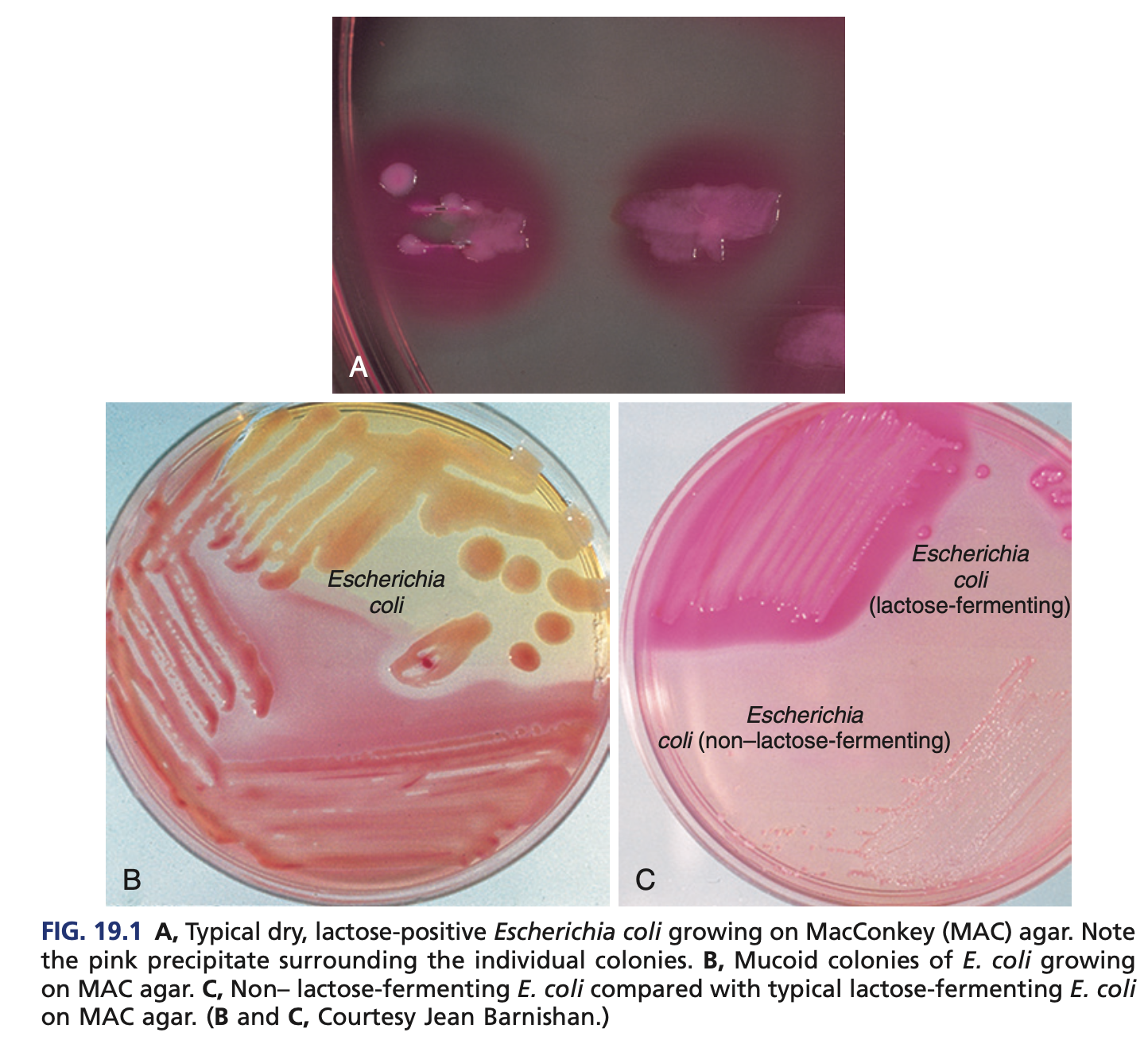
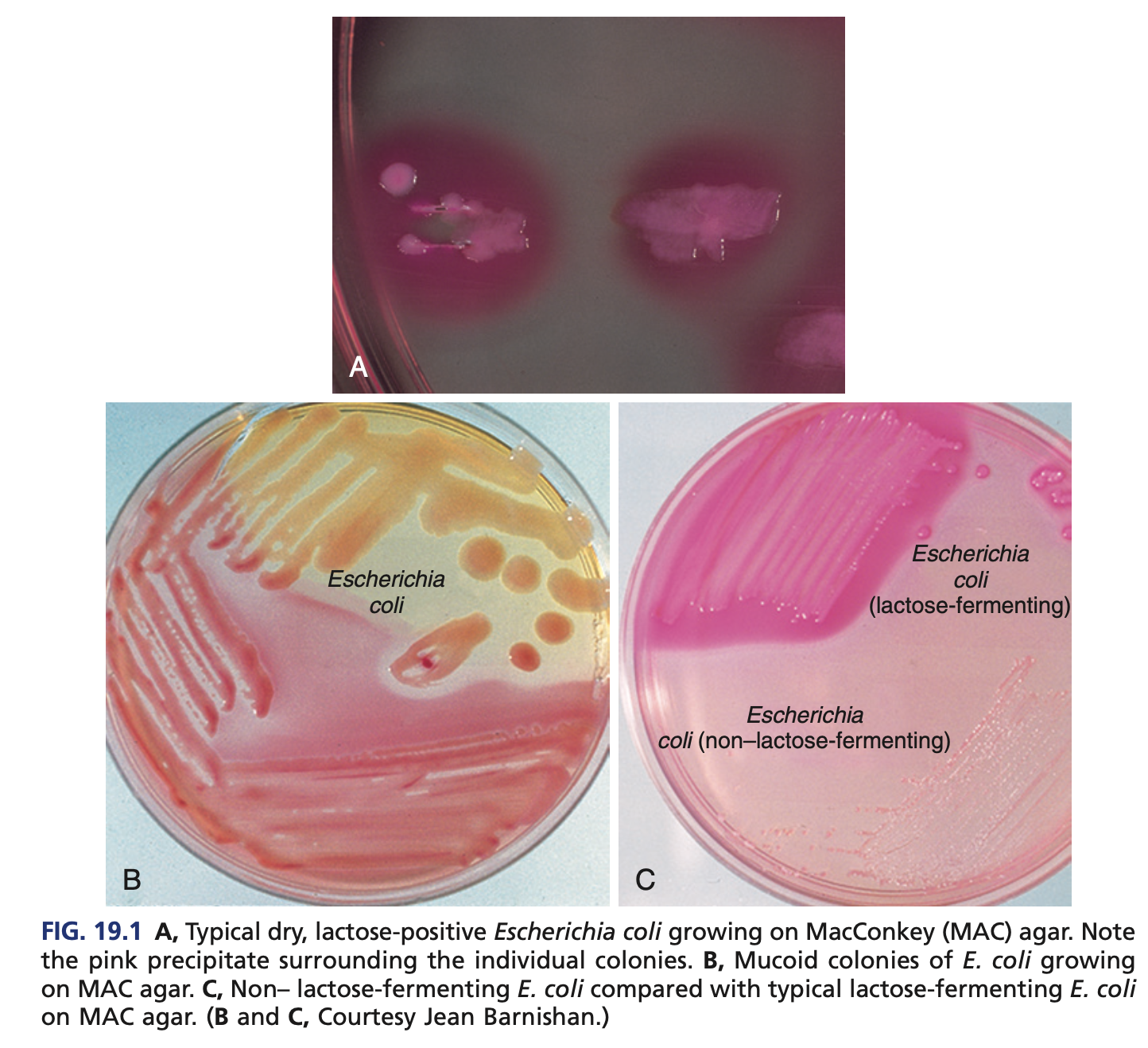
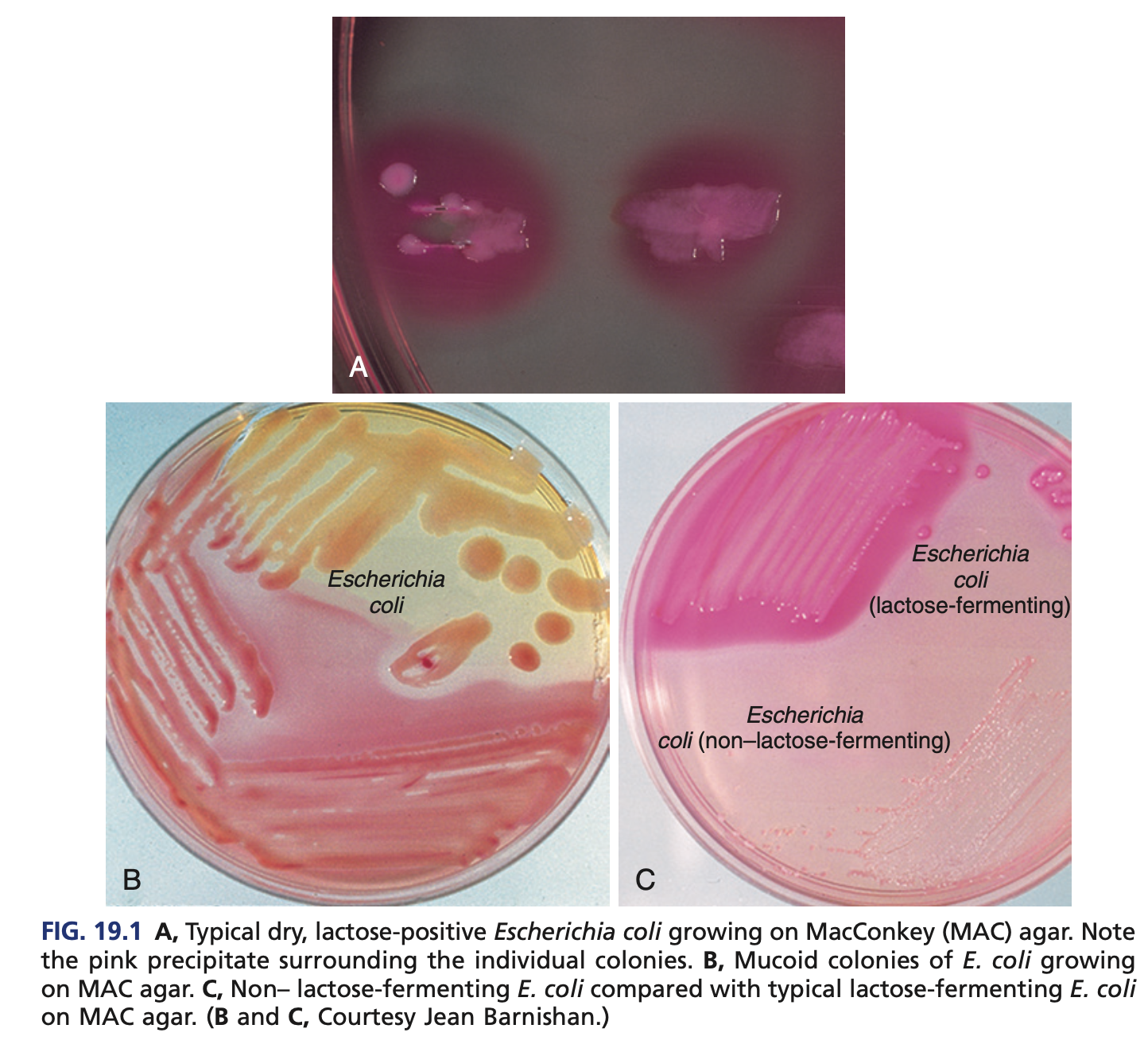
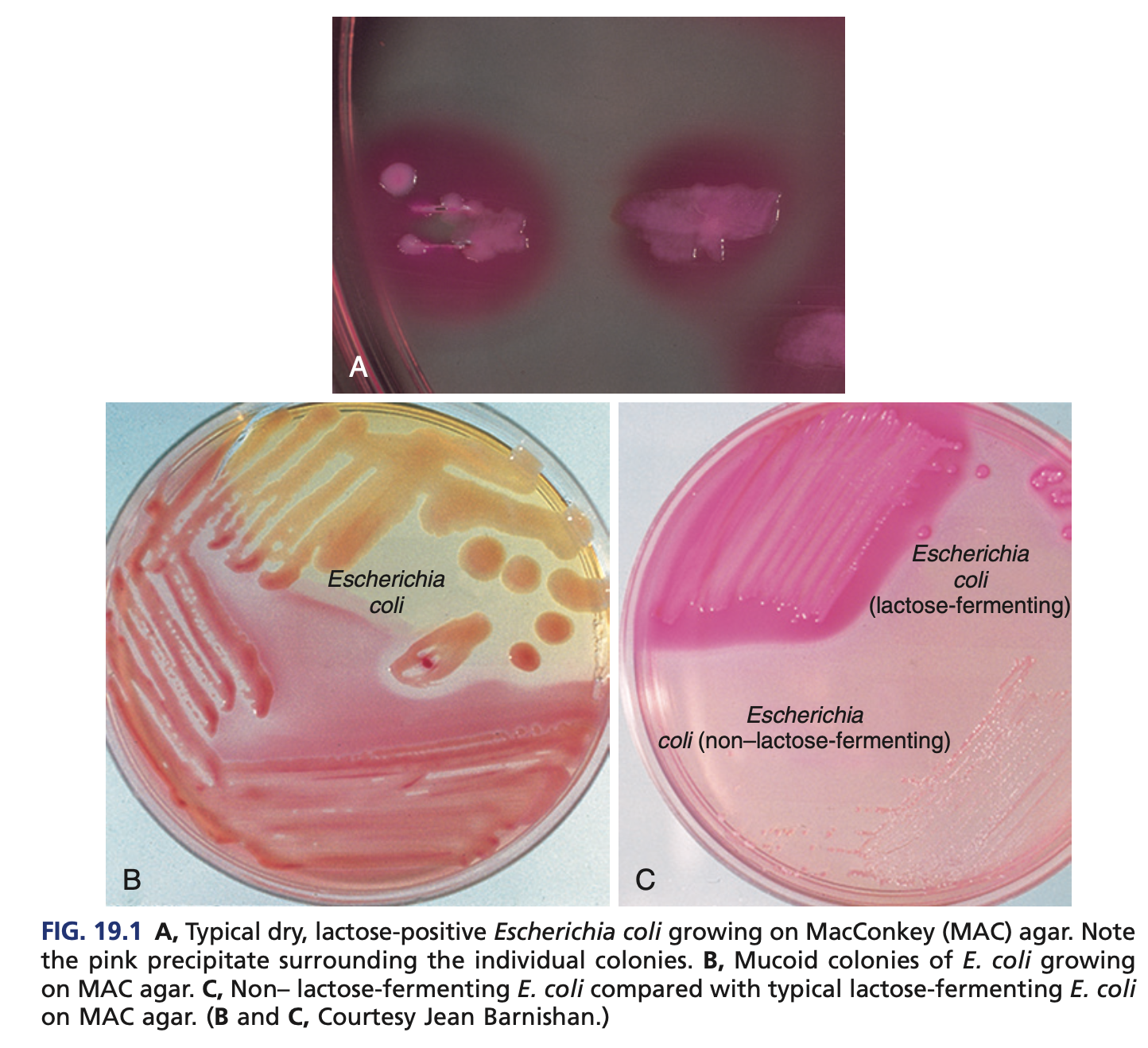
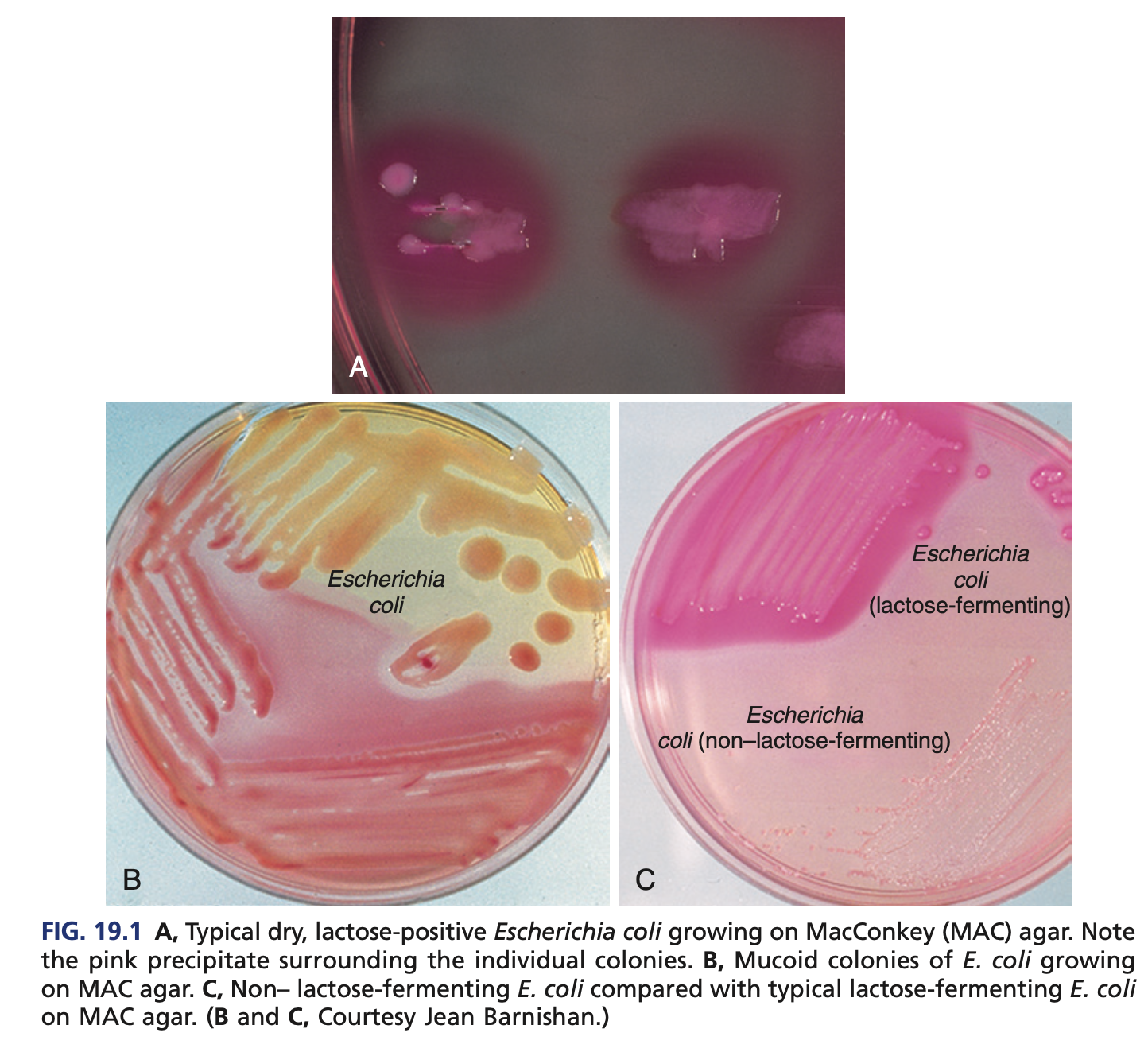
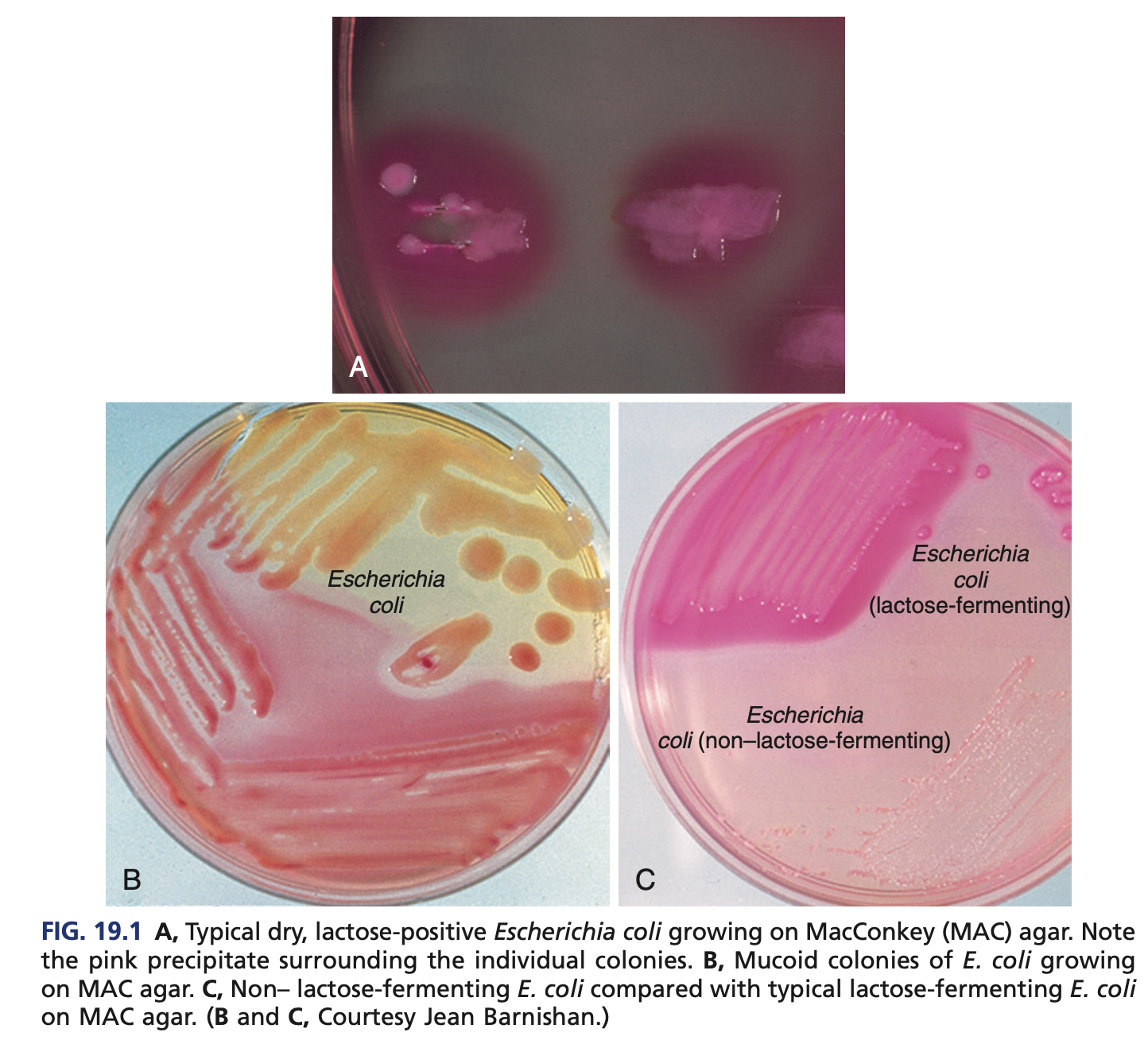
RAPID LACTOSE FERMENTERS (COLIFORMS) – ESCHERICHIA
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Colon’s Bacillus
Escherichia coli aka
T
Escherichia coli is pathogenic when it produces toxin (t/f)
Escherichia coli is the primary marker of fecal contamination in water purification
Escherichia coli is the primary marker of - contamination in -
O, H, K Ag
Escherichia coli ‘s Antigenic
ENDOTOXIN
COMMON PILI
K1 Ag (neonatal meningitis)
Intimin
Virulence Factors of Escherichia coli
UTI
Escherichia coli is the #1 cause of _______, Gram-negative sepsis
neonatal meningitis
