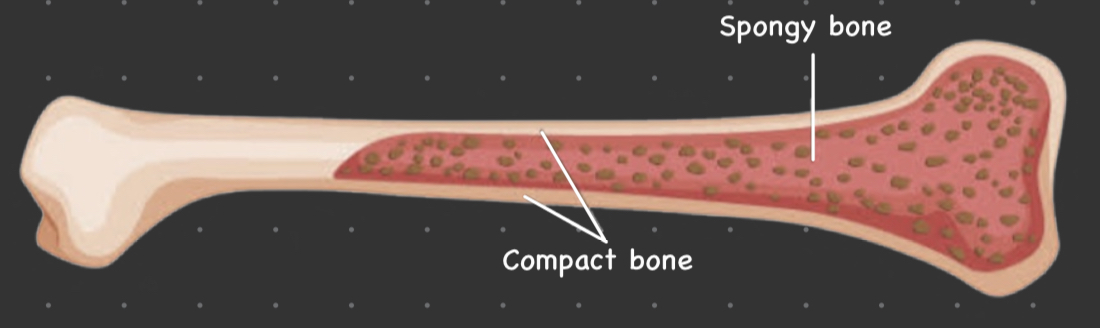
Spongy bone
* also called cancellous or trabecular bone
* have branching structures called trabecular
* contain red bone marrow
* have branching structures called trabecular
* contain red bone marrow
51
New cards
Compact bone
* also called cortical bone
* made up of osteons and have occentric layers
* contain yellow bone marrow
* made up of osteons and have occentric layers
* contain yellow bone marrow
52
New cards
53
New cards
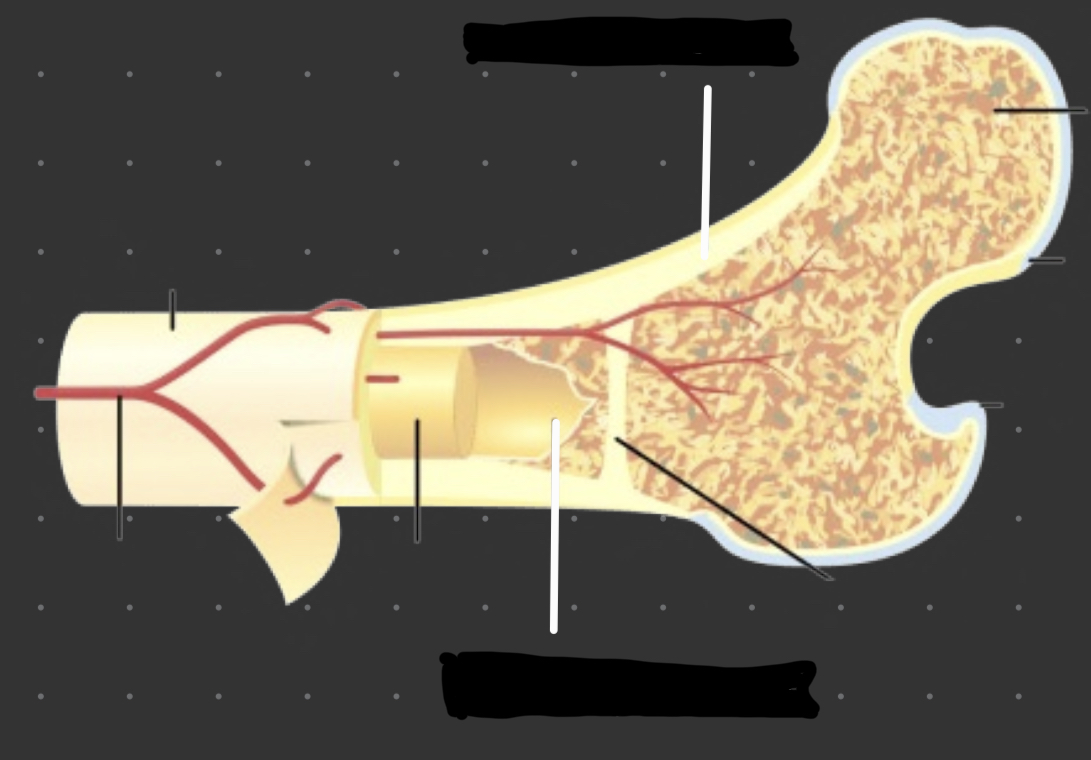
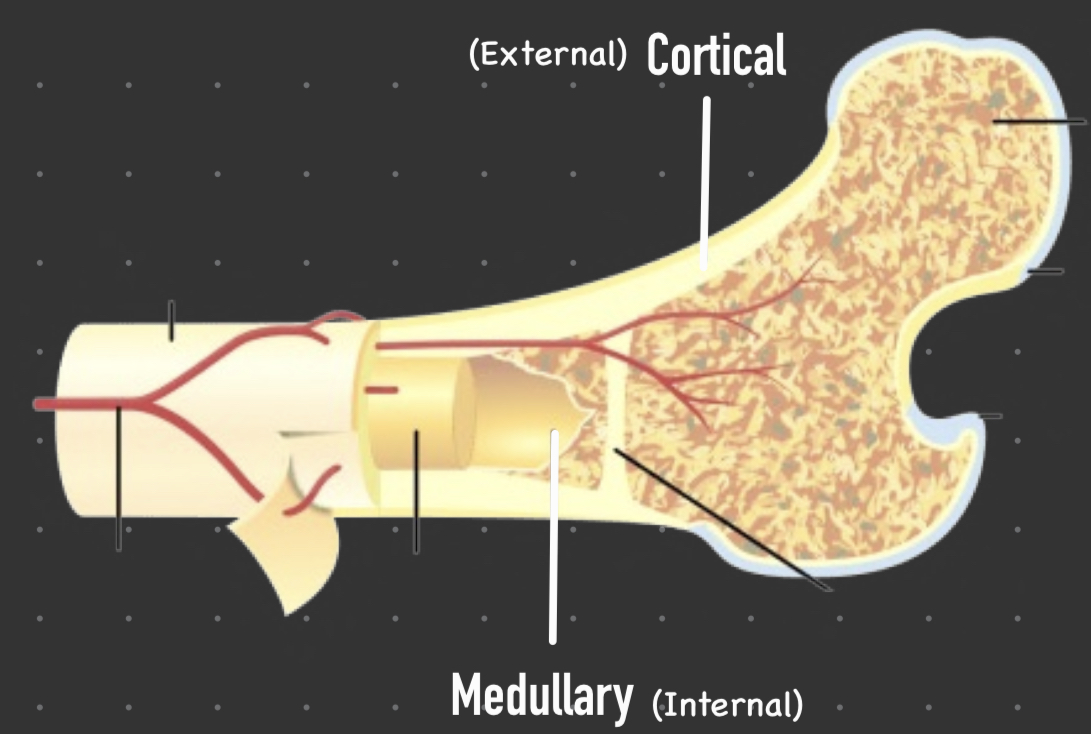
Cortical bone
Outer boundary or cortex of a bone
54
New cards
Medullary bone
Lines the core of the bone
55
New cards
Cellular bone
characterized by a matrix that has enclosed osteoblasts or osteocytes
56
New cards
Acellular bone
characterized by a relatively featureless matrix that lacks these bone-forming cells.
