membrane structure
3.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:23 AM on 11/11/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
1
New cards
energy transformation, organizing chemical reactions, talking to the environment around it, transportation, endo and exocytosis, osmosis, metastasis
cell membranes are important for...
2
New cards
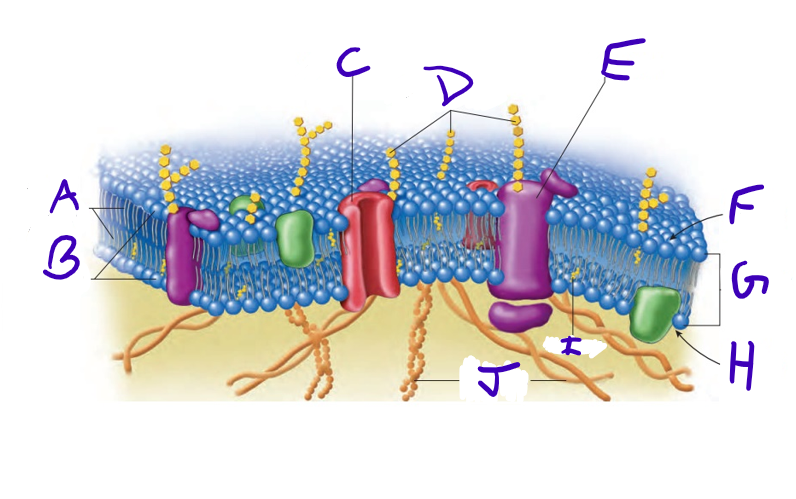
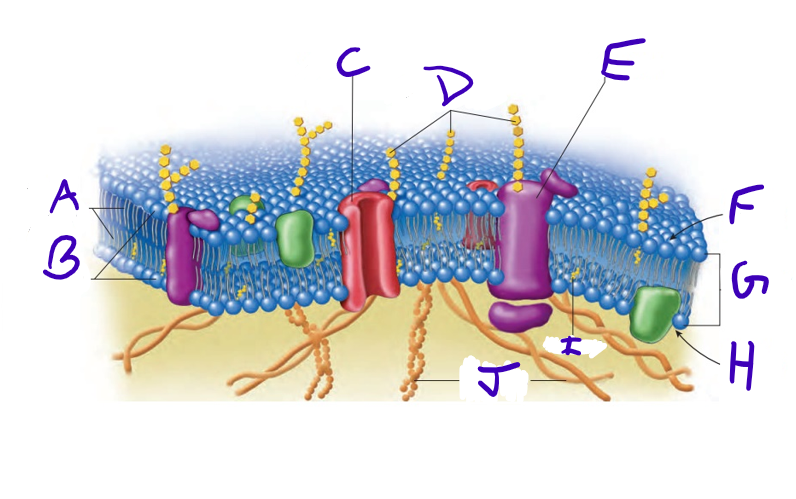
nonpolar region of phospholipid molecules
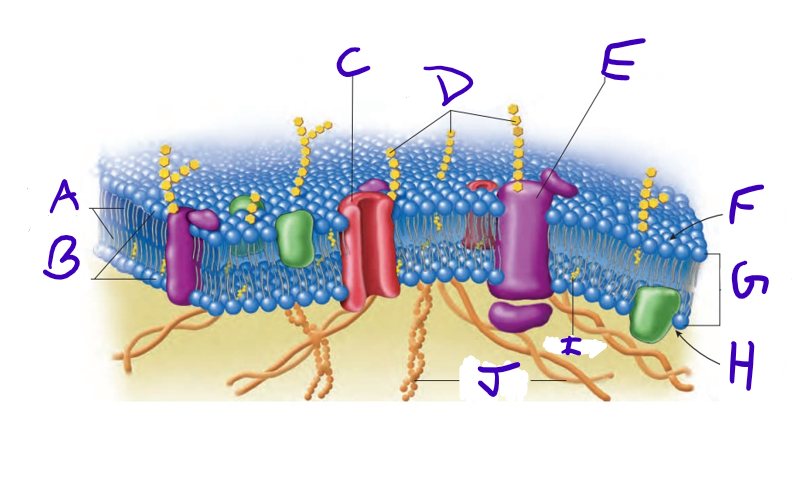
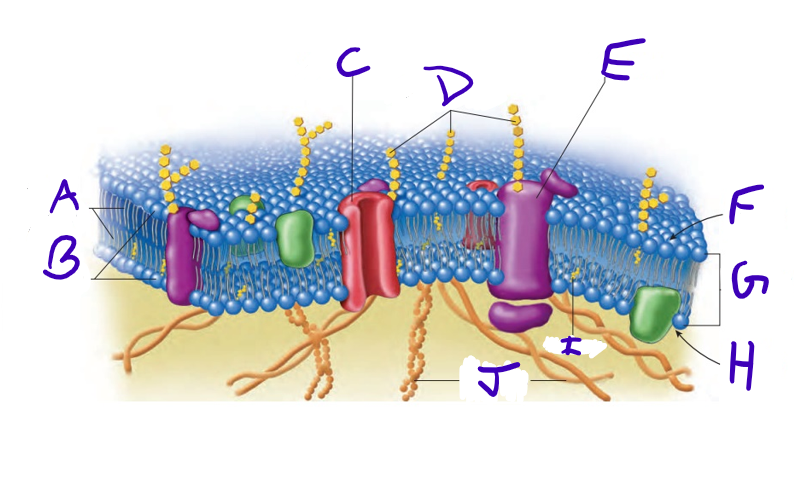
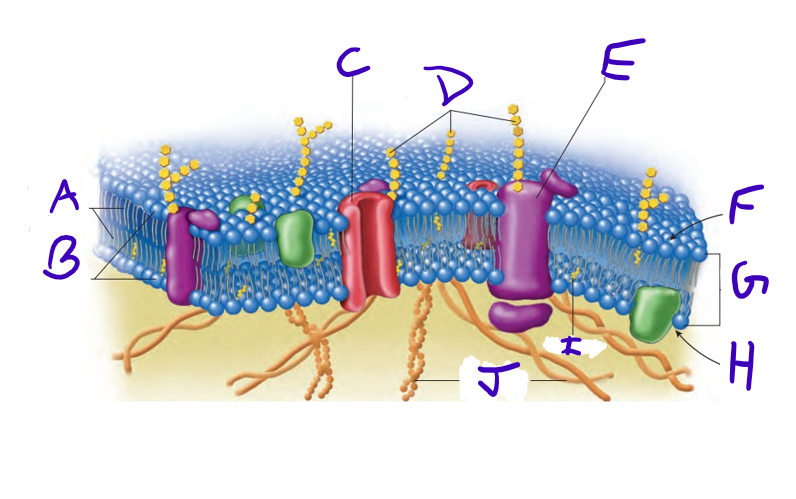
