Unit 1: Chemistry of Life
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
from pearson education test prep book
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
matter
anything that takes up space and has mass
element
substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical reactions
compound
substance consisting of 2 or more elements combined in a fixed ratio
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
which substances make up 96% of living matter?
atoms
smallest units of an element that retain the property of the element
protons
positively charged particles found in the nucleus of the atom
electrons
negatively charged particles that are found in electron shells around the nucleus
electrons
what subatomic particle determines the chemical properties and reactivity of the element?
neutrons
particles with no charge
nucleus
where are neutrons found?
isotopes
forms of an element with differing numbers of neutrons
atomic number
number of protons an element possesses; unique to every element
mass number
sum of an element’s protons and neutrons
chemical bonds
interactions between the valence electrons of different atoms
molecules
atoms are held together by chemical bonds to form _____
covalent bond
occurs when valence electrons are shared by 2 atoms
nonpolar covalent bond
occurs when the electrons being shared are shared equally between the two atoms
electronegativity
a tendency to attract electrons of a covalent bond
polar covalent bonds
1 atom has greater electronegativity than the other, resulting in an unequal sharing of the electrons
ionic bonds
chemical bonds resulting from the attraction between oppositely charged ions
hydrogen bonds
weak chemical interactions that form between the partial positively charged hydrogen atom of 1 molecule and the strongly electronegative oxygen/nitrogen of another molecule
van der waals interactions
very weak, transient connections that are the result of asymmetrical distribution of electrons within a molecule; contribute to the 3D shape of molecules
chemical reaction
make and break chemical bonds, shows reactants with an arrow to indicate their conversion into the products
reactants
starting materials in a chemical reaction
products
ending materials in a chemical reaction
negative
