AP Human Geography Unit 2
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Agricultural Density
Number of Farmers divided by the arable land
Arable Land
Land suitable for farming/agriculture
Physiological Density
Population of a region / arable (farmable) land
Arithmetic Population Density
Population of a region divided by total land area.

Baby Boom
Temporary marked increase in the birth rate

Crude Birth Rate
Total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people in the society
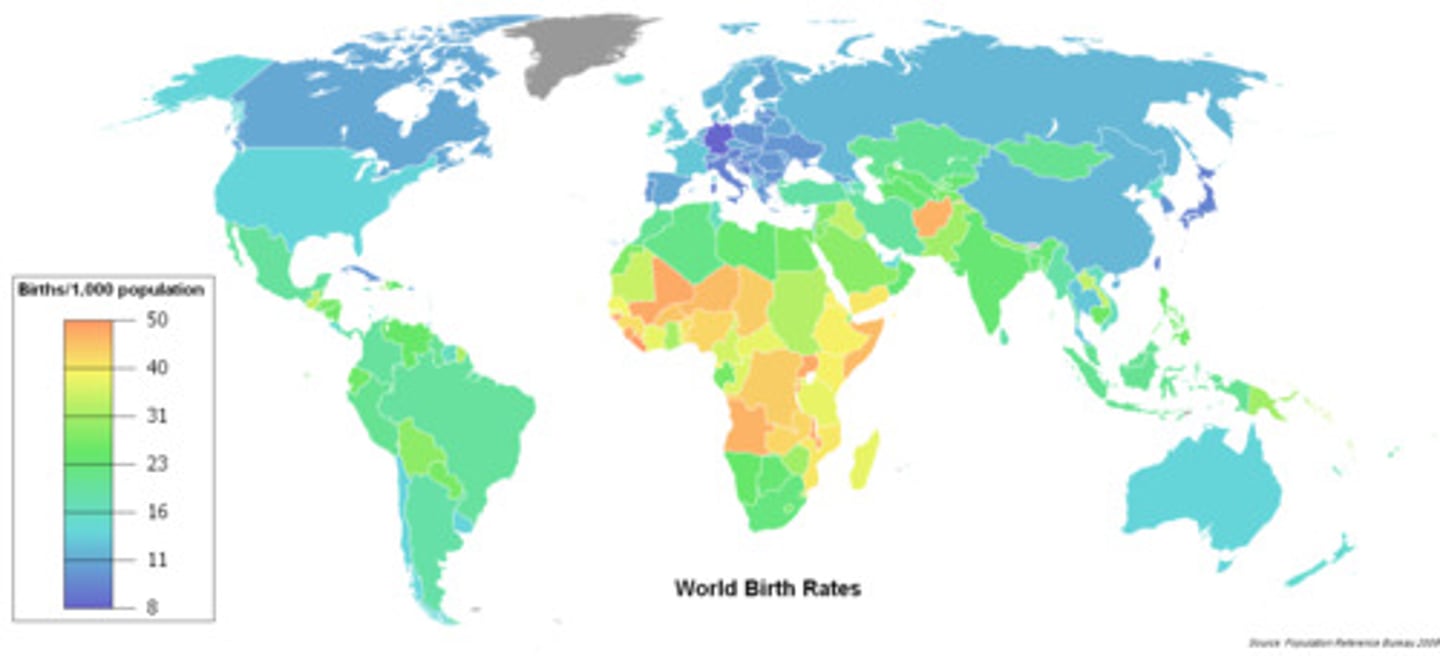
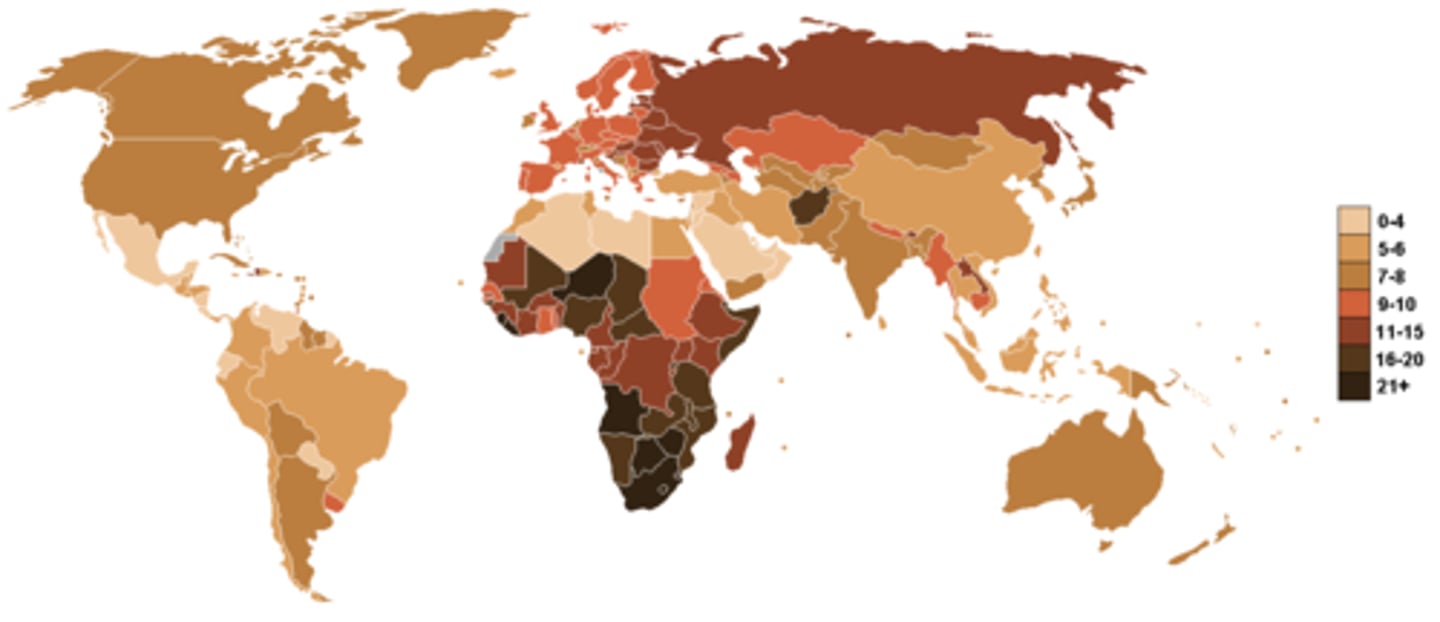
Crude Death Rate
Total number of deaths per 1,000 people in a society
Dependency Ratio
Number of people too young or too old to work compared to workers