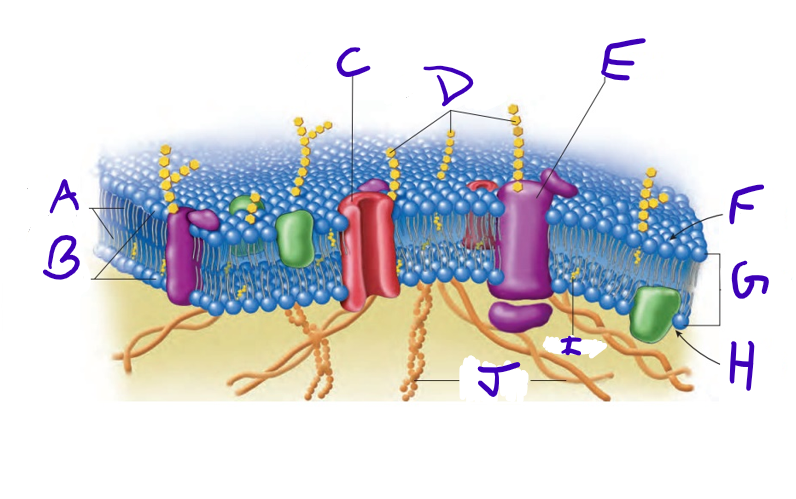
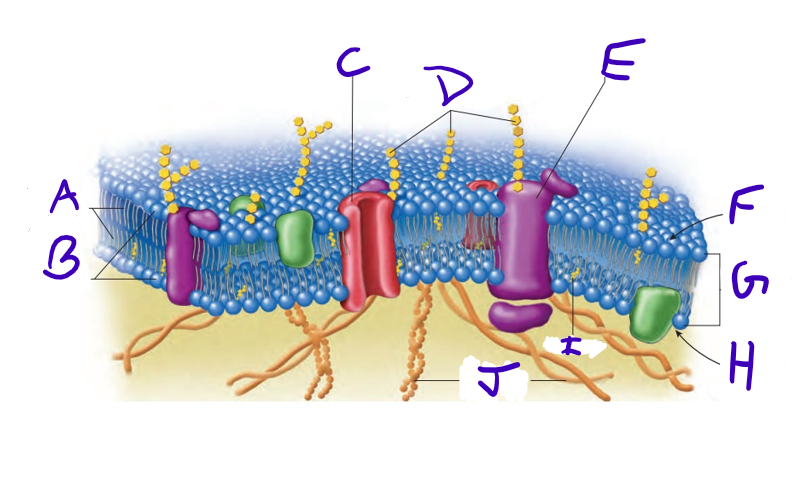
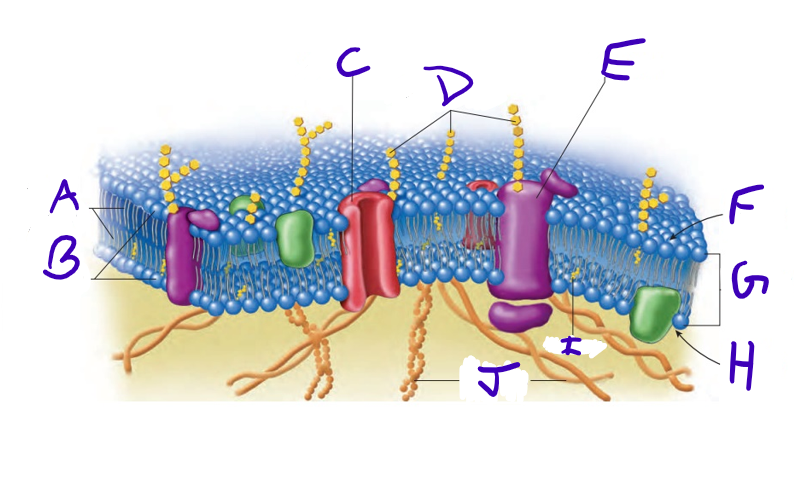
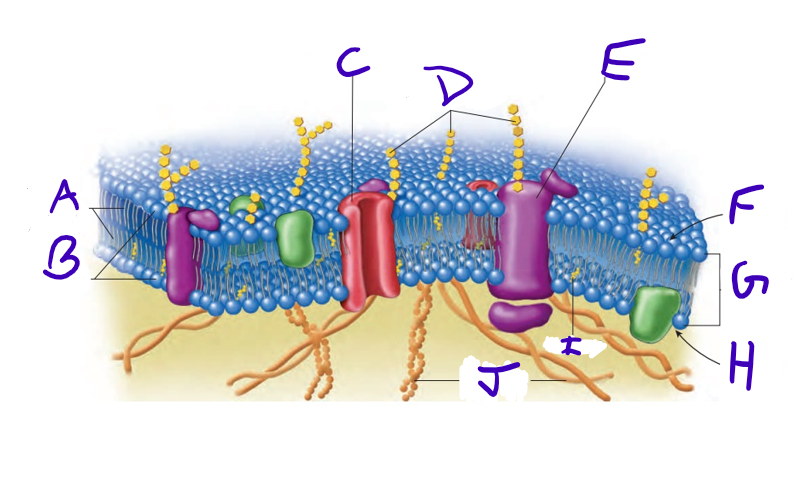
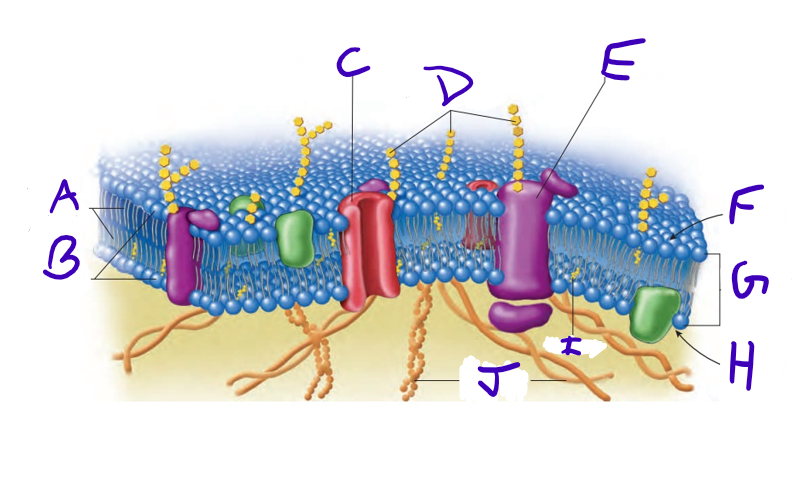
what is A
3
New cards
polar region of phospholipid molecules
what is B
4
New cards
membrane channel
what is C
5
New cards
carbohydrate chains
what is D
6
New cards
receptor molecule
what is E
7
New cards
external membrane surface
what is F
8
New cards
phospholipid bilayer
what is G
9
New cards
internal membrane surface
what is H
10
New cards
cholesterol
what is I
11
New cards
cytoskeleton
what is J
12
New cards
no
do prokaryotes have membrane bound organelles?
13
New cards
longer hydrocarbon FAT and cholesterol
what makes the plasma membrane more rigid?
14
New cards
gives support and anchors proteins so that they don't move
what does the cytoskeleton do for the plasma membrane?
15
New cards
plasma membrane
encloses the cell, defines its boundaries, and maintains the essential differences between the cytosol and extracellular environment
16
New cards
dynamic structure
what does it mean when something is not static, move about in the plane of the membrane
17
New cards
amphiphilic
is the lipid bilayer hydrophobic, hydrophilic, or amphiphilic?
