Summative review
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
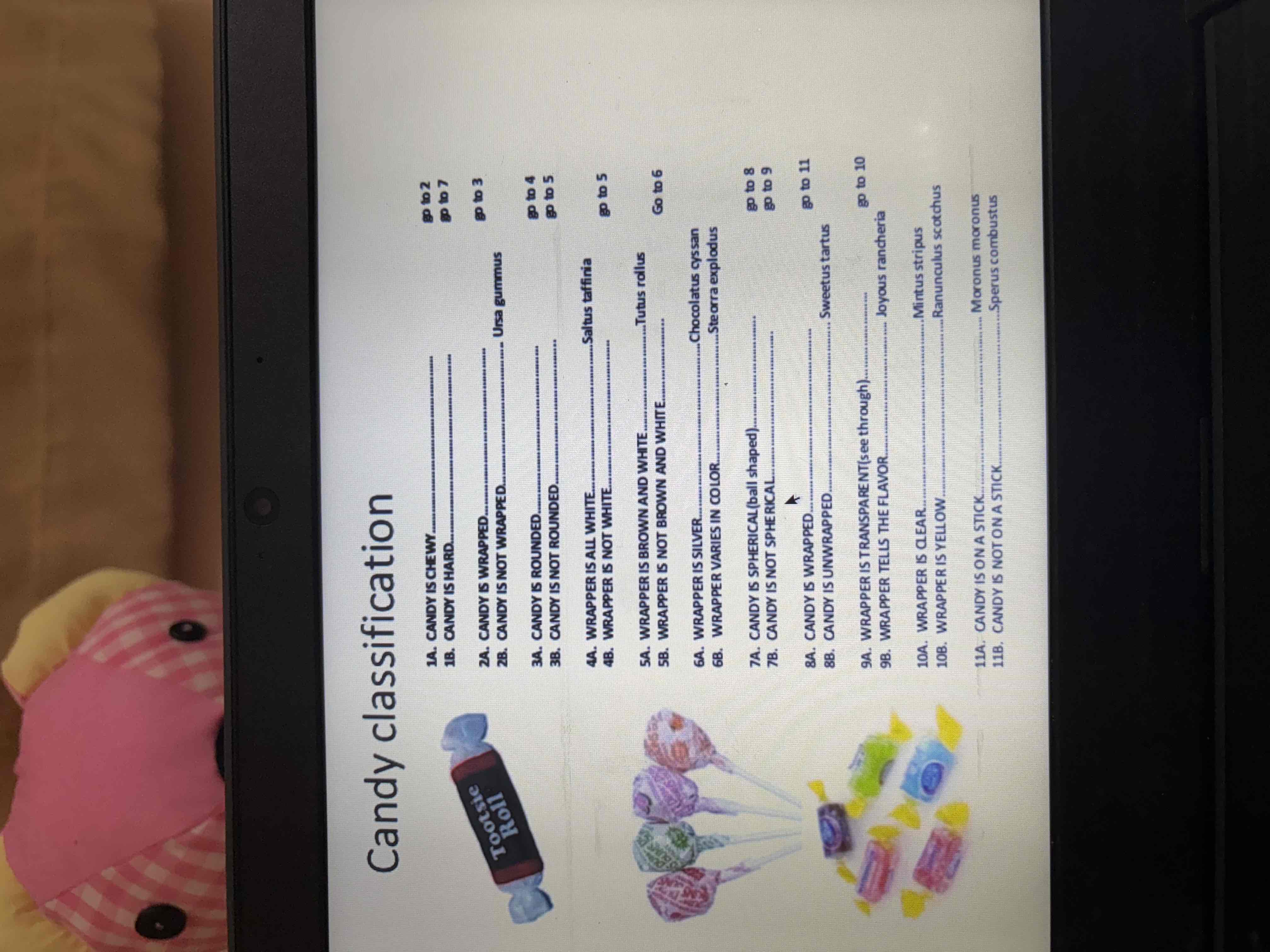
Dichotomous key
classification is used to adapt by organism. A diagnosis key to part is used each spot on the key. A choice must be made which leads to a new branch of the key.
Classification system (7 types)
Kingdom, phylum, class, order,family, genus and species
first level of classification system is domains
Eubacteria-contains kingdom Eubacteria
Archae- contains kingdom archaebacteria, naked dna
Eukaryotes- contains protists, fungi, plants and animals, made up of eukaryotic cells
The six kingdoms
Archaebacteria, ancient bacteria found in weird places, unicellular ex thermophiles
Eubacteria- true bacteria most common types, unicellular ex e.coli
Protists- eukaryotic, unicellular to multicellular mostly aquatic ex euglena, amoeba
Fungi- unicellular, eukaryotic, heterotrophic (must eat) ex yeast, mushrooms
Plants- multicellular autotrophic (makes its own food) eukaryotic example pine trees
Animals, eukaryotic multicellular heterotrophic
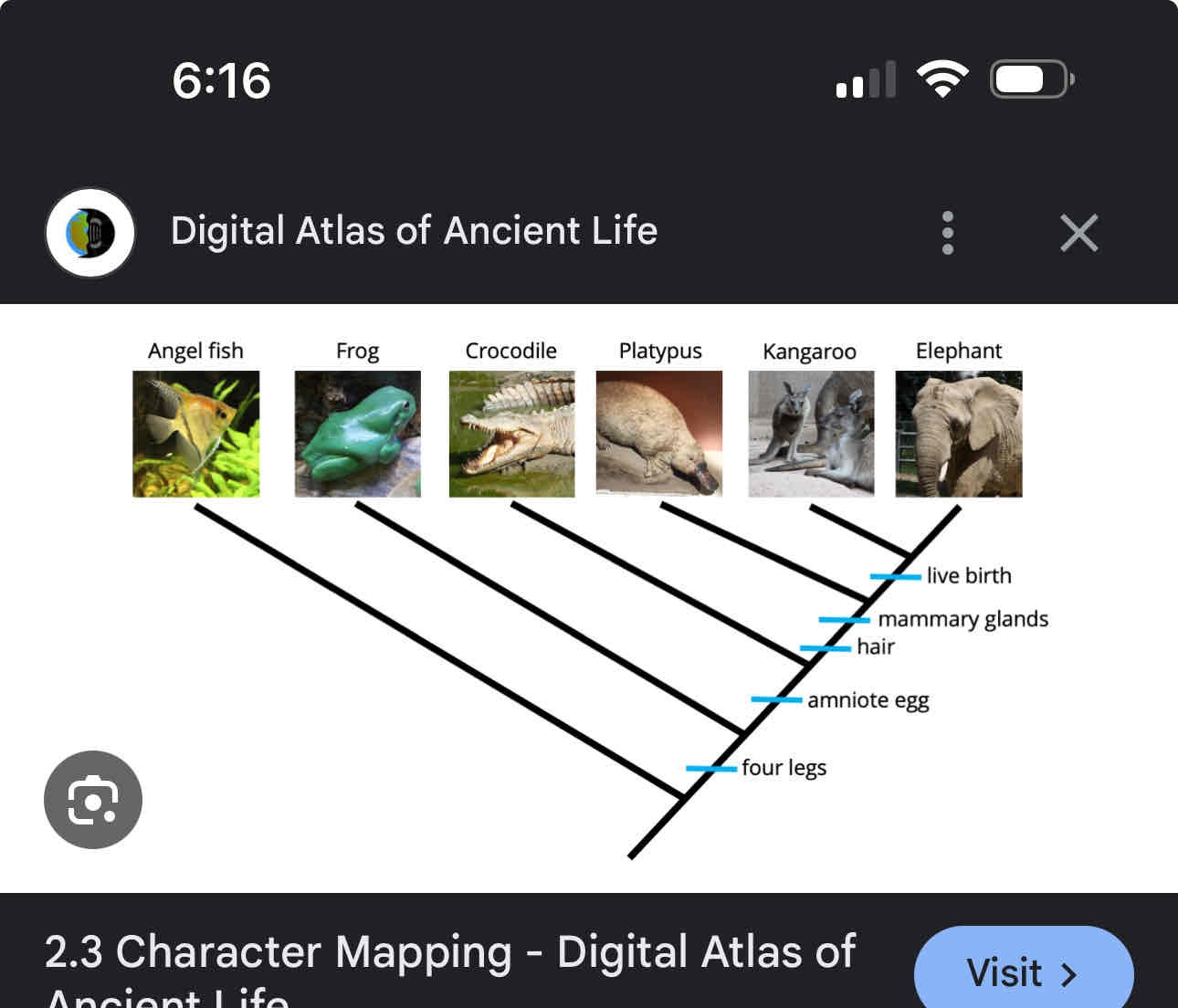
Phylogenetic tree
Is a diagram showing the evolution relationships between species or group?
Binary fission
Process- asexual reproduction
:parent cells duplicates its chromosomes, cell wall divides and gets two new cells
