Traumatic-Infectious & Inflammatory Heart Conditions
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
What does this refer to
Effusion present when accumulated fluid within pericardial sac exceeds small amount that is normally present
Acute or chronic
Hemodynamically stable - unstable
Pericardial effusion
What does this refer to
Small effusions are often asymptomatic
Found in 3% of subjects in autopsy studies
Observed in all age groups
Mean occurrence 30-49yo
Mortality/morbidity dependent on etiology/comorbid conditions
M = F
Epidemiology Pericardial Effusion
What does this refer to
Can occur as a component of almost any pericardial disorder
Acute pericarditis
Viral
Enteroviruses: coxsackie, enterovirus and echoviruses
Autoimmune disease/Neoplastic disease
Postmyocardial infarction or cardiac surgery
Dressler’s syndrome
Sharp or blunt chest trauma
Drugs (procainamide, hydralazine, isoniazid)
Etiology Pericardial Effusion
What does this refer to
Will have no symptoms specific to effusion
May have symptoms of underlying cause
Clinical history-hemodynamically stable Pericardial Effusion (Patients WITHOUT hemodynamically significant effusion)
What does this refer to
Fatigue
Dyspnea
Elevated jugular venous pressure
Edema
Chest pain, pressure, discomfort
Improved by sitting up/leaning forward
Intensified by lying supine
Clinical history-hemodynamically unstable Pericardial Effusion (progressing to cardiac tamponade)
What does this refer to
Pulsus paradoxus
Decrease in systolic blood pressure of more than 10mm Hg with inspiration
Friction rub left lower sternal border
Tachycardia/Tachypnea
Muffled heart tones
Ewart sign
Dullness to percussion beneath angle of left scapula
Extremities
Weak peripheral pulses
Edema
Cyanosis
Physical exam Pericardial Effusion
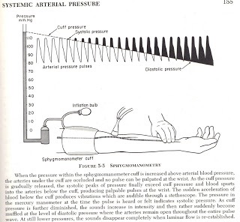
What does this refer to
Place a blood pressure cuff on patient’s arm
Very slowly deflate cuff while listening for Korotkoff sounds
Note pressure you first hear sounds during expiration
Repeat process and record pressure where sounds are heard during inspiration
Difference between the two numbers is pulsus paradoxus
Physical exam pulsus paradoxus - Pericardial Effusion
What does this refer to
Acute Pericarditis
Cardiac Tamponade
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Acute MI
Pulmonary Embolism
Differential diagnosis Pericardial Effusion
What does this refer to
Workup for Pericardial effusion
What does this refer to
Confirming presence of a pericardial effusion
Assessing any hemodynamic impact
Establish cause if possible
Echocardiography*
Imaging modality of choice for diagnosis*
How Pericardial Effusion is diagnosed
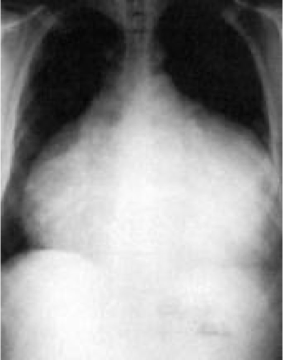
What does this refer to
Findings are variable, depending on etiology and size of effusion
*Not specific and or diagnostic
< 250 mL may not result in significant findings
Larger effusions present with an enlarged cardiac silhouette/clear lung fields
**Water bottle–shaped heart*
CXR Pericardial Effusion
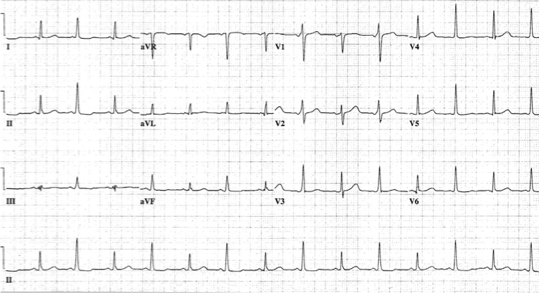
What does this refer to
Early pericardial effusion
ECG typically displays diffuse ST elevation*
Triad
Low QRS voltage
Tachycardia
Electrical alternans
EKG Pericardial Effusion
What does this refer to
Consultations
Cardiologist/Cardiothoracic surgery
Medical care
Focused to determine etiology
Treatment of underlying disease(s)
Clinical management Pericardial Effusion
What does this refer to
Pericardial fluid drainage
Indications for urgent drainage depend on level of hemodynamic compromise
Choice of pericardiocentesis/open drainage based on local preference and experience
Clinical intervention pericardiocentesis – Pericardial Effusion
What does this refer to
HIV/AIDS, cancer or otherwise immunocompromised —> high mortality rates
Complications
Ventricular rupture
Dysrhythmias
Pneumothorax
Myocardial injury
Infection
Recurrence may be 90% in cancer patients
May progress to cardiac tamponade
Prognosis Pericardial Effusion
What does this refer to
________ : Compression of the heart by an accumlation of fluid in the pericardial sac
A clinical syndrome caused by the accumulation of fluid in the pericardial space, resulting in reduced ventricular filling and subsequent hemodynamic compromise.
Is a medical emergency, the complications of which include pulmonary edema, shock, and death.