57
New cards
58
New cards
Vascular bones
Contains blood vessels
59
New cards
Avascular bones
Does no contain blood vessels
60
New cards
61
New cards
Non-lamellar bone
* fibrolamellar bone; woven bone
* Characterized by the disorderly, irregular arrangement of collagen within the matrix
* Typical of fast-growing bone
* Characterized by the disorderly, irregular arrangement of collagen within the matrix
* Typical of fast-growing bone
62
New cards
Lamellar bone
* mature bone
* characterized by the orderly, regular arrangement of collagenous fibers within the matrix, usually accompanied by the regular orientation of bone cells
* Typical of slow-growing bone
* characterized by the orderly, regular arrangement of collagenous fibers within the matrix, usually accompanied by the regular orientation of bone cells
* Typical of slow-growing bone
63
New cards
64
New cards
65
New cards
Cellular bone
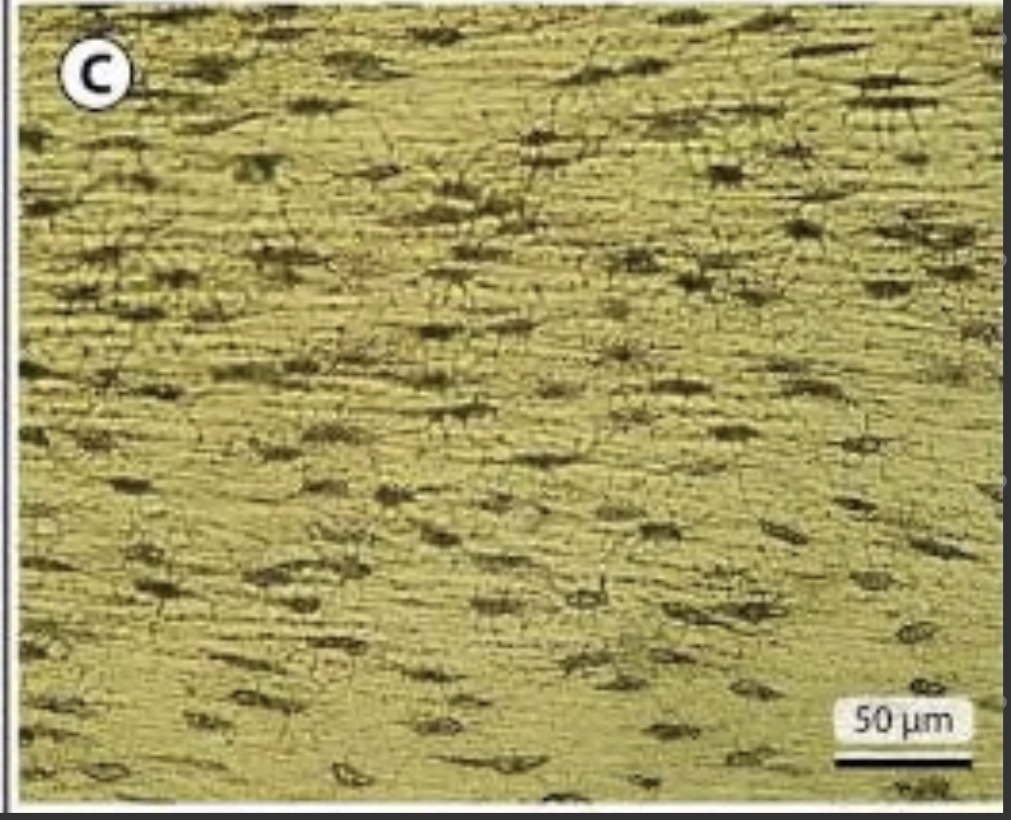

66
New cards
Acellular bone
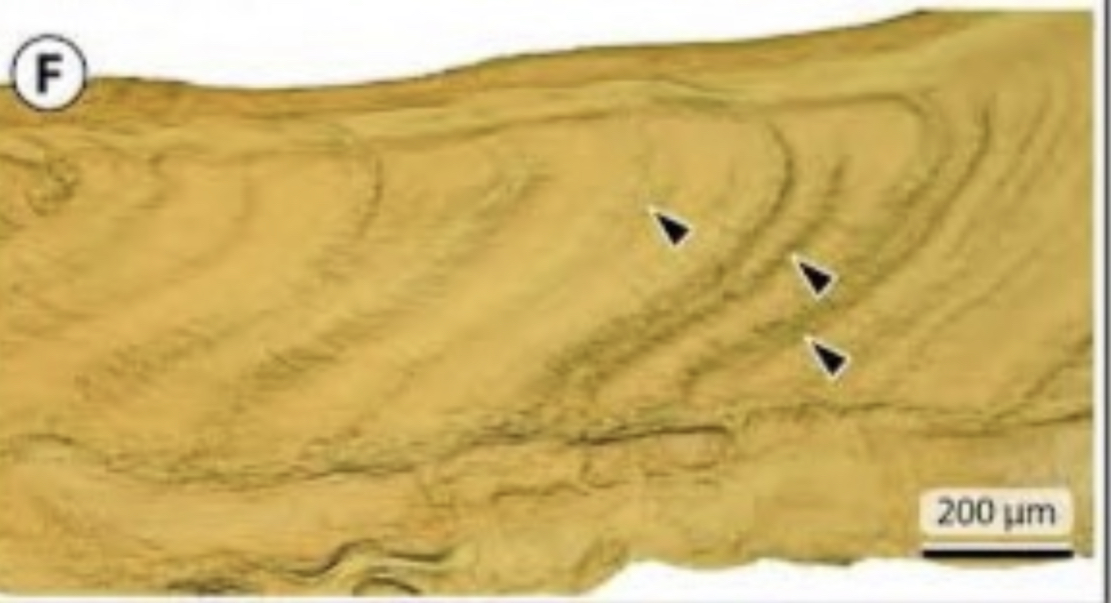

67
New cards
Vascular bone
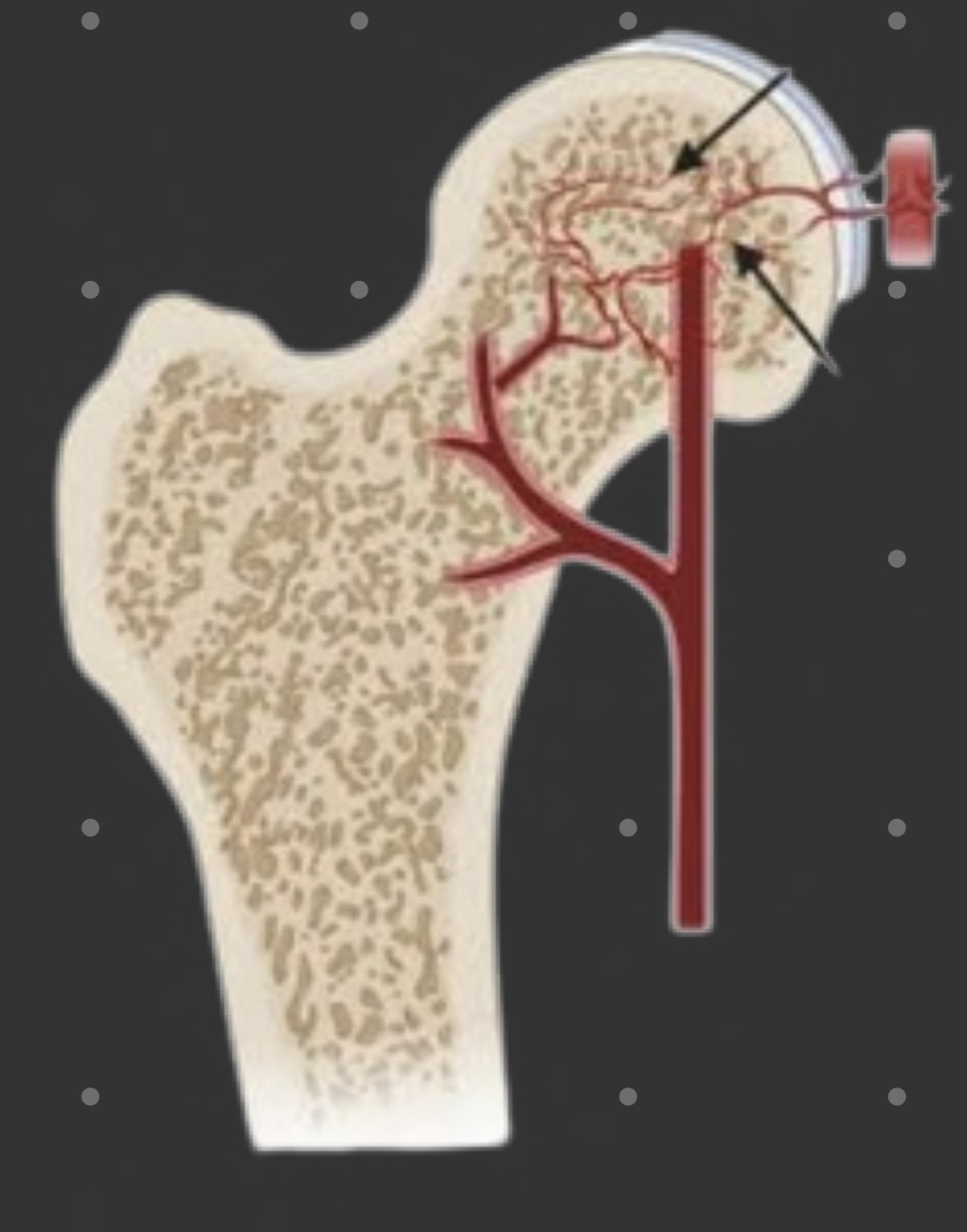
68
New cards
Avascular bone
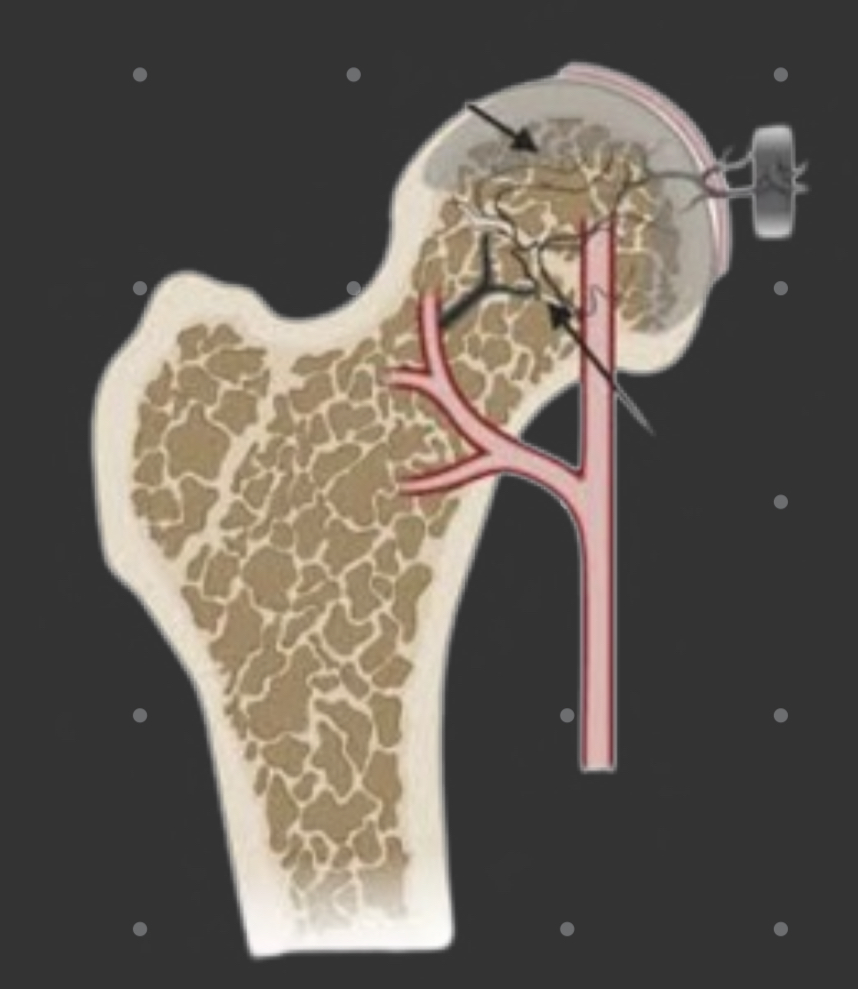
69
New cards
Non-lamellar bone
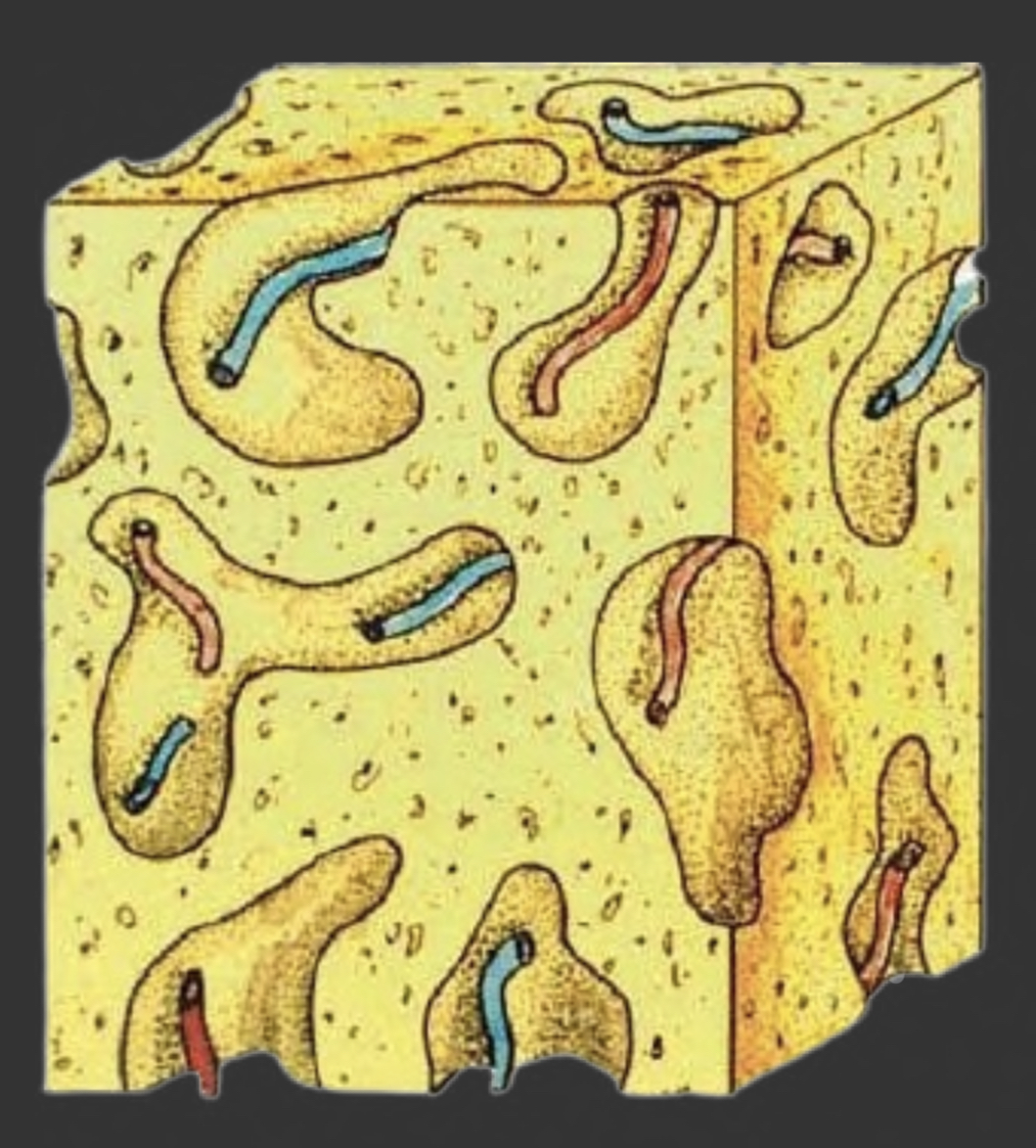
70
New cards
Lamellar bone
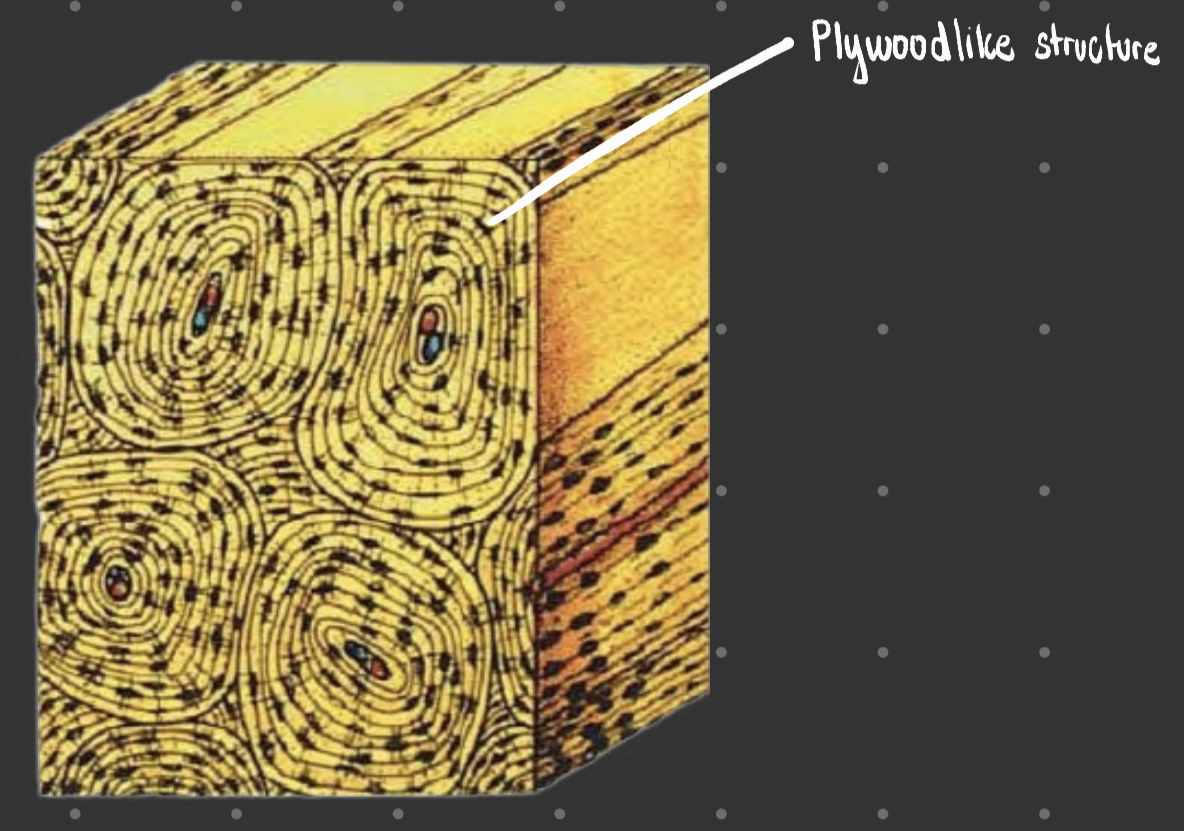
71
New cards
Endochondral bone
* process of bone development from hyaline cartilage
* forms most of skeleton
* forms most of skeleton
72
New cards
Diaphysis
Region of bone; Middle shaft
73
New cards
Epiphysis
Region of bone; Both ends
74
New cards
Metaphysis or epiphyseal plate
Region of bone; region between two ends
75
New cards
Spikelike trabeculae
