Module 2 - Autotrophs
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:58 PM on 9/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1
New cards
Function of roots
-anchors the plant into the ground
- absorbs water and dissolved minerals from the soil for growth and photosynthesis
- absorbs water and dissolved minerals from the soil for growth and photosynthesis
2
New cards
root hairs
larger surface area for which absorption can occur
3
New cards
Internal structures of roots
Epidermis- protective outer layer
• Cortex- act as a storage area for excess materials but also air spaces between cells for the circulation of gases
• Vascular tissue- forms a cylinder in the centre consisting of xylem and phloem
• Cortex- act as a storage area for excess materials but also air spaces between cells for the circulation of gases
• Vascular tissue- forms a cylinder in the centre consisting of xylem and phloem
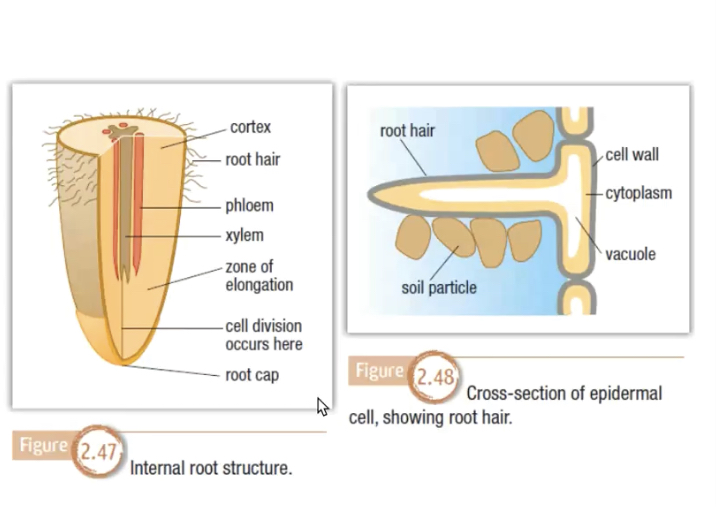
4
New cards
Stems
structural axes of the plant
5
New cards
stem function
• Support for and the elevation of leaves, flowers and fruits.
• Transport of fluids between the roots and the shoots in the xylem and phloem
Storage of nutrients
Production of new living tissue.
• Transport of fluids between the roots and the shoots in the xylem and phloem
Storage of nutrients
Production of new living tissue.
6
New cards
node
holds one or more leaves which can grow into branches
7
New cards
Leaves
external structure visible to naked eye
8
New cards
why are most leaves broad, thin and flat
to achieve a larger surface area for sunlight and gas exchange
9
New cards
Leaf diagram labelled
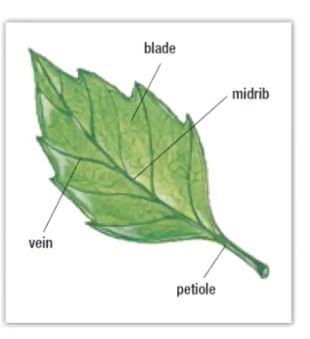
10
New cards
Internal structures of a leaf
• Cuticle- maintains shape and provides protection
• Epidermis- single, transparent layer for sun to penetrate
• Stomates- Pores that open and close for gas exchange
• Mesophyll- contain chlorophyll for gas exchange
• Veins- tubes of vascular tissues
• Epidermis- single, transparent layer for sun to penetrate
• Stomates- Pores that open and close for gas exchange
• Mesophyll- contain chlorophyll for gas exchange
• Veins- tubes of vascular tissues
11
New cards
Internal lead structures diagram
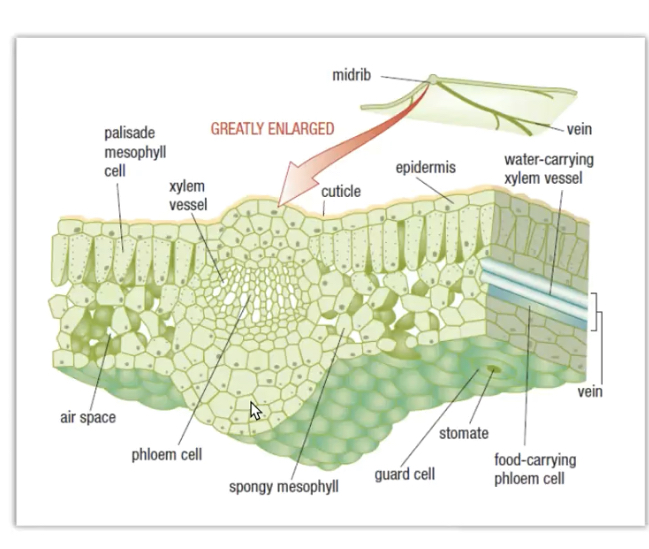
12
New cards
Gas exchange- Stomata
Opening to an air space located in the lower epidermis of a leaf. Each stoma consists of two highly specialised epidermal cells called guard cells.