Cardiac tamponade
What does this refer to
Pericardial effusion that causes accumulation of enough fluid to compress the heart enough to cause cardiac function impairment
Results in a stiffening of the pericardium if not corrected
Classification
Acute
Subacute
Cardiac tamponade
What does this refer to
Approximately 2 cases/10,000 in US
2% of penetrating trauma cases have cardiac tamponade
M > F [1.5 : 1]
Traumatic and infectious sources more common in younger people
Uremic and Neoplastic more common in older populations
Epidemiology Cardiac Tamponade
What does this refer to
Rate of fluid accumulation is very important
Rapid
Slow
Can occur as a result of any process that causes pericarditis
Malignant Effusion
Penetrating trauma
Uremia
Thoracic Aortic Dissection
Infectious disease
Inflammatory process
Ventricular rupture
Etiology Cardiac Tamponade
What does this refer to
Pericarditis of any etiology
Active Cancer
Penetrating Trauma
Acute Renal Failure/Uremia
Tuberculosis infection
Systemic Autoimmune Disease
History of HIV/IV drug abuse
H/O chest radiation
Recent pacemaker/AICD implantation or other recent cardiac surgery
Recent MI
Risk factors Cardiac Tamponade
What does this refer to
Chest Pain
Dyspnea/tachypnea
Cough
Pulsus paradoxus
Clinical history Cardiac Tamponade
What does this refer to
_________ is an abnormally large decrease in stroke volume, systolic blood pressure and pulse wave amplitude during inspiration.
Pulsus paradoxus
What does this refer to

Physical exam Cardiac Tamponade
What does this refer to
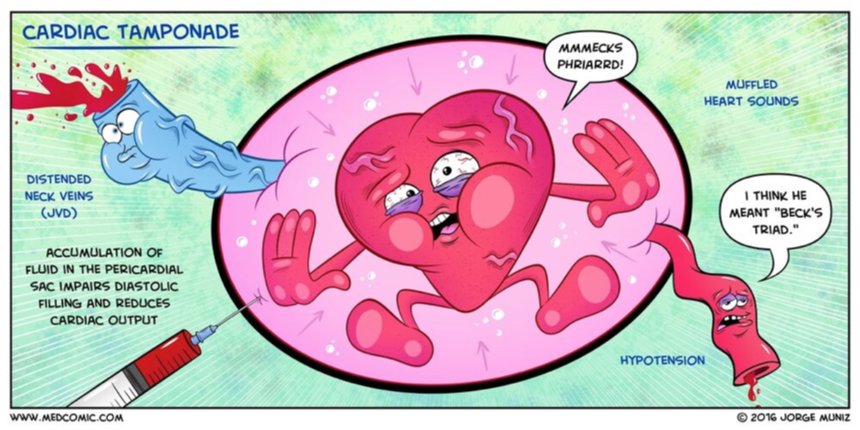
Hypotension
Jugular venous distension
Muffled heart sounds
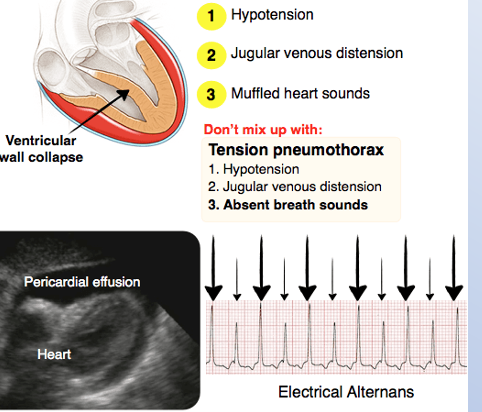
Beck’s Triad (cardiac tamponade)
What does this refer to
Pericarditis/Myocarditis
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS)
Pneumothorax
Pulmonary Embolism
Pleural Effusion
Thoracic Aortic Dissection
Hemopericardium
Differential Diagnosis of Cardiac tamponade
What does this refer to
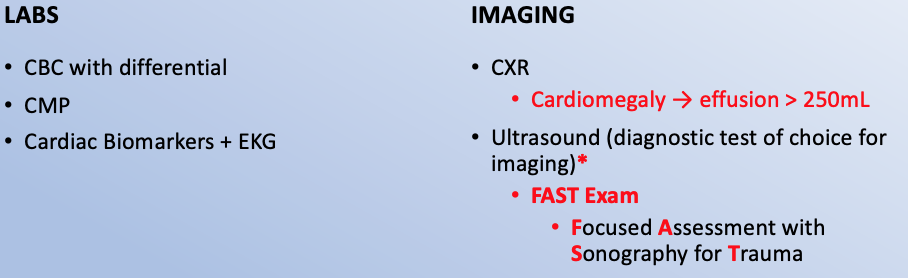
Workup Cardiac Tamponade
What does this refer to
ECG is poorly diagnostic of pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade.