the oxygen region of water has a partial _____ charge
positive
the hydrogen regions of water have a partial _____ charge
4
each water molecule can form a maximum of _____ hydrogen bonds at a time
cohesion
linking of like molecules; causes surface tension
adhesion
clinging of 1 substance to another
transpiration
movement of water molecules up the thin xylem tubes and their evaporation from the stomata in plants
cohesion; adhesion
water molecules cling to each other by _____ and to the walls of the xylem tubes by _____
specific heat
the amount of heat required to raise/lower the temperature of a substance by 1 ºC
solvent
substance that something is dissolved in
solute
substance being dissolved
solution
combination of the solvent and solute
hydrophilic
substances that are water soluble; includes ionic compounds, polar molecules, some proteins
hydrophobic
substances that are nonpolar and do not dissolve in water
cohesion
adhesion
high specific heat
less dense as a solid than a liquid
important solvent
properties of water that result from hydrogen bonds
pH scale
runs between 0-14 and measures the relative acidity and alkalinity of aqueous solutions
acids
have an excess of H+ ions and a pH below 7
acids
[H+] > [OH-]
bases
have an excess of OH- ions and a pH above 7
bases
[H+] < [OH-]
buffers
substances that minimize changes in pH by accepting H+ when they are in excess/donating H+ when they are depleted
carbonic acid (H2C03)
an important buffer in living systems; moderates pH changes in blood plasma and the ocean
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus
major elements of life (P.S. COHN)
carbon
all organic compounds contain _____
4 valence electrons - 4 covalent bonds
can form single, double, or triple bonds
large molecules
chains, rings, and branches
why is carbon unparalleled in its ability to form large, complex molecules?
isomers
molecules that have the same formulas but differ in their arrangement of the atoms
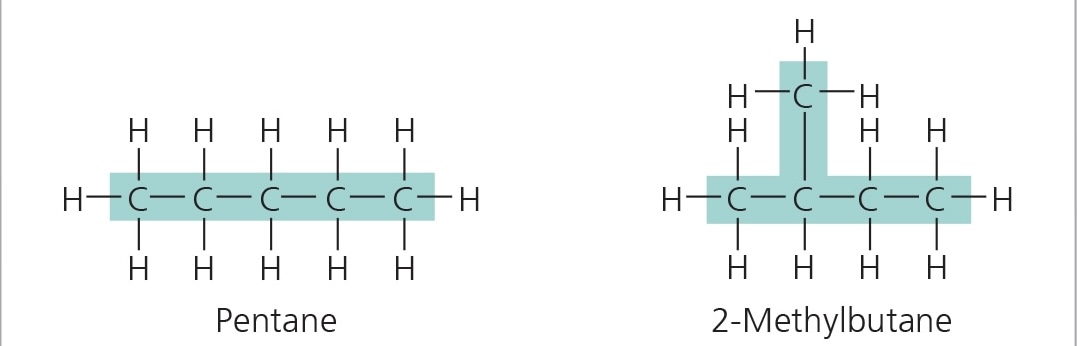
structural isomers
isomers that differ in the covalent arrangements of their atoms
cis-trans isomers
isomers where carbons have covalent bonds to the same atoms, but these atoms differ in their spatial arrangements due to the inflexibility of double bonds

enantiomers
