Polymerase Chain Reaction
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
Polymerase Chain Reaction or PCR is a laboratory procedure performed to ___ and ___ a ___ for genomic sequencing
detect, amplify, specific gene region
This process utilizes short DNA sequences or fragments called ___ complementary to the target region
primers
The amplification is initiated by a ___ wherein ___ to create new copies
Taq polymerase, primers and free nucleotides attach to the target region
target gene (___) will be amplified to serve as a ___ for species identification
Cytochrome C Oxidase Subunit 1/C01, molecular marker
The process of replicating the DNA in vitro was made possible by the discovery of the ___ by ___ and ___
structure of DNA, James Watson, Francis Crick
The process of PCR is a perfect example of ___
biomimicry
PCR, as a laboratory process, can be divided into two major parts:
preparation of the reaction cocktail
amplification procedure
The fine adjustment of these components is a process known as ___
optimization
T or F: PCR is identical to DNA replication
False, similar but not identical
DNA replication versus PCR
DNA replication ⇒ replicates the entire genome (all the genetic composition of the material)
PCR ⇒ amplifying only a portion of the DNA (particular sequence in our gene of interest) to produce thousands to millions of copies
3 specific stages of PCR
Denaturation
Annealing
Extension
8 reagents of the master/cocktail mix
DNA template
Primers
dNTPs (ATCG)
PCR Buffer (Tris, KCl, and MgCl₂)
Taq polymerase
MgCl₂
Ultrapure H₂O
Adjuvants
3 components of PCR Buffer
Tris, KCl, and MgCl₂
Formula for calculating cocktail mix
C₁V₁ = C₂V₂
What are the components in the formula for the cocktail mix
C₁ ⇒ Stock concentration or initial concentration
C₂ ⇒ Working concentration
V₁ ⇒ Volume for 1 reaction
V₂ ⇒ Total volume of reaction
Subunits of DNA structure
nucleotides
Nucleotide bases (4)
Adenine (A)
Thymine (T)
Guanine (G)
Cytosine (C)
Pairing of bases?
Complementary
Polarity or Directionality of DNA
3’ trunk end and 5’ tail end
Orientation of DNA
Antiparallel
Basic structure of DNA
Double-stranded helix
Specific stage where DNA replication occurs
S stage of interphase
Flow of information from DNA to RNA to proteins
Central dogma
Field of study: DNA → RNA
Transcriptomics
Field of study: RNA → protein
Proteomics
Field of study: DNA
Genomics
Field of study: Proteins → metabolites
Metabolomics
Key enzymes in DNA replication (7)
topoisomerase
helicase
single-strand binding proteins
DNA polymerase
primase
exonuclease
ligase
Differentiate topoisomerase I from topoisomerase II
Type I topoisomerase cuts one strand of a DNA duplex, relaxation occurs, and then the cut strand is reannealed
Type II topoisomerase cuts both strands of one DNA duplex, passes another unbroken DNA helix through it, and then reanneals the cut strands
Leading and lagging strand are collectively known as
Replication fork
Direction of DNA synthesis/assembling nucleotides in what direction?
5’ to 3’ end
Replication islets in lagging strand is known as
Okazaki fragments
Template strand is read in what direction
3’ to 5’
3 types of DNA polymerase in prokaryotes
DNA pol I
DNA pol II
DNA pol III
Function of DNA pol I
Exonuclease activity removes RNA primer and replaces with newly synthesized DNA
Function of DNA pol II
repair function
Function of DNA pol III
main enzyme that adds nucleotides in the 5’ to 3’ direction
Eukaryotic DNA polymerase for DNA replication/priming
alpha
Eukaryotic DNA polymerase for base excision repair (2)
beta and lambda
Eukaryotic DNA polymerase for mitochondrial DNA replication
gamma
Eukaryotic DNA polymerase for chromosomal replication with excision repair
delta
Eukaryotic DNA polymerase for chromosomal replication with repair
epsilon
Eukaryotic DNA polymerase for DNA repair
theta
Eukaryotic DNA polymerase for sister chromatid cohesion
sigma
Eukaryotic DNA polymerase for non-homologous end joining
mu
Transiently intertwined DNA molecules formed during DNA replication; two circular DNA molecules are interlocked
Catenanes
3 types of models of DNA replication
Semiconservative
Conservative
Dispersive
Who invented PCR
Kary B. Mullis
7 applications of PCR
Species Identification and Classification
Cloning
Forensic Biology
Population Genetics and Genetic Diversity
Genotyping
Gene Expression
Detection of Pathogens etc.
Name the 4 dNTPs
dATPs (deoxyadenosine triphosphate)
dCTPs (deoxycytidine triphosphate)
dGTPs (deoxyguanosine triphosphate)
dTTPs (deoxythymidine triphosphate)
What kick starts amplification
Primers
A pair of short DNA fragments that ___ with the DNA template and ___
hybridizes, defines the region that will be amplified
Why is CO1/COX1/MTCO1 gene used?