Escherichia coli is the #2 cause of
Nosocomial
Wound
Bacteremia
Pneumonia
Other diseases of Escherichia coli is
diarrhea and gastroenteritis
Escherichia coli may cause
A/A + GAS
Laboratory Diagnosis of Escherichia coli
1. TSI: A/A + GAS
MViC: + + – –
Laboratory Diagnosis of Escherichia coli
2. IMViC: ___________
LOA: ++ –
Laboratory Diagnosis of Escherichia coli
3. LOA: ++-
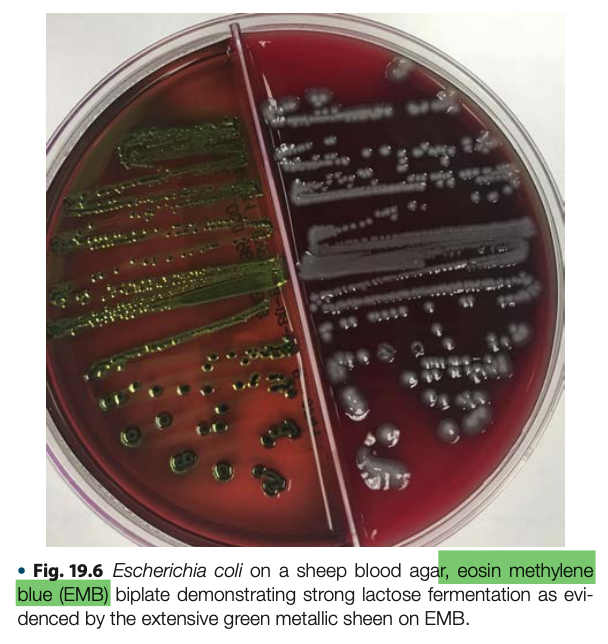
Green Metallic Sheen
Laboratory Diagnosis of Escherichia coli
4. Eosin Methylene Blue: ___________________
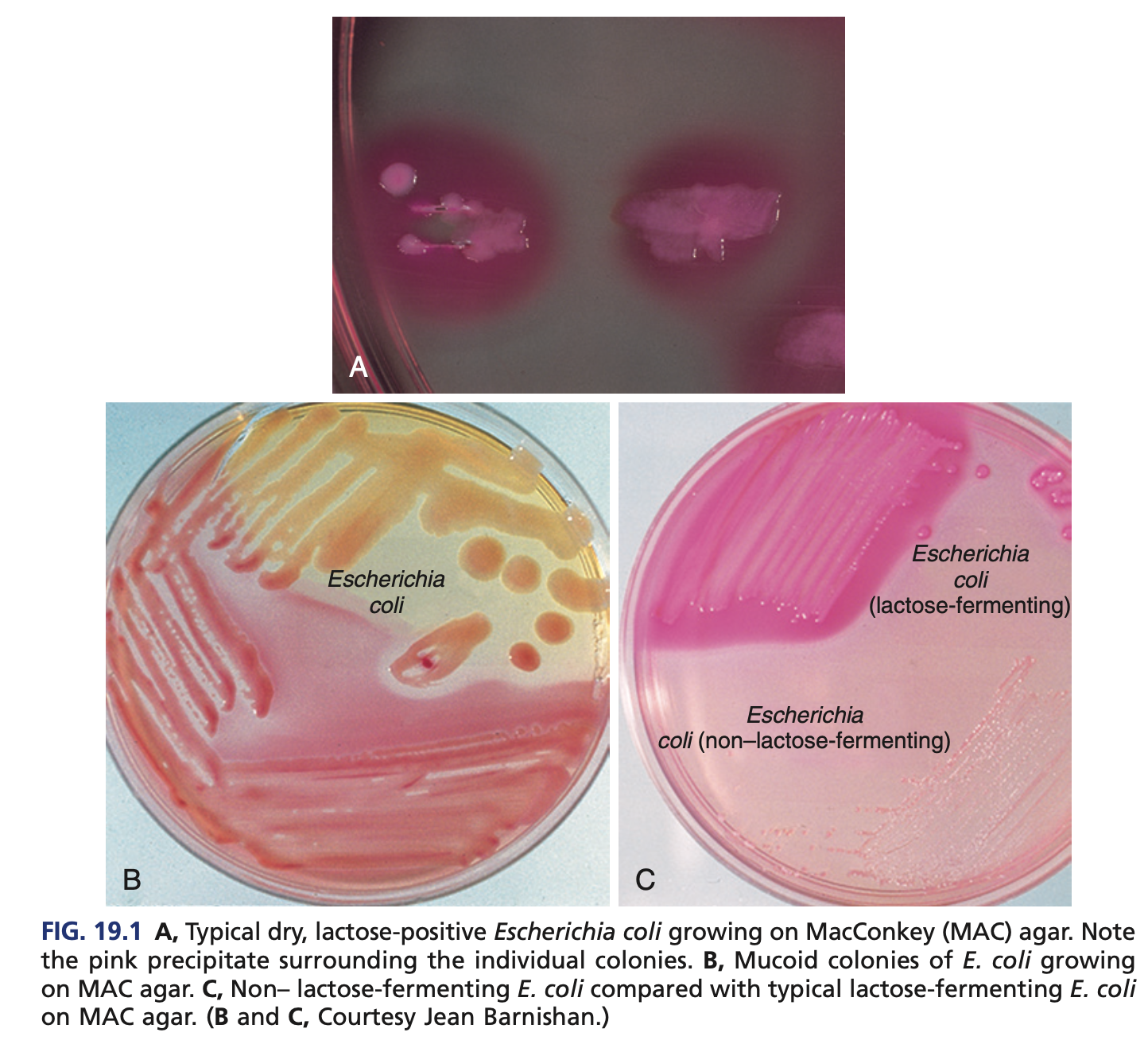
E. coli O157:H7
Laboratory Diagnosis of Escherichia coli
5. MUG (+) except
Limulus Test
Laboratory Diagnosis of Escherichia coli
> detect bacterial endotoxin
Limulus horse crab
Laboratory Diagnosis of Escherichia coli
Limulus Test derived from
