Topic 02 Cell-cell communication in development - slides review
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
How does early development happen?
1. Fertilized egg continues to divide into multiple stem cells, forming into diff cell layers
2. cell layers form diff tissues (neural tube important!)
3. diff tissues form organs
ectoderm-> neural tube-> brain
need migration of cells to destination for this to happen!
What are the 3 initial types of cells in embryo?
1. ectoderm (outside)
2. mesoderm (middle)
3. endoderm
What is an ectoderm?
A cell layer that becomes skin and nerves.
Germ layer covering the embryo's surface.
외배엽은 동물의 발생 과정에서 나타나는 세 가지 원시 배엽 중 하나로, 배아의 가장 바깥층을 이루며 주로 피부, 머리카락, 신경계 등의 조직으로 발달하는 세포층입니다.
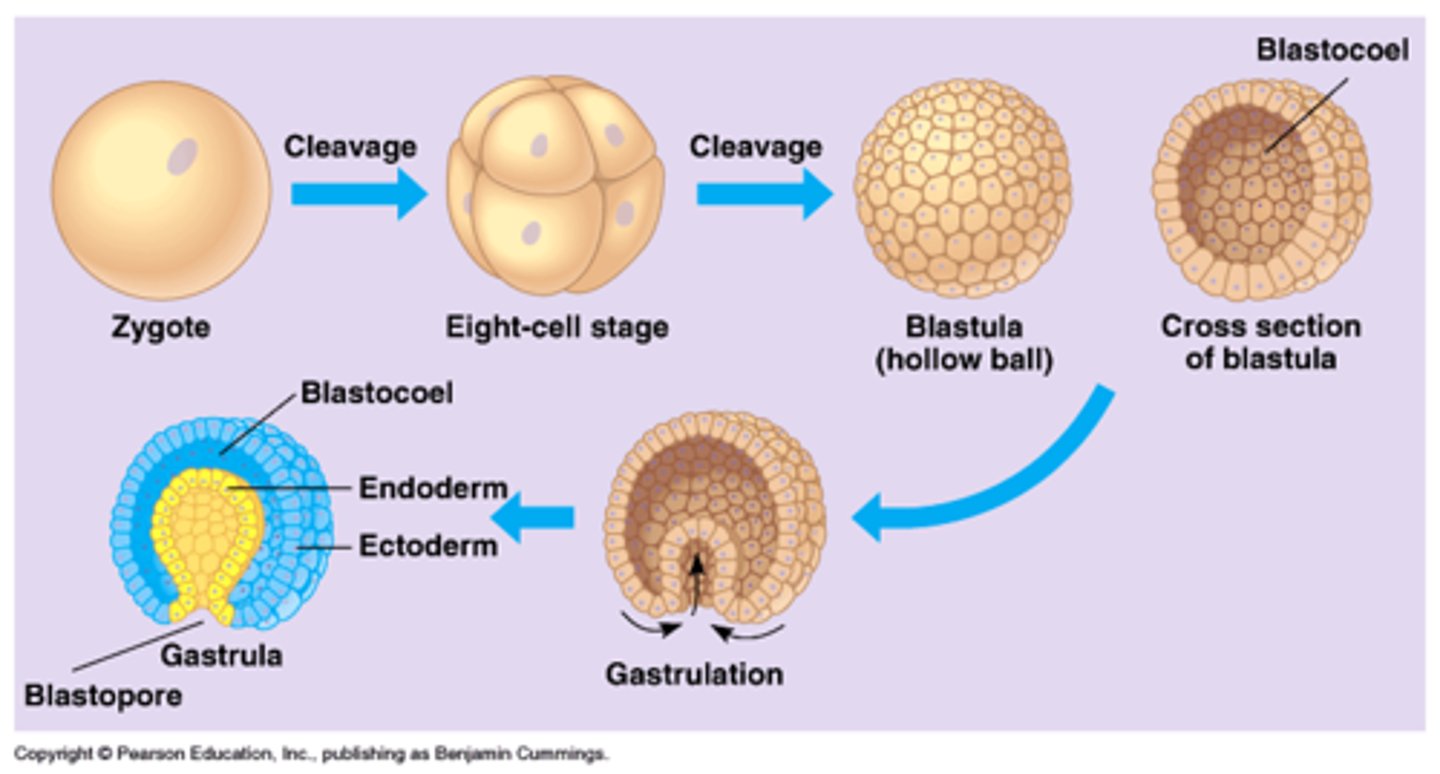
What does cell migration requires? What changes can it cause?
Cell migration requires cell-cell interactions.
These interactions usually cause changes in gene expression.
- transcription, differential nRNA processing, active/inactive mRNA, translation regulation, post-translational modifications of proteins
What is differential cell affinity? (cell adhesion)
- If these embryonic cells are separated from each other, they re-group with their own specific cell type.
- They are able to stick to each other using specific cell surface molecules.
What are cadherins and what are their function?