isomers that are mirror images of each other and that differ in shape due to the presence of an asymmetric carbon
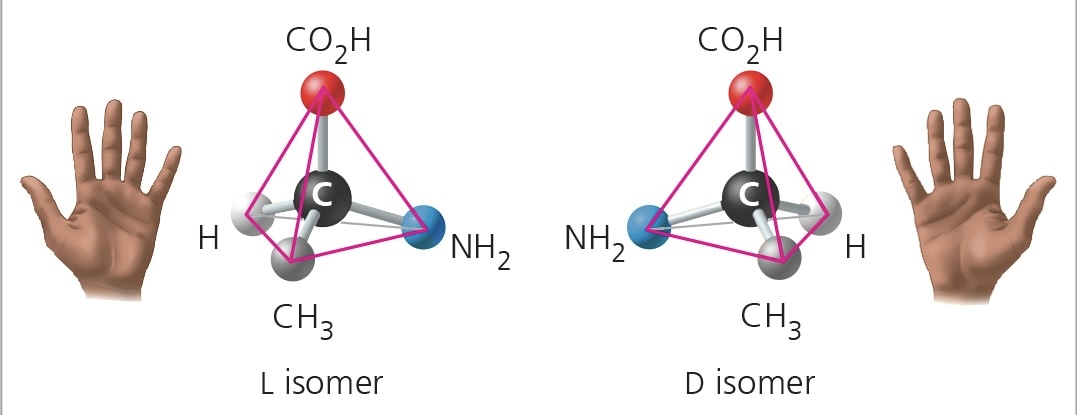
asymmetric carbon
carbon that is attached to 4 different atoms/groups of atoms
hydroxyl group (-OH)
compound name: alcohol (specific name usually ends in -ol)
properties: polar, helps dissolve molecules like sugars
examples: ethanol, methanol

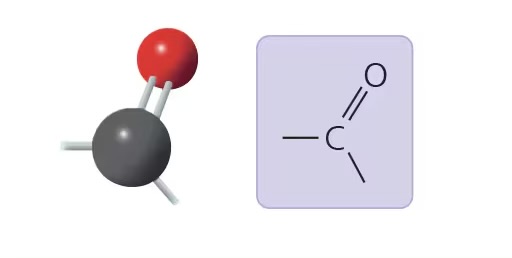
carbonyl group (>CO)
compound name: ketone/aldehyde
properties: acid (tends to ionize), source of H+ ions
examples: acetone, propanol, sugars
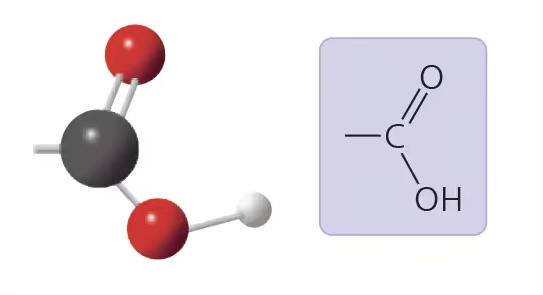
carboxyl group (-COOH)
compound name: carboxylic acid/organic acid
properties: polar, acidic b/c it tends to ionize, source of H+ ions
examples: acetic acid, fatty acids, sugars, carboxylate ions
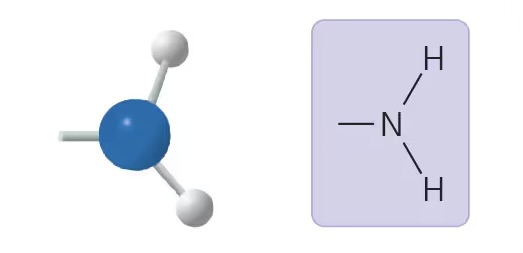
amino (-NH2)
compound name: amine
properties: acts as base
examples: amino acids (e.g. glycine)
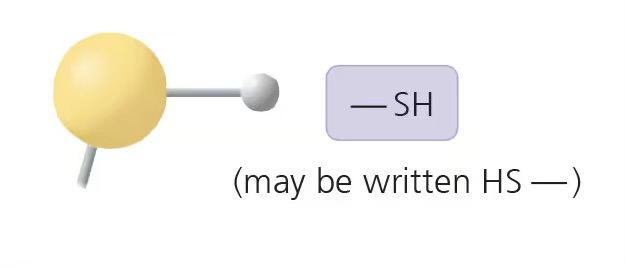
sulfhydryl group (-SH)
compound name: thiol
properties: slightly polar, forms disulfide bridges in proteins
examples: cysteine
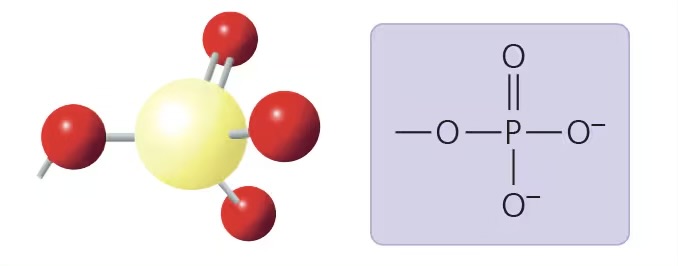
phosphate group (-OPH3 2-)
compound name: organic phosphate
properties: highly hydrophilic, acidic
examples: ATP, DNA, phospholipids
methyl group (-CH3)
compound name: methylated compound
properties: highly stable/unreactive, affects expression of genes
examples: 5-methylcytosine (component of DNA)
polymers
large chain molecules made of repeating subunits called monomers
monomers
repeating subunits that make up polymers
dehydration reactions
reaction that create polymers from monomers, where 2 monomers are joined by removing 1 molecule of water
hydrolysis
reaction that occurs when water is added to split large molecules; reverse of dehydration
carbohydrates
serve as fuel and building material; include both simple sugars and polymers; have a ratio of 1 C:2 H:1 O
monosaccharides
monomers of carbohydrates; contains carbonyl group and multiple hydroxyl groups, e.g. glucose, fructose, galactose, ribose
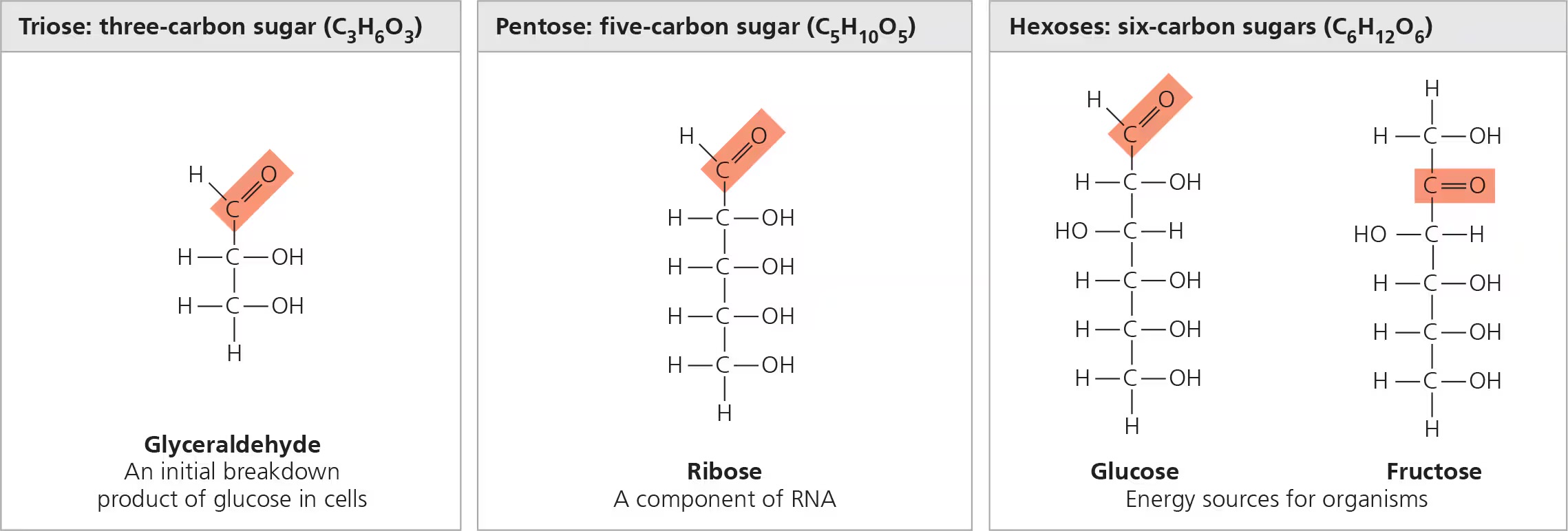
polysaccharides
polymers of monosaccharides; e.g. starch, cellulose, glycogen
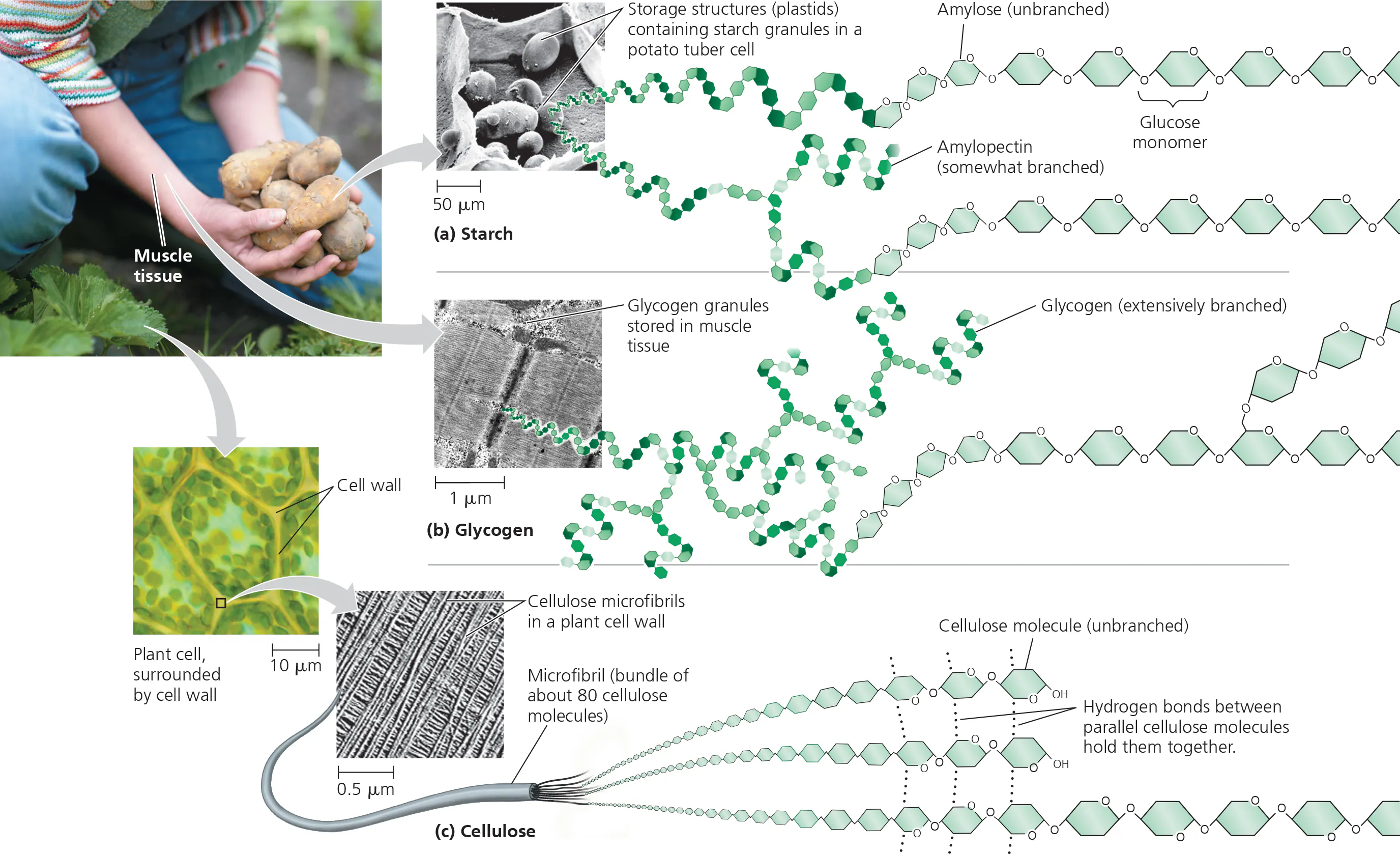
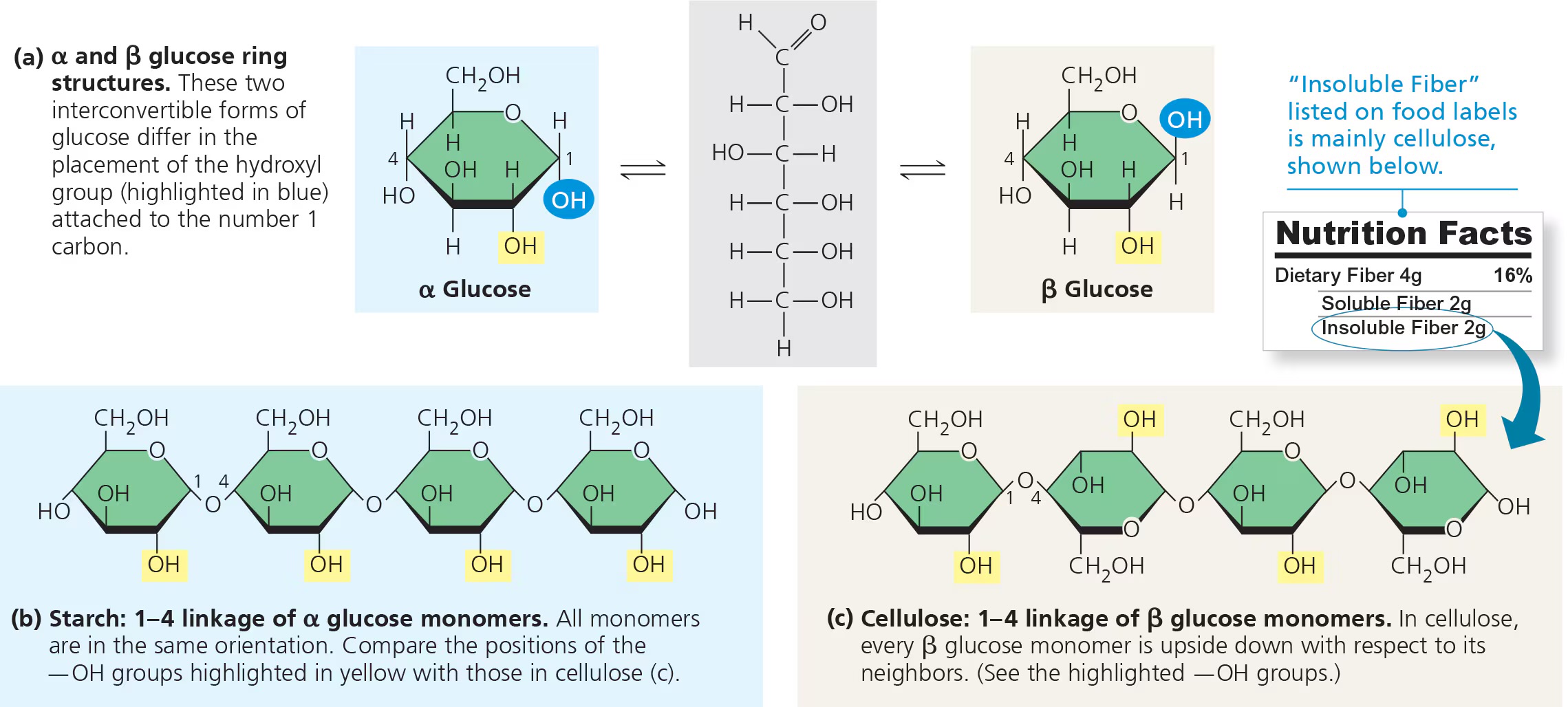
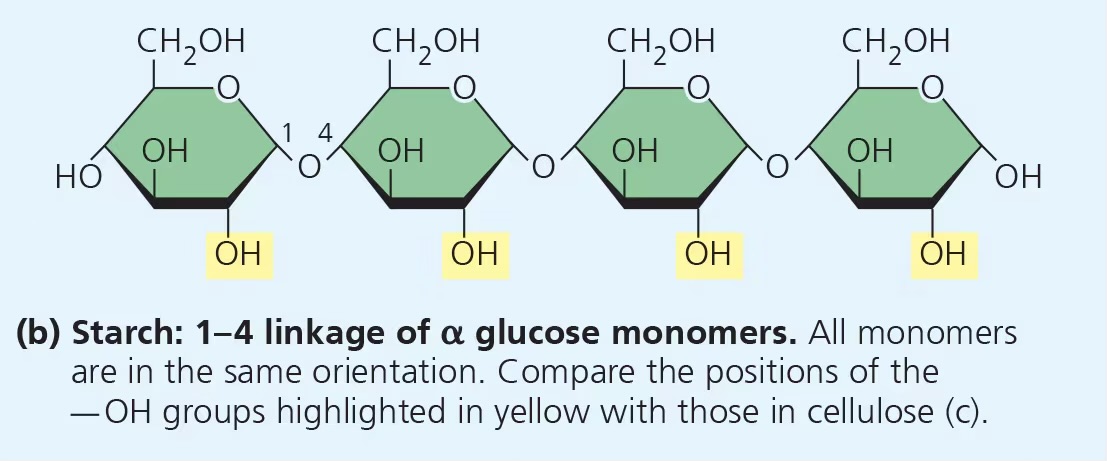
what is the structure of starch?