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC)
Grows only on BAP
Traveler’s Diarrhea / Montezuma’s Revenge (Turista)
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) causes
Heat-Labile Toxin
Heat-Stable Toxin
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) 2 Toxins
Heat-Labile Toxin
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) 2 Toxins
similar to the “choleragen toxin” from V. cholerae
Heat-Labile Toxin
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) 2 Toxins
it also activates adenylate cyclase causing hypersecretion of both electrolytes and fluids into the intestinal lumen leading to WATERY DIARRHEA
Heat-Stable Toxin
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) 2 Toxins
stimulates guanylate cyclase which also leads to hypersecretion electrolytes and fluids into the intestinal lumen
Enteroinvasive Escherichia coli (EIEC )
Primary virulent factor of invasion
Dysentery-like Shigella
Enteroinvasive Escherichia coli (EIEC ) invades INTESTINAL EPITHELIUM causing
F
Enteroinvasive Escherichia coli (EIEC ) Shigella (the infective dose is as few as 10 bacterial cells) is more invasive than EIEC (the infective dose is 106), results to BLOODY STOOL with mucus and WBC (t/f)
Enteroinvasive Escherichia coli (EIEC ) EIEC (the infective dose is as few as 10 bacterial cells) is more invasive than Shigella (the infective dose is 106), results to BLOODY STOOL with mucus and WBC (t/f)
BLOODY STOOL with mucus and WBC
Enteroinvasive Escherichia coli (EIEC ) Shigella (the infective dose is as few as 10 bacterial cells) is more invasive than EIEC (the infective dose is 106), results to
Enteroinvasive Escherichia coli (EIEC)
