Anatomy 1 Semester Final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/202
Last updated 4:01 PM on 12/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
203 Terms
1
New cards
Define anatomy
study of structures
2
New cards
microscopic anatomy studies?
small structures
3
New cards
gross anatomy studies?
large structures
4
New cards
define physiology
study of functions
5
New cards
the study of the structure and functions of cells is...
cytology
6
New cards
the study of microscopic structure of tissues is...
histology
7
New cards
what are the levels of organization
atoms, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms
8
New cards
Integumentary system:
skin, hair
temp regulation and protection
temp regulation and protection
9
New cards
Skeletal system:
bones, tendons
shape and structure
shape and structure
10
New cards
Muscular system:
cardiac and smooth muscle
regulates blood and maintains posture
regulates blood and maintains posture
11
New cards
Nervous system:
brain, spinal cord
transmits signals and responds to stimuli
transmits signals and responds to stimuli
12
New cards
cardiovascular system
heart, blood vessels
delivers oxygen and nutrients
delivers oxygen and nutrients
13
New cards
Respiratory system
lung, nose
moves fresh air, removes gas
moves fresh air, removes gas
14
New cards
Lymphatic system
spleen, lymph nodes
maintain fluid levels, immune responses
maintain fluid levels, immune responses
15
New cards
Urinary system
kidney, bladder
create waste, takes nutrients
create waste, takes nutrients
16
New cards
Digestive system
mouth, stomach
give nutrients, gets rid of waste
give nutrients, gets rid of waste
17
New cards
Endocrine system
ovaries, pancreas
metabolism, fertility
metabolism, fertility
18
New cards
Reproductive system
uterus, ovaries
produce egg and sperm cells
produce egg and sperm cells
19
New cards
Maintenance of a relatively stable internal environment is...
homeostasis
20
New cards
receptors function?
detect changes
21
New cards
control center function?
interprets info from receptors and sends commands to effectors
22
New cards
effectors function?
make adjustments based on commands from control center
23
New cards
Feedback loop that brings conditions back to normal.
EX: sweating, heart and breathing rate
EX: sweating, heart and breathing rate
negative
24
New cards
Feedback loop that accelerates change away from normal
EX: blood clotting, childbirth
EX: blood clotting, childbirth
positive
25
New cards
transverse (up) is...
superior
26
New cards
transverse (down) is...
inferior
27
New cards
frontal (front)
anterior, ventral
28
New cards
frontal (back)
posterior, dorsal
29
New cards
sagittal
left and right
30
New cards
lateral
out
31
New cards
medial
in
32
New cards
what are the 3 major cavities?
dorsal, ventral, abdominal
33
New cards
dorsal sub cavities and organs are...
cranial, vertebral
brain, spine
brain, spine
34
New cards
ventral sub cavities and organs are...
pleural, mediastinum, pericardial
lungs, heart
lungs, heart
35
New cards
abdominal sub cavities and organs are...