1-4 alpha glycosidic linkages (this makes it digestible)
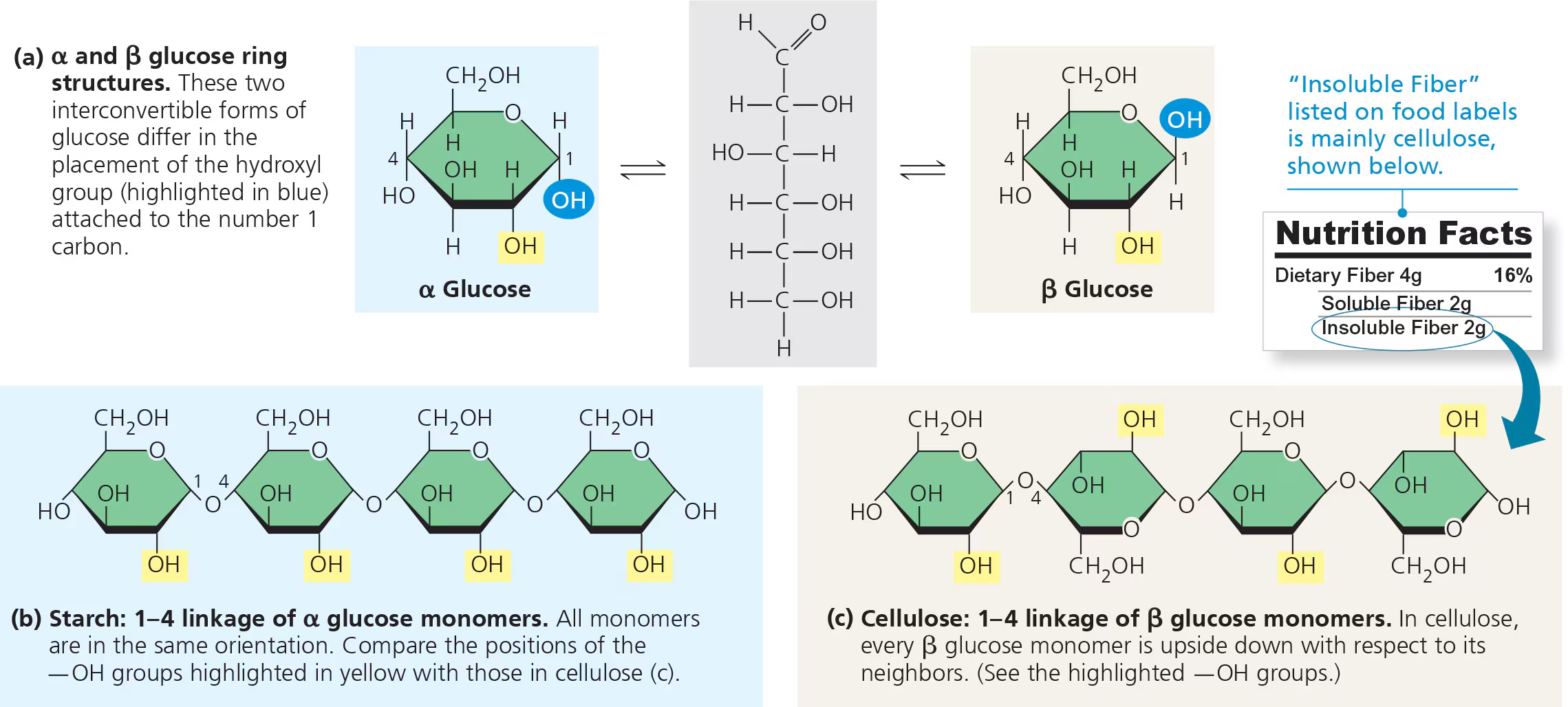
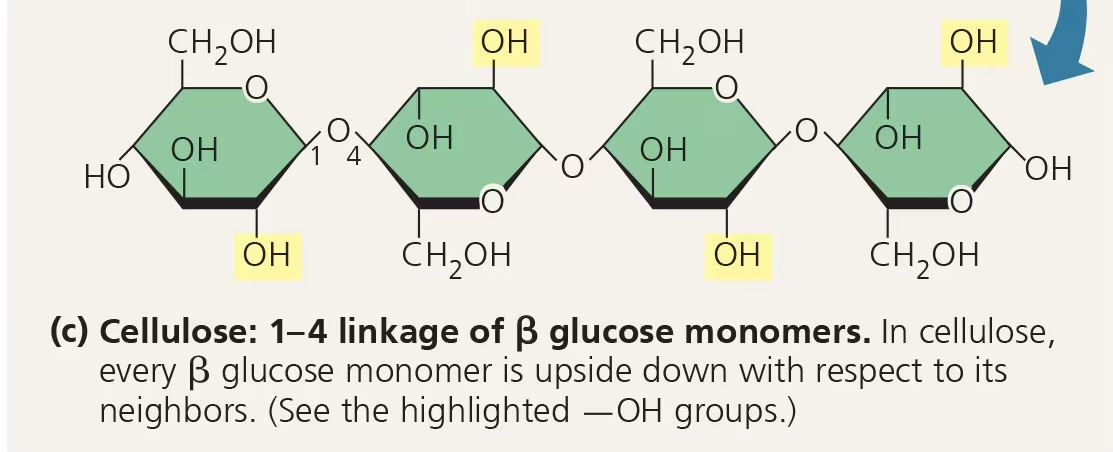
what is the structure of cellulose?