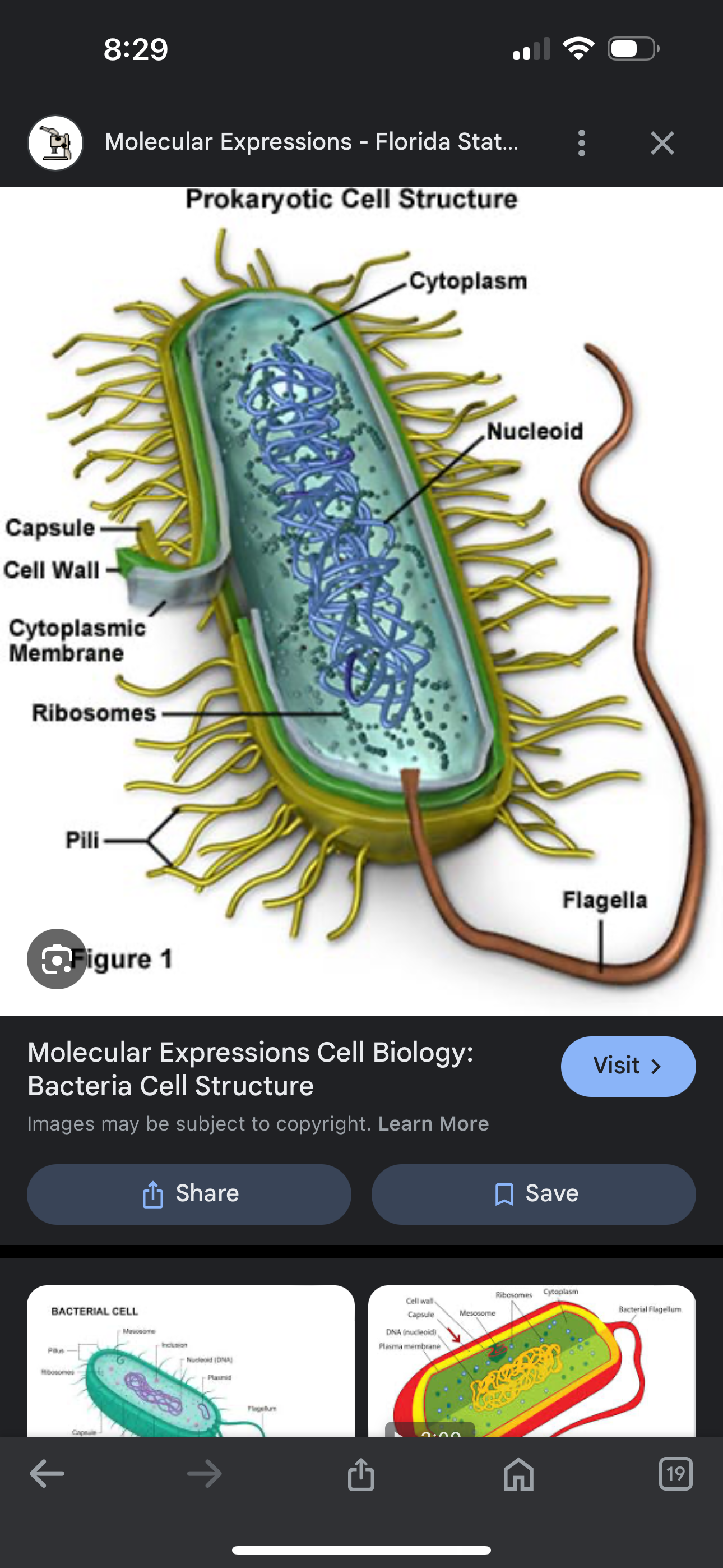
Bacteria
main parts of bacteria are cell wall, plasma membrane, DNA and ribosomes
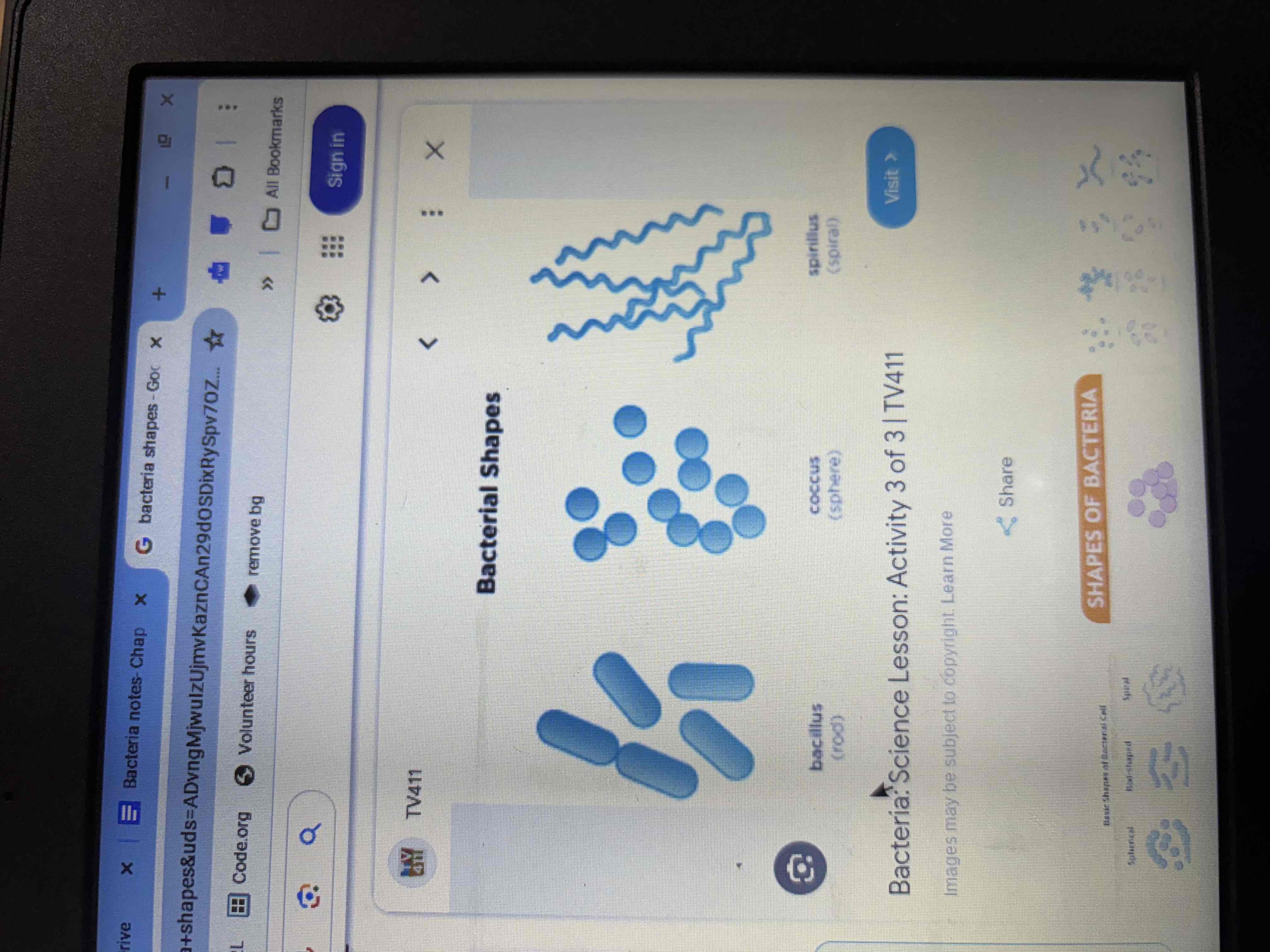
Bacterial shapes
Spherical-coccus
Rod-Bacillus (rectangle)
Spiral-spirillum ( rectangle with spiral in it)
Bacteria prefixes (say before the shape of bacteria)
Staphylo- clump
Strepto- chain
Diplo- pair
Mono- single
Bacteriophage diagram
Is a virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and Archaea
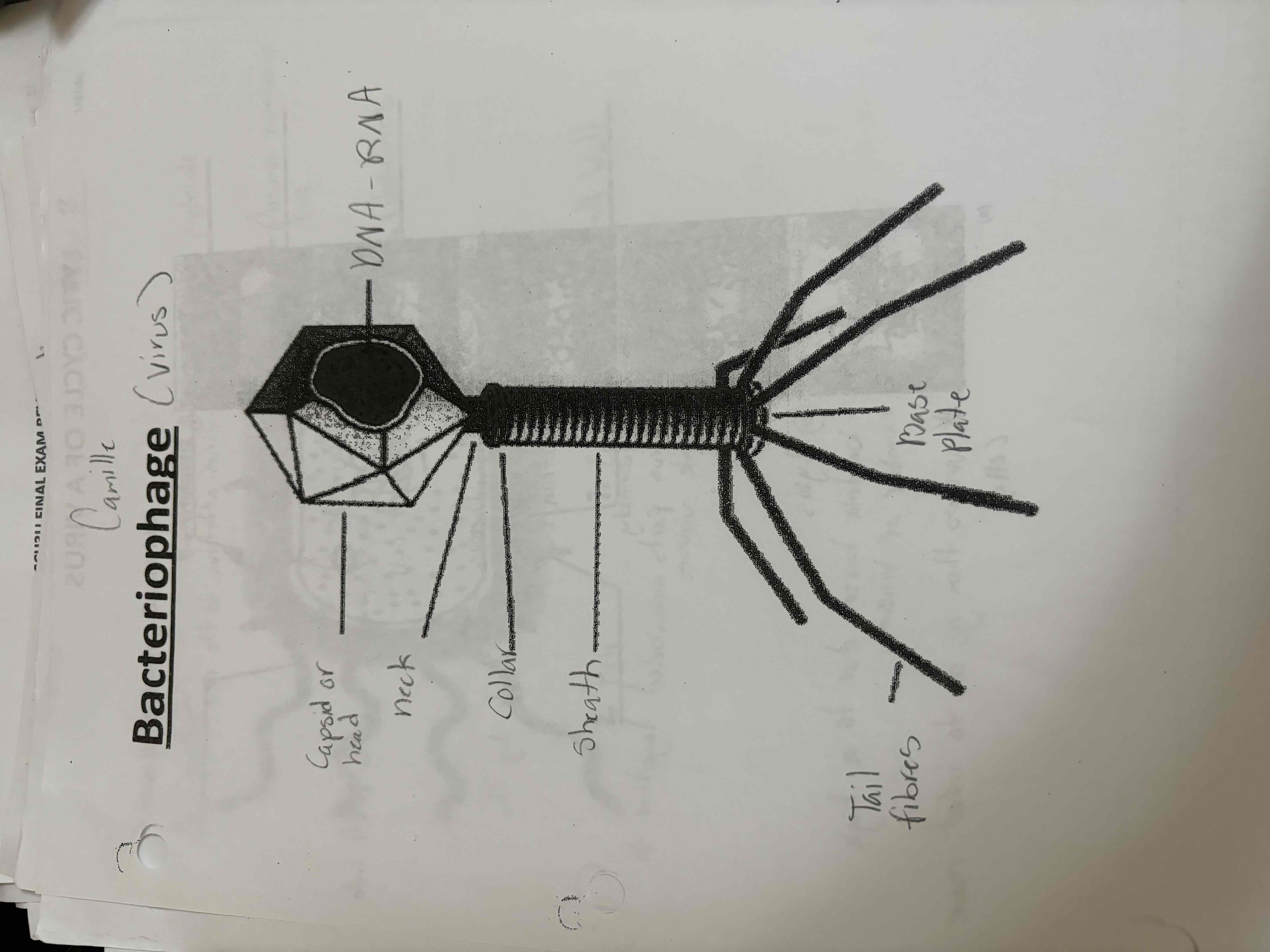
Lytic cycle
is the cycle where the virus infects and destroys the host cell
1.attachment
2. injection
3. synthesis
4. assembly
5 lysis

Lysogenic cyle
Is a dormant state of a virus that enters the hostel then remains in active
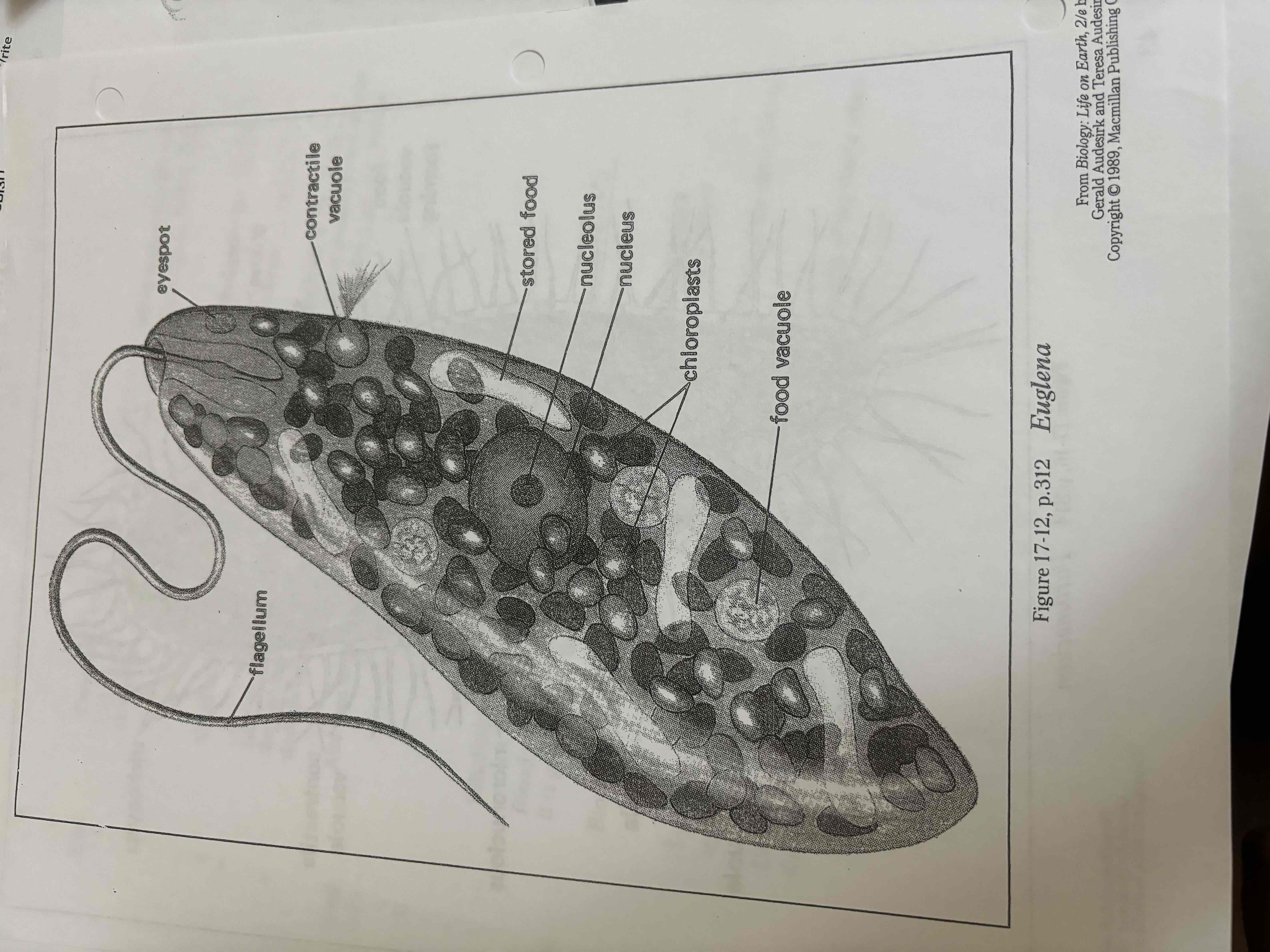
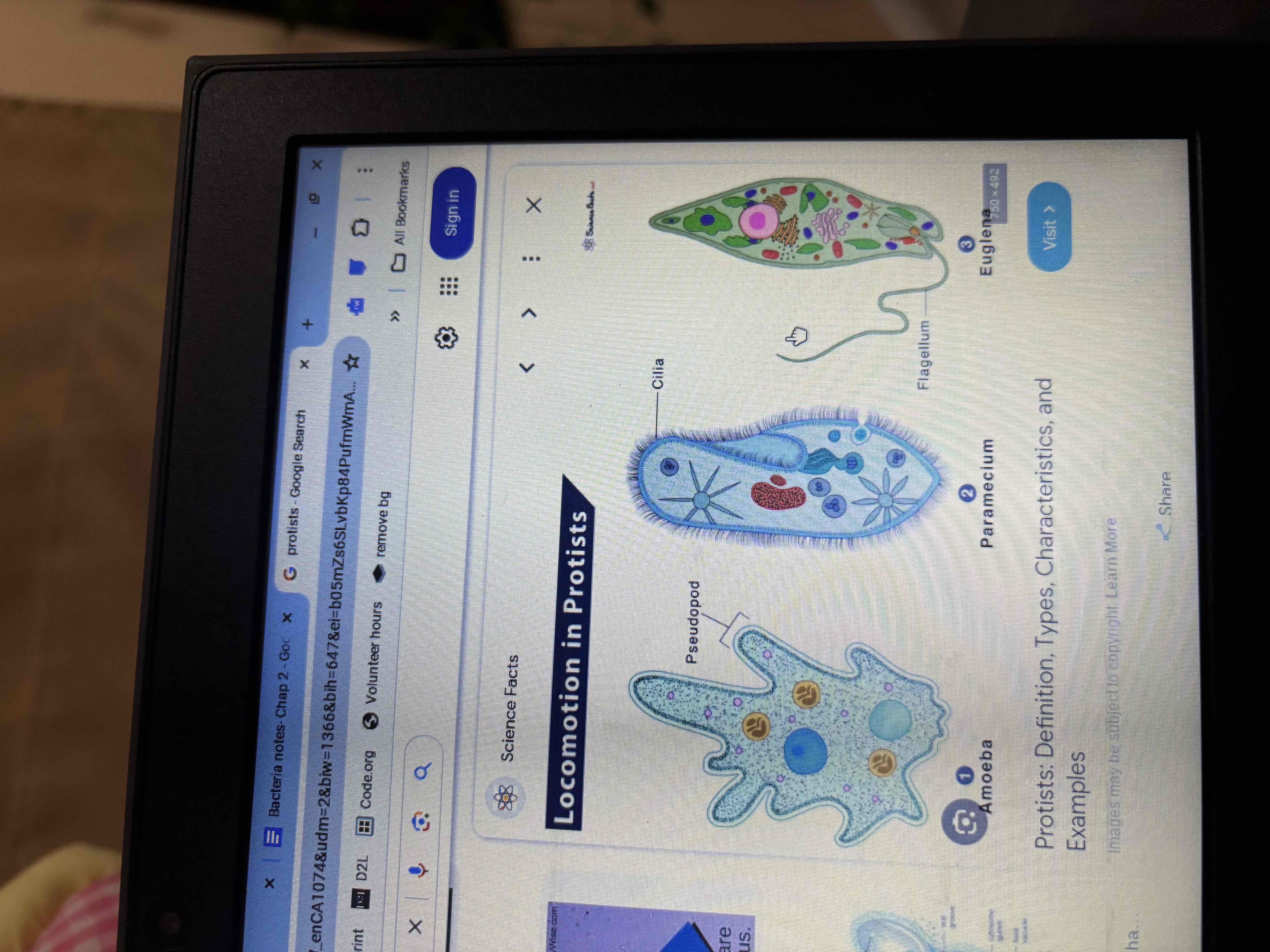
Euglena
Has eyespot to sense light, flagellum is used to move around ,reproduce by binary fusion
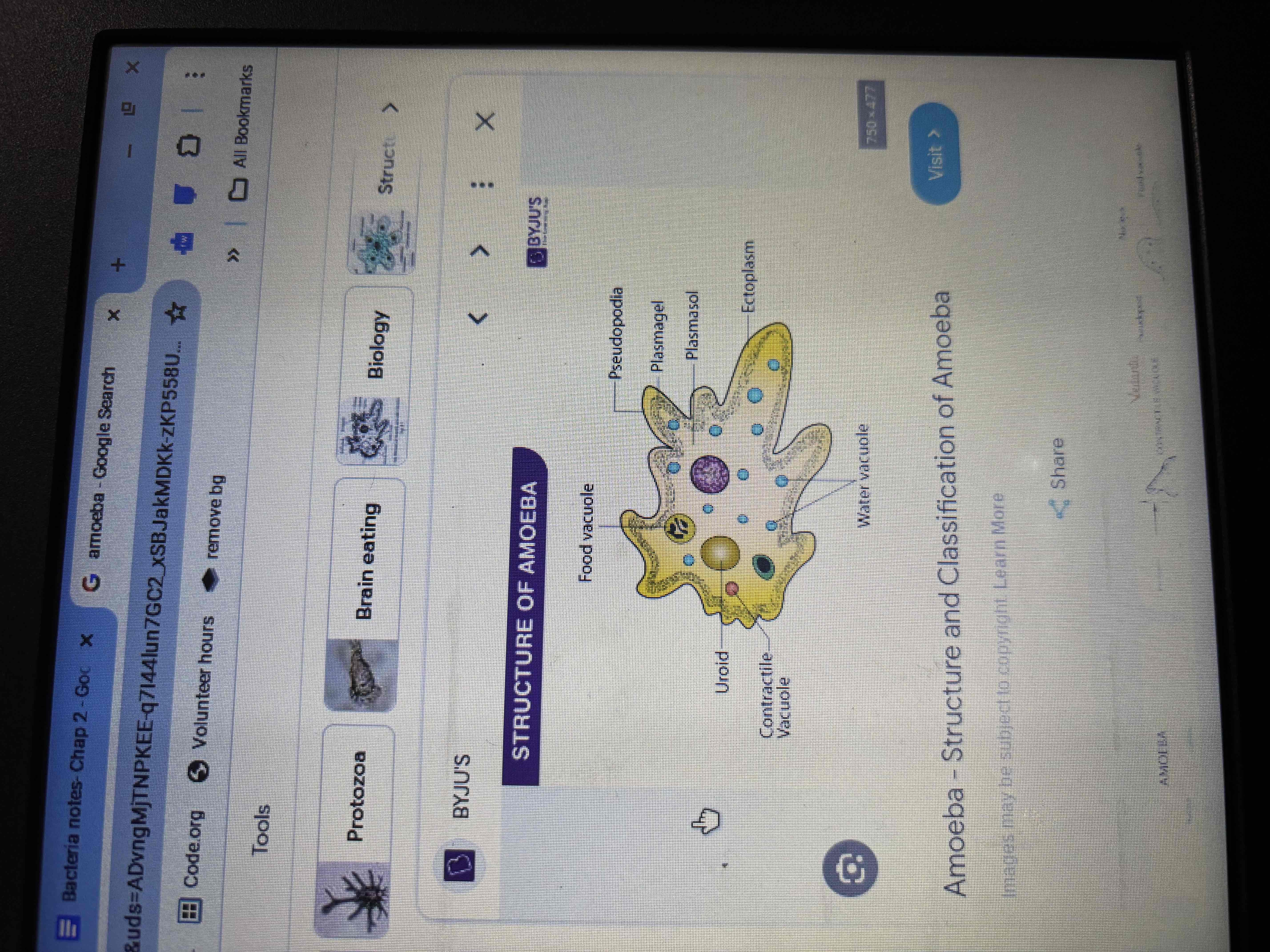
Amoeba
Move pseudopodia (false foot)
Eat by engulfing food
Reproduce by binary fission
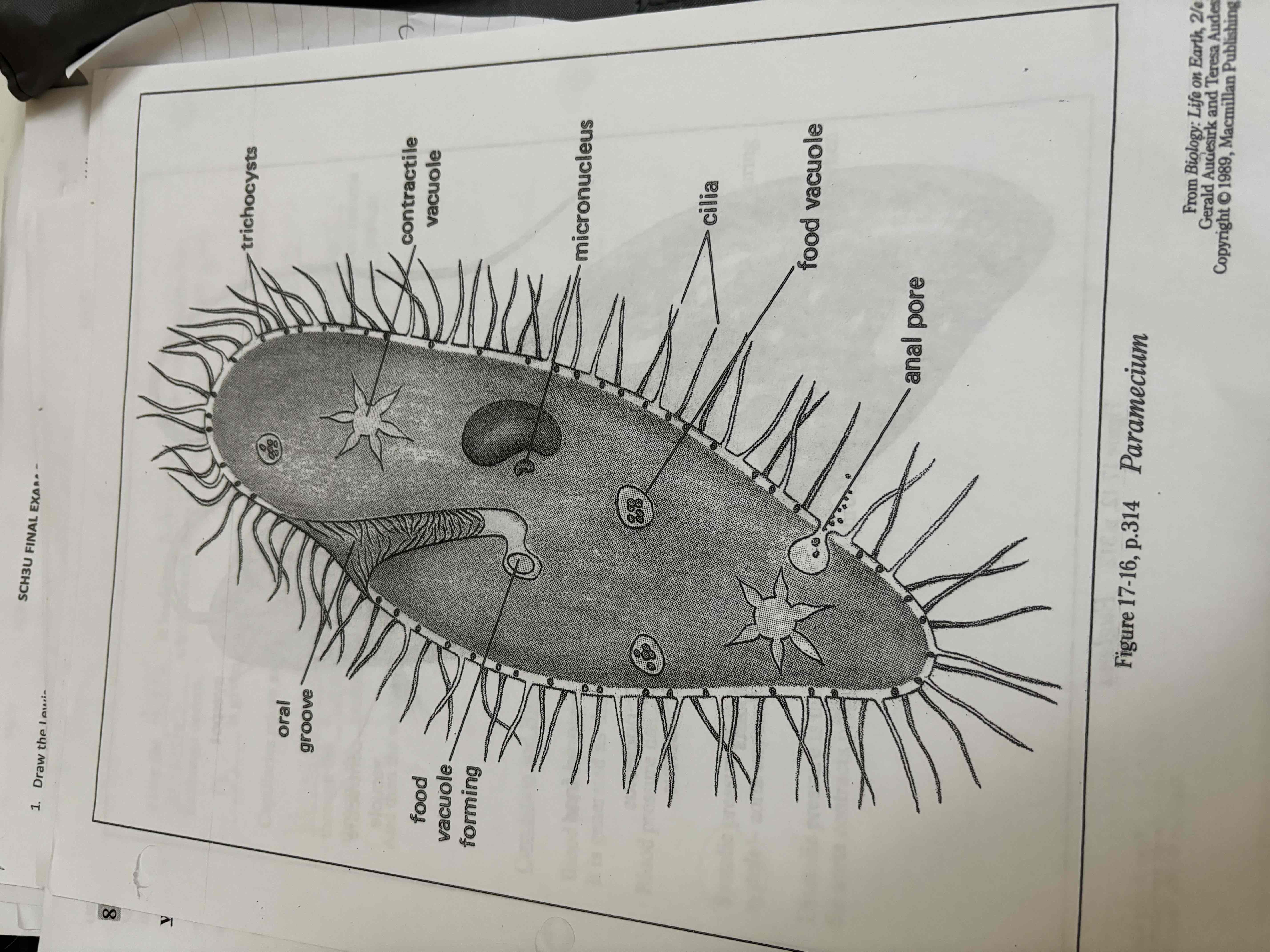
Paramecium
Uses cilla to move around
Has oral grove to eat
Cilla move food to oral grove, digestion takes place in gullet
Waste is expelled from vacuole thru anal pore
Classification of protists
Both unicellular and cellular
Both Heterotroph and autotroph