abdominal, pelvic, epigastric
stomach, liver, pancreas
stomach, liver, pancreas
36
New cards
Name the 4 tissue types
epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous
37
New cards
characteristics of epithelial tissue include
cover surfaces, avascular, cells tightly joined
38
New cards
functions of epithelial tissues
protect, barrier, absorption
39
New cards
Epithelial tissue simple squamous
alveoli
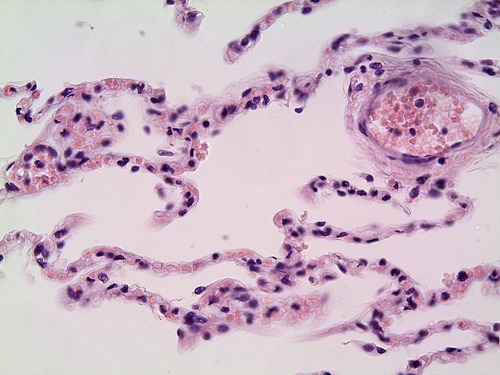
40
New cards
Epithelial tissue stratified squamous
esophagus
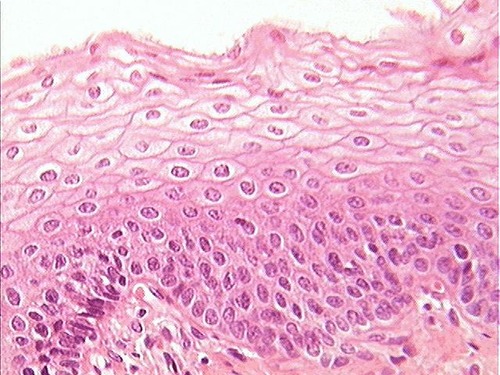
41
New cards
Epithelial tissue simple cuboidal
kidney
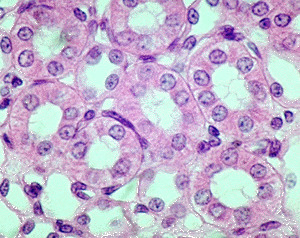
42
New cards
Epithelial tissue simple columnar
stomach
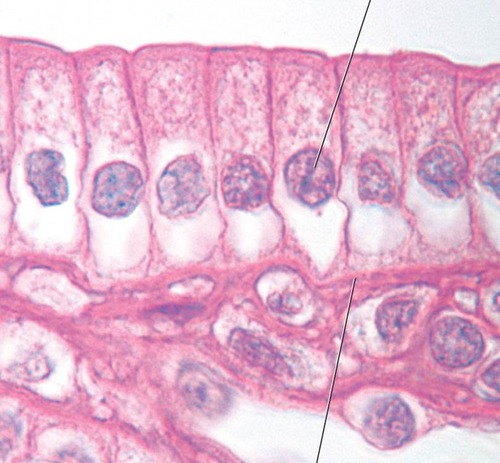
43
New cards
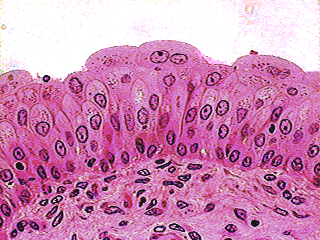
Epithelial tissue transitional
bladder
44
New cards
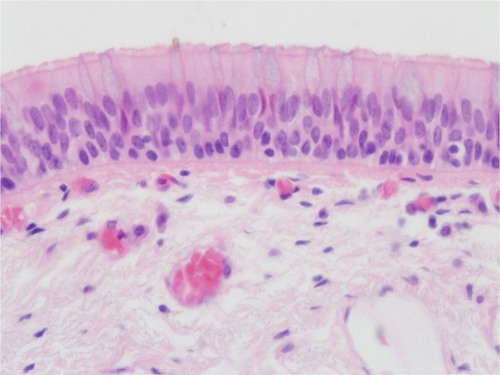
Epithelial tissue pseudostratified columnar
trachea
45
New cards
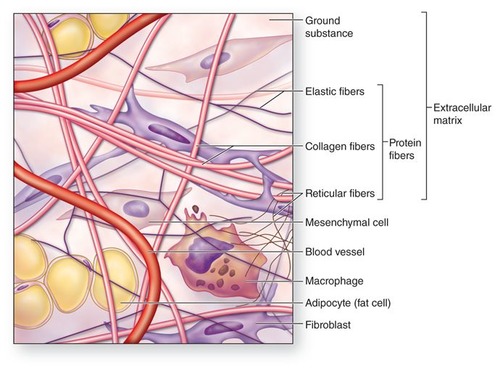
A ground mixture of ground substance, protein fibers, and fluid in connective tissue
extracellular matrix
46
New cards
List the 3 types of connective tissue proper
areolar, adipose (stores fat), reticular
47
New cards
bone to bone dense regular connective tissue is...
ligament
48
New cards
muscle to bone dense regular connective tissue is...
tendon
49
New cards
Ex of dense irregular tissue is...