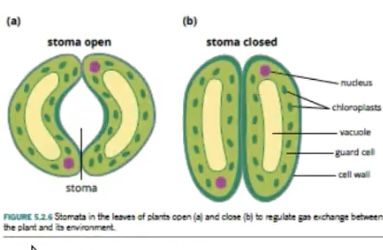
13
New cards
Vascular system
Vascular tissue is used by vascular plants to transport water and mineral ions absorbed from the soil and sugars produced in the leaves to cells throughout the plant
It is visible as parallel veins in grasses, branching veins in many other leaves
It is visible as parallel veins in grasses, branching veins in many other leaves
14
New cards
Xylem
Transports water and inorganic nutrients (mineral ions) absorbed by the roots from the soil to the aerial (above ground) parts of the plant
15
New cards
what is xylem composed of
It is composed of xylem vessels and elongated cells called tracheids
16
New cards
Xylem vessels
long, water-filled tube consisting of elongated cells joined end to end. As the cells mature, the cell wall is strengthened with lignin, making them stronger and more rigid
17
New cards
phloem
Phloem
Transports organic nutrients (dissolved sugars) produced in the leaves by photosynthesis throughout the plant. Other organic substances, such as amino acids, are also transported in the phloem
The main material transported through the phloem is known as phloem sap.
Plants can store sugar in their cells as starch. Starch can be used for structural support, or as an energy source when the plant cannot photosynthesise
Transports organic nutrients (dissolved sugars) produced in the leaves by photosynthesis throughout the plant. Other organic substances, such as amino acids, are also transported in the phloem
The main material transported through the phloem is known as phloem sap.
Plants can store sugar in their cells as starch. Starch can be used for structural support, or as an energy source when the plant cannot photosynthesise
18
New cards
Transpiration - water pathways
Extracellular pathway- most water and some mineral ions pass in or between cell walls
• Cytoplasmic pathway- most mineral ions and some water pass through the cytoplasm of living root cells. Involves substances entering a root hair cell by crossing the cell's membrane, and then passing from cell to cell through plasmodesmata,
• Cytoplasmic pathway- most mineral ions and some water pass through the cytoplasm of living root cells. Involves substances entering a root hair cell by crossing the cell's membrane, and then passing from cell to cell through plasmodesmata,
19
New cards
Xylem transport types
Xylem- Transport Types
Active transport- most dissolved mineral ions are selectively taken into roots by active transport.
Osmosis- the high concentration of ions in the vascular tissues of terrestrial plants creates a very large osmotic concentration gradient.
Diffusion- some mineral ions, such as potassium and phosphate, enter the roots by diffusion. The uptake of these nutrients therefore depends on the rate of water uptake
Active transport- most dissolved mineral ions are selectively taken into roots by active transport.
Osmosis- the high concentration of ions in the vascular tissues of terrestrial plants creates a very large osmotic concentration gradient.
Diffusion- some mineral ions, such as potassium and phosphate, enter the roots by diffusion. The uptake of these nutrients therefore depends on the rate of water uptake
20
New cards
What is transpiration
The passive movement of water through the xylem of vascular plants, from the roots to the leaves
21
New cards
What does transpiration enable the plant to do
• Absorb the water necessary for photosynthesis
• Transport mineral salts to leaf cells and fruits
• Cool down and not become overheated.
• Transport mineral salts to leaf cells and fruits
• Cool down and not become overheated.
22
New cards
What is the theory that explains the primary mechanisms of water movement in plants?
Transpiration-Cohesion-tension theory
23
New cards
features of Transpiration-cohesion-tension theory
• Cohesion between water molecules- evaporation from the surface of the leaf pulls adjacent water molecules and is replaced from the roots
• Adhesion between water molecules and plant cell walls
• Tension (differential pressure) created when water evaporates from the leaves
• Adhesion between water molecules and plant cell walls
• Tension (differential pressure) created when water evaporates from the leaves
24
New cards
Transpiration stream
continuous one-way flow of water from roots to leaves
25
New cards
Factors that affect transpiration rates
• Humidity- rate decreases when there is a lot of water vapour in the air
• Temperature- rates increase as temperature increases because heat energy increases the rate of evaporation of water
• Wind- air currents increase the rate of transpiration by moving water vapour away from the leaf and increasing the rate of evaporation of water
• Temperature- rates increase as temperature increases because heat energy increases the rate of evaporation of water
• Wind- air currents increase the rate of transpiration by moving water vapour away from the leaf and increasing the rate of evaporation of water
26
New cards
translocation
the transport of dissolved material within a plant
27
New cards
Sources of translocation
Sources: sites where sugars are produced during photosynthesis- leaves in plants.
28
New cards
Sinks of translocation
sites where sugars are translocated to. Includes roots, bulbs, stems, flowers and fruits