mobile yes
Reproduction binary and conjunction
Role Helps the production of food like yoghurt and cheese
Example e.coli
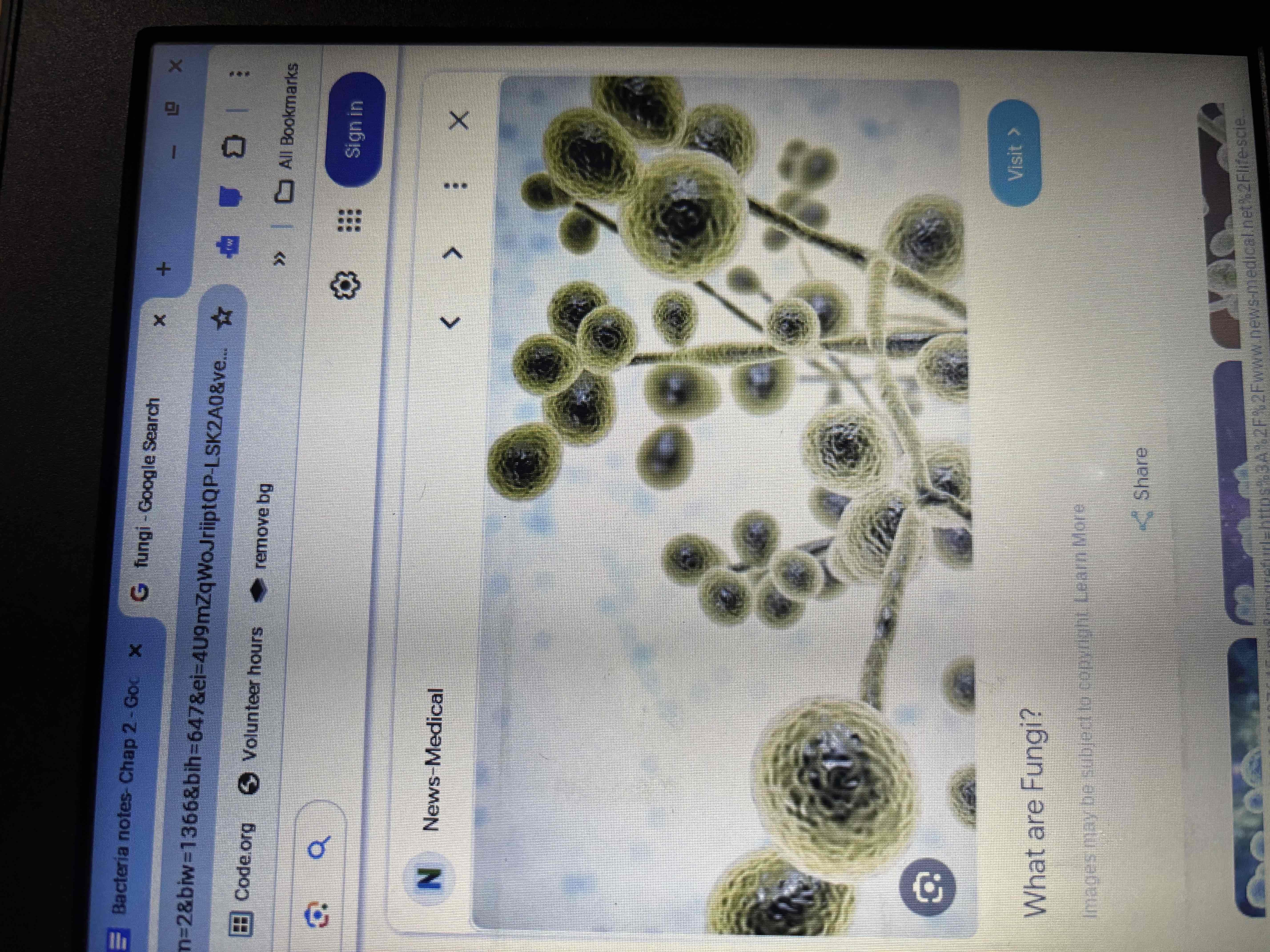
Fungi
Both and cellular or multicellular
Eukaryotic
Heterotrophic
more than 100,000 different species
Saprophytic (decomposer)
Fungi types
Chytridiomycota, blastocladiomycota, neocallimastigomycota, microporidia, glomeromycota, ascompycota, basidiomycota
Plant life cycle
Plant in diploid stage is to sporophyte (2N)
Sporophyte cell divide by meiosis to Produce asexual Haploid spores
Zygote grows into sporophytes and then cycle continues
Plant characteristics
Multicellular
Eukaryotic
Autotrophic thru synthesis
Cannot move
Plant types
Non vascular ( bryophytes)
Vascular (tracheophytes)
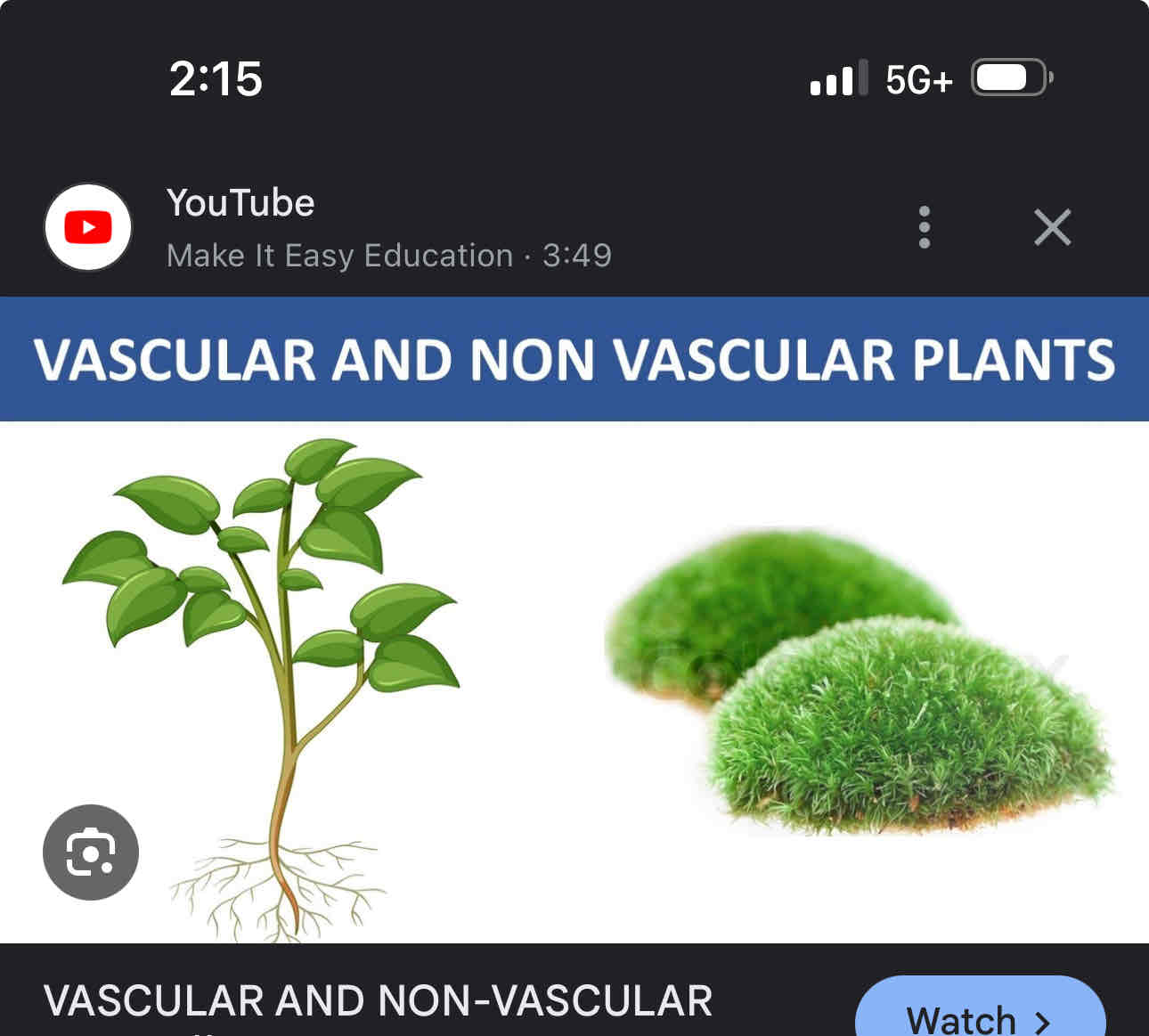
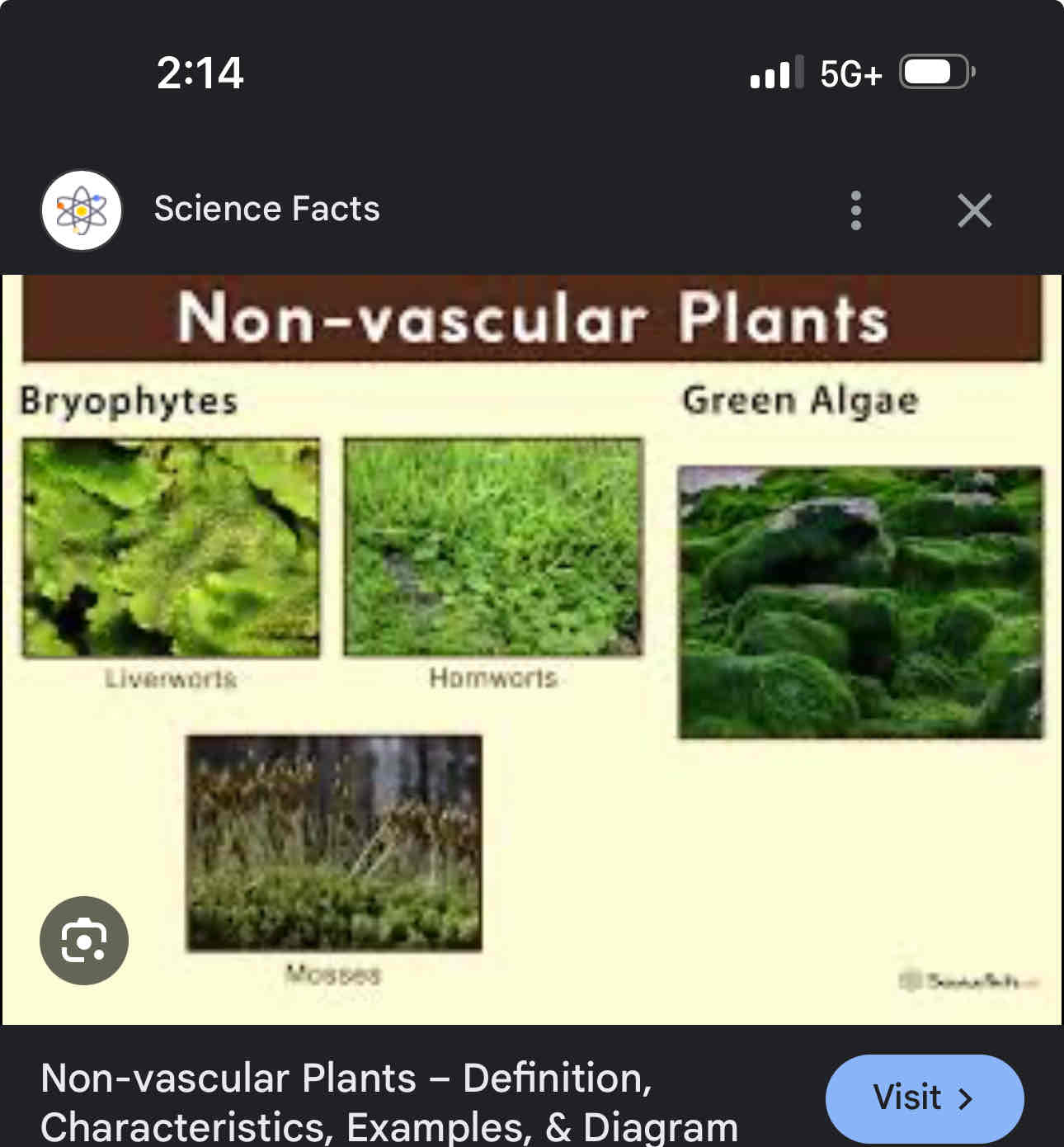
Non vascular plants bryophytes
Lack true roots, stem with a vascular tissue growth and grows moist environment, only grows several centimetres in height, example mosses, liverwort, and hornworts
Lycophytes
Ferns
Lignin Makes plant strong
Have non photosynthesis gametophytes
Contains spores
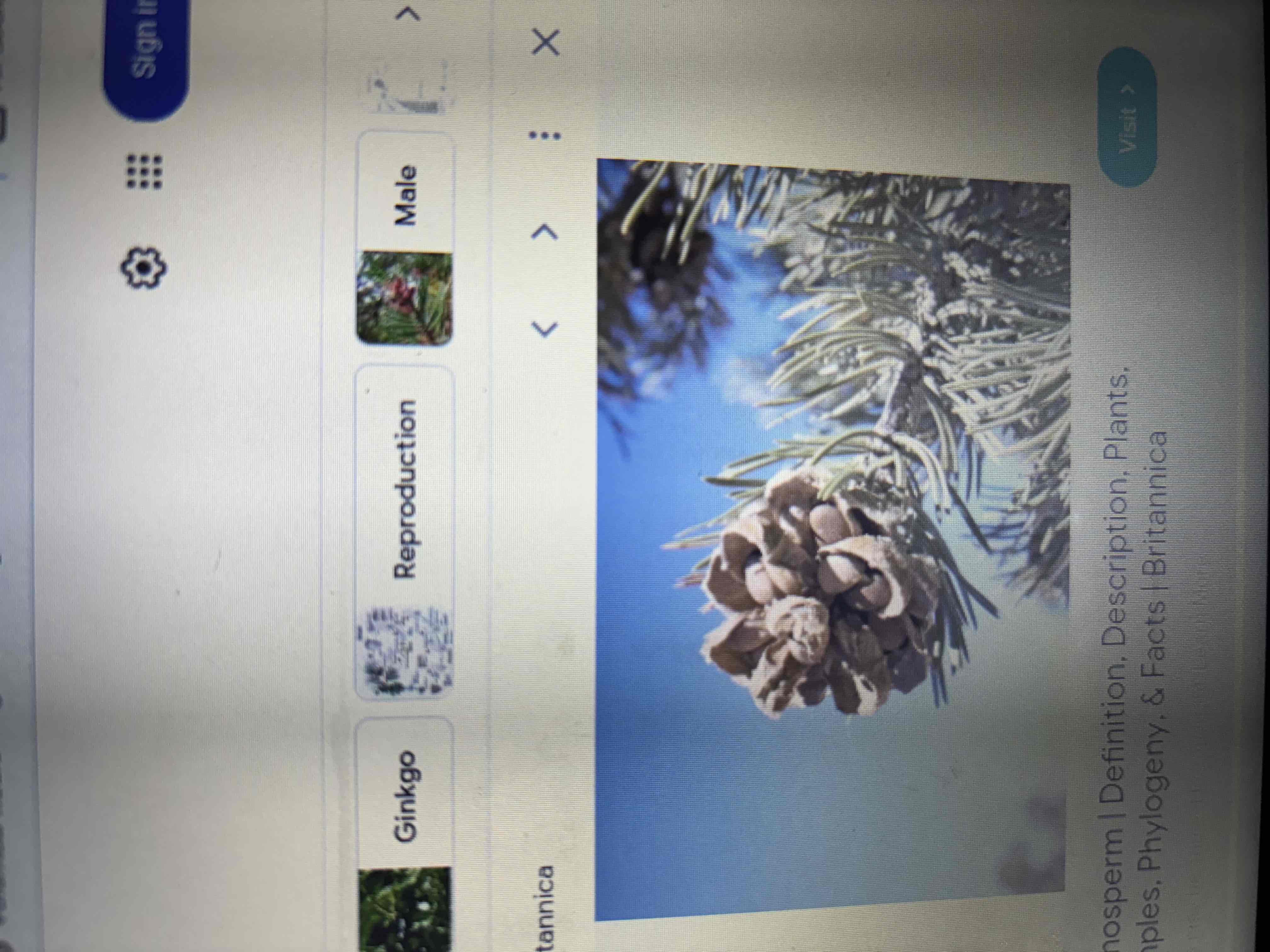
Gymnosperms
Includes coniferous trees like pines, spruce and cedar
Males cones produce and release pollen
Female cones produce eggs
Have needle like leaves and thick cuticles