1-4 beta glycosidic linkages (this means humans cannot digest it)
what are the functions of polysaccharides?
energy storage, structural support
what are examples of energy storage polysaccharides?
starch, glycogen
starch
storage polysaccharide found in plants (e.g. in potatoes)
glycogen
storage polysaccharide found in animals (within vertebrate muscle & liver cells)
what are examples of structural support polysaccharides?
cellulose, chitin
cellulose
structural polysaccharide that is a major component of plant cell walls
chitin
structural polysaccharide that is found in the exoskeleton of arthropods (lobsters, insects) and the cell walls of fungi; similar to cellulose but has a nitrogen-containing attachment
fats/triglycerides
made up of a glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acid molecules
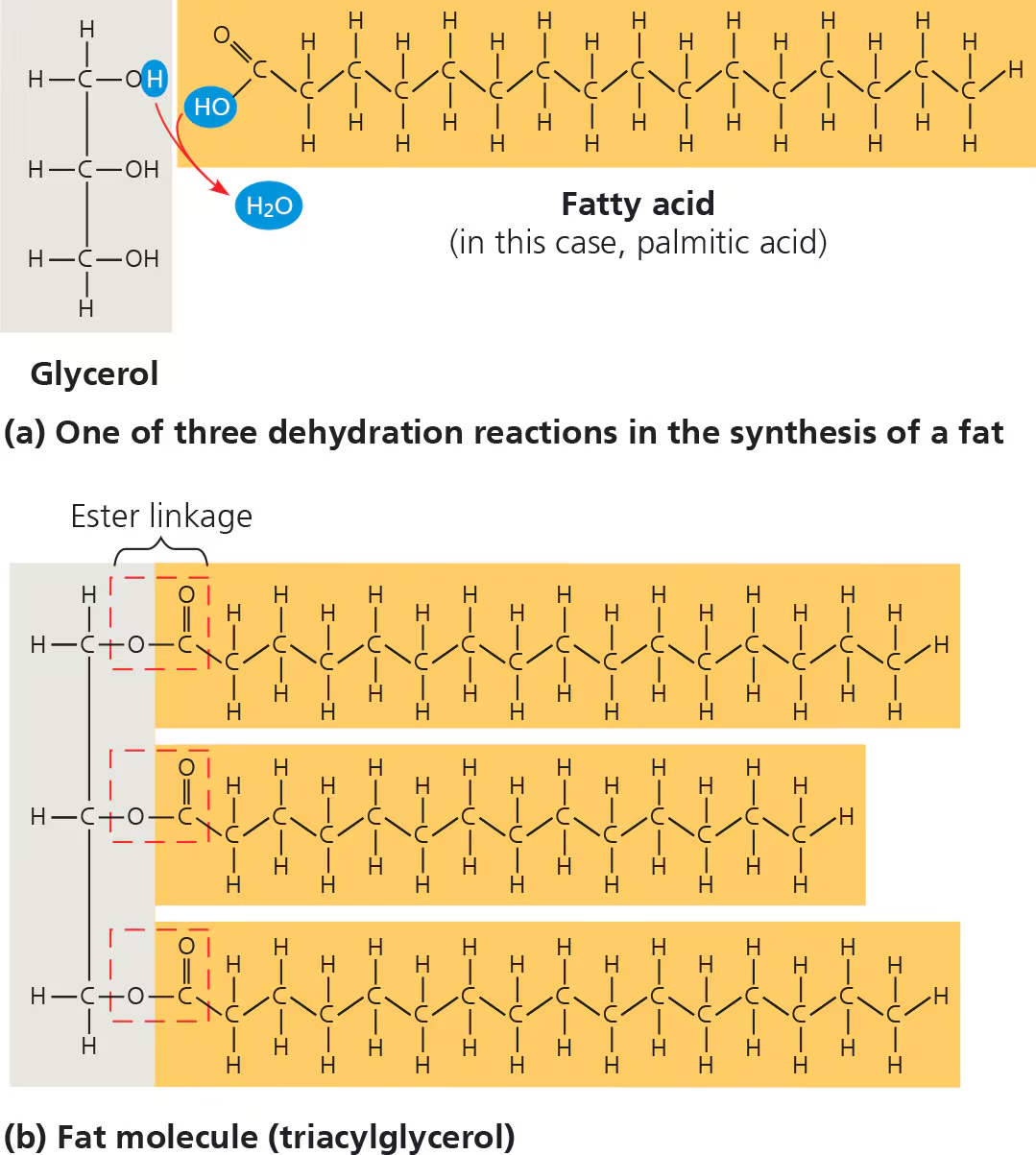
fatty acids