scar tissue
50
New cards
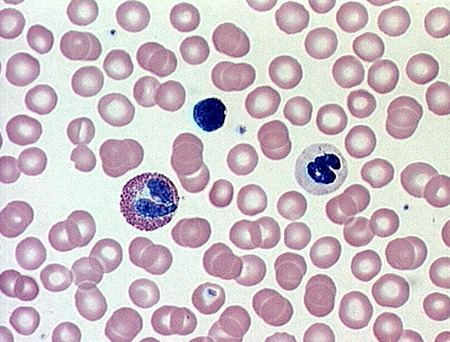
Identify the 2 fluid connective tissues
blood, lymph
51
New cards
Identify 2 broad types of supportive connective tissue
cartilage, bone
52
New cards
Hyaline cartilage can be found...
ends of bones
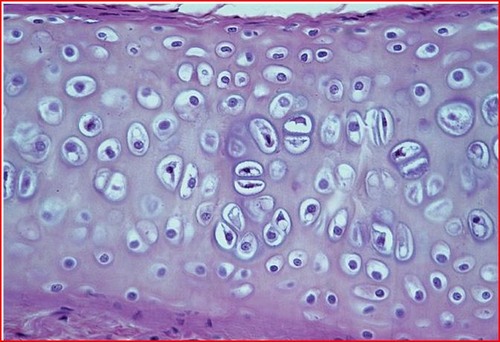
53
New cards
Fibrocartilage can be found...
between vertebrae, in knee and jaw joints
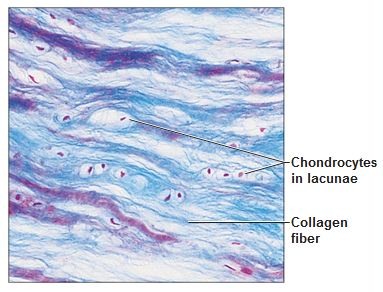
54
New cards
Elastic cartilage can be found...
ear, nose
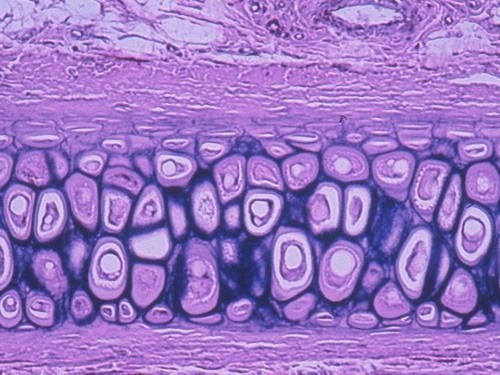
55
New cards
What is the function of muscle tissues?
contraction, movement
56
New cards
Tapered not striated, single nucleus muscle tissue
Involuntary control. Found in the stomach and intestines
Involuntary control. Found in the stomach and intestines
smooth muscle
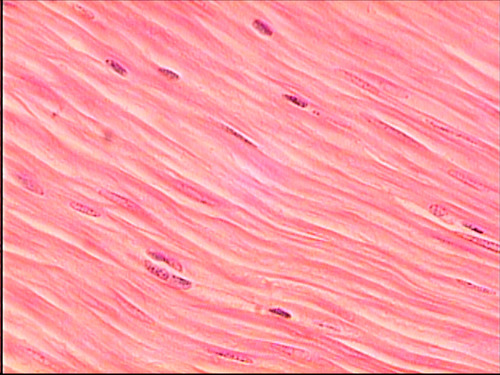
57
New cards
Long cylinders (fibers) striated multiple nuclei muscle tissue
Involuntary control. Found in tendons such as shoulder & hamstring
Involuntary control. Found in tendons such as shoulder & hamstring
skeletal muscle
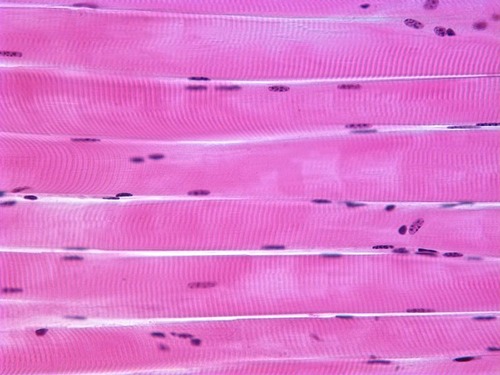
58
New cards
Branched striated (bands), single nucleus
Voluntary control. Found in the heart
Voluntary control. Found in the heart
cardiac muscle
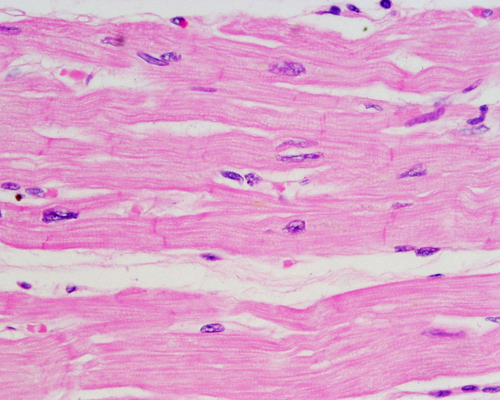
59
New cards
What are the 2 types of neural tissue?