Angiosperm
Flowering plants 90% Of all plants species are angiosperms Three main parts
1. Flower-specialized structure that produce pollen
Fruit- the main ovary of flowering plants that contain seeds
Cotyledon- Stores food by growing embryo
Two sub divisions of angiosperms
Monocots
have one seed, parallel veins in the leaves
diacots
Have 2 seeds leaves
Have a net like pattern of veins in leaf
Animal
Eukaryotic multicellular
Most are mobile
have senses
Sexual reproduction
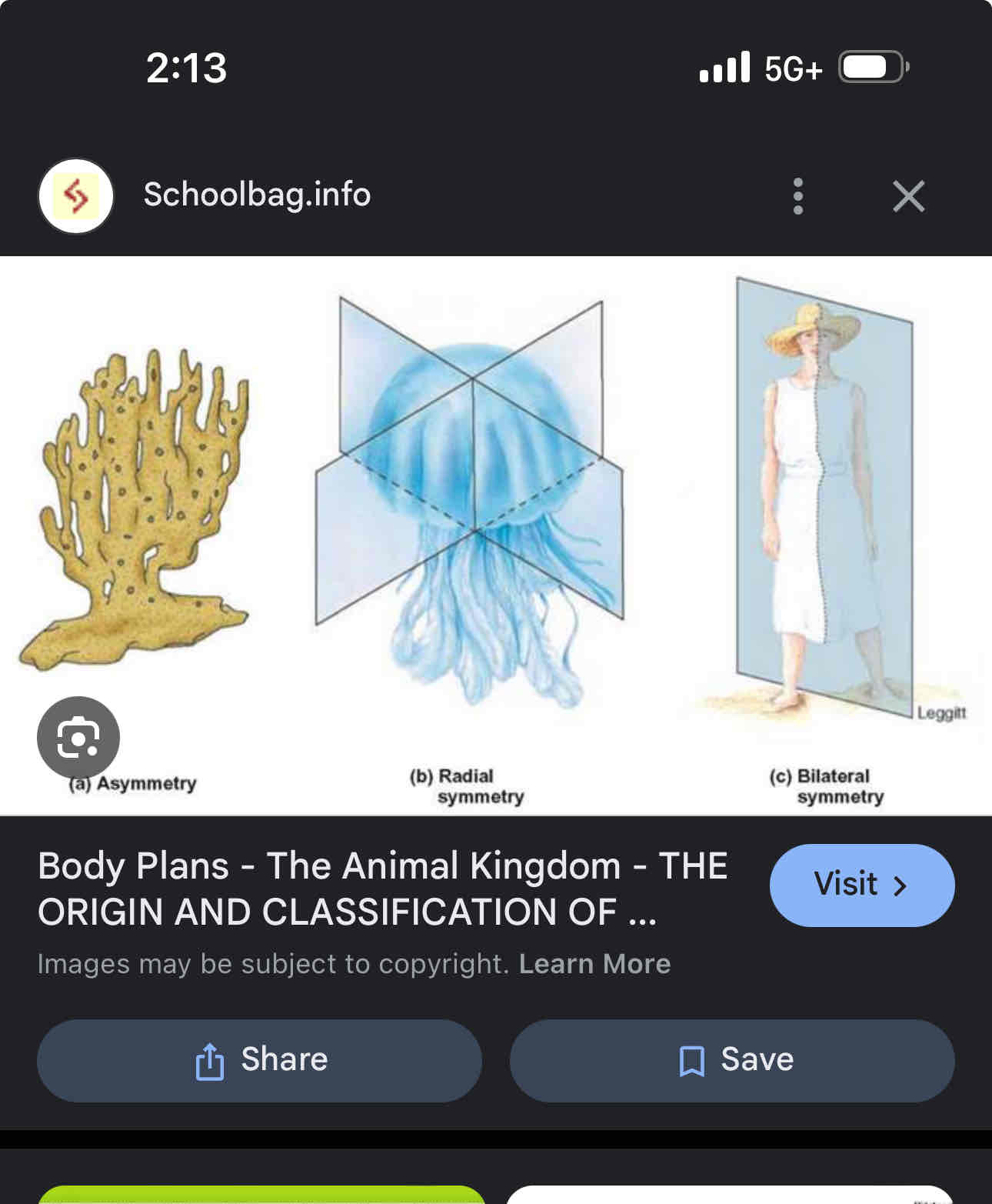
Animal body plan
Three types
Asymmetrical
Radial- one central axis
Bilateral symmetry two
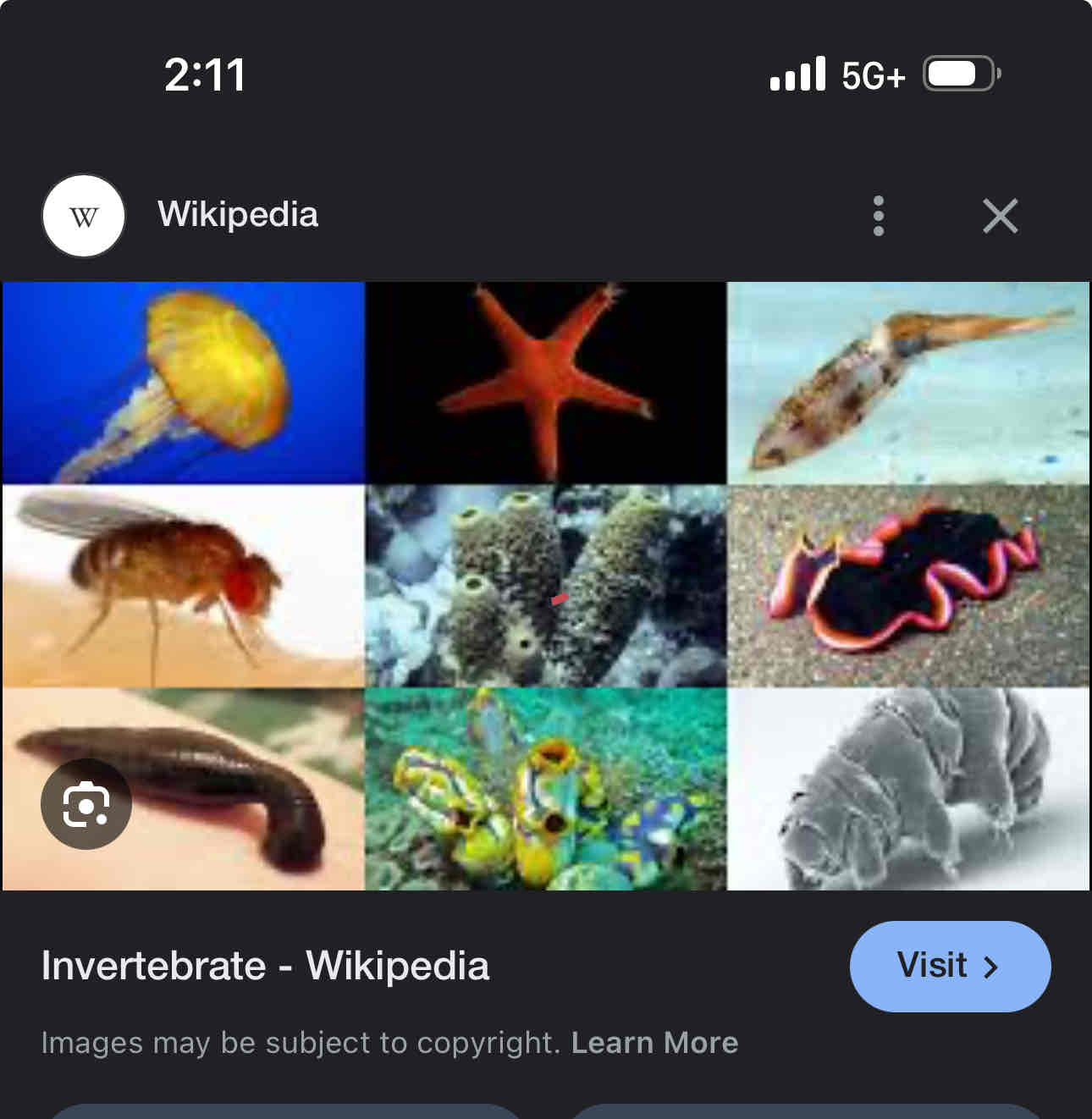
Invertebrate
Are animals without backbones
Vertebrates
Have a internal skeleton and backbone
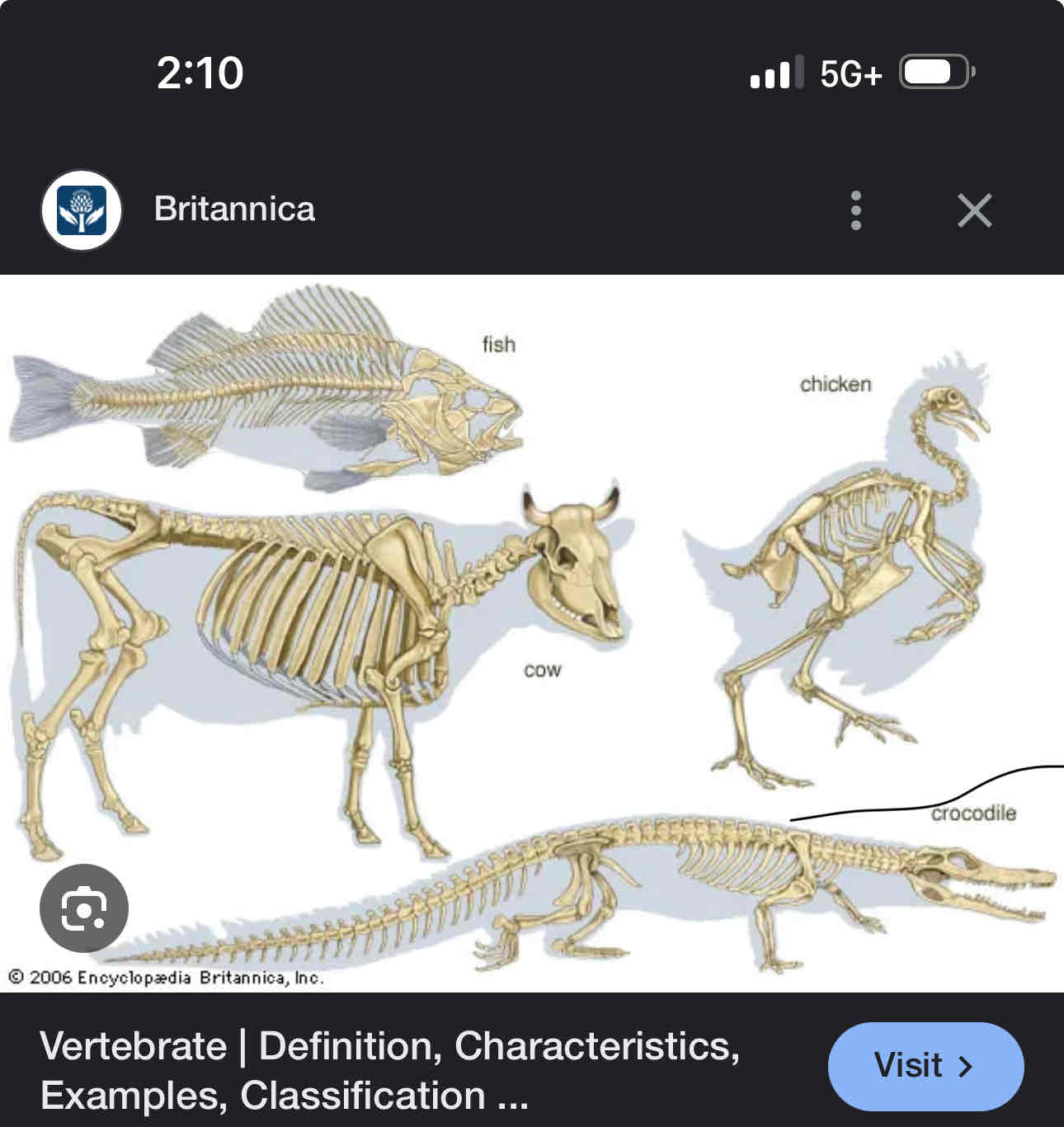
Five main groups of animals
Mammals, fish birds, reptiles and amphibians
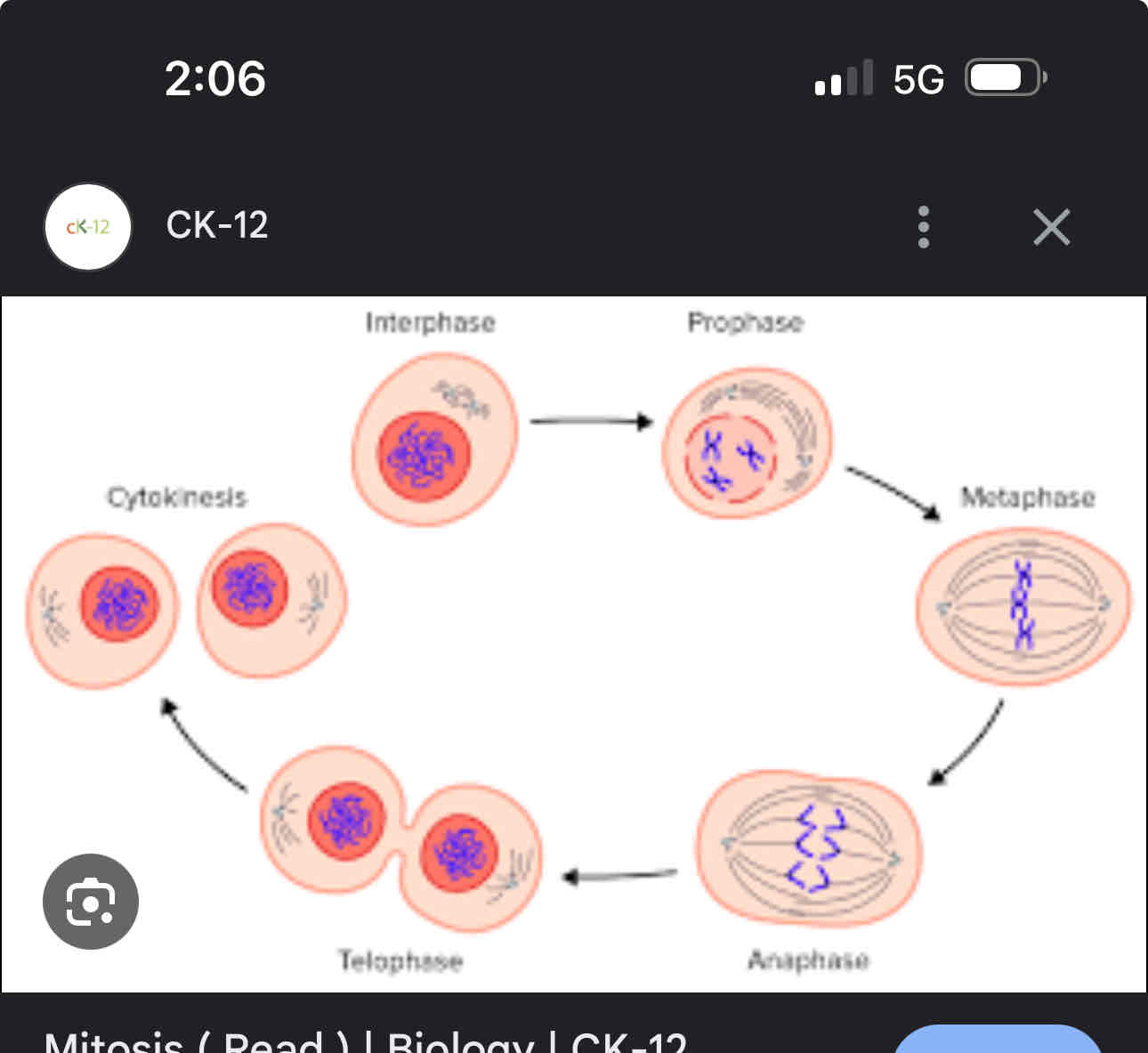
Mitosis stages and parts
Interphase G1- growth
Interphase G2- Reputation of DNA and growth
Prophase- Nuclear membrane dissolves nucleus dessolves, sister chromtids coil up and condense, spinal fibres form
Metaphase- sister chrometids lineup in the middle
Anaphase- sister chromotids pulled apart
Telophase- nucleuar membrane appear, cell divides into 2 new cells
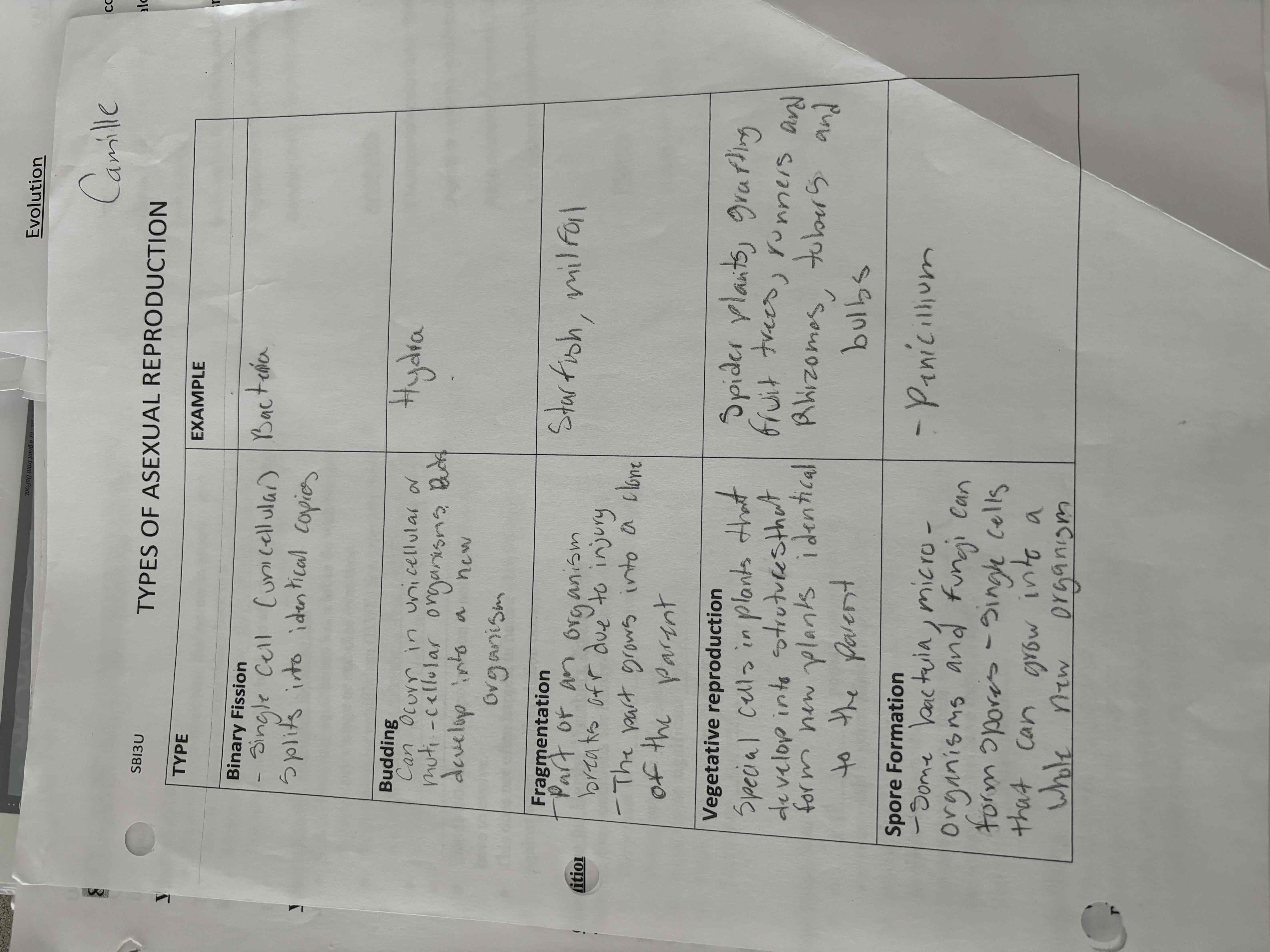
Asexual types