transitional composites of new bone and resorbing calcified cartilage
76
New cards
Trabeculae
Bone spicules
77
New cards
Dermal bones
* form directly through ossification of mesenchyme
* lies within the dermis of the skin
* ex: skull, pectoral girdle, and integument
* lies within the dermis of the skin
* ex: skull, pectoral girdle, and integument
78
New cards
Sesamoid bone
* form within tendons
* derived from connective tissues
* ex: patella of the knee and the pisiform bone of the wrist
* derived from connective tissues
* ex: patella of the knee and the pisiform bone of the wrist
79
New cards
Perichondral and periosteal bone
* formed from the deep cell layer of the fibrous connective tissue covering cartilage (perochondrium) or bone (peristoneum)
* develops early and retains the ability to form bone directly in adult
* develops early and retains the ability to form bone directly in adult
80
New cards
Surface bone formation
Appositional growth
81
New cards
Compact bone
* lamellar, with concentrically arranged, mineralized bundles of collagen around a central canal
* Osteon (haversian system): unit of compact bones
* superficailly lined with periosteum
* Osteon (haversian system): unit of compact bones
* superficailly lined with periosteum
82
New cards
Spongy bone
* characterized by trabecular organization
* trabecula: assemblage of beams, bars, and rods with cavities in between
* trabecular cavities: lined with endosteum and contain marrow
* trabecula: assemblage of beams, bars, and rods with cavities in between
* trabecular cavities: lined with endosteum and contain marrow
83
New cards
Dentine
* odontoblasts not trapped within lacunae during osteogenesis