neurons, neuroglia
60
New cards
What is the function of neurons?
conduct cells, send info throughout body
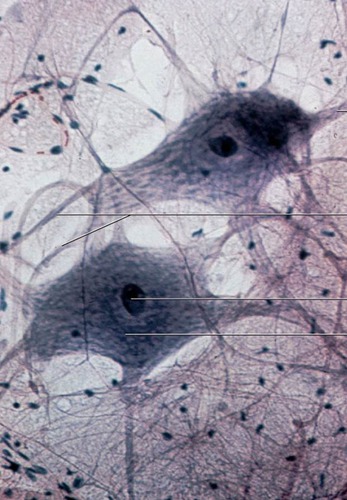
61
New cards
What is the function of neuroglia?
support, protect, insulate neurons
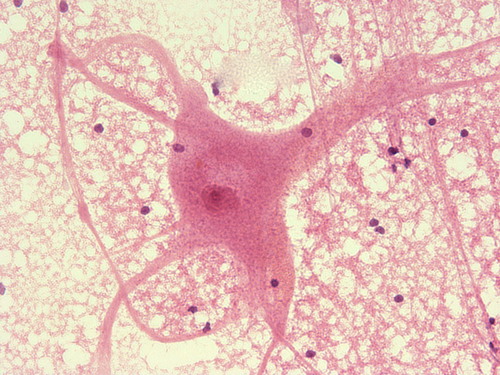
62
New cards
What are the layers of the integument from superficial to deep?
epidermis, dermis, hypodermis
63
New cards
What are the functions of the integument?
protection, temp control, sensory reception, excretion and secretion
64
New cards
What major tissue makes up the dermis?
highly vascular connective tissue
papillary layer, reticular layer
papillary layer, reticular layer
65
New cards
What major tissues make up the epidermis?
stratified squamous
5 layers strata/stratum
5 layers strata/stratum
66
New cards
What major tissues make up the hypodermis? NOT part of the integument!!!
abundant adipose tissue
vascular
vascular
67
New cards
Is the epidermis vascular or avascular?
avascular
68
New cards
Explain how skin pigmentation is determined.
melanin production, darkens skin
dermal blood supply, red/pink skin
dermal blood supply, red/pink skin
69
New cards
What are the three broad categories of accessory structures of the integument?
hair, nails, glands
70
New cards
Name the tough waterproof protein that makes up hair, nails and skin.
keratin
71
New cards
Hair is made of...
dead keratinized cells produced in hair follicles
72
New cards
Peach fuzz hair is...
vellus hair
73
New cards
Head and armpit hair are examples of...