include hydrocarbon chains of variable lengths; nonpolar/hydrophobic
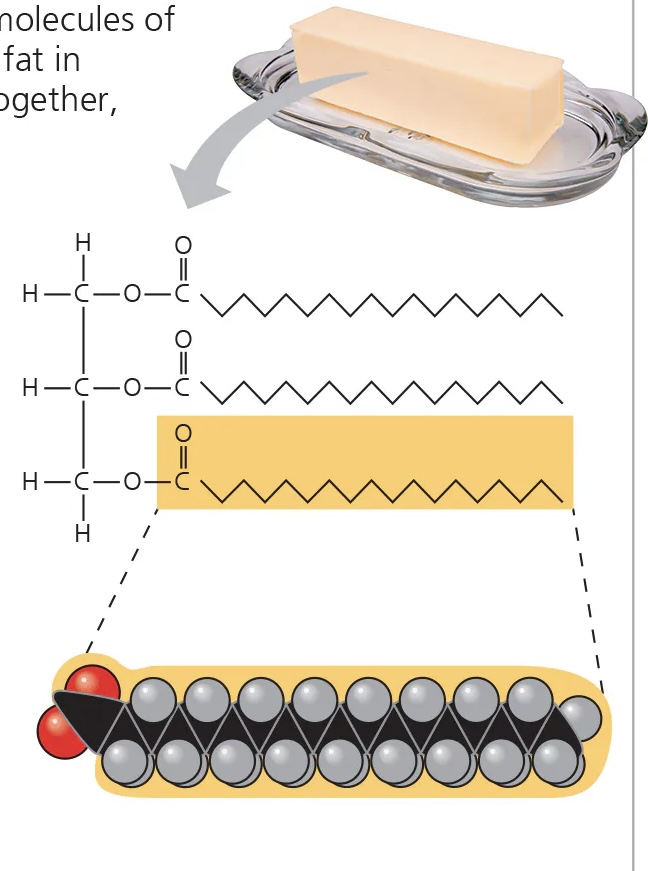
saturated fatty acids
no double bonds between carbons
pack solidly at room temp
linked to cardiovascular disease
commonly produced by animals
e.g. butter, lard
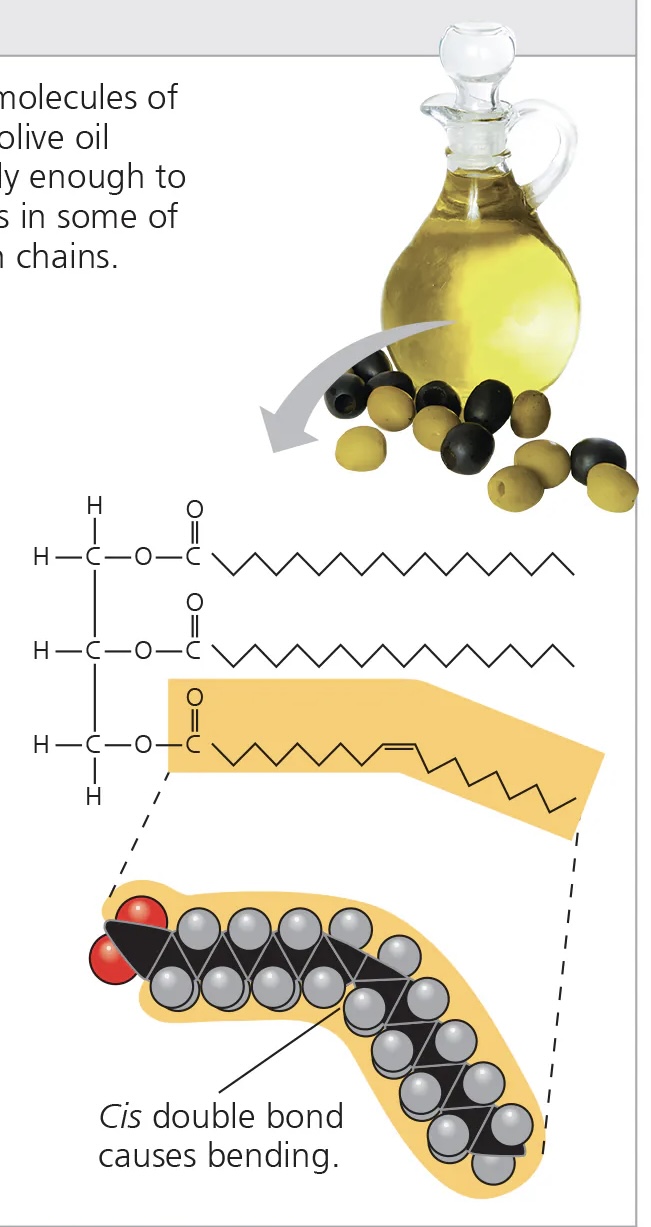
unsaturated fatty acids
have some carbon double bonds - result in kinks
liquid at room temp
commonly produced by plants
e.g. corn oil, olive oil
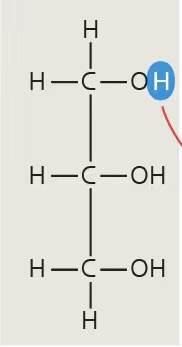
glycerol
alcohol made up of 3 carbons, each with a hydroxyl group
what are the functions of lipids
energy storage, protection, insulation
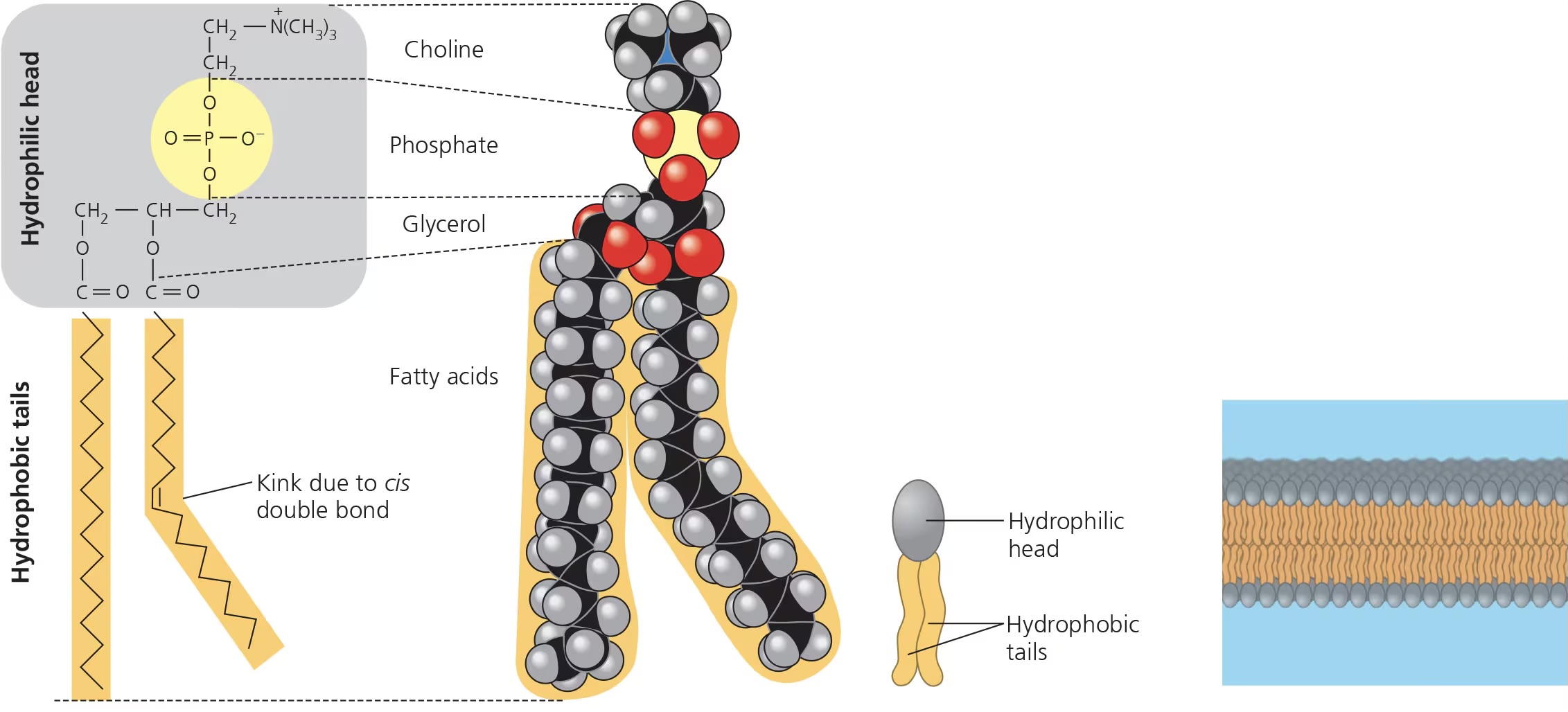
phospholipids
major component of cell membranes
hydrophilic head w/ phosphate group
2 hydrophobic fatty acid tails
steroids
lipids with a carbon skeletons of 4 rings fused together
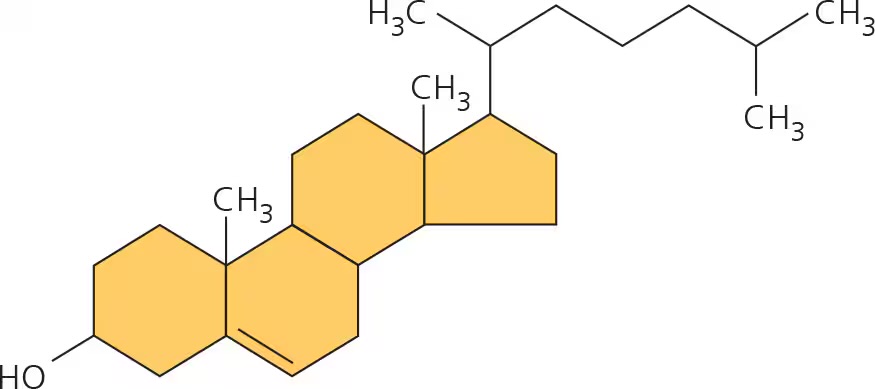