Developed Country
A country that has progressed further along in development

Developing Country
A country making some progress toward development

Doubling Time
Number of years needed to double the population
Ecumeme
The areas of earth occupied by human settlement

Epidimiology
Branch of medical science concerning diseases
Industrial Revolution
Time during the 19th century, major improvements in manufacturing goals and delivering them to market

Infant Mortality Rates
Annual number of deaths of infants(one and under) compared to the number of live births

Less Developed Countries (LDC)
Non-industrialized/poor countries.
Stage two, early three
Life Expectancy
Average number of years an infant can expect to live

Thomas Malthus
An English economist who was one of the first to argue that the world's population increase was far outrunning the development of food production
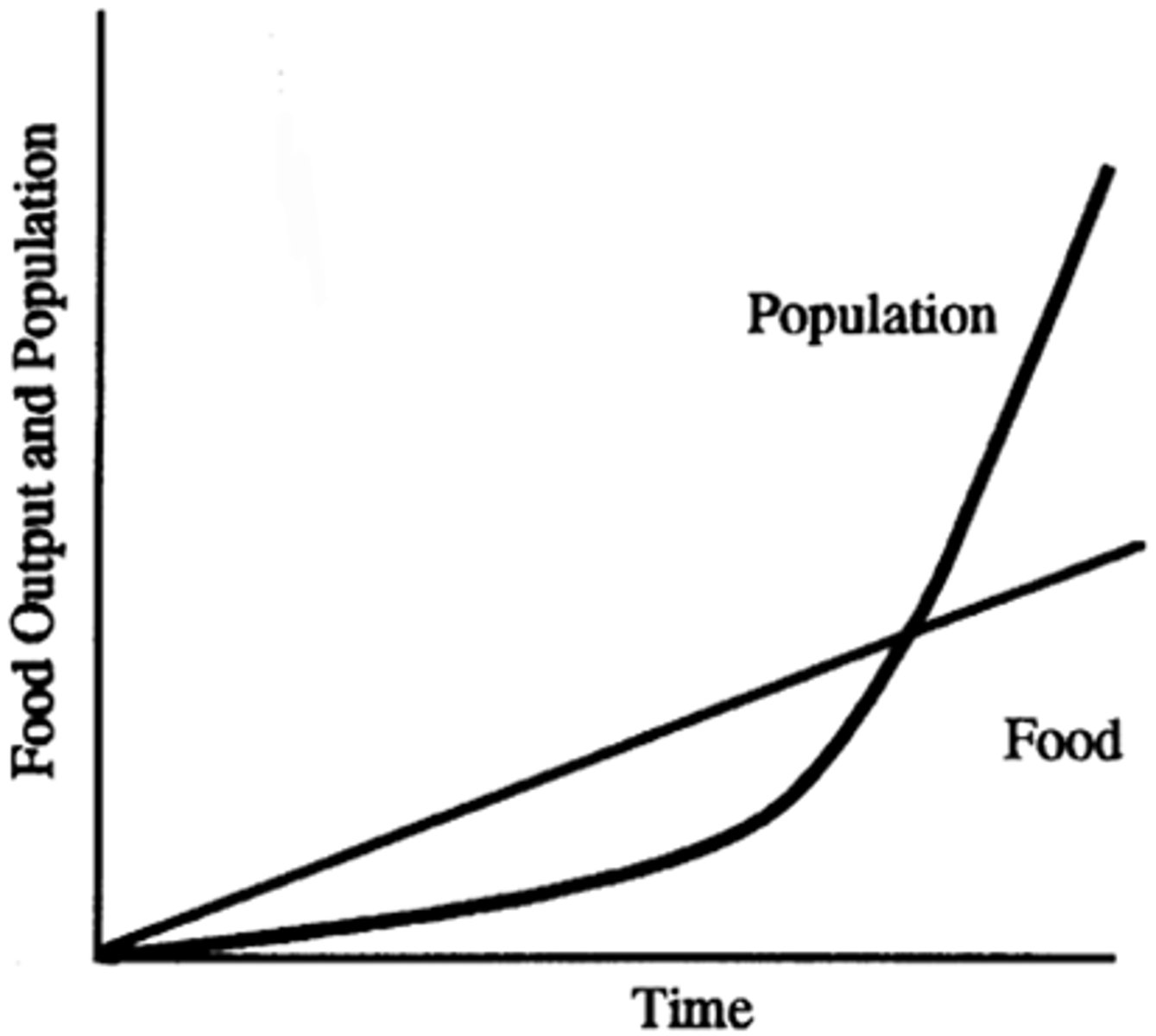
Malthusian Theory
The theory that population grows faster than food supply
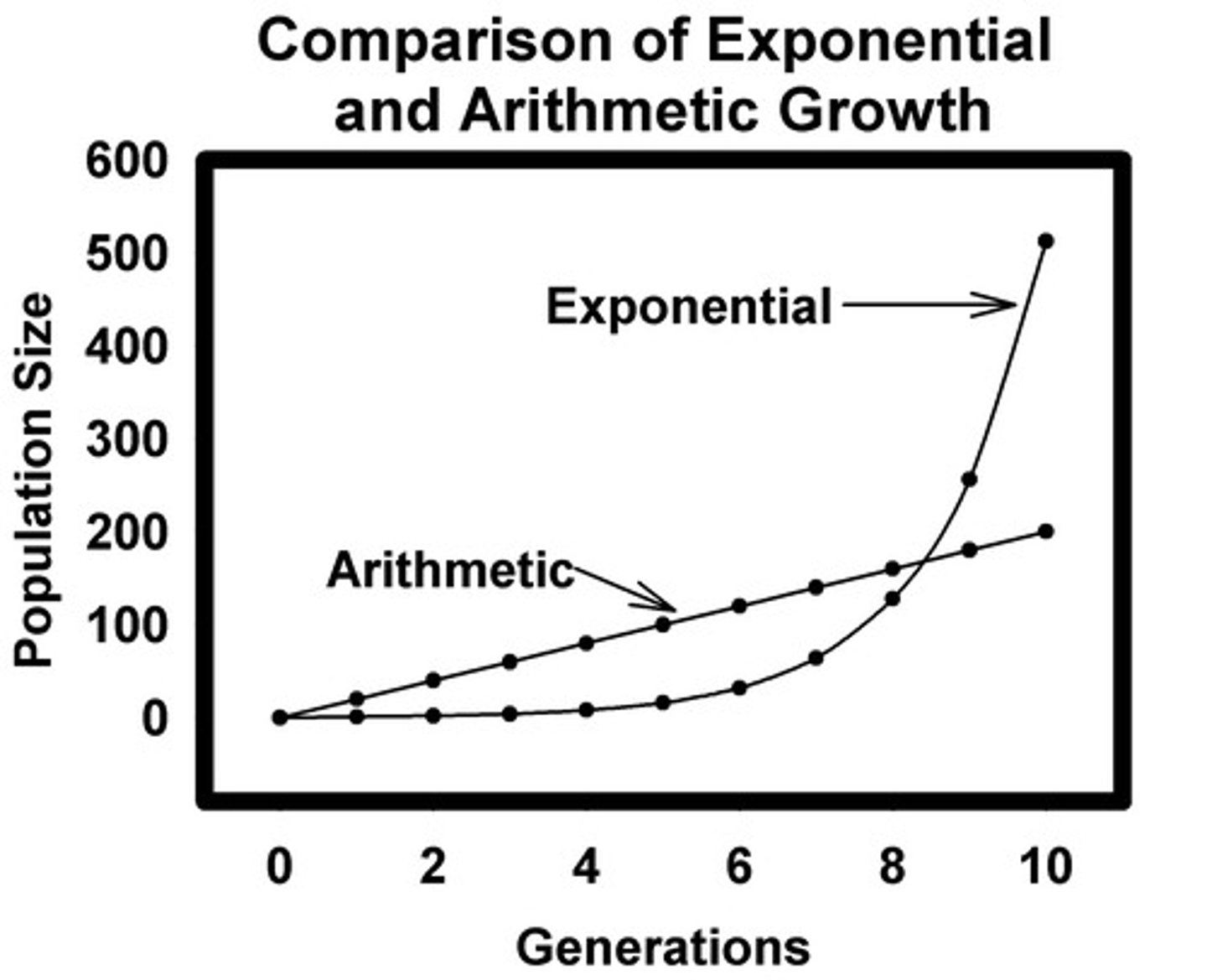
Medical Revolution
Time during the late 20th countries, when medical technology from Europe and North America diffused to developing countries
More Developed Countries
industrialized country.
Stage 4/5