terminal hair
74
New cards
grows hair
hair follicle
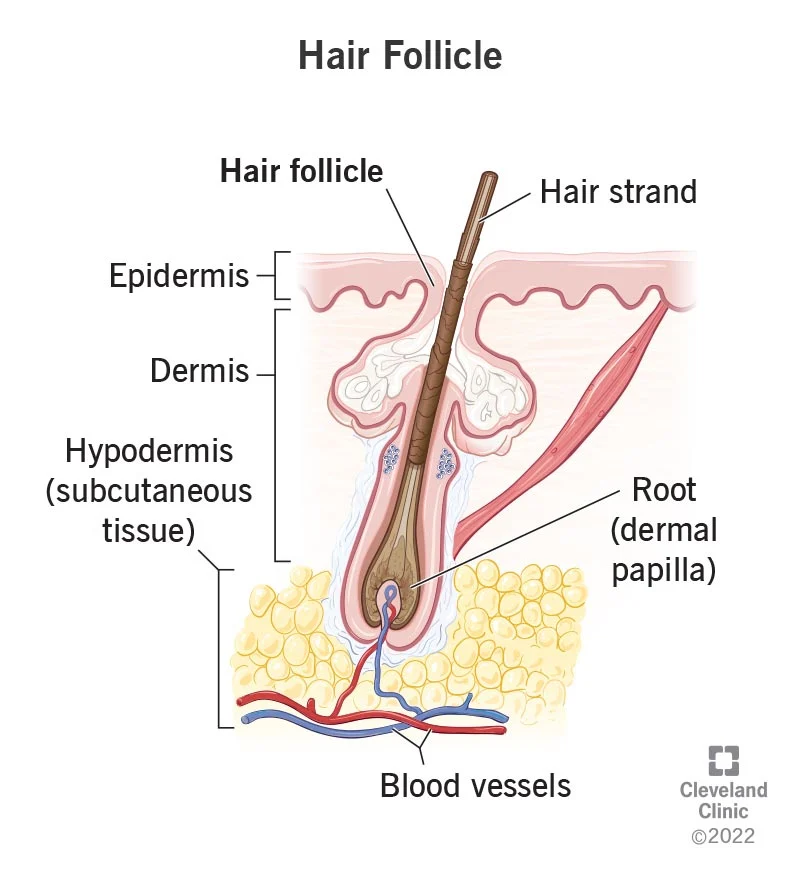
75
New cards
start of hair (where it begins) is called...
hair root
gives nutrients
gives nutrients
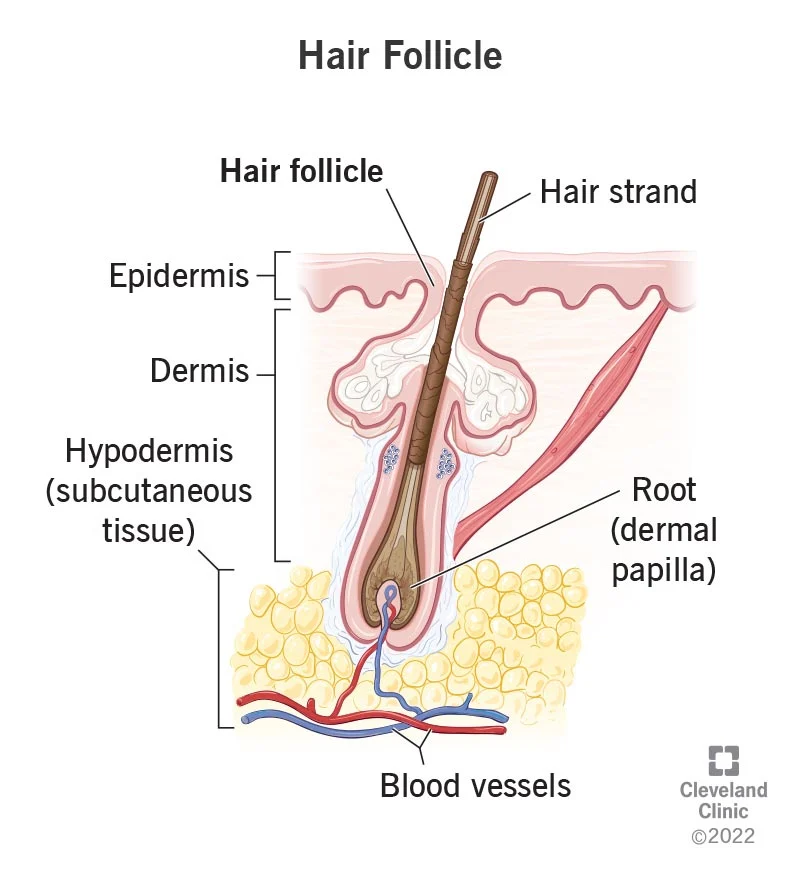
76
New cards
Top of hair (where it ends) is called...