What does this refer to
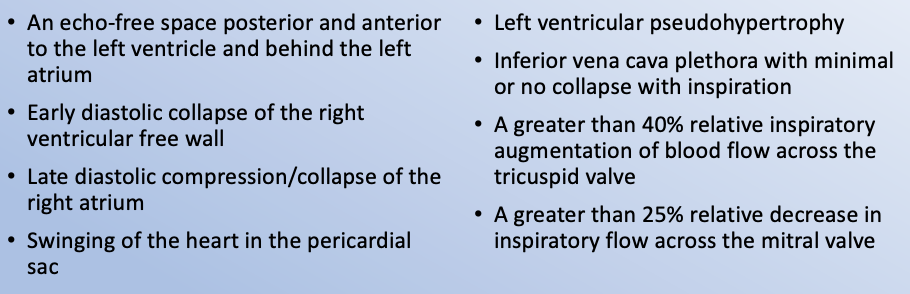
How’s it diagnosed? Cardiac Tamponade (Echo)
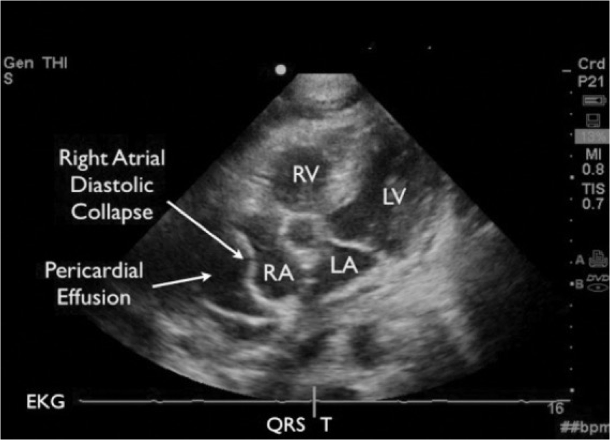
What does this refer to
2D echocardiography that shows dilation of the IVC (>20 mm in an adult size heart) and hepatic veins, known as IVC plethora, not specific but a sensitive sign of cardiac tamponade)
What does this refer to
Mechanical drainage/removal of fluid
ER treatment
Pericardiocentesis 1st line
Open drainage
Pericardial window (recurrent)
Need for Intubation
Ventilatory support
IV Fluid (IVF) bolus 500-1000mL
Be aware of adverse effects to include pulmonary edema/↓ cardiac output
Clinical intervention Cardiac Tamponade
What does this refer to
IV Fluid (IVF)
Bolus 500-1000mL
Vasopressors
If needed
Not contraindicated
Clinical management Cardiac Tamponade
What does this refer to
Outcome associated with etiology of cardiac tamponade and pre-existing comorbidities
Mortality
1-year mortality rate 77% for malignant effusion
13% mortality rate for non-malignant effusion
Prognosis Cardiac Tamponade
What does this refer to
Pregnancy category: C
Lactation: Drug does not enter breast milk; use with caution because of potential vitamin loss in mother
Cholestyramine
What does this refer to
“: Generally acceptable. Controlled studies in pregnant women show no evidence of fetal risk.”
Pregnancy category A
What does this refer to
“May be acceptable. Either animal studies show no risk but human studies not available or animal studies showed minor risks and human studies done and showed no risk”
Pregnancy category B
What does this refer to
“Use with caution if benefits outweigh risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies not available or neither animal nor human studies done”
Pregnancy category C
What does this refer to
“Use in LIFE-THREATENING emergencies when no safer drug available. Positive evidence of human fetal risk.”
Pregnancy category D
What does this refer to
“Do not use in pregnancy. Risks involved outweigh potential benefits. Safer alternatives exist.”
Pregnancy category X
What does this refer to
“: Information not available”
Pregnancy category N/A
What does this refer to
_____________ are used to treat hyperlipidemia (HLD) in pregnancy
Bile Acid Sequestrants
Bile acid sequestrants increase the risk of developing _________ so they should not be used to treat HLD in patients who are already at risk or who have osteopenia/osteoporosis