Binary fusion ,budding, fragmentation, vegetated reproduction, spore formation
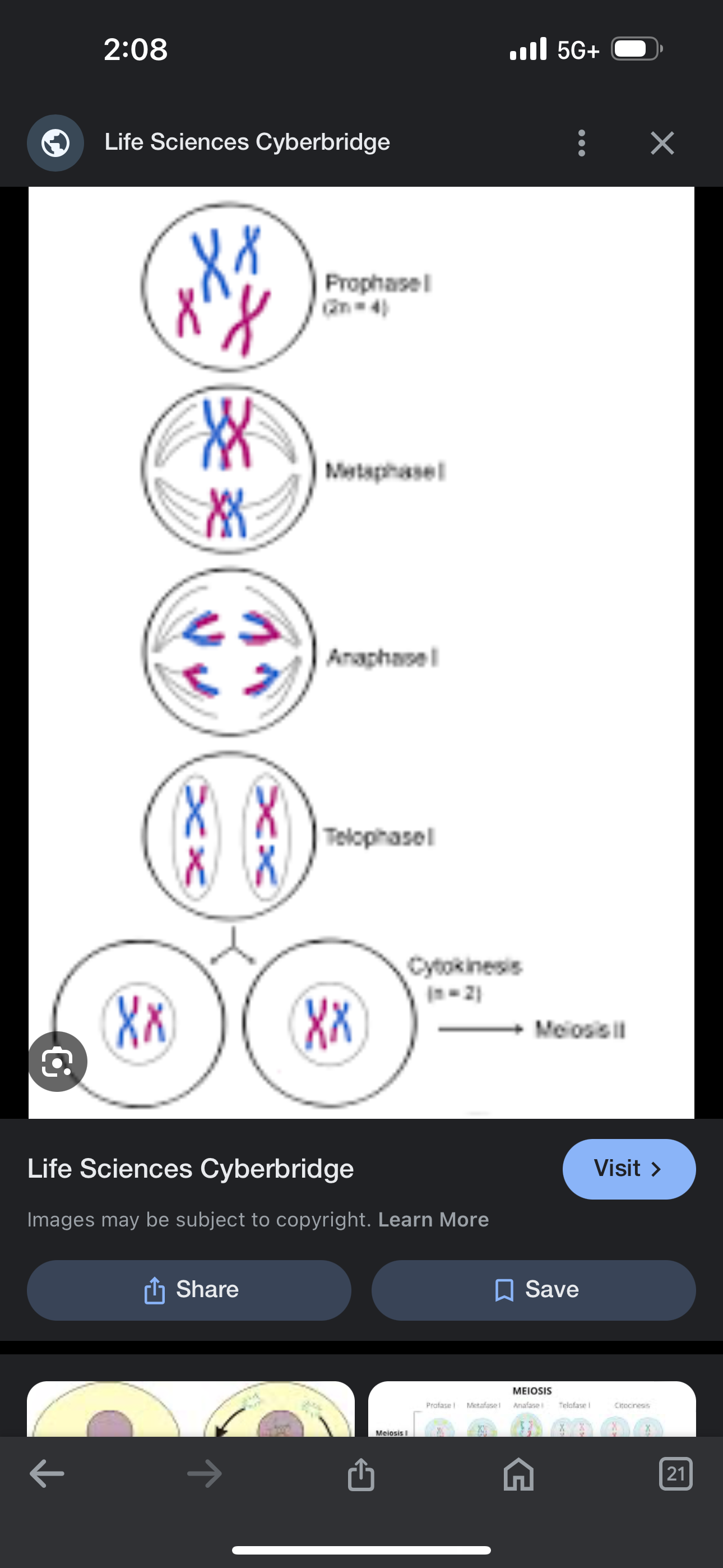
Meiosis stage 1
Prophase 1- chromosome thicken
Metaphase 1- tetrads migrate toward middle
Anaphase 1- homologous chromosomes separate and move towards opposite sides
Telophase 1- cells now haploid, nuclear membrane begins to form
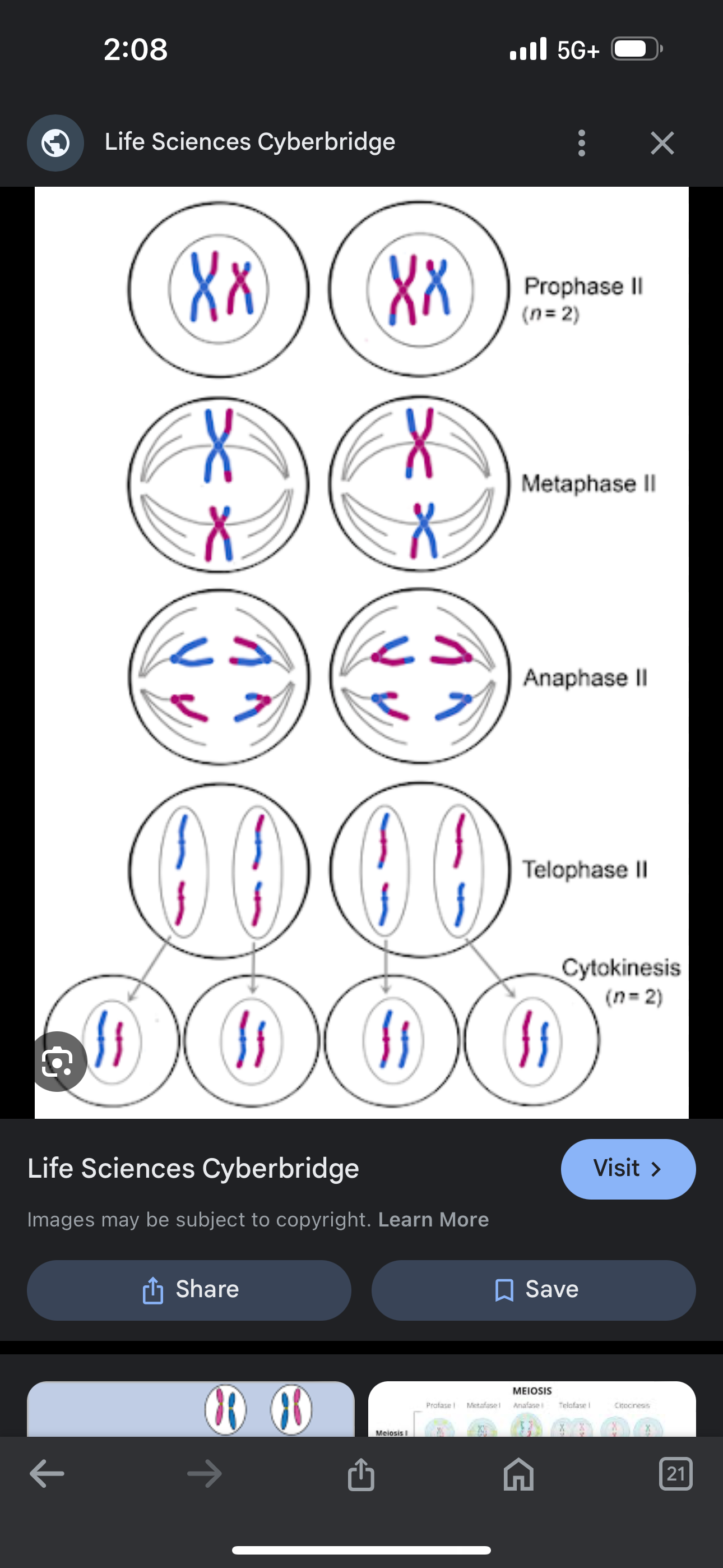
Meiosis stage 2
Prophase- nuclear membrane dissolves
Metaphase 2- chromosomes (2 chromotids) line up on the equator
Anaphase 2- nuclear membrane begins to form around the chromatids now called chromosomes
Telophase and cytokinesis- nuclear membrane form, 4 daughter cells produced
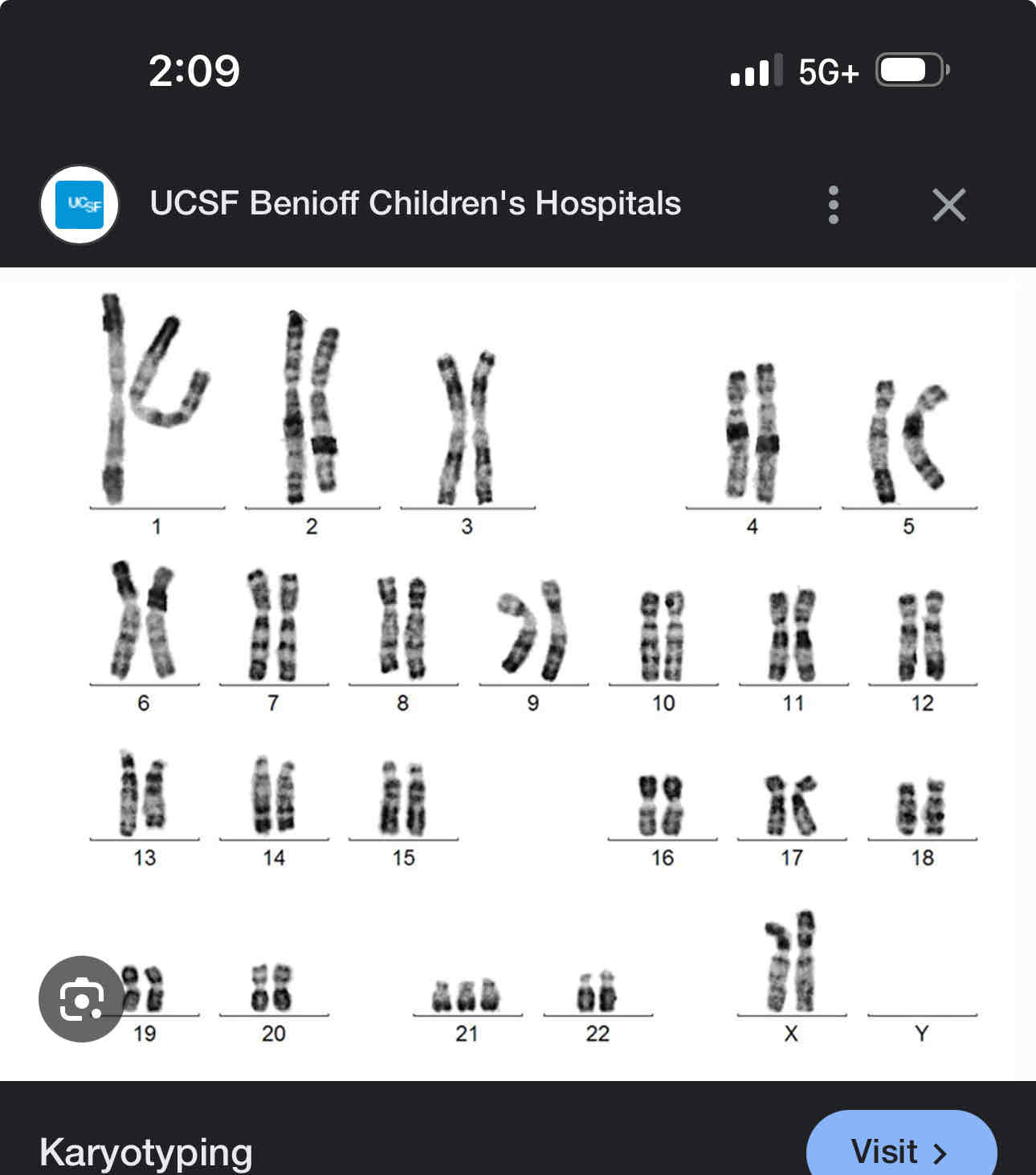
Karotypes
Are pictures of chromosomes that has been arranged according to number, size, shape or other characteristics
Genotype vs phenotypes
Genotype is the letter ex Rr
Phenotype is what it is so R=Red r=white
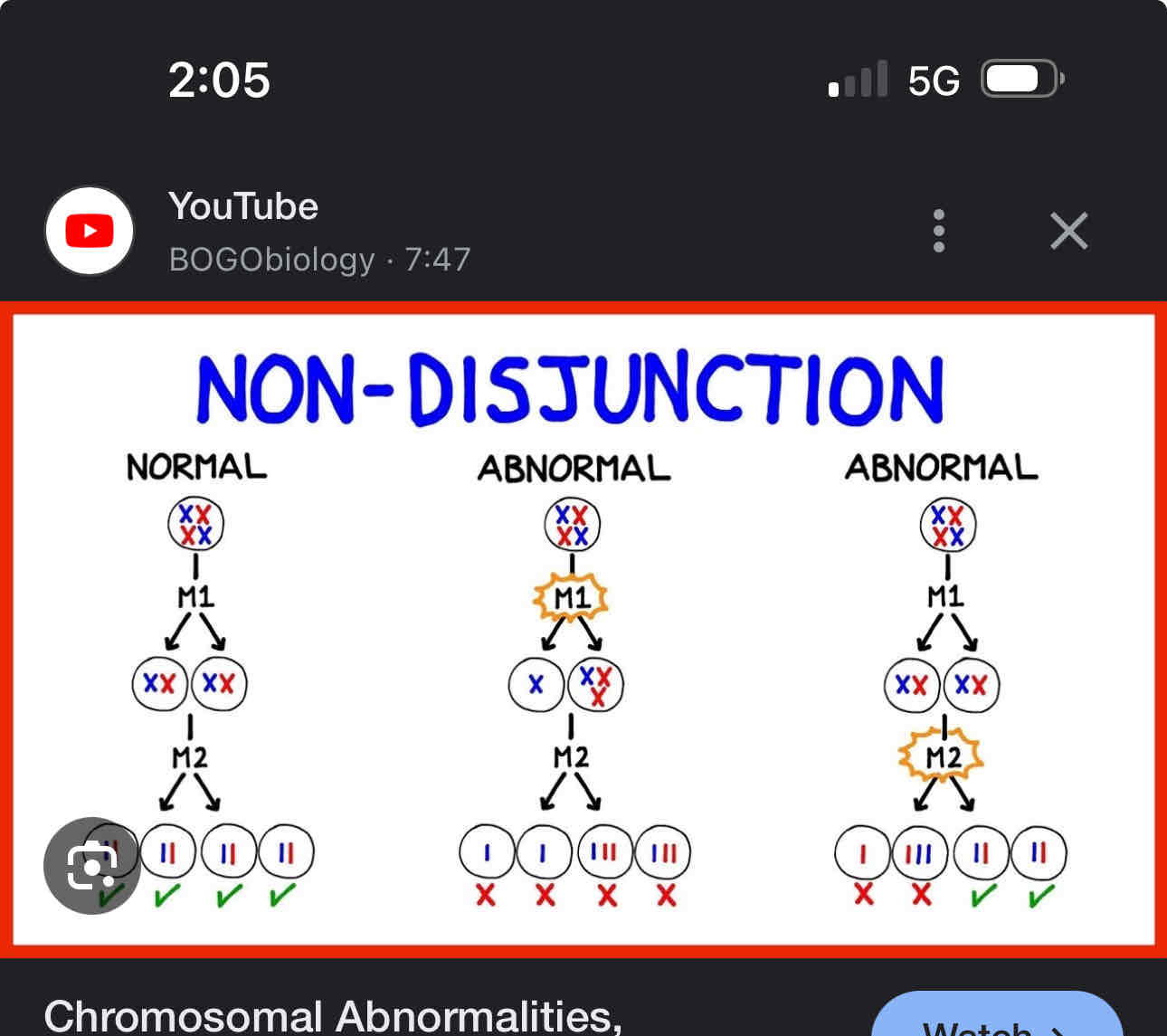
Non disjunction
Is the failure of chromosomes to separate during meiosis, resulting in an odd number of chromosomes ex
Monotomy, trisomy
Types of mutations
Turner’s syndrome, klinefelters syndrome, patau syndrome, Edgeworth syndrome,down syndrome
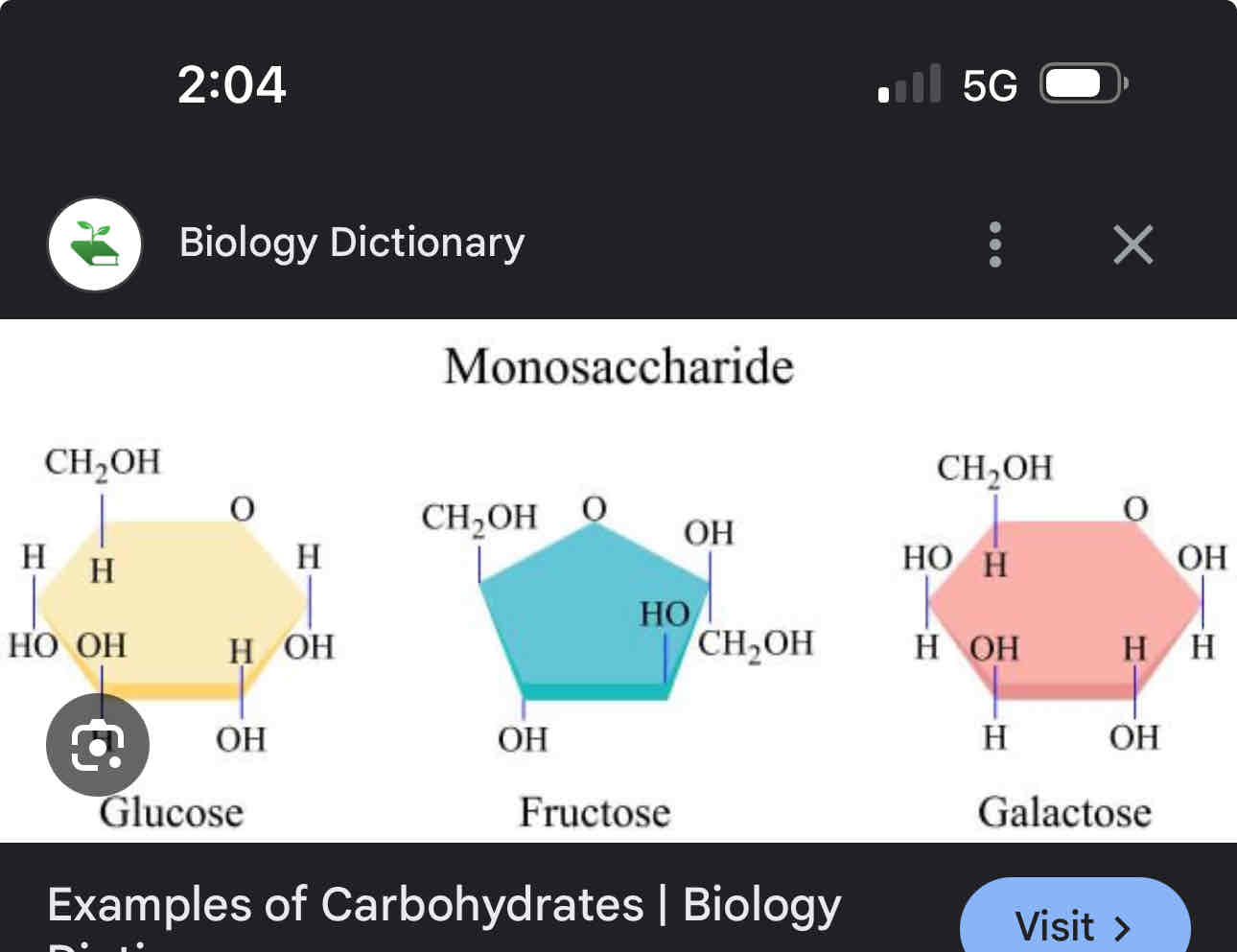
Carbohydrates
Monosaccharides, Diasccharides, polysaccharides
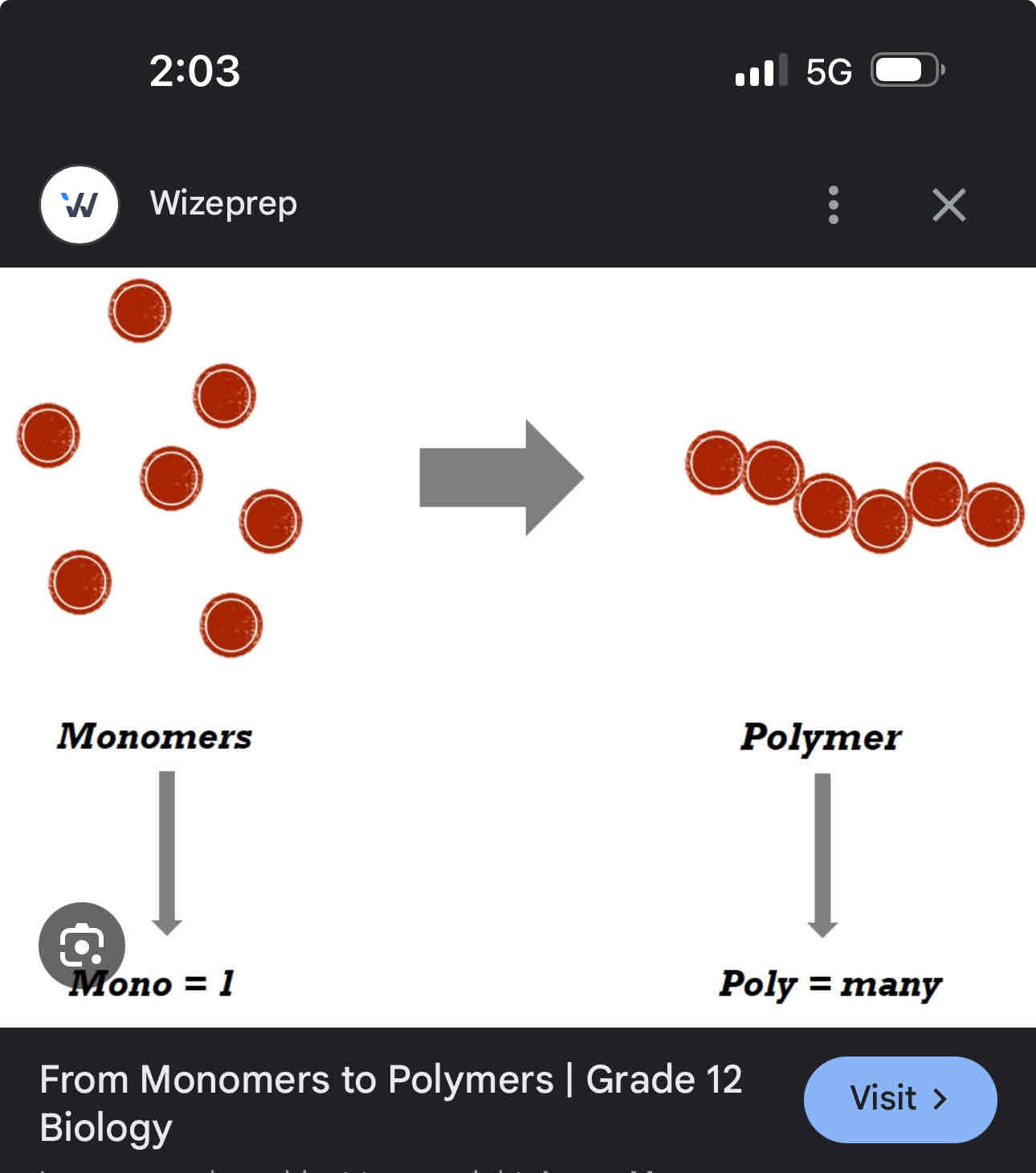