Highly conserved gene
Taq polymerase is derived for the thermophilic eubacteria
Thermus aquaticus
Habitat of Taq polymerase
hot sulfur springs
PCR in action, 6 steps
Initial denaturation
Amplification
a. Denaturation
b. Annealing
c. Extension/elongation
Final extension/elongation
Temperature range and duration for initial denaturation
94˚-96˚C, 2 minutes
Temperature range and duration for denaturation
94˚-96˚C, 30 seconds
Range of cycles in PCR
25-40 cycles
Temperature and duration of annealing
PRIMER-SPECIFIC; 45˚C-60˚C (54˚C in Taq polymerase) for 1 minute
Temperature and duration of extension
72˚C for 1 minute
Temperature and duration of final extension
72˚C for 10 minutes
Temperature range for hold
4˚C—10˚C
Differentiate in-vivo from in-vitro DNA replication (5)
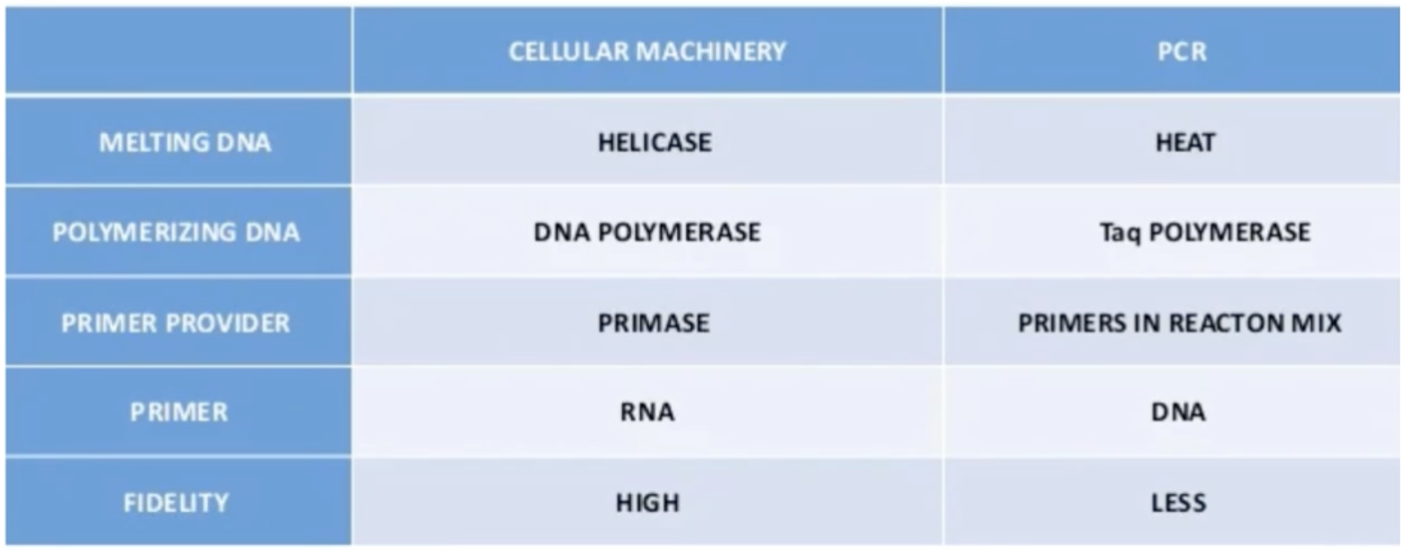
What is fidelity
Accuracy of polymerase to attach to the correct nucleotides
Faint bands beyond the DNA ladder in PCR
primer dimers
Cause of primer dimers (2)
Excess primers that did not anneal or attach
Some primers may also attach to each other if they are poorly designed
3 general guidelines for PCR
Aseptic Technique: Avoid Cross-contamination!
Double check your Master Mix Calculation
Avoid pipetting error!
Order in creating the cocktail mix
ddH₂O
PCR buffer
MgCl₂
dNTPs
Primers
Taq polymerase
Typical container for cocktail mix
1.5mL microcentrifuge tube
PCR products are known as
amplicons
How to check PCR results
agarose gel electrophoresis
In AGE, DNA fragments migrate toward?
Positive cathode, anode
How many base pairs can the primers amplify?
800 to 1000 base pairs for C01
Meaning of TBE
Tris-borate-EDTA
Concentration range of TBE and TAE
0.5x—1x
Meaning of TAE
Tris-acetate-EDTA
When to use TAE versus TBE?
TBE for separating larger fragments, cloning, and gel extraction
TAE for separating smaller fragments and longer AGE runs
4 loading dye options
Xylene cyanol
Bromophenol blue
Cresol red
Tartrazine
6 options for agarose concentration (w/v%)
0.5%
0.7%
1.0%
1.2%
1.5%
2.0%
DNA size range for 0.5%
1000 to 30,000 bp
DNA size range for 0.7%
800 to 12,000 bp
DNA size range for 1.0%
500 to 10,000 bp
DNA size range for 1.2%
400-7,000 bp
DNA size range for 1.5%
200-2,000 bp
DNA size range for 2.0%
50-2,000 bp
6 options for binding/fluorescent dyes
SYBR Gold
SYBR Green
Gel Red
SYBR Safe
EVA Green
High quality DNA AGE result?
Dark DNA bands with no smearing
After DNA extraction, bands beyond the DNA ladder are?
RNA
After PCR, bands beyond the DNA ladder are?
Primer dimers
After PCR, bands that are not the target region
Non-specific Amplifications
Cause for Non-specific Amplifications
Poorly-designed primers leads to a higher chance of amplifying a different gene
4 options for optimizing template DNA
Longer cycles
Fewer cycles
Dilution of DNA samples with contaminants brought about by the extraction method
Re-extract DNA
With longer PCR cycles, DNA template should be?
Diluted
With shorter PCR cycles, DNA template should be?
Increase concentration
Possible reasons for poor PCR attributed to template DNA (2)
Low quality DNA
Too much contaminants
Possible reasons for poor PCR attributed to primers (3)
Hairpin/dimer formation
Wrong melting temperature
Too low concentration
2 options for optimizing primers
Adjust primer concentration
Redesign primer
Ideal primer concentration range
0.05 µM to 1 µM
Possible reasons for poor PCR attributed to MgCl₂
Concentration is too low