osteoporosis
Can you use statins in pregnancy?
Can you use ezetimibe in pregnancy?
No it is category C and a contraindication
Can you use ezetimibe + statin in patients with osteopenia or osteoporosis?
Yes, there is no contraindications
There does not seem to be a “protective” feature to prevent or reduce risk of developing osteopenia/osteoporosis
What does this refer to
Infection in the heart valves or endocardium
Infective Endocarditis

Is this acute or subacute bacterial endocarditis?
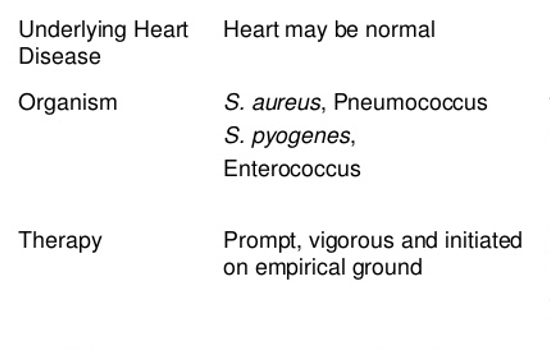
Acute
Is this acute or subacute bacterial endocarditis?

Subacute
What does this refer to
M > F
No racial predilection
Prevalence > 60 yo
Dx at younger age often related to IV drug abuse (IVDA)
Epidemiology Infective Endocarditis
What does this refer to

Etiology Infective Endocarditis
What does this refer to
Native valve endocarditis
S. aureus and streptococcal species account for majority of cases
Fungi account for a small percentage (MC IVDA)
S. aureus most common cause among injection drug users
Prosthetic valve endocarditis
Early disease MC caused by S. epidermis
Enterococci
Recent GU or GI infection
Pathogens Infective Endocarditis
What does this refer to
2/3 of patients have no prior hx of heart disease or murmur
Murmur may be absent with tricuspid valve involvement
MC pathogen is MRSA
Present with pleuritic chest pain
Etiology with ivda Infective Endocarditis
What does this refer to
IV drug use/abuse (IVDA)
Poor dentition or dental infection
Structural (valvular) heart disease
History of infective endocarditis
Hemodialysis
HIV infection
Risk factors Infective Endocarditis
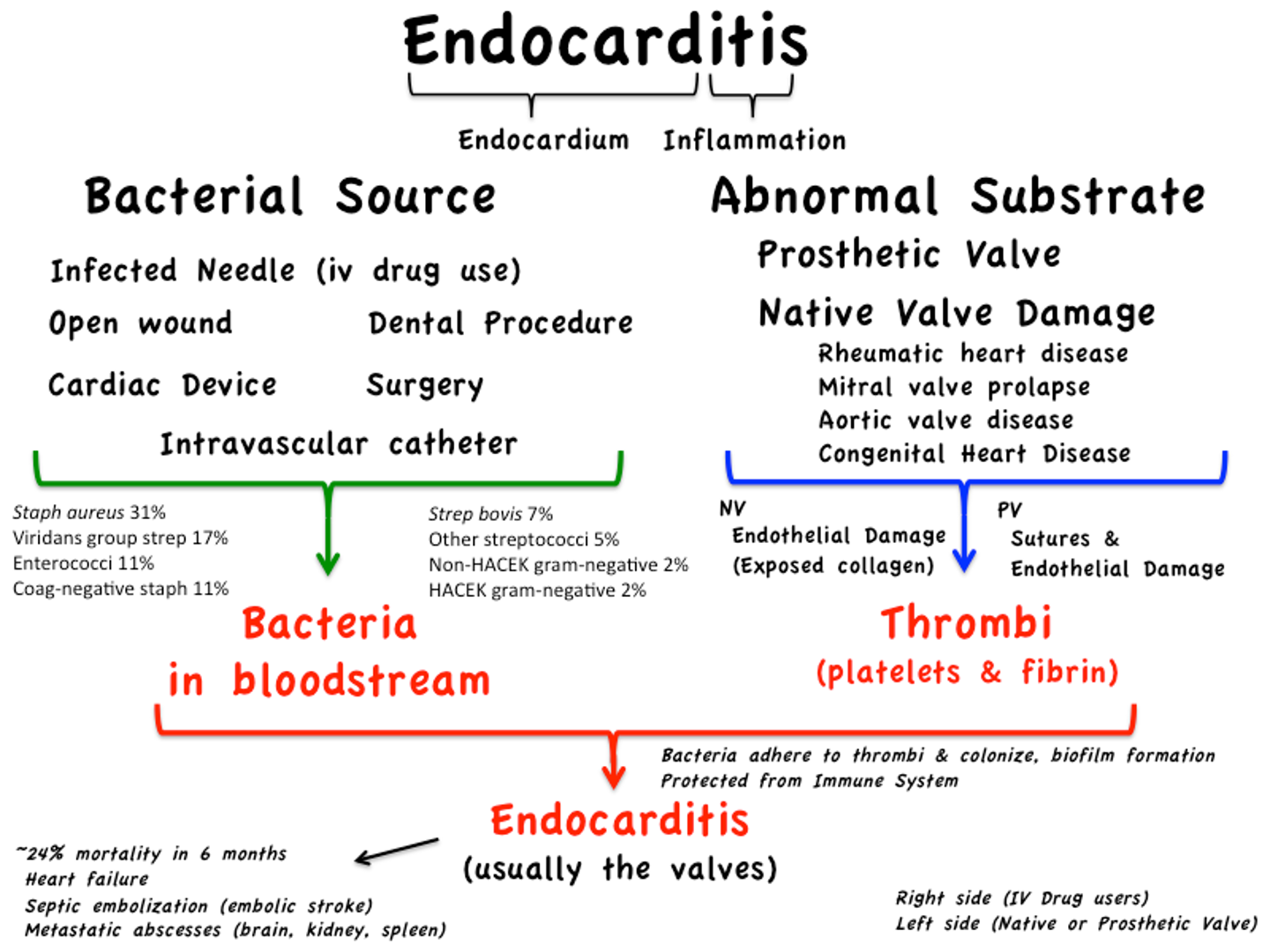
What does this refer to
Endocarditis
What does this refer to
Valve replacement
Refractory CHF
Persistent infection
Invasive infection
Previous prosthetic valve
Recurrent systemic emboli
Fungal infections
Surgical (operative) intervention for infective endocarditis
What is the non-operative management of native valve endocarditis (NVE) —> 4-6 weeks (clinical pharmcotherapeutics empiric therapy, infective endocarditis)
Ceftriaxone OR Gentamicin
MRSA or PCN allergy —> vancomycin
What is the non-operative management of Prosthetic valve endocarditis (PVE) —> 4-6 weeks (clinical pharmcotherapeutics empiric therapy, infective endocarditis)
Vancomycin + Gentamicin + Rifampin