Monomers and polymers
Carbs, protein and fats are all polymers made up as several repeating units called monomers -monomers are simple building blocks of longer chain polymers
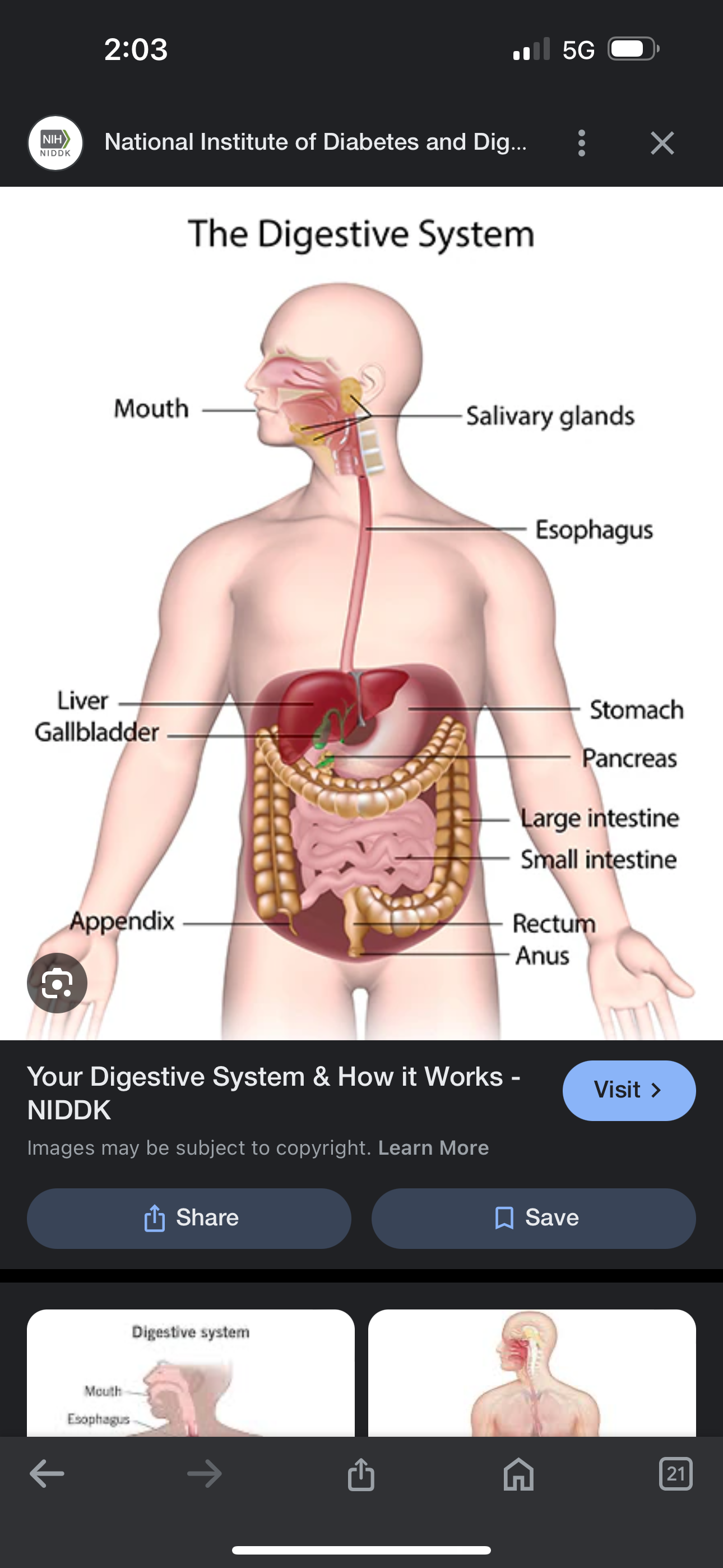
Digestive system
A system that breaks some food nutrients which are absorbed and transported by the cell circulatory system
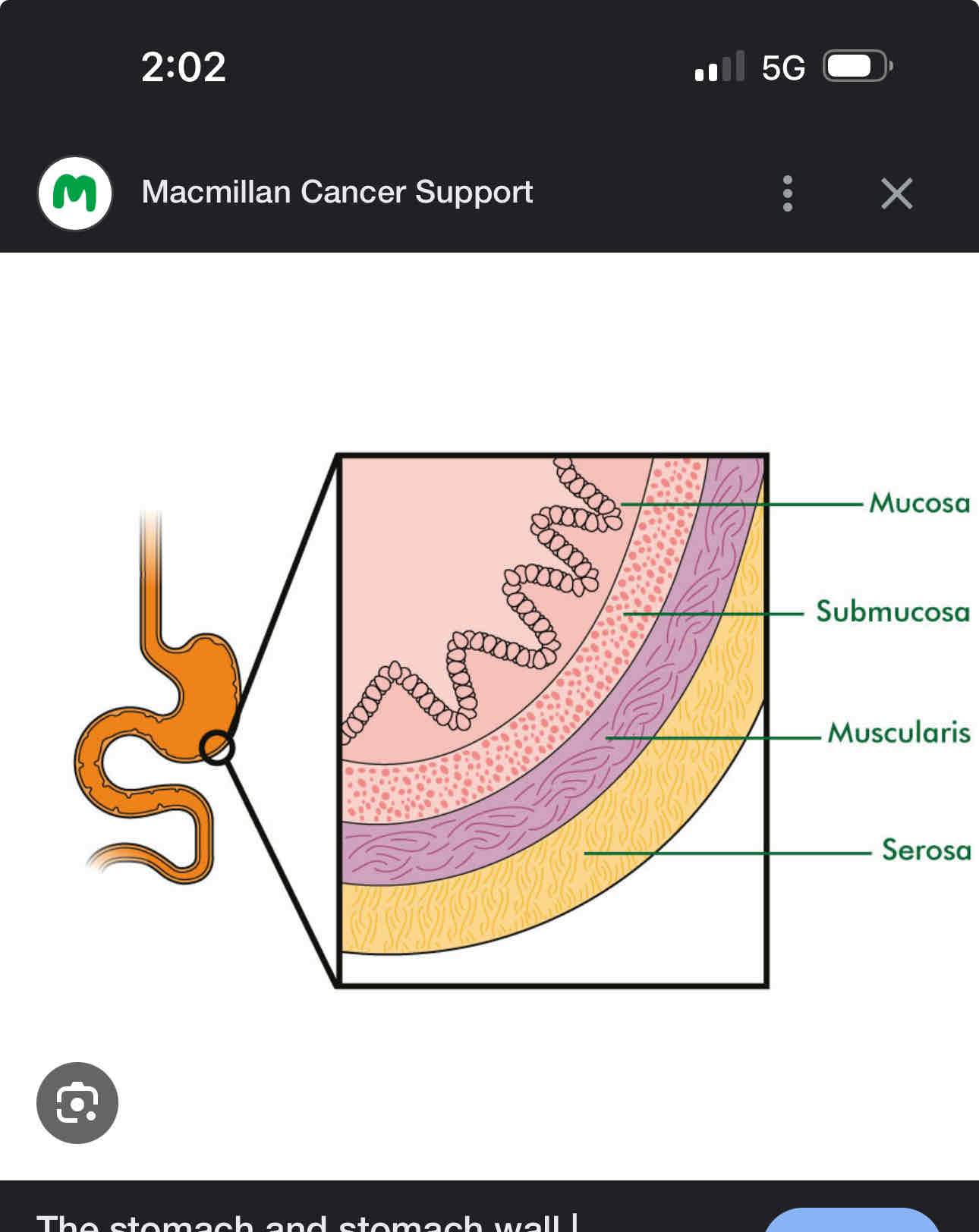
Four layers of the stomach
Mucosa- innermost layer
Submucosa- layer of connective tissues
Muscular- contains smooth muscle
Serosa-outermost layer hold stomach in place
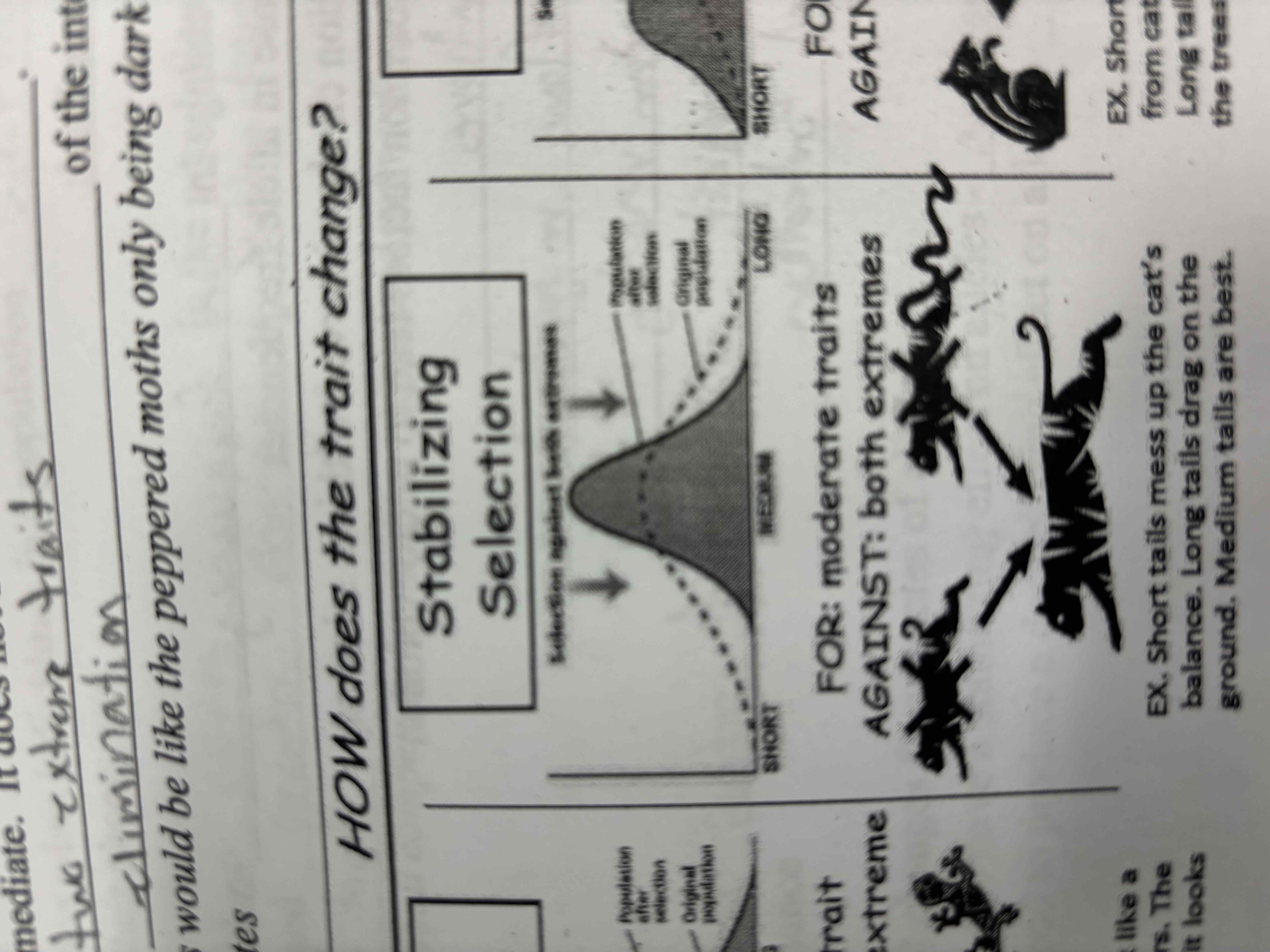
stabilizing selection
Stabilizing selection favours the average trait
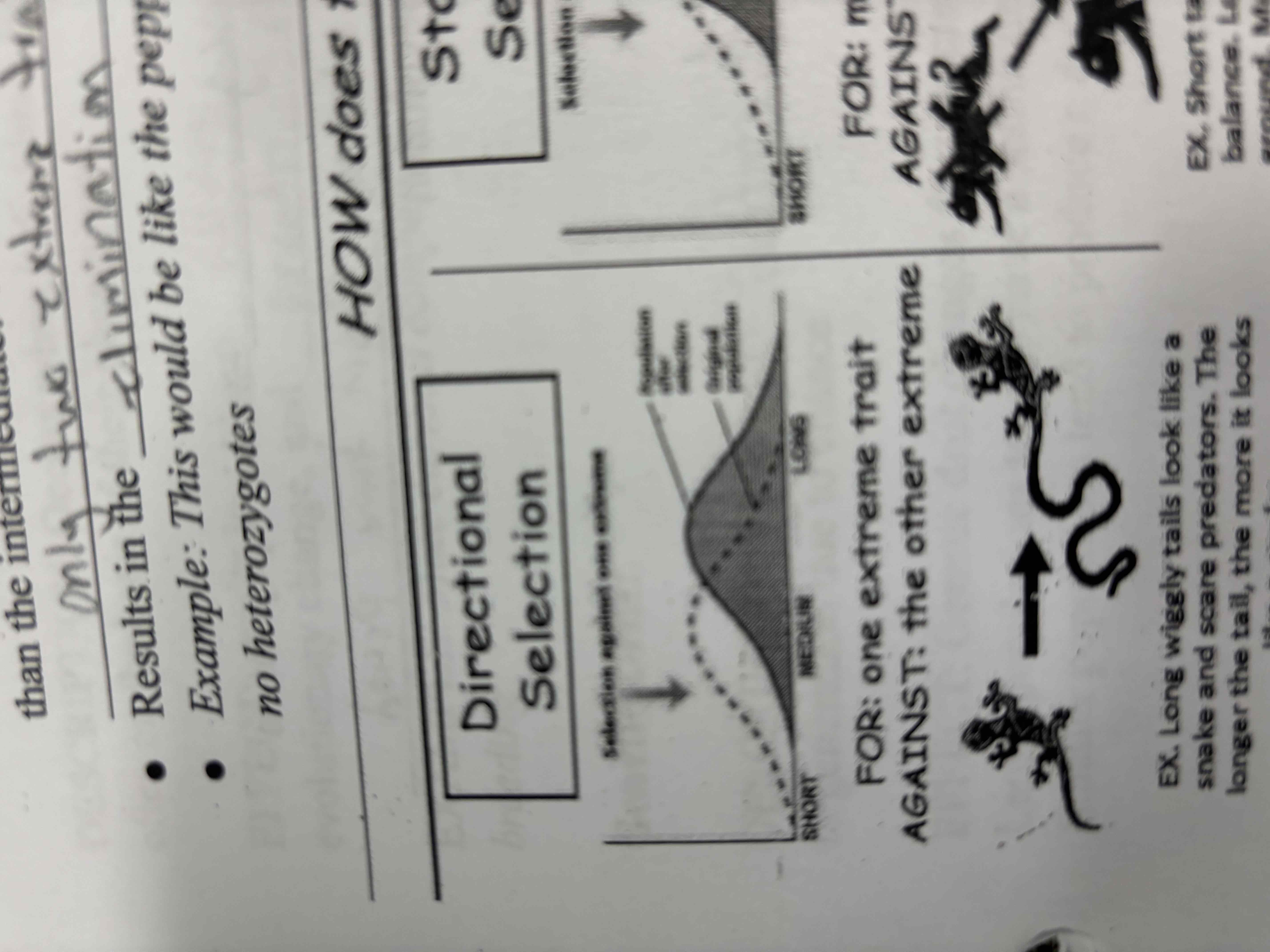
Directional selection
Favours one extreme over the another
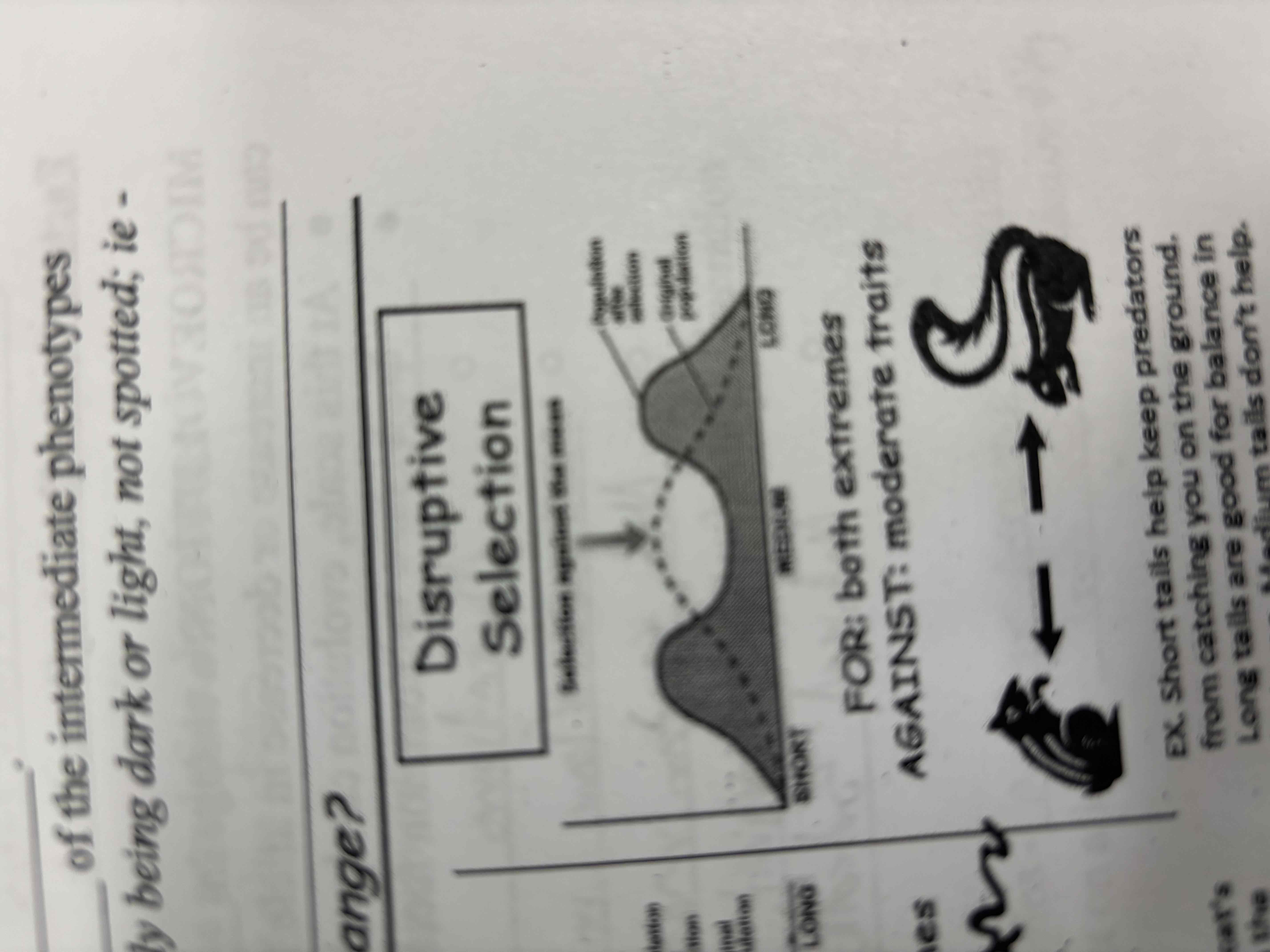
Disruptive selection
Favours the extreme of range
Bottleneck
A change in gene distribution that results from a rapid decrease in population size

Founder effect
A change in gene pool when a few individuals start a new population

Divergent evolution
A pattern of evolution in which species that were once similar to an ancestral species diverge or become distinct
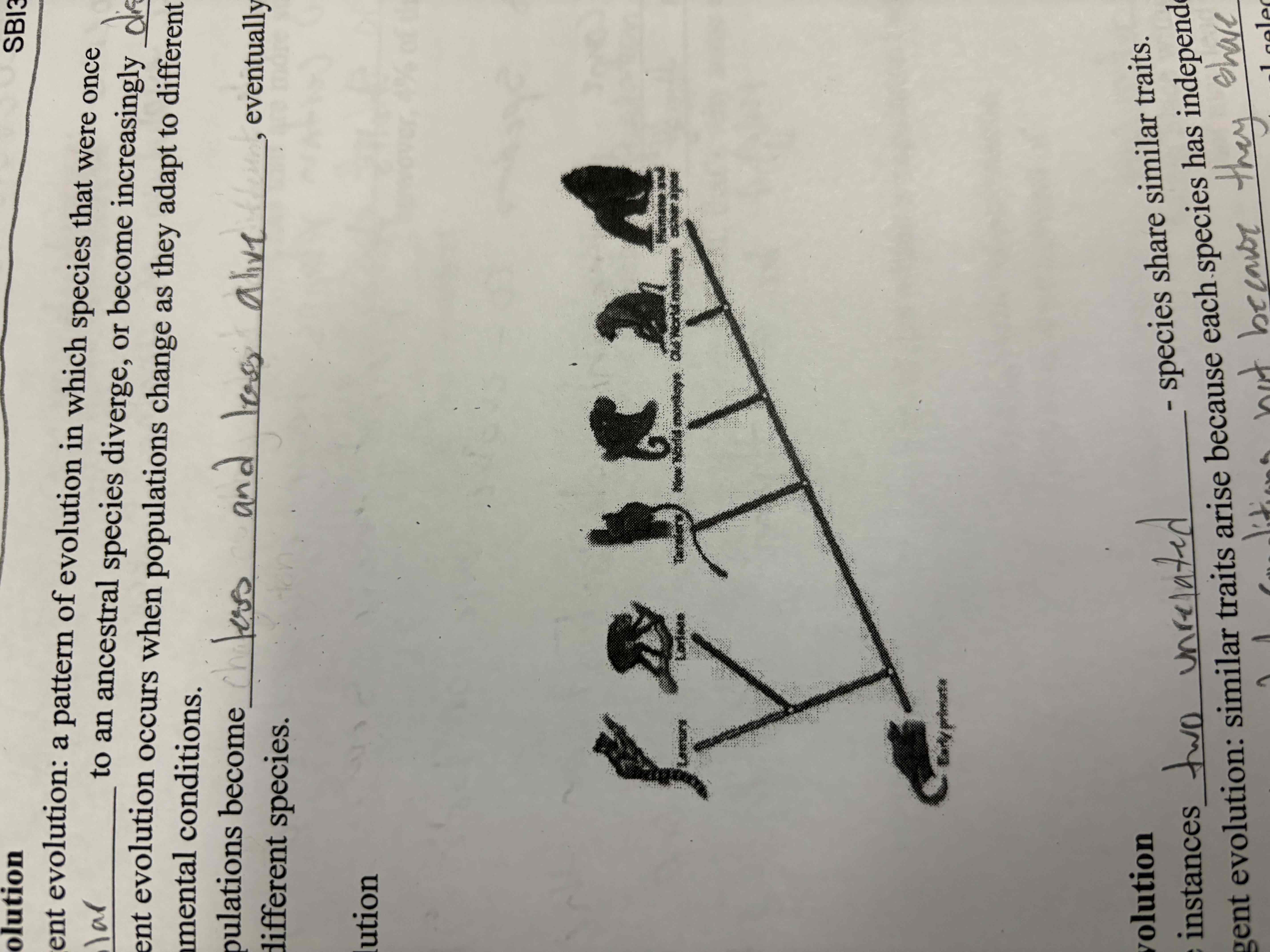
Convergent evolution
Two unrelated species share similar traits

Co evolution