Previously used to determine the virulence of both Shigella and EIEC
Enteroinvasive Escherichia coli (EIEC)
It determines the organism’s ability to produce KERATOCONJUNCTIVITIS in Guinea pig
SERENY TEST (+)
Enteroinvasive Escherichia coli (EIEC )
SERENY TEST
Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC
nosocomial; outbreak of DIARRHEA among hospital nurseries
Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC)
lacks the toxins of ETEC and invasiveness of EIEC and causes “INFANTILE DIARRHEA”
Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC)
STOOL with LARGE AMOUNT OF MUCUS without blood
Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC)
lacks the toxins of ETEC and invasiveness of EIEC and causes “INFANTILE DIARRHEA”
Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli (EAEC)
adheres to Hep2 cells, packed in a “STACKED BRICK” pattern
Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli (EAEC)
causes Acute or Chronic Diarrhea
Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli (EAEC)
causes diarrhea by adhering to the surface of intestinal mucosa
Diffusely adherent Escherichia coli (DAEC)
- associated with both UTI and gastrointestinal infections; “DIFFUSED PATTERN
Diffused Pattern
Diffusely adherent Escherichia coli (DAEC) is associated with both UTI and gastrointestinal infections; with what kind of PATTERN
Cystitis
Diffusely adherent Escherichia coli (DAEC) causes what dx in children
Acute pyelonephritis
Diffusely adherent Escherichia coli (DAEC) causes what dx in pregnant women
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) / Vero-cytotoxic Escherichia coli (VTEC)
