Macroeconomics Exam One Study Set
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
economics
the study of how society manages its scarce resources
what is scarcity?
idea that we have unlimited wants and limited resources
Two Branches of Econ
Mirco & Macro
Microeconomics
individuals making decisions
Macroeconomics
economy as a whole or group decision making
How many econ principles are there?
8 (well that we go over)
1. People face trade offs
since every resource is scarce and not enough time
2. Cost of something is what you give up to get it
Opportunity cost: the value of the best alternative that you give up when you make a choice
3. Rational people think at the margin
A rational decision-maker takes action if and only if the marginal benefit of the action exceeds the marginal cost.
4. People respond to incentives
Behavior changes when costs or benefits change. (attendance policy)
5. Trade can make people better off
people specialize in different goods and services meaning that someone can make it possibly quicker and more efficiently so it makes more sense to trade something the other person may be able to do better
6. Markets are usually a good way to organize economic activity
under markets we have decisions to decide what to buy, what to sell, how much to sell for, etc.
7. Government can sometimes improve market outcomes
provide polices to provide stabilization
8. The 3 most important Marco variables are
GDP
Inflation
Unemployment
Father of Economics
Adam Smith
Model
Simplified version of the world
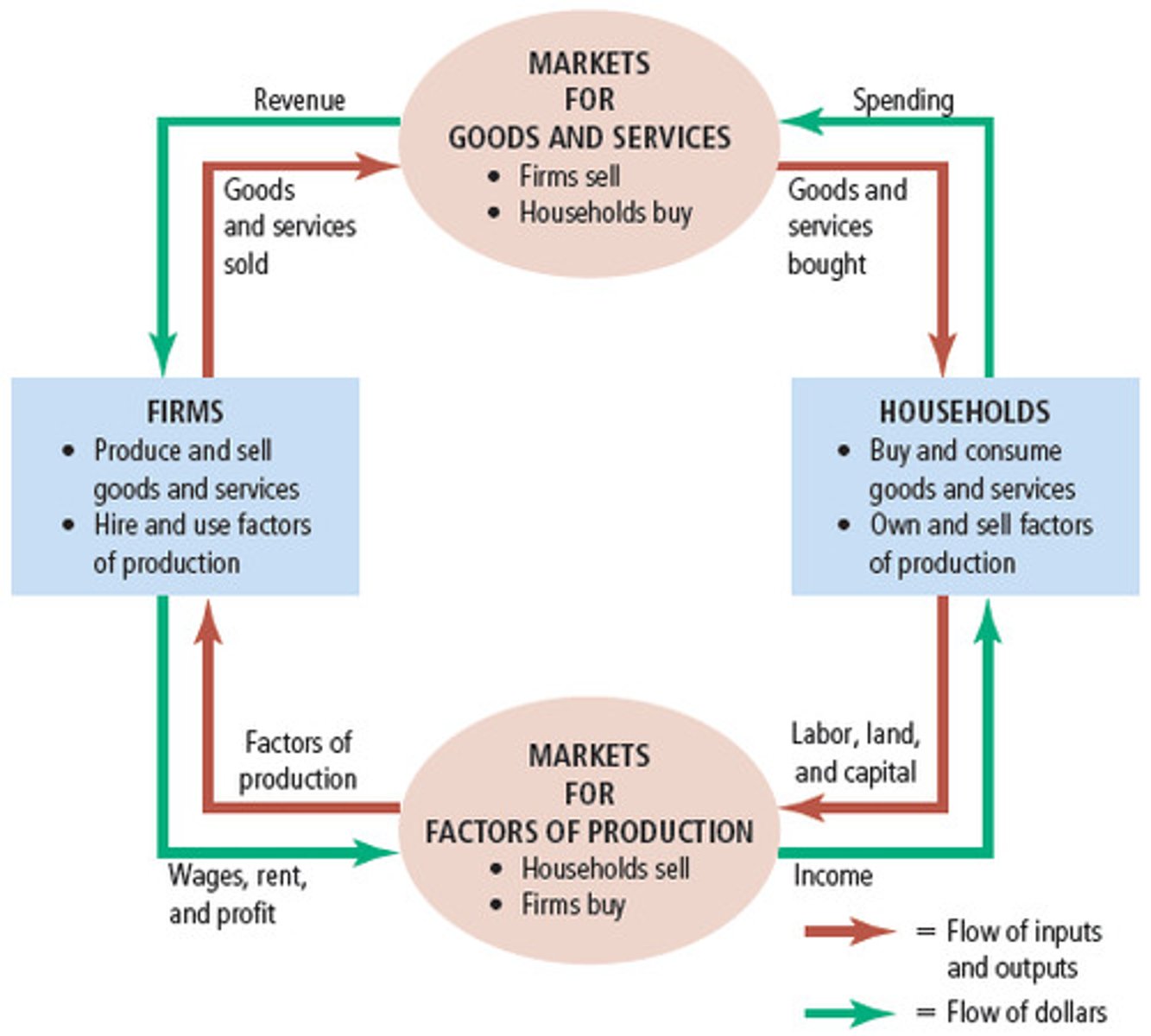
Circular Flow Diagram
shows firms & households and how they trade
Comparative Advantage
the ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another producer
Absolute Advantage
the ability to produce a good using fewer inputs than another producer
Why economists disagree?