A process in which one species is evolved in response to the evolution of another species
Adaptive radiation
how a species evolves to its environment while remaining very similar
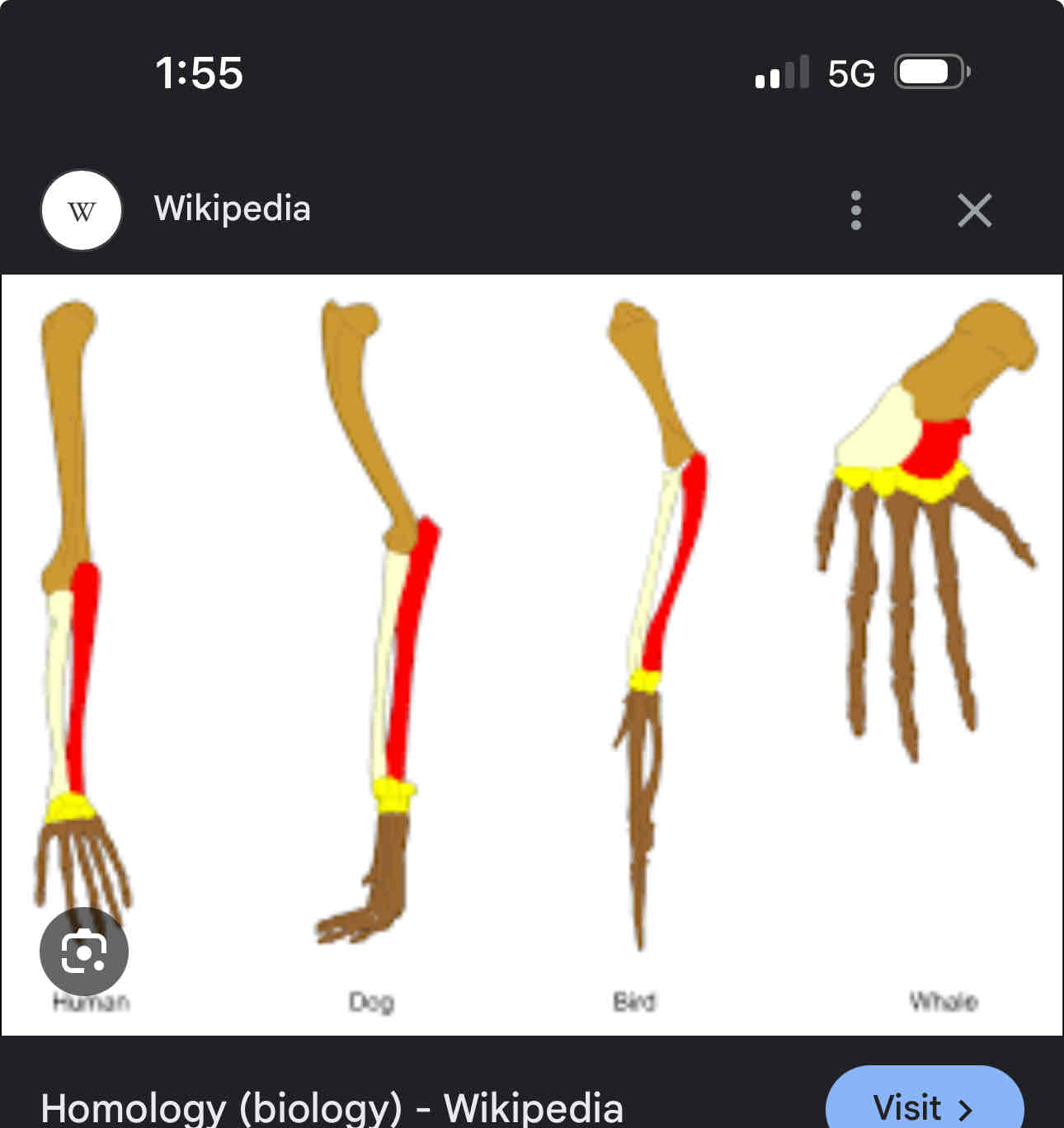
Homologous structures
Have similar structural element and origin but has different functions
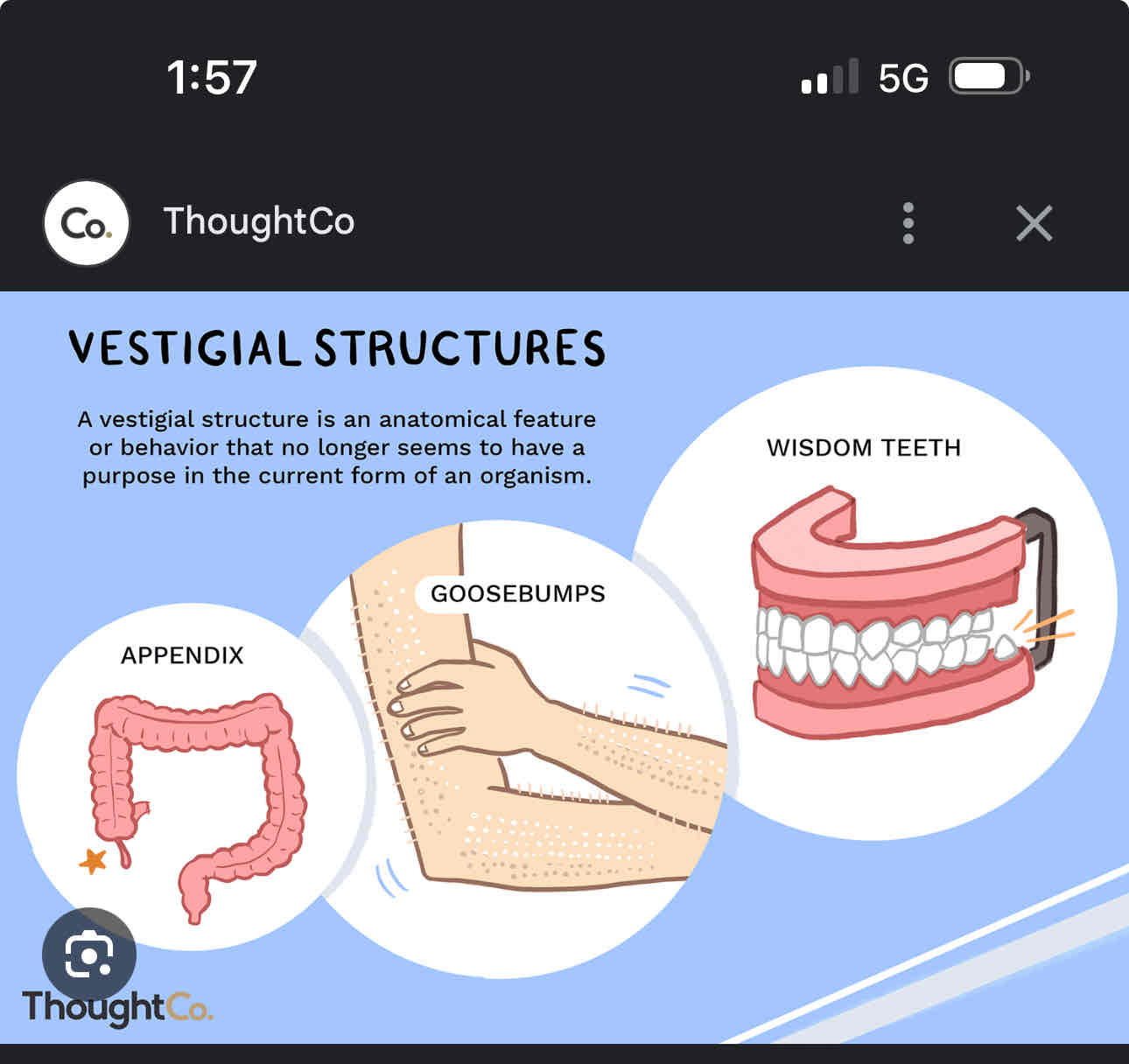
Vestigial structures
Structure that once had a use but now is less functional or useful
Analogous structures
Organisms that do not have a common evolutionary origin but perform similar functions

Circulatory system
moves oxygen, nutrients and hormones to your body's cells to use for energy, growth and repair
Fossil evidence
Provides a record of how creature evolved and how this process can be represented by a tree of life. Showing that all species are related to each other
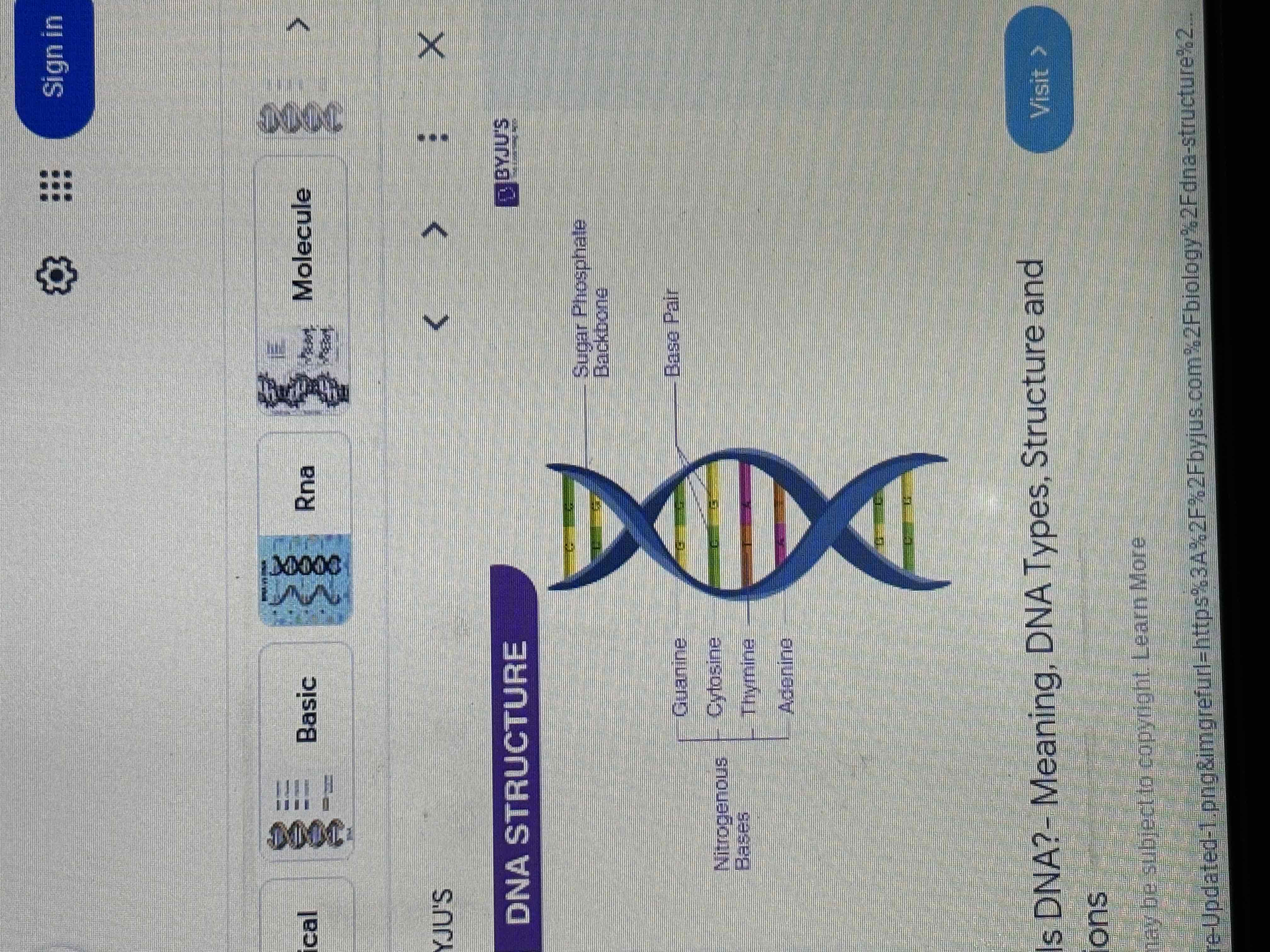
DNA structure
A dna molecule consists of two long polynucleotide chains composed of 4 types of nucleotide subunits
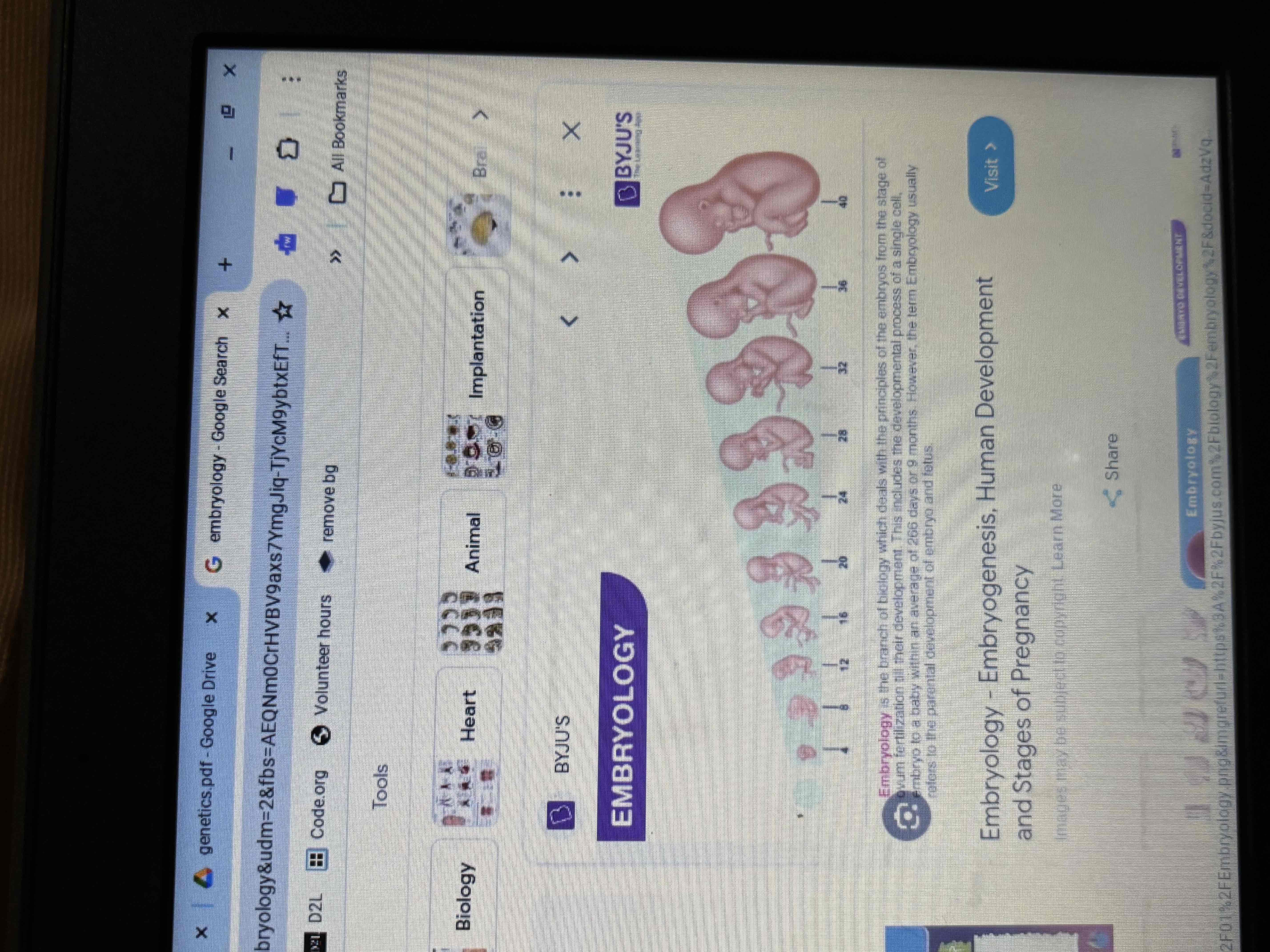
Embryology
The study of formation and development of an embryo and fetus
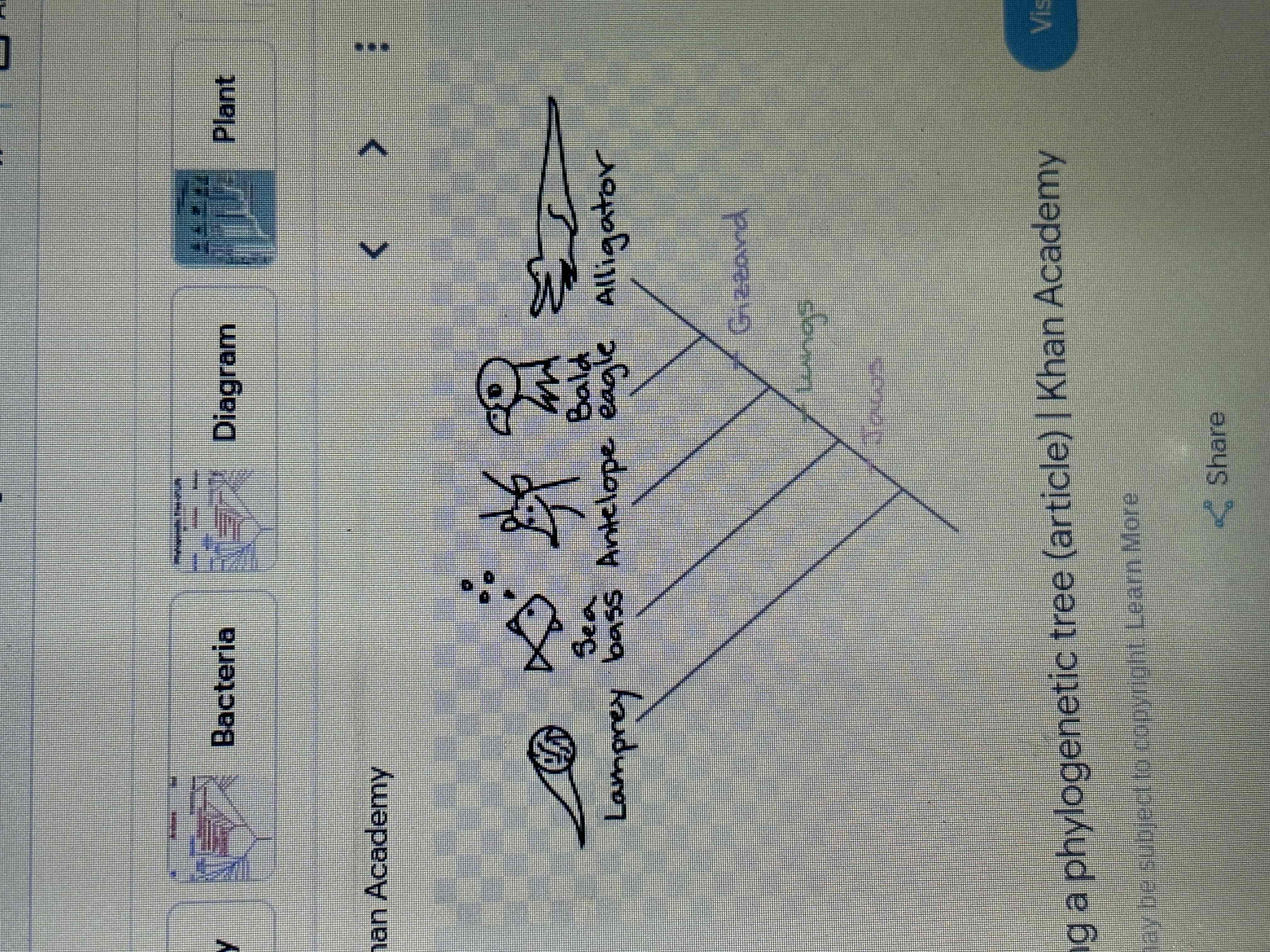
Plylogentic tree and clades
Is a diagram that depicts the lines of evolutionary descent of different species, organisms or genes from a common ancestor
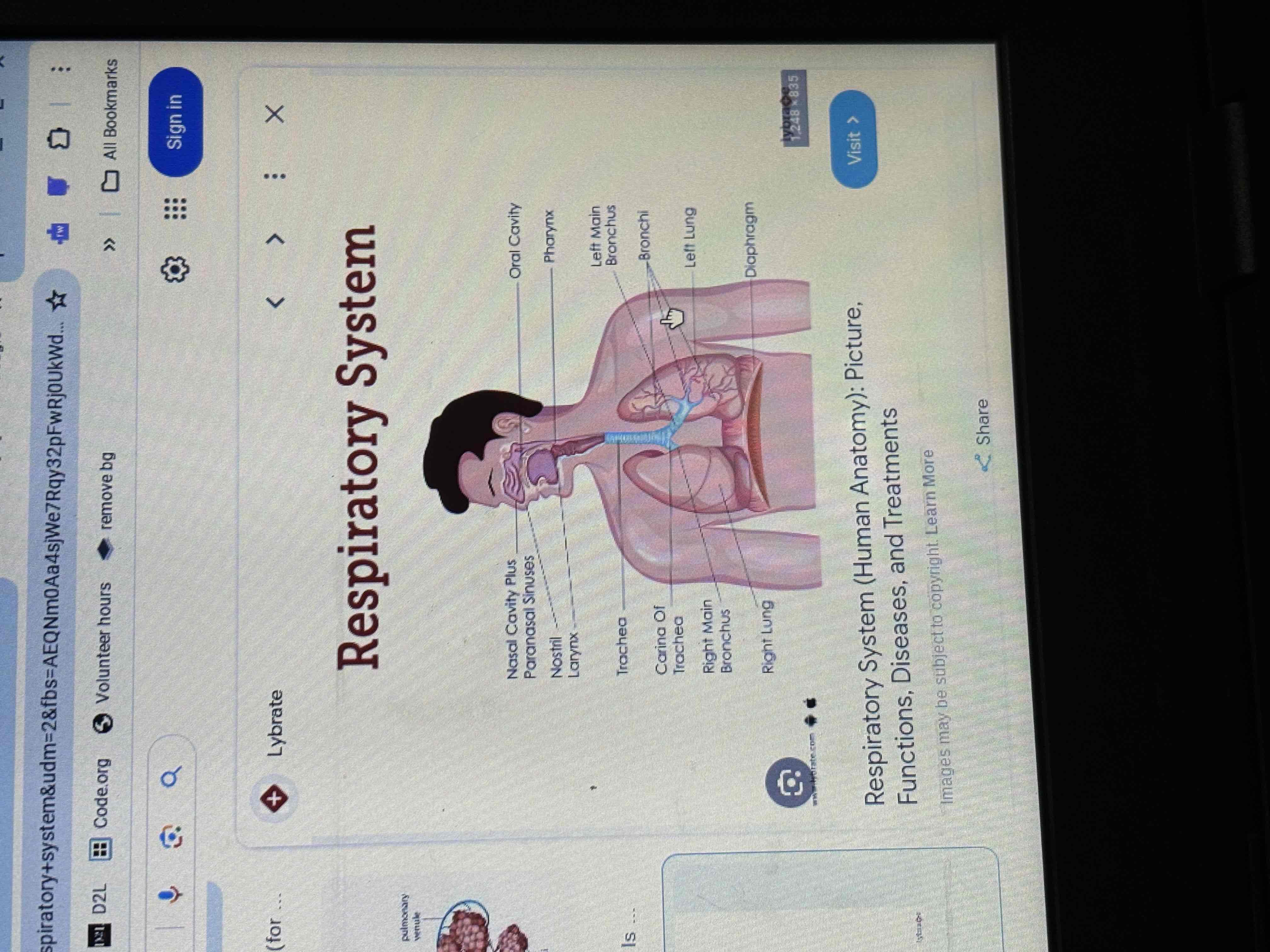
respiratory system