hair shaft
protection, temp control
protection, temp control
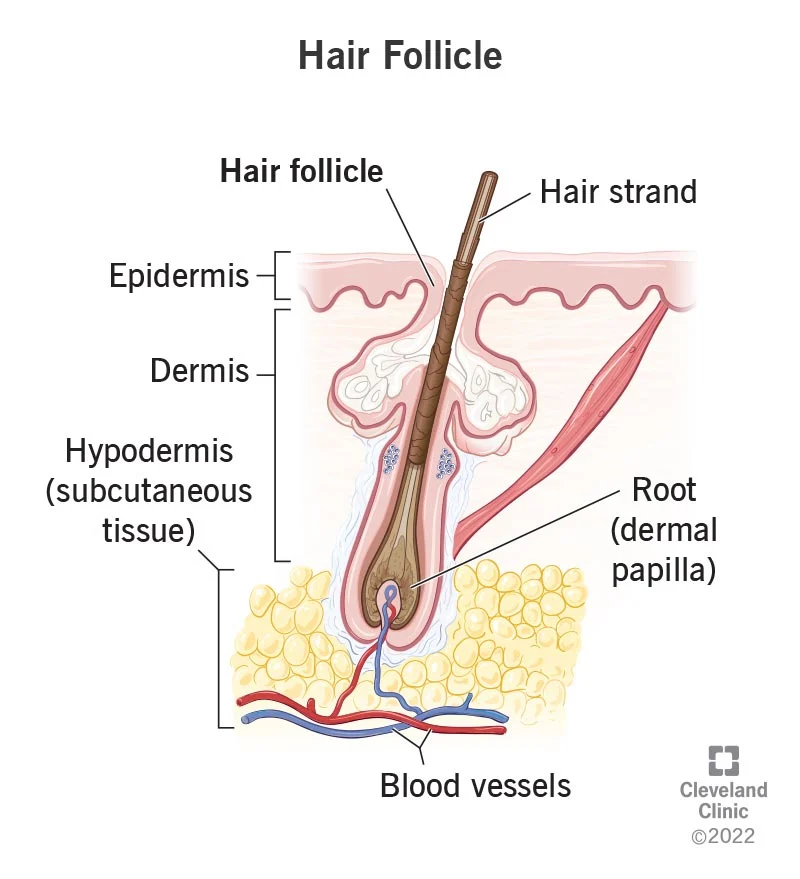
77
New cards
Muscle that controls temp
EX: hair stands up when cold
EX: hair stands up when cold
arrector pili
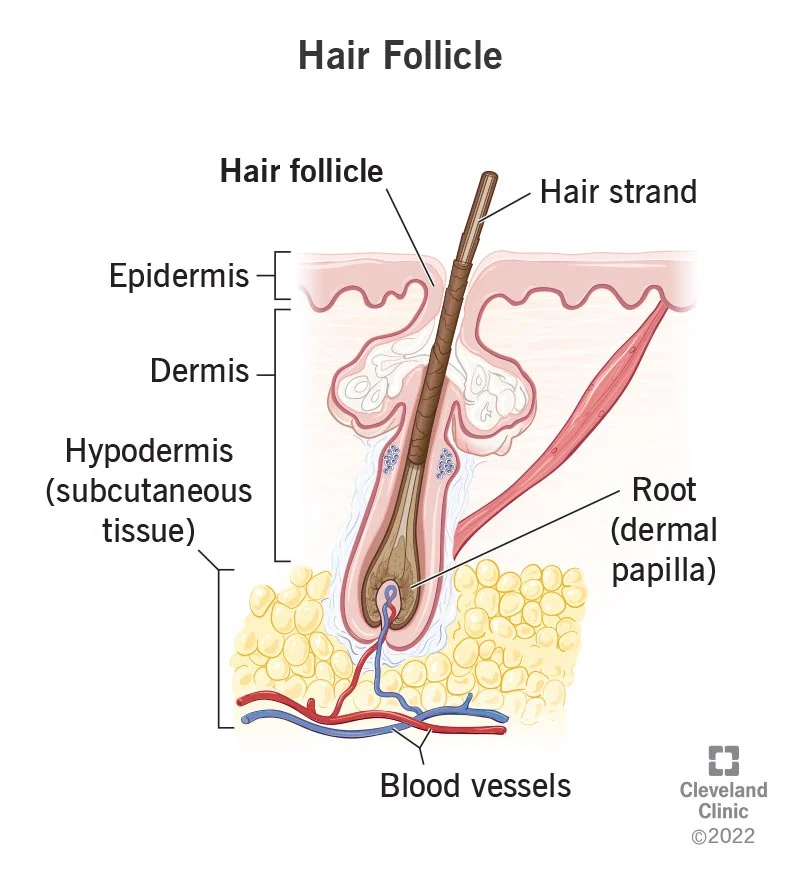
78
New cards
Gland found along the hair follicles
Oily secretion, waterproof property
Oily secretion, waterproof property
sebaceous glands
79
New cards
Sweat Gland found across body that produces watery sweat EX: palms
eccrine
80
New cards
Sweat gland found within hair that produces "milky sweat" EX: B.O/puberty
apocrine
81
New cards
Identify basic structure of the nail
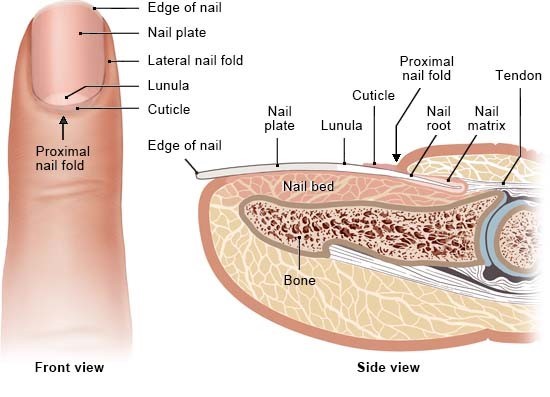
82
New cards
Any receptor that provides an organism with information about mechanical changes in its environment such as movement, tension, and pressure
mechanoreceptor
83
New cards
Any receptor that detects a change in temperature such as hot and cold stimuli
thermoreceptor
84
New cards
Any receptor that detects pain such as EXTREME painful temps, mechanical, and chemical
nociceptors
85
New cards
Describe the mechanisms your body uses to maintain a relatively constant body temperature. Hypothalamus
shivering, sweating
86
New cards
Explain the variation in your skin’s ability to distinguish two-point touch stimuli across different body regions
more sensory neurons
87
New cards
What are the 5 functions of the skeletal system?
support, protection, muscle attachment, blood cell production, storage of minerals
88
New cards
T or F Each bone is an organ.
t
89
New cards
T or F Bone is made of several different types of tissues
t
90
New cards
Organic component that provides tensile strength. Resists stretching and twisting forces. (Protein)
collagen fibers
91
New cards
Inorganic component that provides compressive strength. Resists compressive forces. (Mineral)
calcium hydroxyapatite
92
New cards
hard dense tissue that gives bones strength
compact bone
93
New cards
porous tissue that reduces bone weight
spongy bone
94
New cards
build bone
osteoblasts
95
New cards
break down bone
osteoclasts
96
New cards
send signals
osteocytes
97
New cards
a layer of dense irregular connective tissue rich in blood vessels
periosteum
98
New cards
a layer of membrane that lines the center of bone that contain bone marrow
endosteum
99
New cards
Shapey's penetrating fibers attach...
periosteum to the bone
100
New cards
Type of bone seen in vertebrae
irregular