Cadherin: Calcium-dependent adhering molecules
- establish&maintain intercellular connections
- cover membranes and connect cells
ex) some help placenta stick to uterus, others connect skin cells
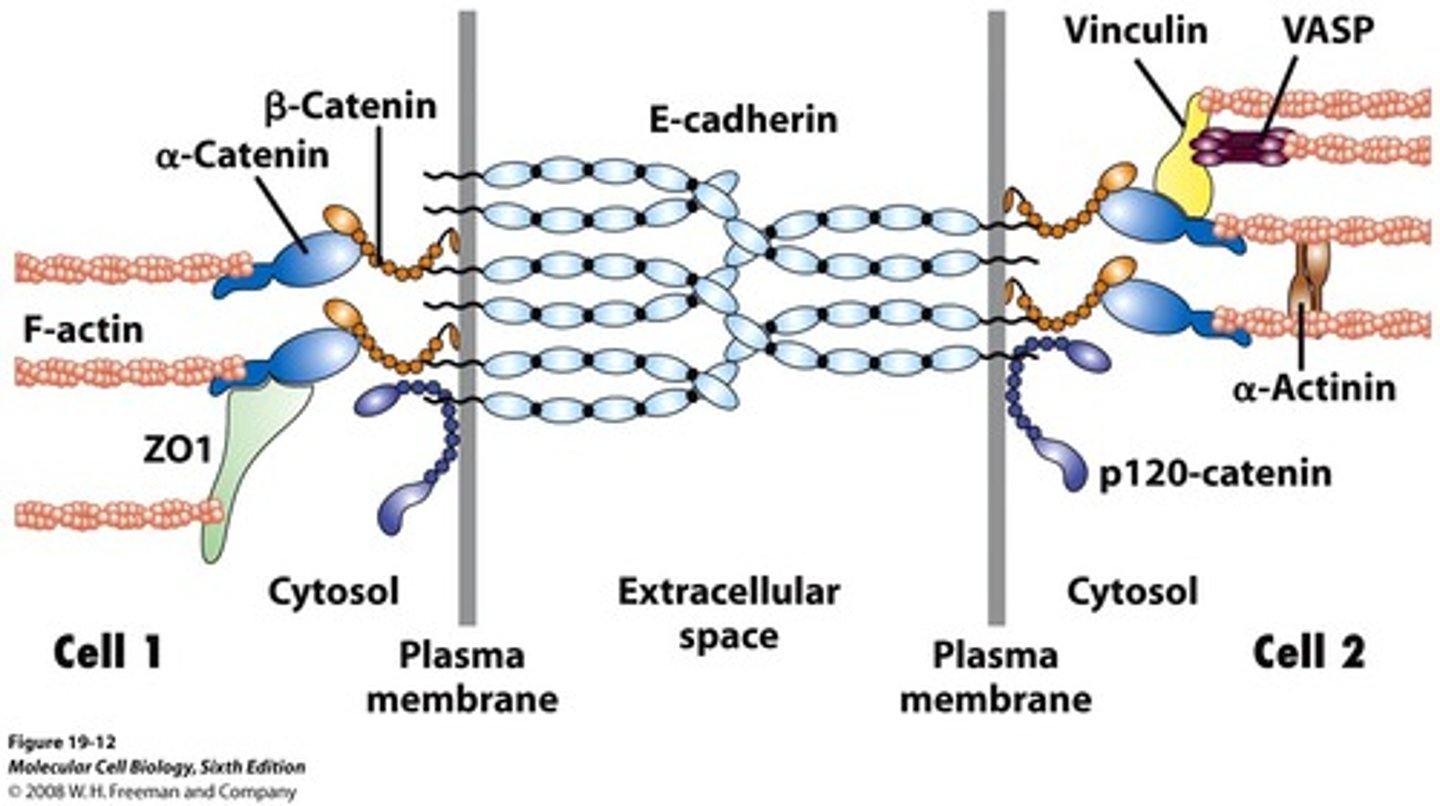
What role cadherins play in cell adhesion?
- Intracellular portion of cadherin attaches to cytoskeleton.
-cells are stabilized to each other bc of the stabilizing of the cytoskeleton.