Natural Increase Rate
Percent a population grows in a year
Neo-Malthusians
People who believed in Malthusian Theory and in the idea that population was not only outstripping food but other resources
Population Density
Measurement of population per area or unit
Population Distribution
Pattern of where people live- how people are spread out
Population Pyramids
Country's distinctive population showed on a bar graph- males on left
Anti-Natalist Policies
Government policies to reduce the rate of natural increase

Pro-Natalist Policies
Government policies to increase the rate of natural increase
Sex Ratio
Number of males per 100 females
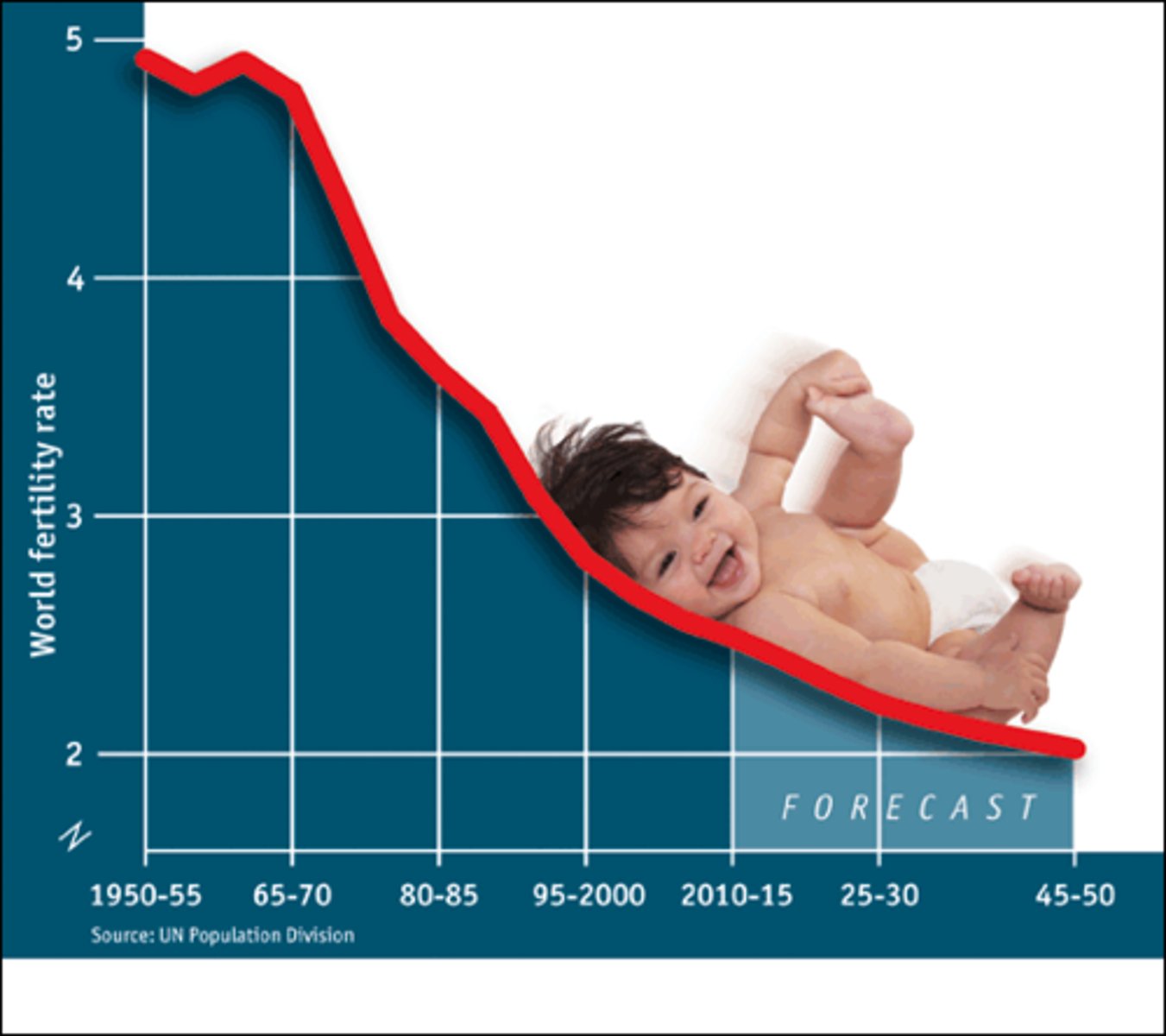
Total Fertility Rate
Average number of children a woman will have during her 'birthing' years
Zero Population Growth
When the CBR and the CDR are equal and the NIR approaches zero
Demography
The scientific study of population characteristics
Over-Population
When the number of people in an area exceeds the capacity of the environment to support life at a decent standard of living.
Population Concentration
An area of land where people are most dense, including East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, and Europe.
Demographic Transition Model
A model that demonstrates the shift in population growth throughout time
Stage 1 DTM
Low Growth: A pre-industrial agrarian society with a High CBR, High CDR, and a Zero NIR
Stage 2 DTM
High Growth: Industrializing society with a CBR that remains high but stable, a CDR that declines dramatically, and a NIR in rapid increase.
Stage 3 DTM
Decreasing growth: Industrializing society with a CBR that declined significantly, a CDR that continues to decline, and a NIR that begins to moderate.
Stage 4 DTM
Low Growth: A Modern Industrialized Country with a low CBR, low CDR, and virtually no NIR
Stage 5 DTM
A Modern Industrialized Country with a very low CBR, an increasing CDR, and a negative NIR
Declining Birth Rates
Education and Health care and Contraceptives have been useful methods
Epidemiologic transition model
A model highlighting the distinctive causes of death in each stage of the demographic transition
Stage 1 ETM
Pestilence and Famine (high CDR)
-infectious and parasitic diseases, accidents and attacks by animals and humans, and other natural causes are principal reasons for human death
-ex. the Black Plague
Stage 2 ETM
Receding Pandemics (rapidly declining CDR)
-results from overcrowding
-ex. cholera outbreak
Stage 3 ETM
Degenerative/Chronic Diseases (moderately declining CDR)
-a decrease in deaths from infectious diseases and an increase in chronic disorders (e.g. cardiovascular diseases) associated with aging
Stage 4 ETM
Delayed Degenerative Diseases (low but increasing CDR)
-The major degenerative causes of death - Cardiovascular diseases and Cancers- linger, but the life expectancy of older people is extended through medical advances
Stage 5 ETM
Reemergence of infectious diseases
-Infectious diseases thought to have been eradicated or controlled return and new ones emerge
-Evolution, Poverty, and increased connections
3 reasons for stage 5 of the ETM
1. Evolution-infectious diseases have evolved and developed resistance to drugs