It includes your lungs, nose, mouth and the tube like structures that connect them
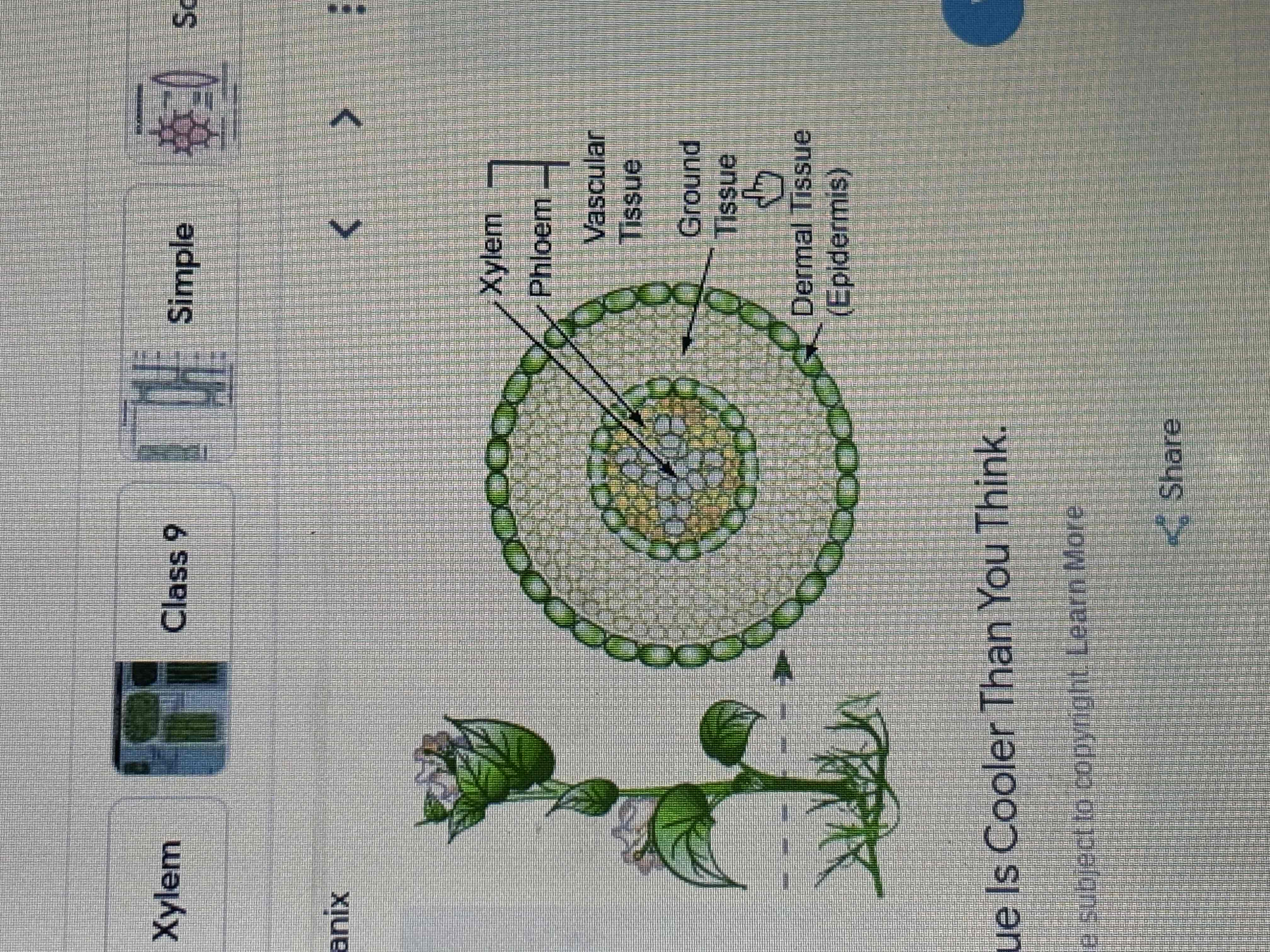
Plant tissue
4 type of tissue
Meristematic tissue-cell growth
Dermal tissue- outermost tissue (protection)
Ground tissue- innermost layer( nutrients stored)
Vascular tissue- cells involves on transporting water and nutrients though the plant
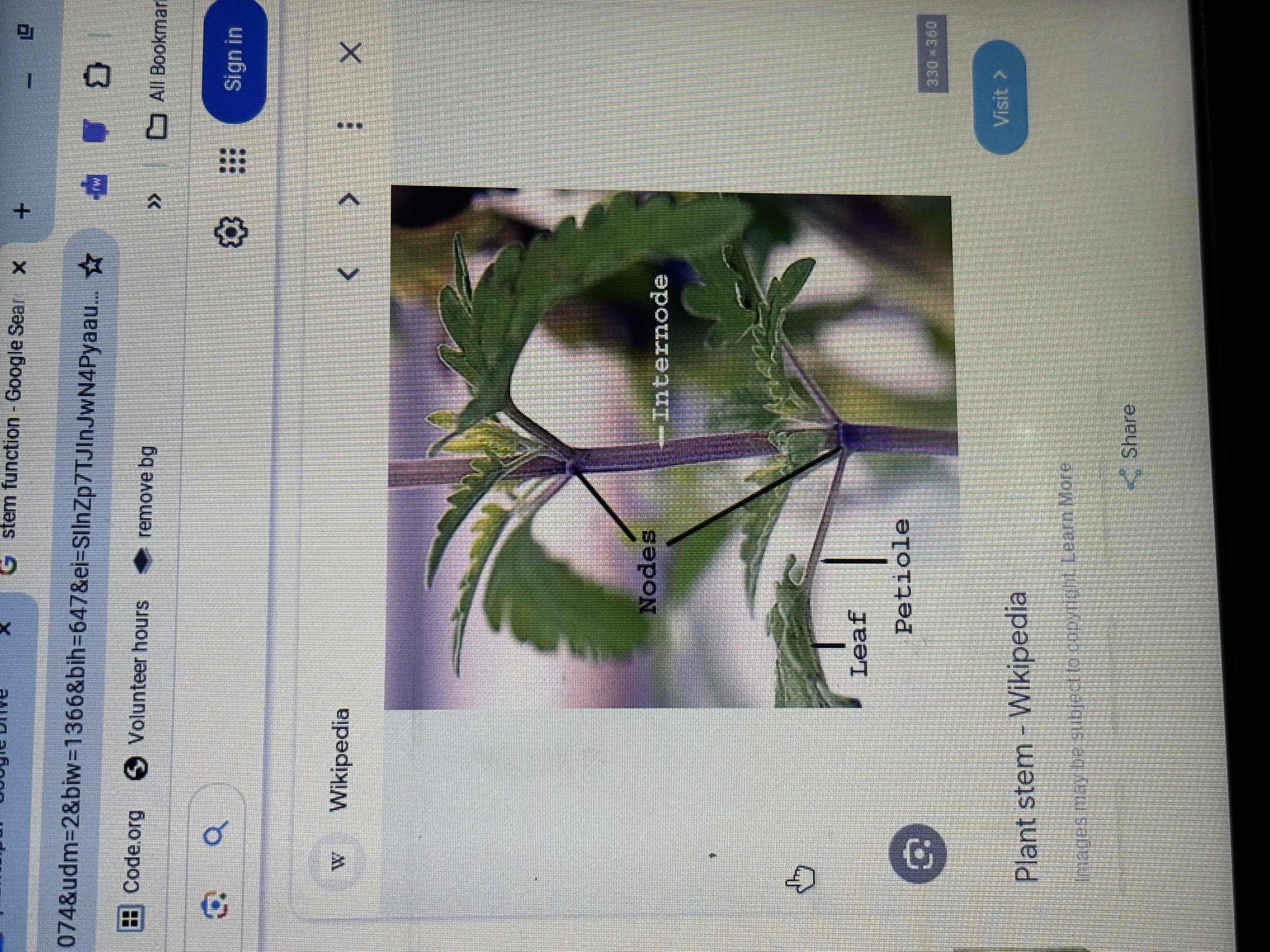
Stem function
Supports and attachments for leaves, flowers and fruits
Transport of material between the root and the leaves
Nutrients storage
Plant growth
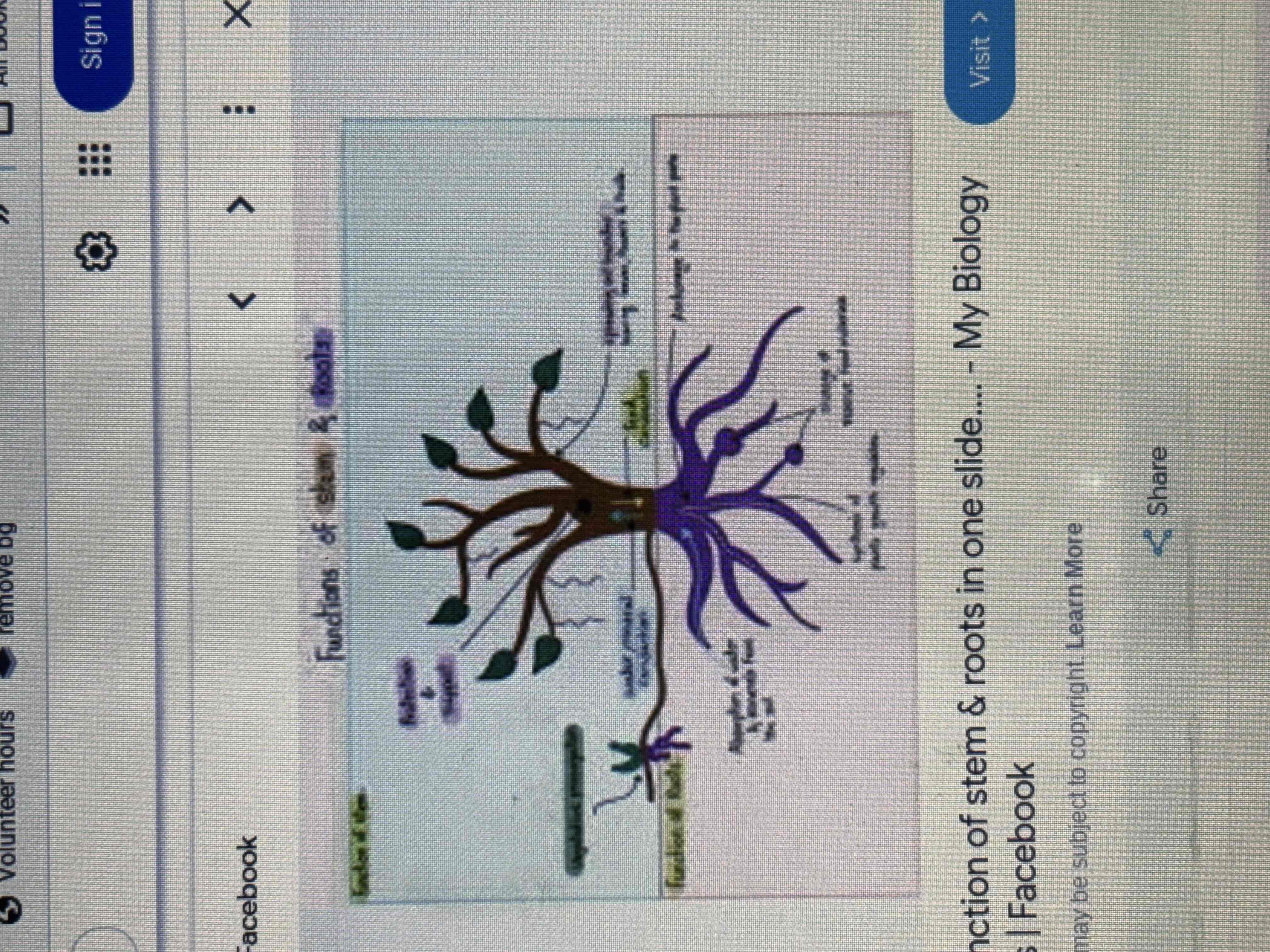
Roots function
1.Anchor of the plant
Absorb water and inorganic nutrients
Storage of water
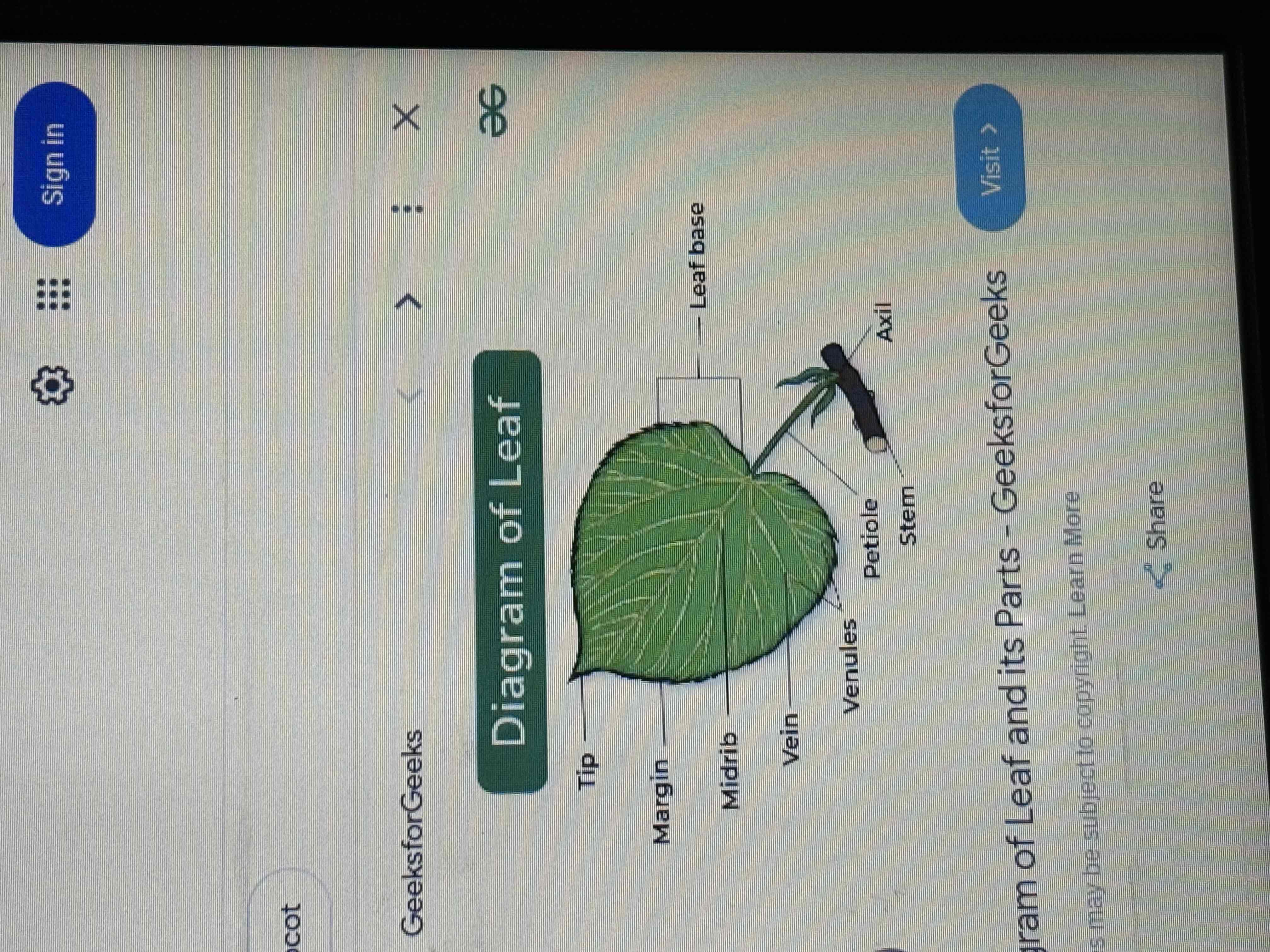
Leaf diagram
Consist of a tip, margin, midrib, vein, venules, petiole, steam, axil and leaf base
Tropisms
A phenomenon indicating the growth or turning point of an organism usually a plant in respond to an environment stimulus
Total lung capacity
The total amount of air that can be in your lungs
Tidal volume
Normal amount of air that can be exhaled
Vital capacity
Maximum amount of air that can be exhaled
Inspiratory reserve volume
Extra intake of air after max inhalation
Expiratory reserve volume
Extra exhalation of air after max exhalation
Residual volume
Little bit of air left over in your long after a big exhalation