- more cadherin molecules = stronger linkage between cells
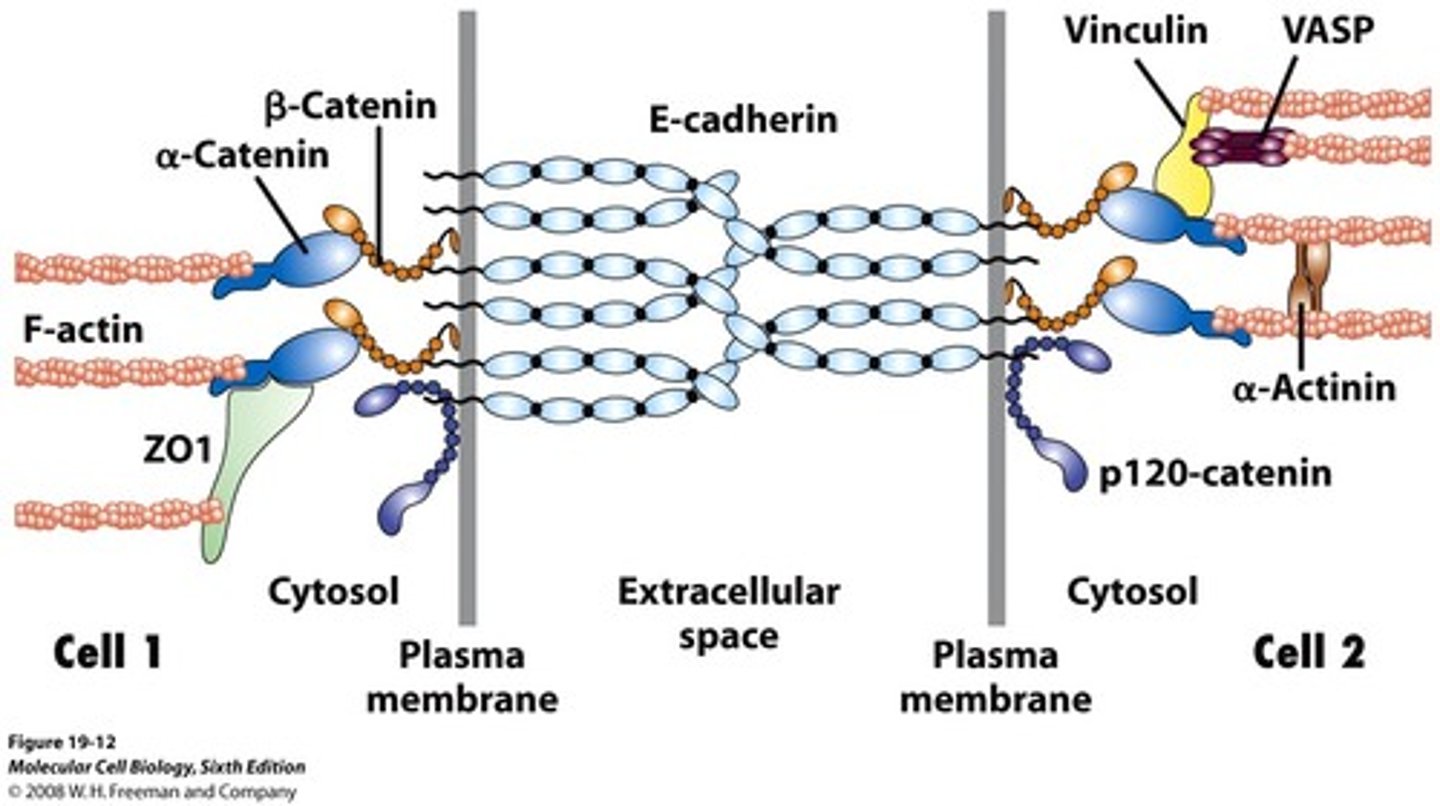
What is cytoskeleton and its importance?
The cytoskeleton is a network of protein fibers that determines the shape of a cell, with microtubules and microfilaments being the most important components.
- its involved in every change in cell, such as shape alteration, movement, transport, or regulation of individual genes.
- it can also transmit "envt" signals to nucleus and implements its response
What is one example of cytoskeleton?
Actin cells add rails and give structure to the cell. Cadherins will go in and anchor to it, and this is helpful for cells to stick to where they belong, but also for migration.
- anchor cells to right place at right time will be an important factor for brain development in the first place.
How can cadherins regulate development?
Timing of developmental events can depend on cadherin gene expression.
ex) Getting a fertilized egg to adhere to uterine wall depends on expression of specific cadherins on surface of that egg and on uterine wall at the right time.
No cadherins = egg lost!