* with dentinal tubules resulting from protoplasmic processes left in canaliculi
* with dentinal tubules resulting from protoplasmic processes left in canaliculi
84
New cards
Enamel
* cells: Ameioblasts
* superficially located
* more superficially than dentine
* superficially located
* more superficially than dentine
85
New cards
Acellular bone (aspidin)
* osteoblasts retreat and do not leave processes or canaliculi behind
* modern bony fishes scales
* cementum of vertebrate touch
* modern bony fishes scales
* cementum of vertebrate touch
86
New cards
Joint (Arthrosis)
junction between two bones or cartilages
87
New cards
Diarthrosis
freely movable in at least one plane
88
New cards
Amphiarthrosis
Limited movement
89
New cards
Synarthrosis
Sutured, immovable
90
New cards
Symphysis
Midline joint, very limited movement
91
New cards
Diarthrosis
defined by a synovial (or joint) capsule whose walls consist of dense fibrous connective tissue lined by a synovial membrane, which secretes a lubricating synovial fluid into the confined space; the ends of contacting bones are capped with articular cartilage.
92
New cards
Synarthrosis
lack synovial structures (capsule, membrane, fluid) and, in this, are structurally distinguished from diarthroses.
93
New cards
Synostosis
Bone connection; represents the fusion of formerly separate bones, the firm union is regarded as ankylosed.
94
New cards
Synchodrosis
Cartilage; formed at the midline, are termed symphyses
95
New cards
Syndesmosis
* fibrous connective tissue
* sutures
* sutures
96
New cards
Membrane bone
* Bone deposited directly within a membranous blastema without having been preceded by a cartilaginous model
* May be compact or spongy, and lamellar or non-lamellar.