What is the non-operative management of critically ill/unstable (clinical pharmcotherapeutics empiric therapy, infective endocarditis)
Vancomycin + cefepime + piperacillin-tazobactam
Suspect pseudomonas a
What is the non-operative management of fungal endocarditis (clinical pharmcotherapeutics empiric therapy, infective endocarditis)
Amphotericin B (6-8 weeks)
Surgical intervention often needed with fungal pathogens
What does this refer to
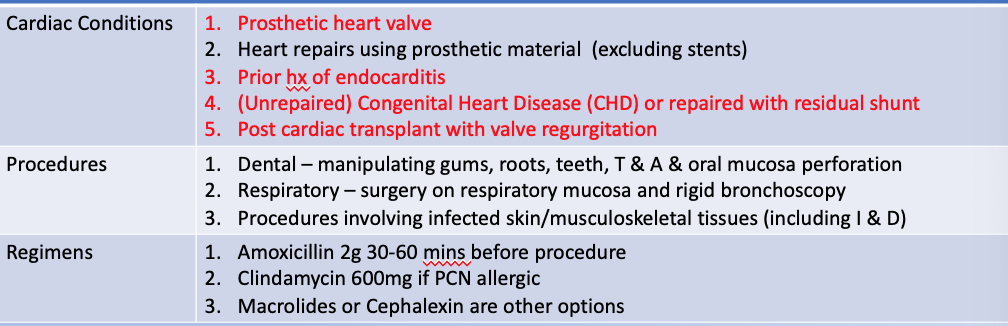
Infective Endocarditis Prophylaxis prevention
What does this refer to
Largely dependent on whether or not complications resulted from the infection
Best cure rates by organism
Strep viridans and strep bovis —> 98%
Enteroccoci and s. aureus (IVDA) 90%
Non-IVDA community acquired S. aureus 60-70%
Aerobic gram-negative organisms 40-60%
Fungal organisms < 50%
Complications include HF, new valve disease, conduction abnormalities, cerebral embolism, renal embolism and/or infarct
Untreated almost always fatal
Prognosis of infective endocarditis
What does this refer to (*on test)

Infective Endocarditis
What does this refer to
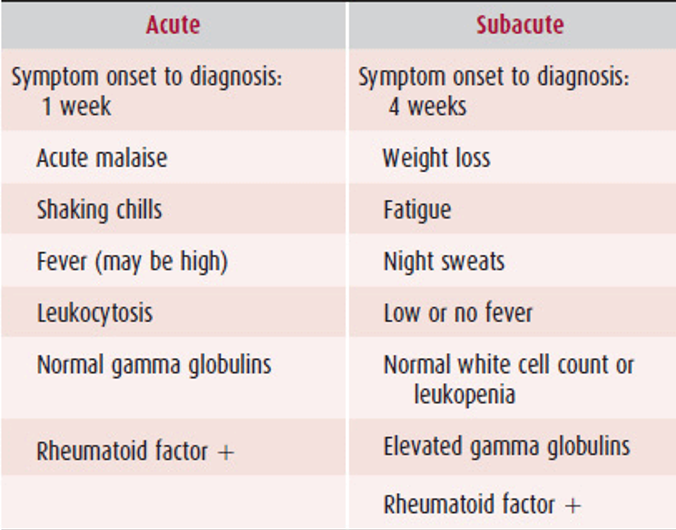
Infective Endocarditis
What does this refer to
Mechanical ______
Limiting acute dilation
Maintaining ventricular compliance
Distributing hydrostatic forces
Membranous ________
Reduces external friction
Barrier against infection and malignancy
Ligamentous ______
Anatomically fixes heart
Function of the pericardium
What does this refer to
Inflammation of pericardium characterized by
Chest pain
Pericardial friction rub
Serial electrocardiographic changes
Acute pericarditis
What does this refer to
Uremic etiology common in patients with advanced renal disease (before dialysis)
Malignant disease is the most common cause of pericardial effusion with tamponade in developed countries
M > F
More common in men under age 50
More common in adults than children
Epidemiology of acute pericarditis
What does this refer to
MC cause in immunocompetent patients —> post-viral infection or idiopathic (80%)
Uremic pericarditis is a common complication associated with chronic renal failure
Inflammatory disorders
RA, SLE, Rheumatic fever
Cardiovascular
AMI
Dressler syndrome = post MI + fever + pleural effusion
Aortic dissection
Metabolic disorders
Neoplasms, drugs, trauma
Etiology of acute pericarditis
What does this refer to
Presentation depends on underlying etiology
Major clinical manifestations