2. Poverty-infectious diseases are more prevalent in poor areas because of unsanitary conditions
3. Increased Connections-more contact with people through relocation diffusion, lead to a greater spreading of the disease
Epidemiology
The branch of medical sciencee concerned with the incidence, distribution, and control of diseases
Pandemic
A disease that prevails globaly and affects a very high proportion of the population
Mobility
A general term covering all types of movement from one place to another
Cyclical movement
A regular journey that begins at a home base and returns to the exact same place.
Periodic movement
Time away from the home base; don't necessarily return to the same place.
Net migration
The difference between the number of immigrants and the number of emigrants
Net in-migration
When the number of immigrants exceeds the number of emigrants and the net migration is positive
Net-out-migration
If the number of emigrants exceeds the number of immigrants and the net migration is negative
Reasons for migration
Economic opportunity, cultural freedom, and environmental comfort.
Intaregional Migration
Movement within a region
Interregional Migration
Movement from one region to another
Migration Transition
Change in migration patterns in a society caused by industrialisation, population growth, and other social and economic changes that also produce the demographic transition
Stage 1 MTM
High daily or seasonal mobility in search of food
Stage 2 MTM
High international emigration and interregional migration from rural to urban areas
Stage 3 MTM
High international emigration and interregional migration from rural to urban areas
Stage 4 MTM
Same as Stage 3: high international immigration and intraregional migration from cities to suburbs
17th and 18th Centuries
U.S. Immigration from Europe and Sub-Saharan Africa
Mid-Nineteenth to Early Twentieth Century
U.S. Immigration from Ireland, Germany, Scandinavia, and Southern and Eastern Europe
Late 20th to Early 21st Century
U.S. Immigration from Asia and Latin america
Ravenstien's Laws
-Most migrants travel only a short distance
-The number of migrants to a destination declines as the distance they must travel increases.
-Migrants who move longer distances tend to choose major cities
-Every migration flow generates a return or counter flow.
-Families are less likely to make international moves than young adults.
-Men migrate long-distances.
-Women migrate shorter distances but more often than men.
Consequences of migration
Demographic Consequences
-Occurs when migrants change the basic structure of a population
Economic Consequences
-Increase in cost and building of health care, education, public services, and housing
-Lost tax revenue from illegal migrants.
Social Consequences
-Better cultural understanding.
-Conflict among groups
Migrant Workers
These immigrants serve a useful role in Europe, taking low-status and low skill jobs that local residents won't accept
Refugee
Refugee: "a person who has a well-founded fear of being persecuted for reasons of race, religion, nationality, membership of a particular social group, or political opinion."
Asylum seeker
Someone who says he or she is a refugee, but whose claim has not yet been definitively evaluated.