* Lacks haversian canal
* E.g. Periosteal bone
* May be compact or spongy, and lamellar or non-lamellar.
* Lacks haversian canal
* E.g. Periosteal bone
97
New cards
Replacement bone
* Deposited where hyaline cartilage already exists
* Undergoes degenerative changes and disappears
* Eroded and replaced by compact bone, spongy bone, or a marrow cavity, depending on its location
* Undergoes degenerative changes and disappears
* Eroded and replaced by compact bone, spongy bone, or a marrow cavity, depending on its location
98
New cards
Skeletal remodeling
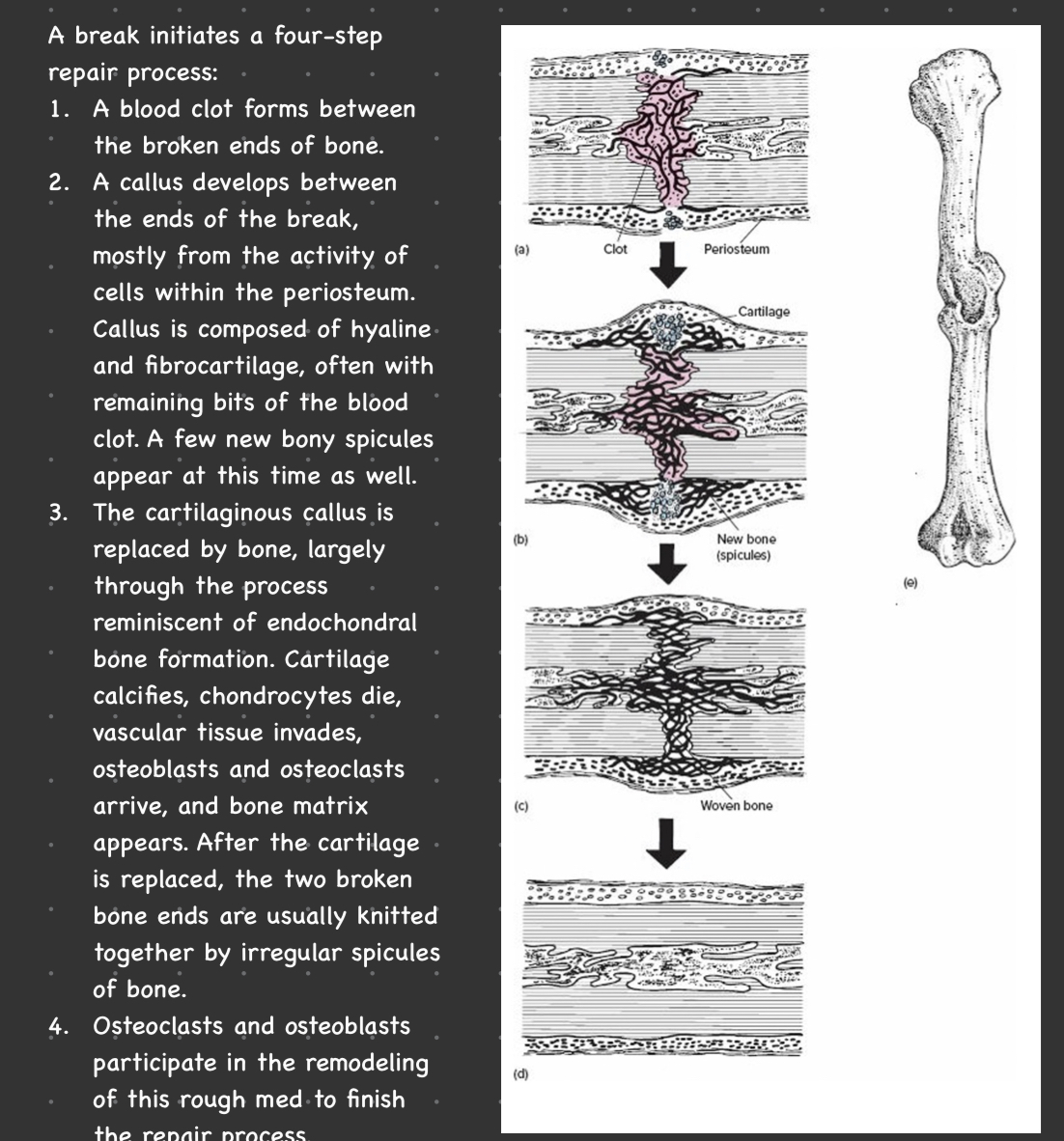
99
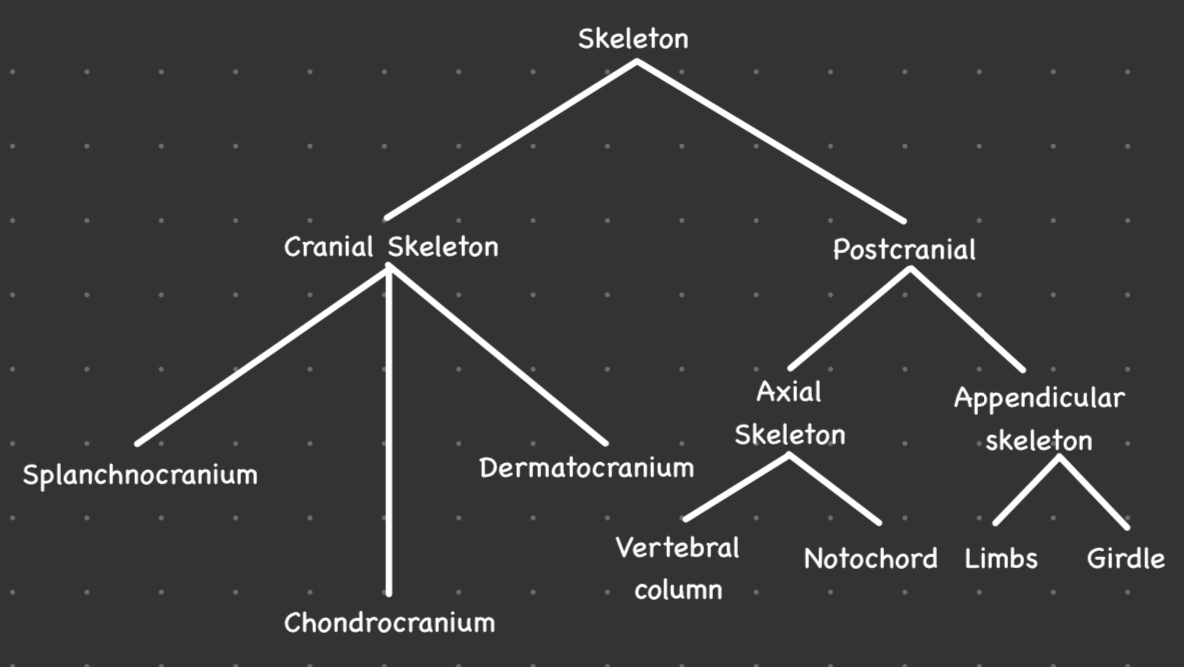
New cards
Regional components of the skeleton
100
New cards
Heterotropic bones
develop by endochonral or intramembranous ossification in areas subject to continual stress in amniotes.