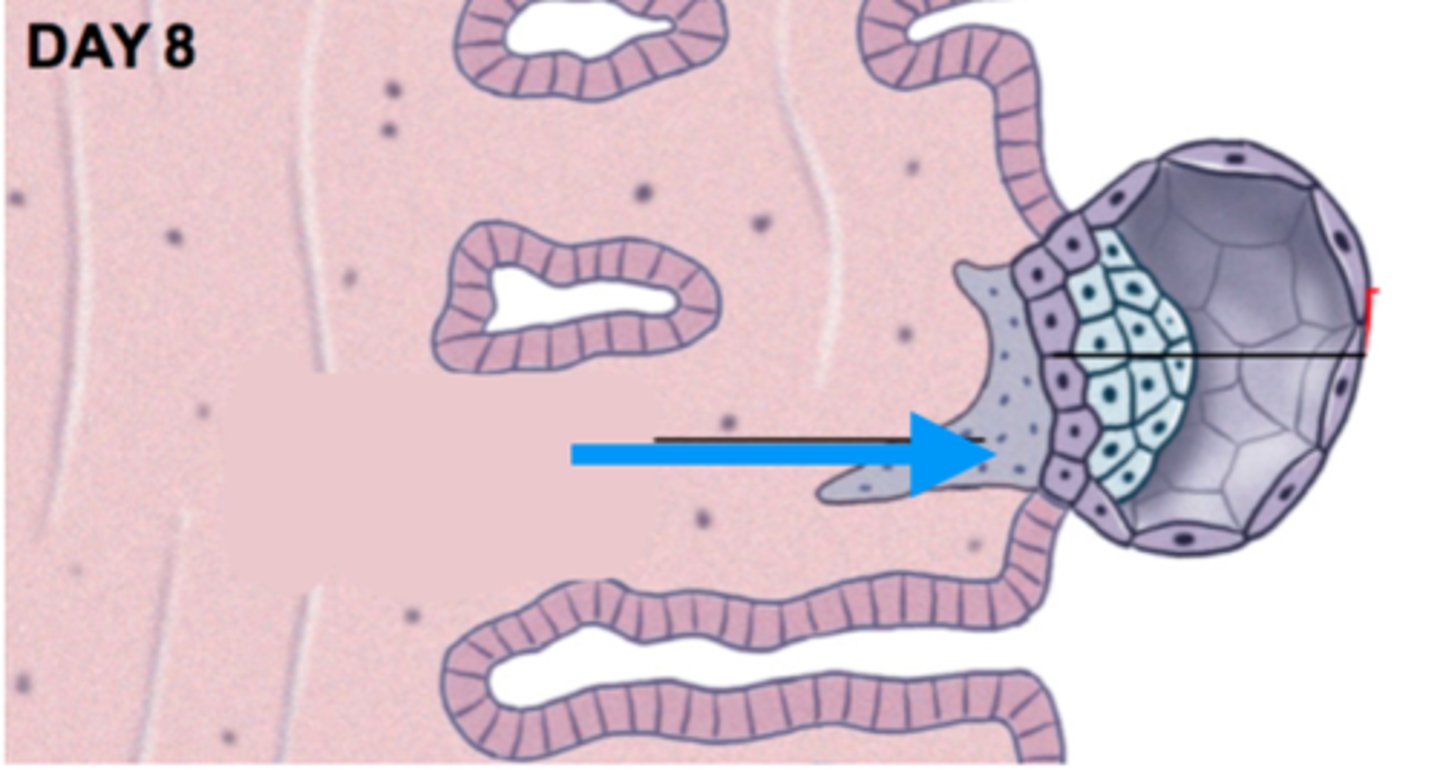
What are the mech for cell migration?
1. guidance cues -> signals that direct mvt and migration
2. cellular motility -> cells being to move around
- reorganization of cytoskeleton/actin molecules+microtubules
- cytoskeleton assembles & dis-assemble to move cell in one direction (as long as it has cadherins leaving front, you can build and scaffold in the front to build the complete part. Push onto and latch onto a new surface)
What is cell signaling (induction)?
Induction: specific mech where 2 nearby components interact
2 players:
1. inducers: chem signals released by or on the surface of nearby cells
2. responders: must have receptors that receives the signal & must respond or change when inducer binds to receptor protein/cell
What happens if the gene that codes for receptor protein on the responder cell has been mutated?
If faulty pdt and receptor doesn't work, it won't hear the signal.
Vertebrate eye as an example of induction (mechansim)
1. Surface of embryo will form the skin (dark blue) and the nervous sys (light blue)
2. Edges of early neural tissue (neural plate) start to close
3. As edges of neural plate fold and come tgt, another folding starts to take place laterally.
4. neural tube has formed and pockets on the sides of the neural tube will produce the eyes.
- As neural tube (optic vesicle in pic) bulges out toward ectodermal layer, it is induced to fold in, forming an optic cup.
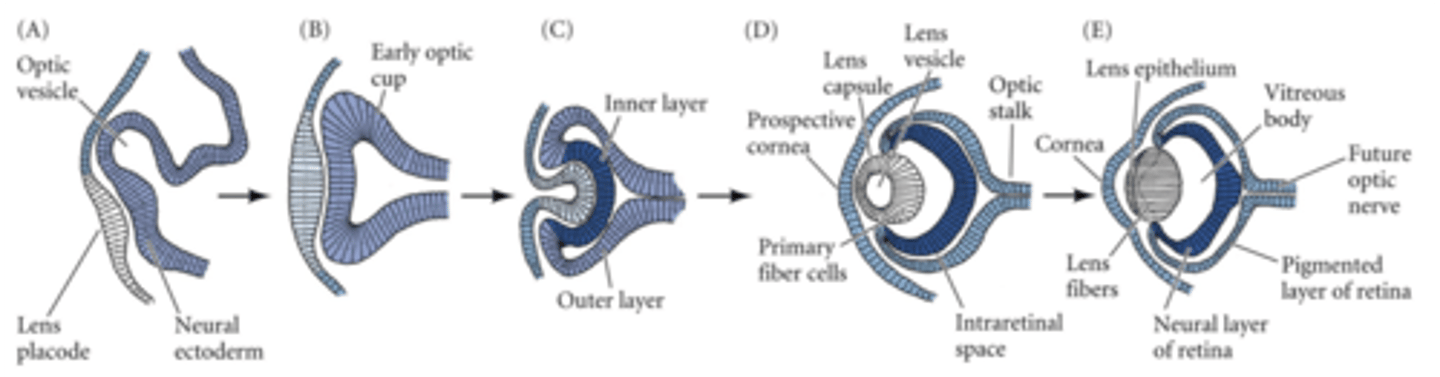
What is reciprocal induction in context of vertebrate eye formation?