caused by the production of 2 cytotoxins: Verotoxin I and Verotoxin II
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) / Vero-cytotoxic Escherichia coli (VTEC)
Associated with poorly cooked meat
Verotoxin 1
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) / Vero-cytotoxic Escherichia coli (VTEC) may cause BLOODY DIARRHEA due to the production of
VEROTOXIN I
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) / Vero-cytotoxic Escherichia coli (VTEC)
a cytotoxin resembling those of S. dysenteriae; produces damage to Vero cells (African-Green Monkey Kidney Cells)
VEROTOXIN II
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) / Vero-cytotoxic Escherichia coli (VTEC)
biologically similar but immunologically different from Shiga toxin and Verotoxin I
HEMOLYTIC UREMIC SYNDROME (HUS)
O157:H7
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) / Vero-cytotoxic Escherichia coli (VTEC) most severe manifestation is - associated with serotype E. coli -
E. coli O157:H7
a historical outbreak in fast-food chain (“JACK IN THE BOX”) serving undercooked burgers in 1993
Mug Test –
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) / Vero-cytotoxic Escherichia coli (VTEC)
Mug Test
Mug Test –
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) / Vero-cytotoxic Escherichia coli (VTEC)
do not produce glucuronidase
SMAC – colorless
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) / Vero-cytotoxic Escherichia coli (VTEC)
SMAC
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) / Vero-cytotoxic Escherichia coli (VTEC)
causes ENTERIC DISEASE HEMORRHAGIC COLITIS
Uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC)
Most common cause of UTI in humans