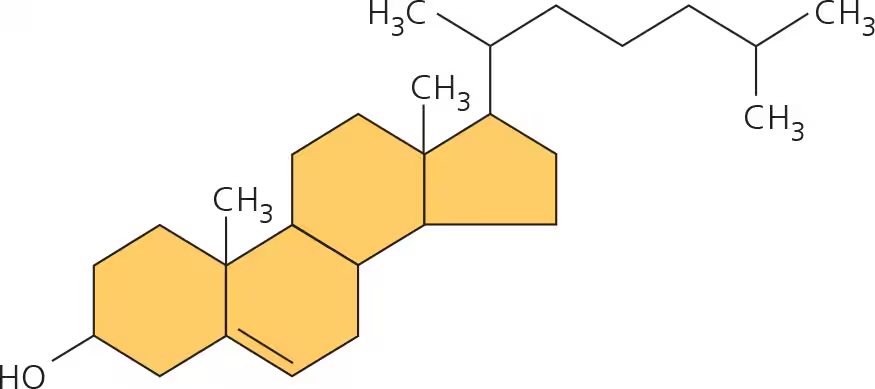
cholesterol
steroid; common component of animal cell membranes
estrogen, testosterone
steroid hormones
proteins
polymers made up of amino acid monomers
amino acids
contain central carbon bonded to carboxyl group at one end, an amino group at the other end, an H atom, and an R group
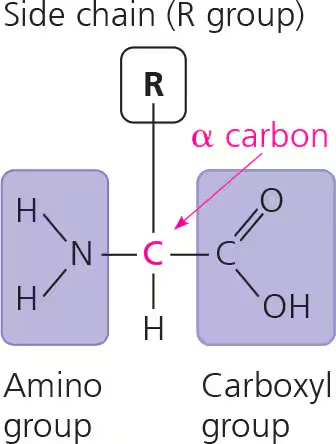
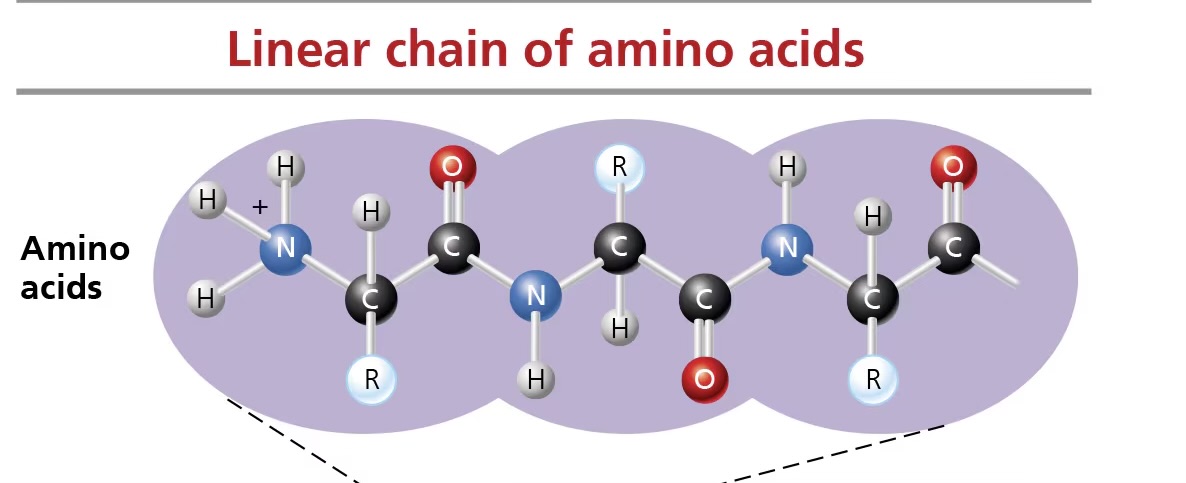
peptide bonds
link amino acids; formed by dehydration synthesis between amino and carboxyl groups of adjacent monomers
primary structure (proteins)
unique sequence in which amino acids are joined
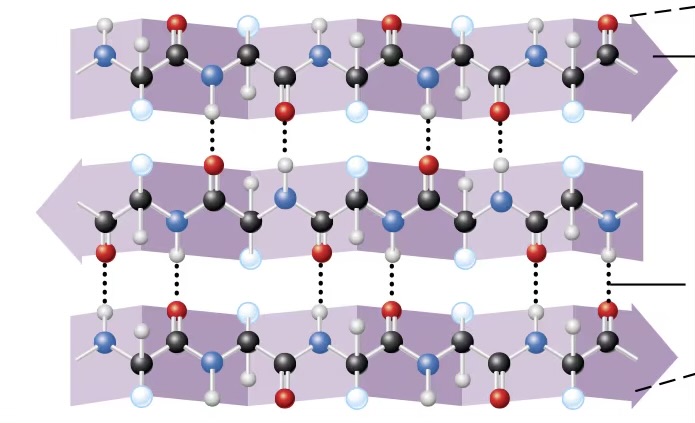
secondary structure (proteins)
refers to 1 of 2 3D shapes that are the result of H bonding between members of the polypeptide backbone (not amino acid side chains)
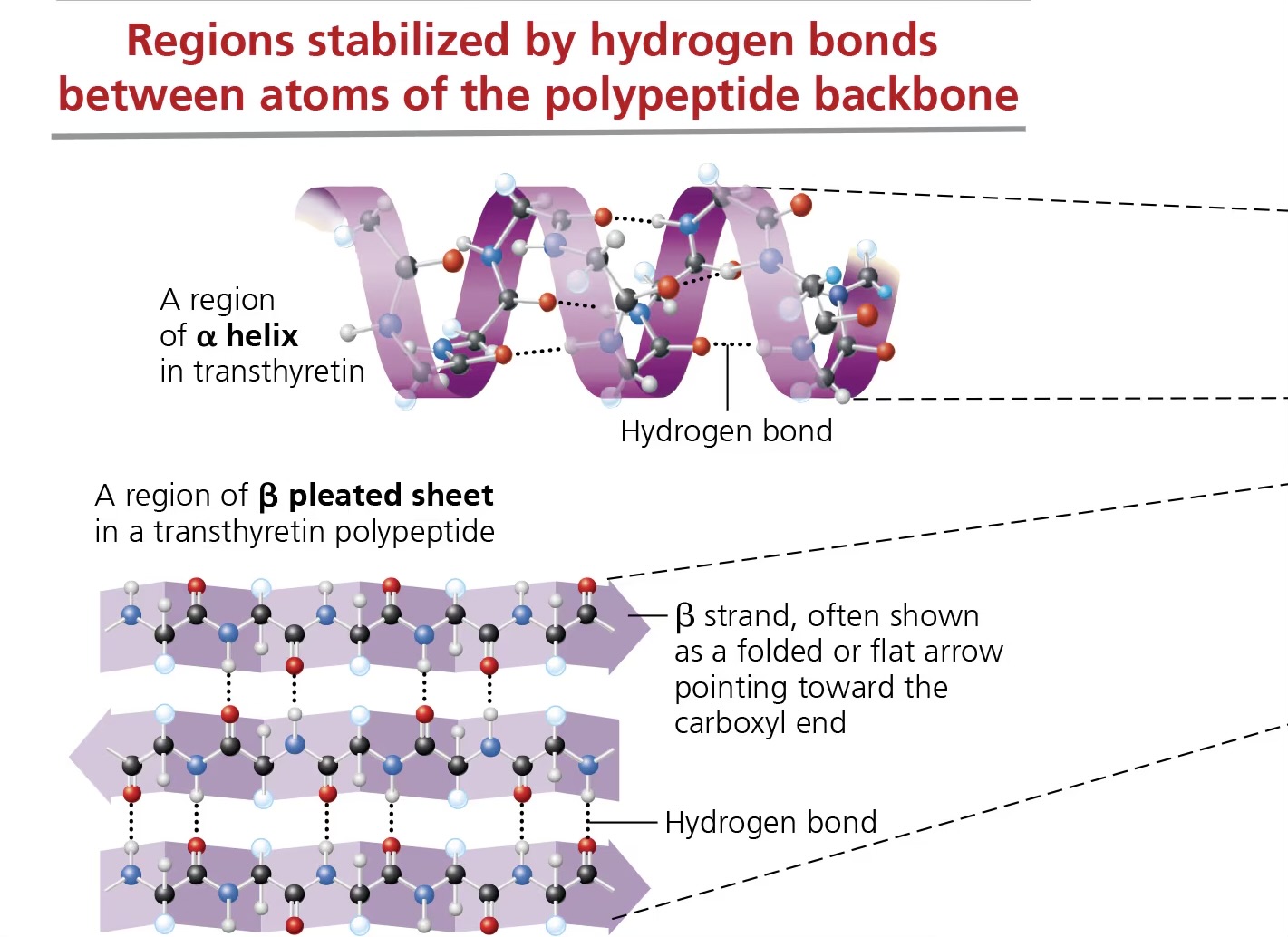
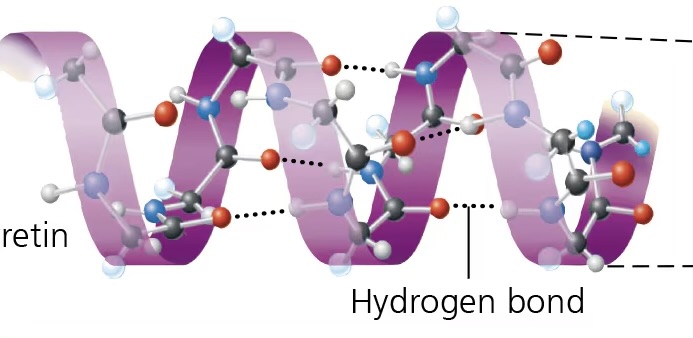