Talking back and forth.
- As neural tube folds inward to form the optic cup, overlaying ectodermal layer is induced to form lens of the eye. (factor released by optic vesicle cause activation of lens-specific genes)
- As optic vesicle and lens capsule continue to fold inward, new ectodermal surface layer is induced to form the cornea.

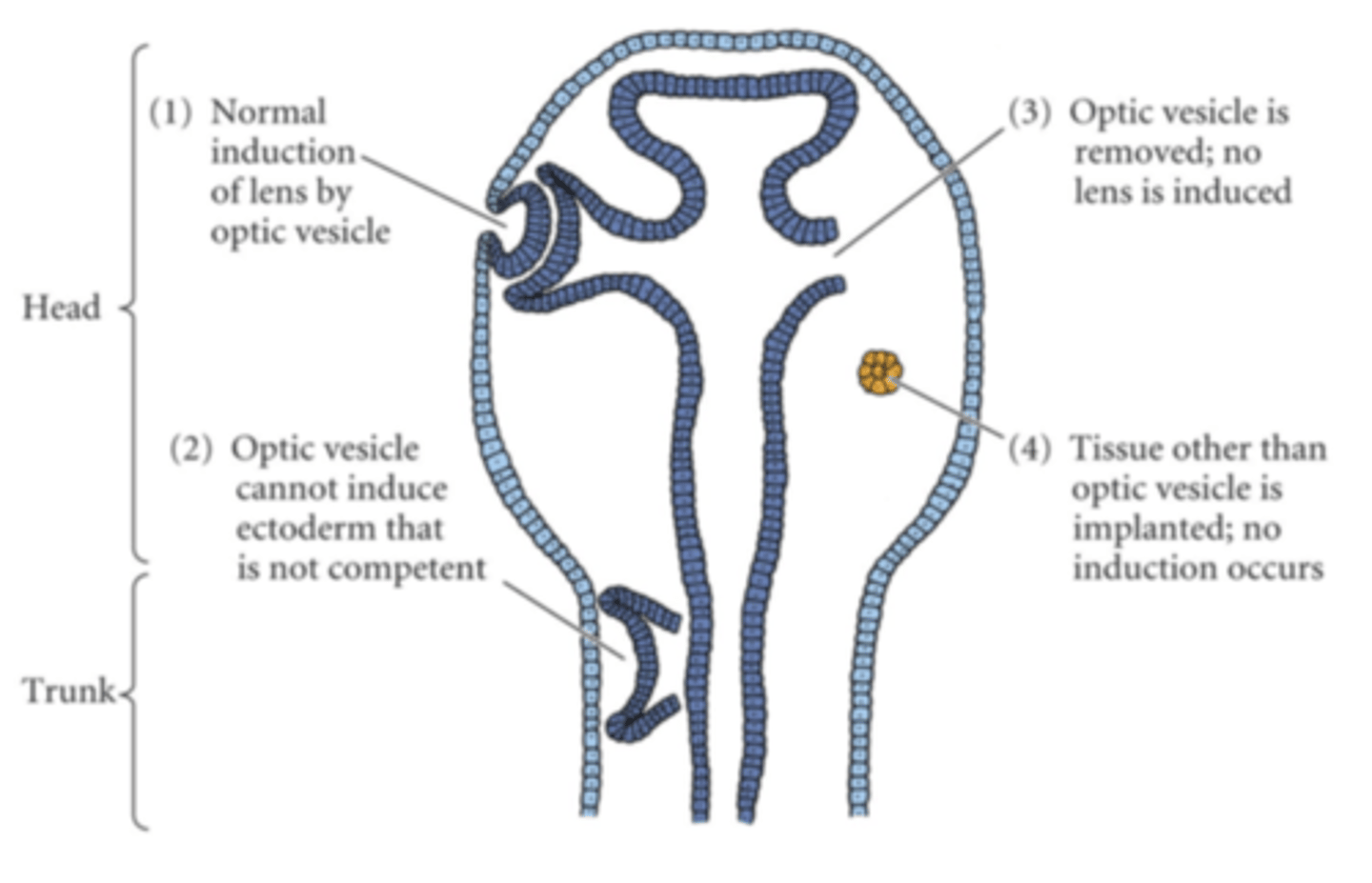
What is induction by specific surface ectoderm in context of vertebrate eye formation?