Differences in positive statements and normative statements
Positive Statements is
testable
Normative Statements is
not testable (opinion)
GDP
the market value of all final goods & services produced within a country in a given time period
GDP equation
Y = C + I + G + NX
Y=
GDP
C=
Consumption
I=
Investment
G=
government spending
NX=
net exports (exports-imports)
Do imports effect GDP?
No they do not increase or decrease GDP
GDP deflator
Nominal GDP/Real GDP x 100
inflation deflator
( deflator current - deflator previous ) / ( deflator previous ) x 100
Inflation
general rise in overall prices
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
measure of the overall cost of goods & services bought by a typical consumer
5 Steps to Calculate CPI (inflation)
1. Fix the Basket
2. Find Prices (things in basket)
3. Compute cost of the basket
4. Chose a base year & compute CPI
5. Compute inflation rate
inflation rate equation
CPI Year 2 - CPI Year 1/ CPI Year 1 x 100
CPI equation
100 x (cost of basket in current year/cost of basket in base year)
Shadow Inflation
occurs when prices stay the same but the quality of products declines
2 types of unemployment
Cyclical & Natural Rate of Unemployment
What does it mean to be unemployed?
out of work and actively looking for a job
Categories to measure unemployment
Employed: paid, work with family, temporary absences
Unemployed: not employed, available for a job, looked for a job in the last 4 weeks
Not in labor force: not employed & not unemployed (students & elderly people)
unemployment rate formula
unemployed/labor force x 100
labor force formula
employed + unemployed
labor force participation rate formula
labor force/adult population x 100
real gdp
GDP adjusted for inflation
nominal gdp
the production of goods and services valued at current prices
marginal benefit
the additional benefit to a consumer from consuming one more unit of a good or service
marginal cost
the cost of producing one more unit of a good
final goods
goods and services that have been purchased for final use and not for resale or further processing or manufacturing
intermediate goods
goods used in the production of final goods
can one person have comparative advantage for both goods?
No
A person can have absolute advantage in producing both goods
true
Specialization and trade based on comparative advantage increase total output and make everyone better off.
True
CPI tends to overstate inflation by about 1%.
True
Due to biases (quality change, new goods, substitution), CPI overstates inflation by about 1%.
Household production is included in GDP
False
Household production (like cooking at home) is not bought or sold in markets, so it is excluded.
Black market activity is included in GDP.
False
Black market activity is illegal and unreported, so it is not counted in GDP.
New housing is counted as consumption
False
New housing is counted as investment, not consumption.
Stocks and bonds are considered investment in GDP
False
Stocks and bonds are financial assets and do not represent current production
Marginal Principle
states that decisions should be made by comparing marginal benefits (MB) and marginal costs (MC). The rational rule is to continue an activity until MC exceeds MB
Explain how the Circular Flow Diagram illustrates the relationship between households, firms, factor markets, and product markets. Include how income equals expenditure.
● Households supply labor and other factors of production
● Firms hire factors and produce goods and services
● Income flows to households through wages, rent, and profit
Spending flows to firms through product markets
Explain the three biases that cause the CPI to overstate the cost of living and why they matter for measuring inflation.
● Quality improvements: Better products raise prices but also raise value
● New goods bias: CPI is slow to reflect new products
● Substitution bias: Consumers substitute cheaper goods, but CPI assumes a fixed basket
● These biases cause CPI to overstate inflation
Explain the difference between final goods and intermediate goods, and why only final goods are counted in GDP
Final goods are fully processed and ready for consumption, while intermediate goods are inputs used to produce other goods. Only final goods are counted in GDP to avoid double counting the value of inputs already included in final products
Describe the difference between nominal GDP and real GDP and explain why economists prefer real GDP
Nominal GDP measures output using current prices, while real GDP measures output using base-year prices. Economists prefer real GDP because it removes the effects of inflation and better reflects true changes in production.
What is opportunity cost, and why is it central to economic decision-making?
Opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative that must be given up when a choice is made. It is central to economics because all decisions involve trade-offs due to scarcity.