Acute onset chest pain
Substernal and may radiate to neck/shoulders
Typically pleuritic
Improved by sitting up and leaning forward
Clinical history of acute pericarditis
What does this refer to

Physical exam of acute pericarditis
What does this refer to
Two of the following four criteria:
1. Non-ischemic chest pain
2. ECG evidence of PR depression or ST segment deviation
3. Detection of a pericardial rub on auscultation
4. Pericardial effusion on 2-D echocardiography (best INITIAL test)
BEST TEST – T2 Weighted Cardiac MRI (does NOT require contrast)
Make the “best test” better by using gadolinium contrast
Diagnostic criteria
What does this refer to
Diagnosis suspected
Pleuritic chest pain, and confirmed if a pericardial friction rub
Persistent fever and pericardial effusion or new unexplained cardiomegaly
Angina Pectoris/Myocardial Infarction
Aortic Dissection
Esophageal Rupture
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Pulmonary Embolism
Differential Diagnosis of Acute Pericarditis
What does this refer to

Workup Acute Pericarditis
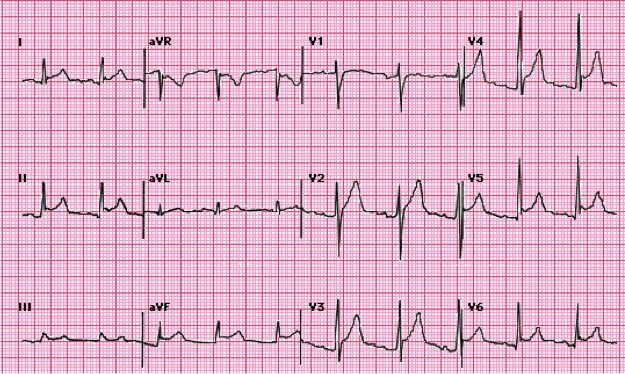
What does this refer to
Diffuse ST segment elevations seen in leads II, aVF, V2 to V6
Diffuse ST elevation at onset of acute pain is a hallmark of acute pericarditis
Workup stage 1 EKG acute pericarditis
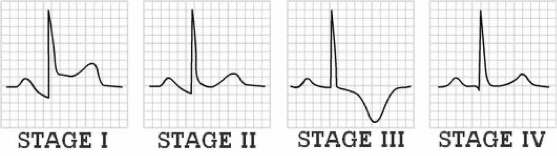
What does this refer to
(Workup - subsequent ekg changes Acute Pericarditis)
Stage 2
ST segment returns to baseline in a few days
Stage 3
T waves become inverted
Stage 4
Returns to baseline in weeks to months
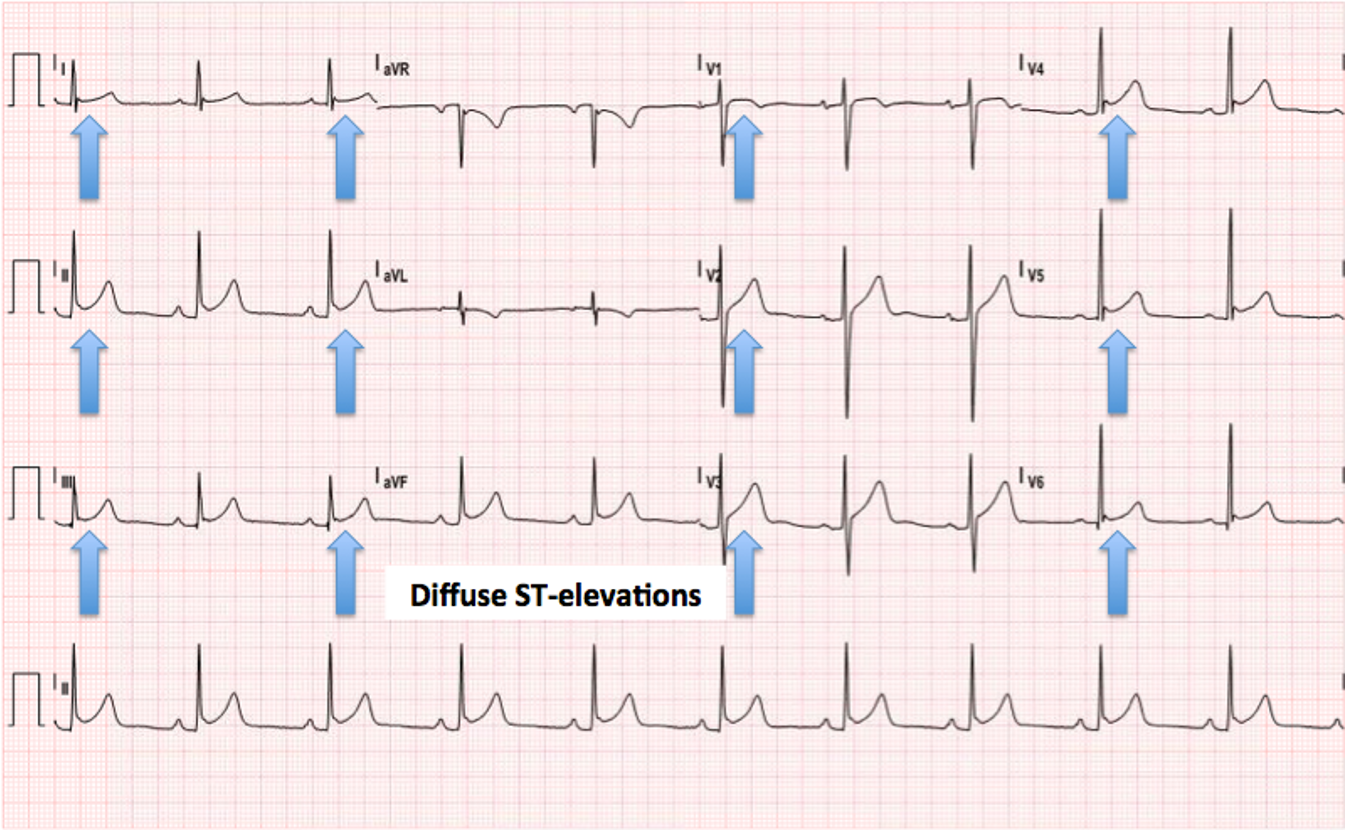
What does this refer to
EKG workup for acute pericarditis
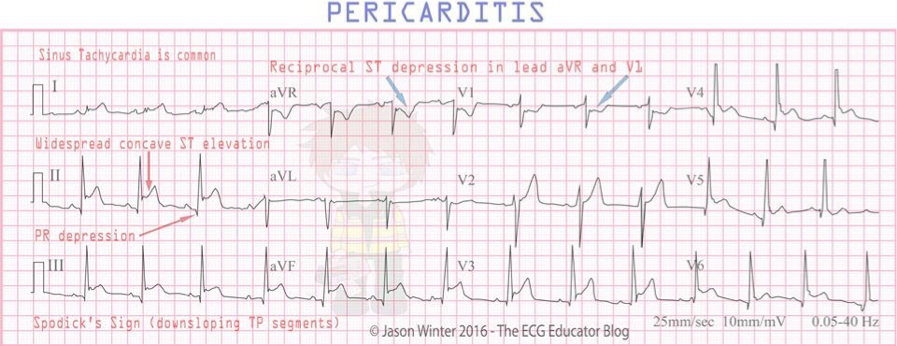
What does this refer to
Workup - EKG stage II acute pericarditis
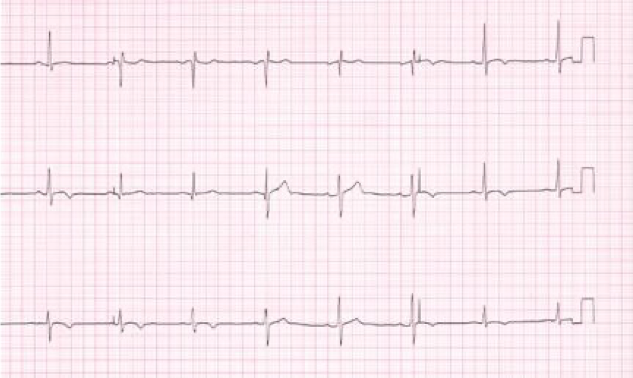
What does this refer to
Workup stage 4 ekg (atypical) - acute pericarditis
What does this refer to
Echocardiogram
Often normal
Essential for evaluation of pericardial effusion
CT scan
Provides details of entire pericardium
Normal thickness by CT is < 2 mm
Thickening suggestive of acute pericarditis
MRI
Provides details without contrast or radiation
Imaging Acute Pericarditis
What does this refer to
Cardiology consultation
Surgical intervention
Pericardiectomy (best for constrictive pericarditis)
Pericardiocentesis (effusions > 250mL)
Pericardial window placement
Pericardiotomy (refractory cases)