- After lens vesicle is made, lens vesicle cells release factors to induce the formation of the retina (our decorder for light)
- Not all surface ectoderm can induce lends formation.
> case 2: optic vesicle cannot induce ectoderm that is not competent
> case 3: optic vesicle removed ; no lens is induced
> case 4: tissue other than optic vesicle is implanted ; no induction (bc not the right signal)
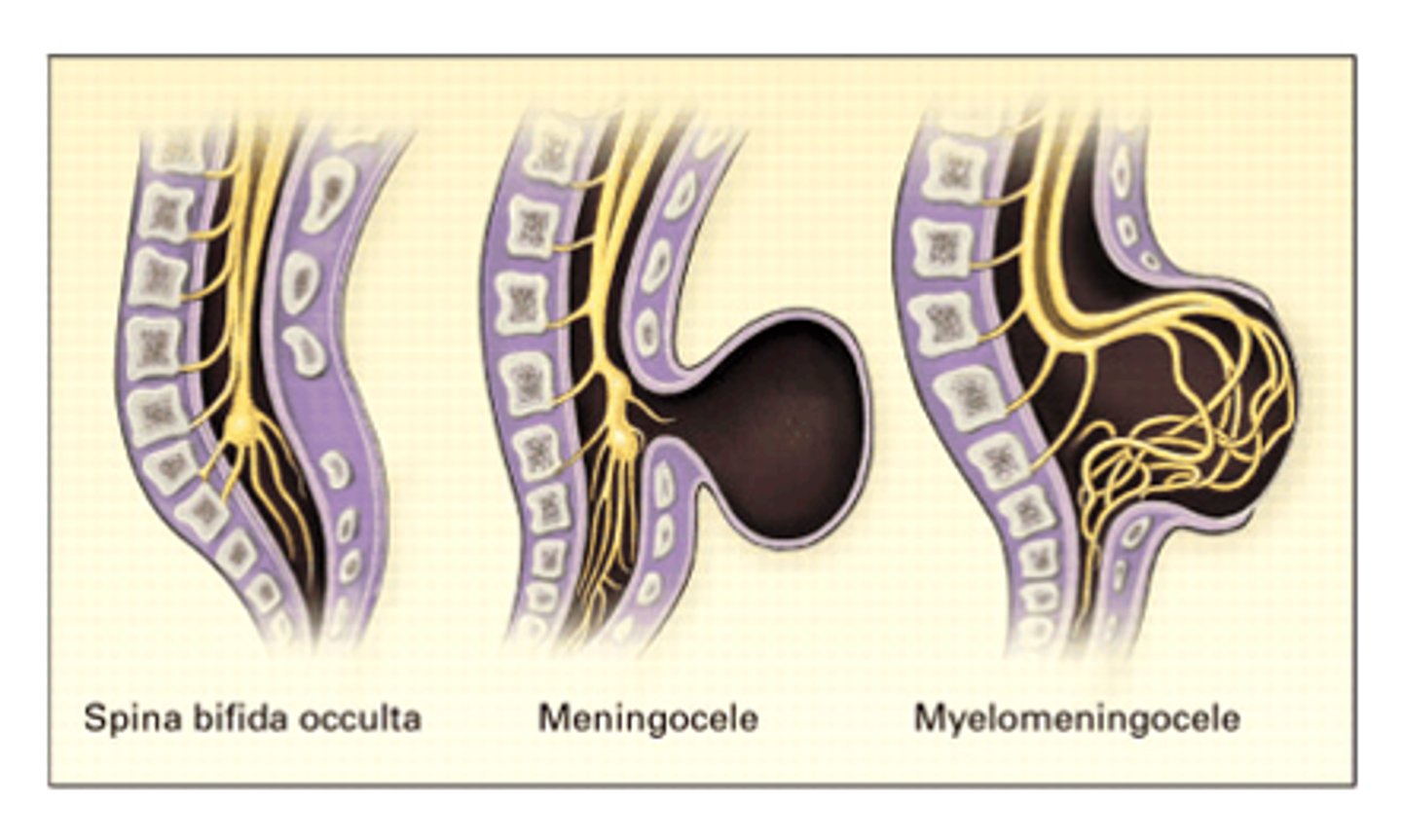
What is Spina bifida?
A birth defect in which a developing baby's spinal cord fails to develop properly.
- neural tube does not fully close
- caused by exposure to things that interfere with induction during pregnancy (ex: alcohol, folate deficiency, anti-convulsants, unmanaged diabetes & obesity)
What is signal transduction cascade?
After inducer binds to receptor and pass down the signal, domino effect of chem interactions occurs inside receiving cell.
What is the importance of having multiple steps in signal transduction pathway?