alpha helix
coiled shape, like slinky, of proteins
beta pleated sheet
accordion shape of proteins
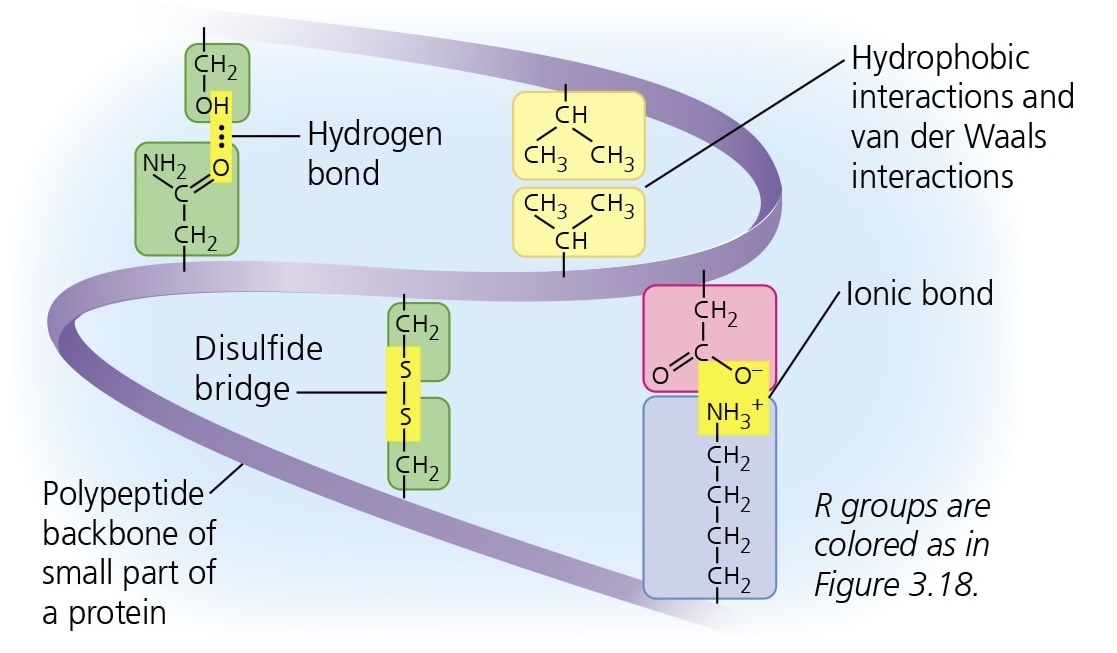
tertiary structure (proteins)
complex globular shape resulting from interactions between R groups (H bonds, hydrophobic interactions, van der Waals interactions, disulfide bridges)
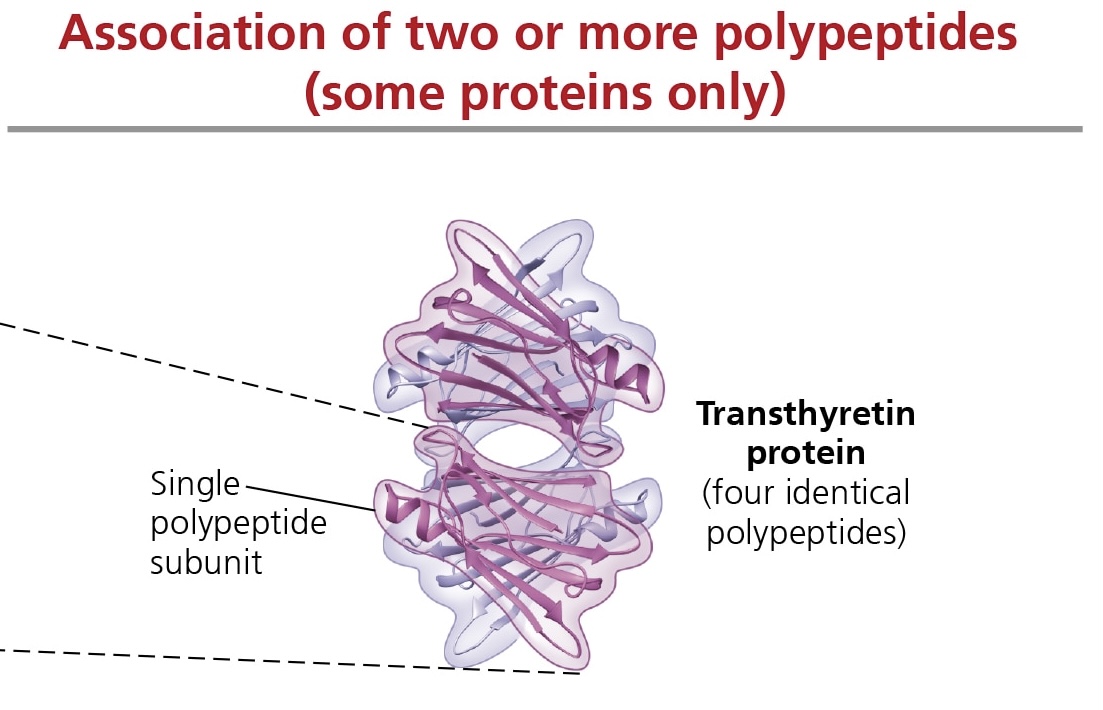
quaternary structure
refers to the association of 2 or more polypeptide chains into 1 large protein
denatured protein
protein loses its shape and ability to function because of heat, a change in pH, or some other
functions of proteins
enzymes, defense, storage, transport, hormones, receptors, contractile/motor, structural
3 parts of nucleotides
nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, phosphate group
dna
molecule of heretidy
double stranded helix
A, T, C, G
A bonds to T
C bonds to G