Clinical intervention of acute pericarditis
What does this refer to
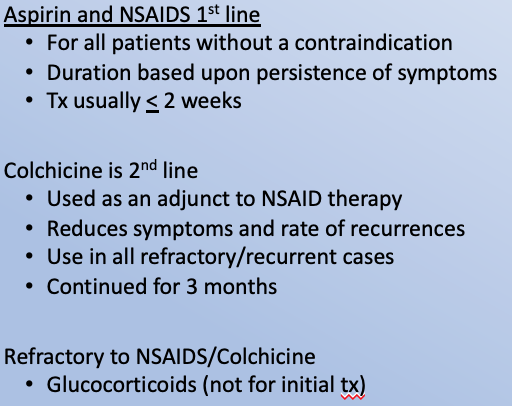
Clinical pharmacotherapeutics of acute pericarditis
What does this refer to
Depends on etiology
Idiopathic and viral etiologies usually have a self-limited course
Most post–MI cases have a benign course
With 1st occurrence co-existing pleural effusion is common
Prognosis of acute pericarditis
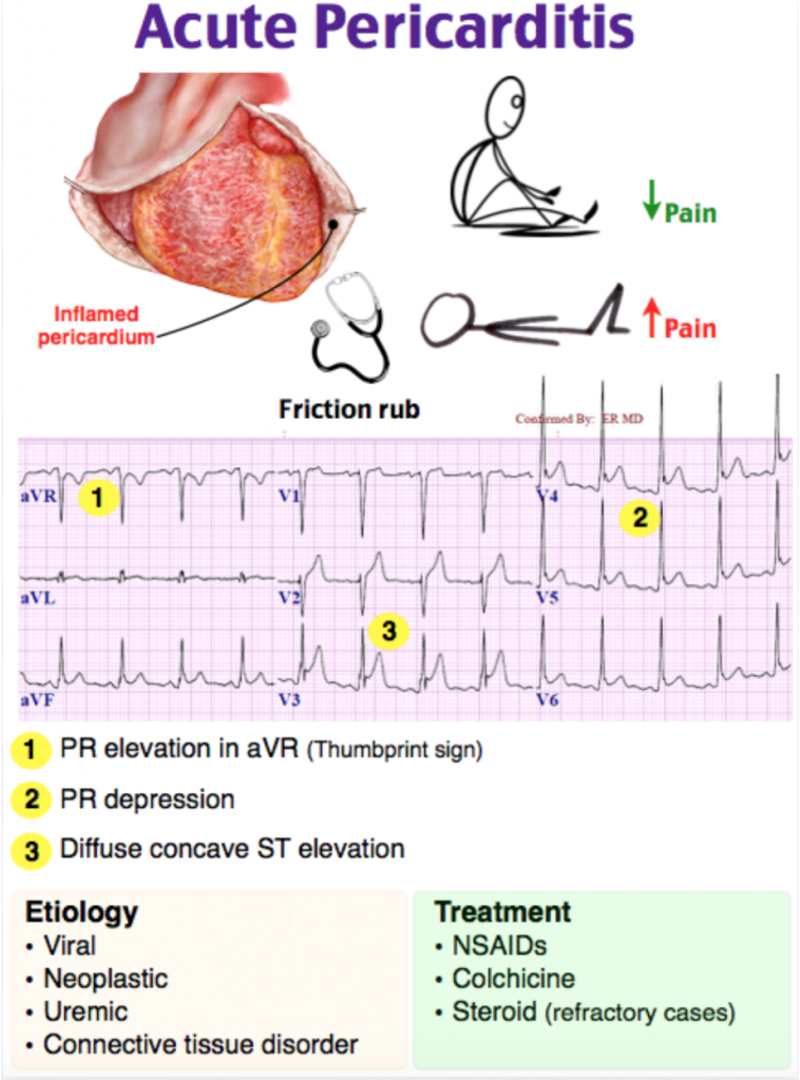
What does this refer to
Long term/chronic inflammation of the pericardium
Thickening and scarring
Restriction of ventricular diastolic filling
Constrictive Pericarditis
What does this refer to
Effects those with conditions related to the Etiology
Epidemiology Constrictive Pericarditis
What does this refer to
Occurs due to things that cause inflammation to develop around the heart
Heart Surgery
Radiation therapy to the chest
Tuberculosis
Any cause of acute pericarditis can cause constrictive pericarditis
Etiology Constrictive Pericarditis
What does this refer to
Dyspnea that develops slowly and gets worse (MC sx)
Fatigue
Orthopnea
Chronic edema of the legs and ankles
Ascites
General weakness
Clinical history constrictive pericarditis
What does this refer to
Fever
Tachycardia
Palpitations
Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
Diaphoresis
Heart tones
“Pericardial knock”
Physical exam constrictive pericarditis
What does this refer to
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
CHF
Valvular disease
Atherosclerotic disease
Fatty deposits in vessels
Cardiac Tamponade
Differential Diagnosis of constrictive pericarditis
What does this refer to
Workup constrictive pericarditis
What does this refer to
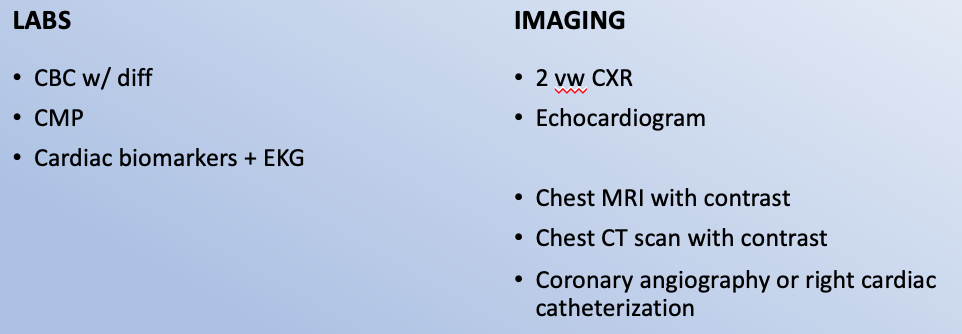
generalized T wave flattening or inversion, with normal QRS
Constrictive pericarditis ECG
What does this refer to
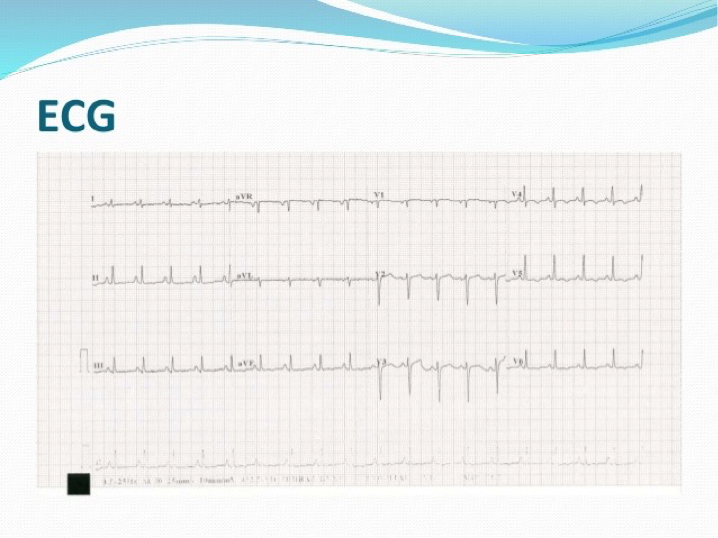
Pericardial calcification (lateral)
Lung fields clear
Workup CXR constrictive pericarditis
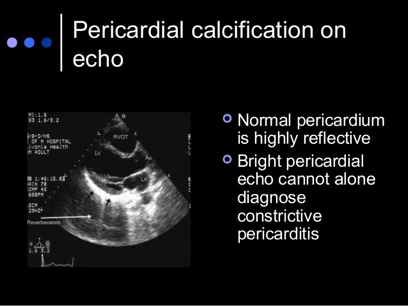
What does this refer to
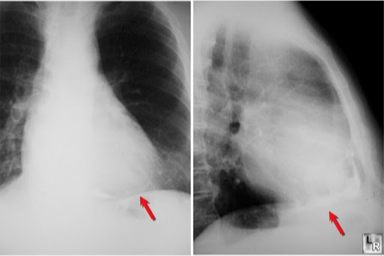
Pericardial thickening/calcification
Exclude restrictive cardiomyopathy
Workup – Echo Constrictive Pericarditis
What does this refer to
Invasive hemodynamic procedure
Direct measurement of right-sided cardiac pressures and calculation of cardiac output.
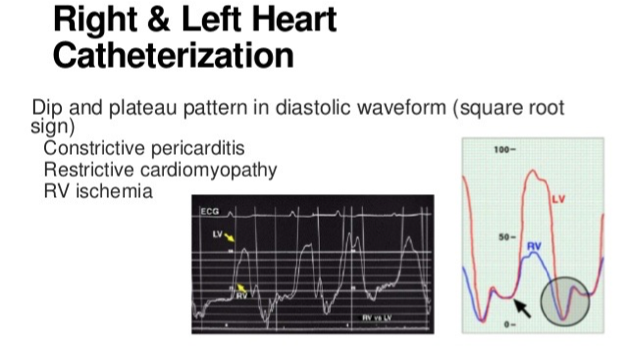
Right heart cath (workup heart catheterization, differentiate right and left heart cath)