More control points!
ex: HPA access (stress response in general)
- brain will tell hypothalamus to start receiving stress response sys -> talk to pituatory galndds to release hormones-> talk to adrenal glands to mobilize (high blood sugar, bp)
What sort of stuff can having multiple steps do?
- Inductor/inducer molecules attach to receptor proteins on cell surface.
- TF are eventually activated, changing gene expression
- There are multiple signal transduction pathways
- can turn on/off certain genes
While previous inducers were diffused, some inducers can remain attached to the inducer cell. What is required for this to happen?
Cells need to be close to each other so that inducer molecule and the protein receptor molecule can touch and attach.
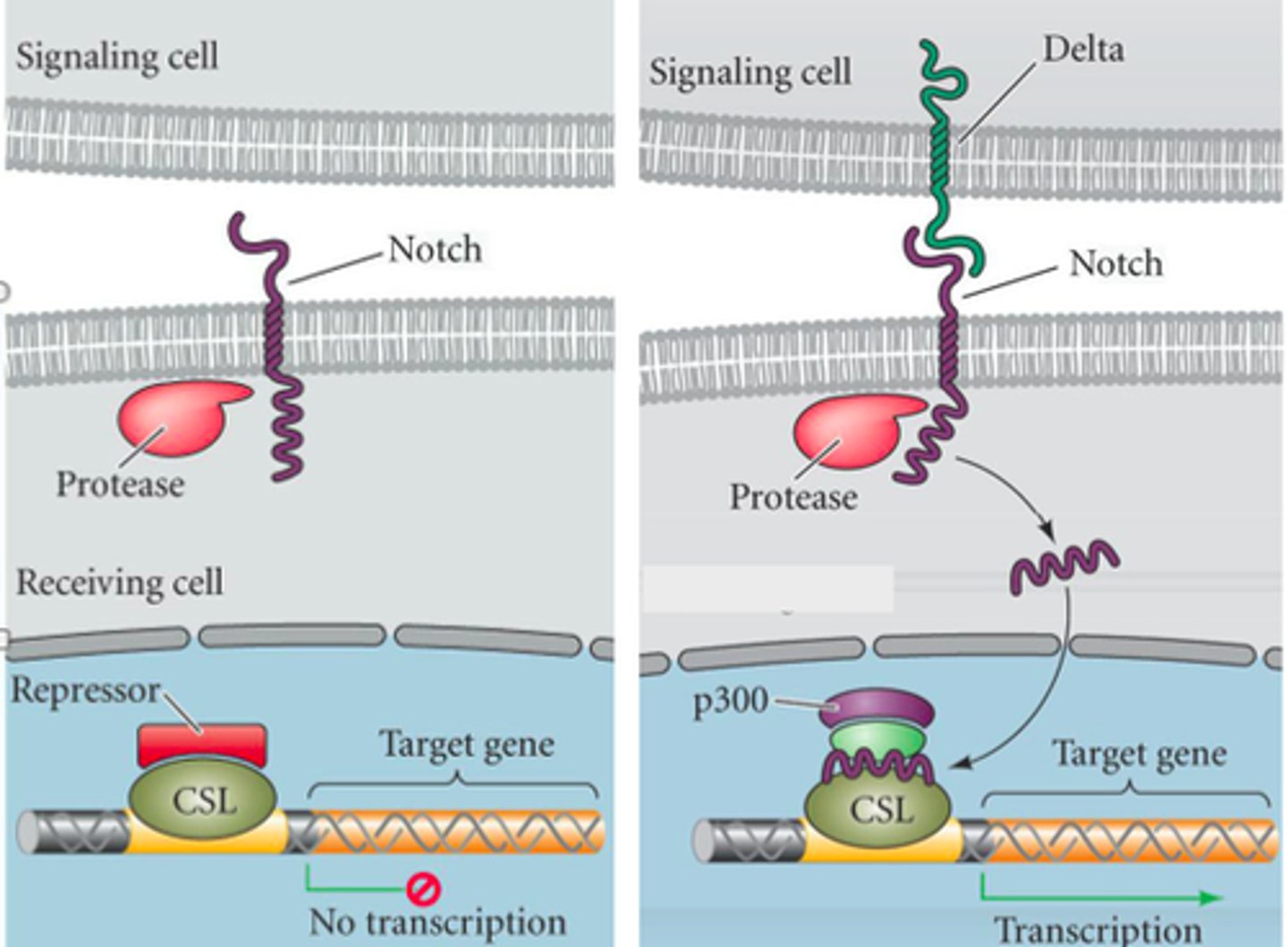
What does Notch pathway do in terms of inducer&receptor in membranes?
Notch proteins are invovled in formation of kidney, pancreas, heart. In nervous sys, Notch regulates which cells become neurons and which cells become glia (아교세포를 의미하며, 그리스어 'glue'에서 유래한 말로, 신경계를 함께 지지하고 연결하는 역할을 하는 비신경세포들을 통칭하는 용어)
We have the part of notch protein activated and bending and comes into the enzyme protease that cut it. That piece will flow into nucleus and kick out the use of diff gene. Repressor cannot bind anymore so transcription can happen.