What does this refer to
Diagnostic and therapeutic
Assess cardiac hemodynamics and valvular lesions
Main diagnostic role is the assessment of coronary artery disease
Left heart cath (workup heart catheterization, differentiate right and left heart cath)
What does this refer to
Square root sign
Workup – Right heart cath Constrictive Pericarditis
What does this refer to
Improve heart function → treat underlying etiology
Diuretics
Loop or thiazides
Aldosterone antagonists
Low Sodium diet
Indication for surgical pericardiectomy
Refractory to medical management
Involves cutting or removing the scarring and part of the sac-like covering of the heart
Clinical management constrictive pericarditis
What does this refer to
Must be treated to avoid complications and exacerbations
Mortality rate as high as 15% if pericardiectomy needed
Predictors of poor prognosis
Prior radiation
Renal disease
High pulmonary systolic pressures
Abnormal LV systolic fxn
Advanced age
Prognosis constrictive pericarditis
What does this refer to
A 26-year-old man presents to his primary care physician due to shortness of breath and mild palpitations.
He reports that his symptoms have progressively worsened over the course of a month.
His shortness of breath is most apparent with climbing the stairs or low-intensity jogging.
Approximately 2 months ago, he experienced an upper respiratory infection.
Physical examination is unremarkable.
An electrocardiogram demonstrates nonspecific cardiac abnormalities and cardiac biomarkers and chest radiograph are unremarkable. Preparations are made to obtain a cardiac echocardiogram.
Myocarditis
What does this refer to
Inflammatory disease of the myocardium
Wide range of Physical Exams (subtle to devastating)
2 stages of myocardial damage
Acute
Chronic
Myocarditis
What does this refer to
Equal among races
M = F
Susceptible populations
Immunocompromised
Pregnant women
Children (esp neonates)
Epidemiology of myocarditis
What does this refer to

Etiology of Myocarditis
What does this refer to
Myocyte destruction
Results in cytotoxicity and cytokine release
Furthers myocardial damage
Detection of causal agent in this stage is rare
Acute (first 2 weeks) stages of myocardial damage (myocarditis)
What does this refer to
Continuing myocyte destruction is autoimmune
Abnormal expression of HLA in myocytes
Chronic (> 2 weeks) stages of myocardial damage (myocarditis)