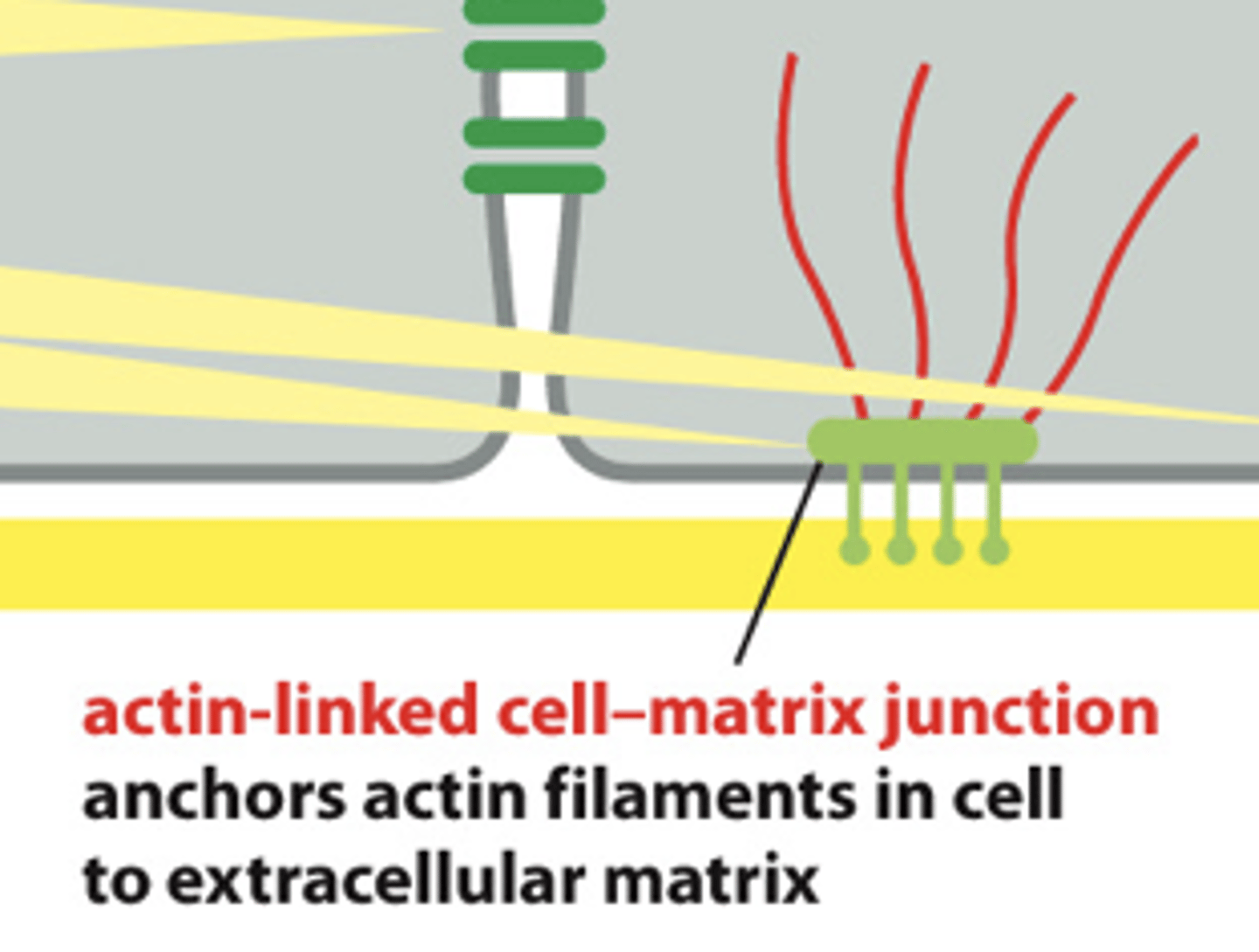
What is an extracellular matrix and what can it do?
Gelatinous&fibrous network of molecules secreted by cell. (mesh net that is outside of cell)
- can tether many inducer molecules (they cannot diffuse away) grab like a net and allows for more sensitivity
- fibronectin helps to anchor everything tgt (ground things from this web onto actual cell membranes)
- Internal cytoskeleton also anchored to membrane via integrin

What role does extracellular matrix play in gene expression?
- Integrins can also signal from the outside of the cell to the inside of the cell, altering gene expression.
- Integrin is crucial for inducing specific gene expression in developing tissues, especially for liver, testis, and mammary gland.
Summary
- Importance of cell communication?
- how does it occur?
- what does it activate?
- can it change GE?
- important for building tissues and organs
- communication occurs by diffusible or surface-attached inducers
- communication activates signal transduction cascades
- yes / via TF interacting with DNA of receiving cell