18
New cards
amphiphilic
has hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties
19
New cards
glycerol head
which part of the lipid bilayer is hydrophilic
20
New cards
fatty acid tail
which part of the lipid bilayer is hydrophobic?
21
New cards
sealed like a ball
is the bilayer energetically favorable when it is sealed by being triggered by water or when it is flat?
22
New cards
fluidity
the ease of which lipid molecules move within the plane of the bilayer
23
New cards
flexion
lipid tails moving side to side
24
New cards
rotation
lipid tail rotates
25
New cards
length of hydrocarbon tail and number of double bonds
what does fluidity depend on when in relation to the phospholipid composition?
26
New cards
unsaturated
what is it when the hydrocarbon tail contains at least one double bond?
27
New cards
saturated
what is it when the hydrocarbon tail does not contain any double bonds?
28
New cards
unsaturated
is vegetable oil saturated or unsaturated?
29
New cards
saturated
is margarine saturated or unsaturated?
30
New cards
cholesterol
what is found in animal cells where the fluidity is modulated by its inclusion which is insoluble. It also fills the spaces between neighboring phospholipids by the kinks
31
New cards
scamblase
what removes selected phospholipids from one half of the lipid bilayer and insert them in the other? This can result the new phospholipids to be redistributed equally in the membrane
32
New cards
flippase
what is housed in the golgi, removes more specific phospholipids from the noncytosolic monolayer and flips them to the cytosolic side which allows the outer membrane to be larger?
33
New cards
peripheral membrane protein
types of protein that are temporarily associated with the plasma membrane; can stick to a small portion of the lipid bilayer or to an integral protein
34
New cards
integral membrane protein
permanently embedded in the plasma membrane' can form transmembrane proteins or monotopic protein which attach to only one side
35
New cards
transmembrane proteins
what protein crosses through the lipid bilayer all the time that can have covalent attachment of a fatty acid chain that inserts into the cytosolic monolayer of bilayer
36
New cards
GPI anchor
what allows proteins to be on non-cytosolic side?
37
New cards
detergent
what is a small amphipathic lipid molecule that can disrupt the lipid bilayer and separates proteins from phospholipids
38
New cards
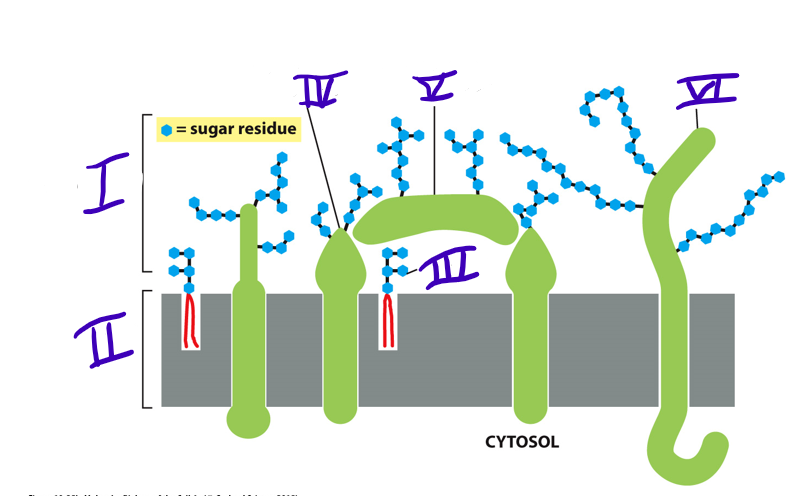
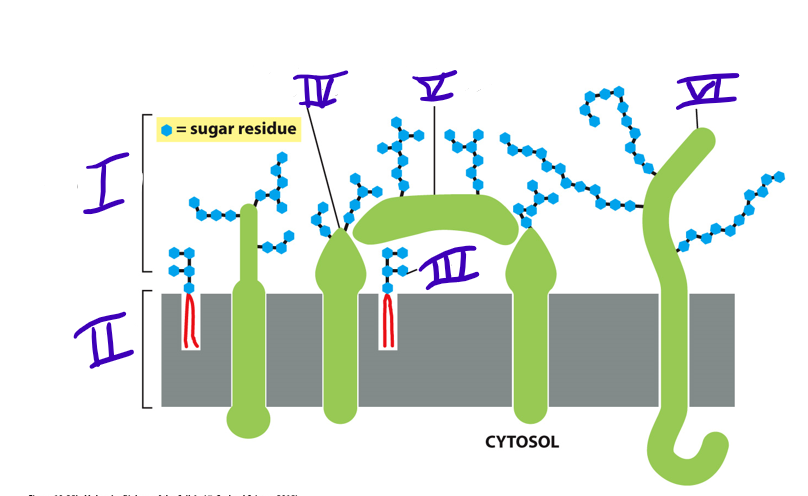
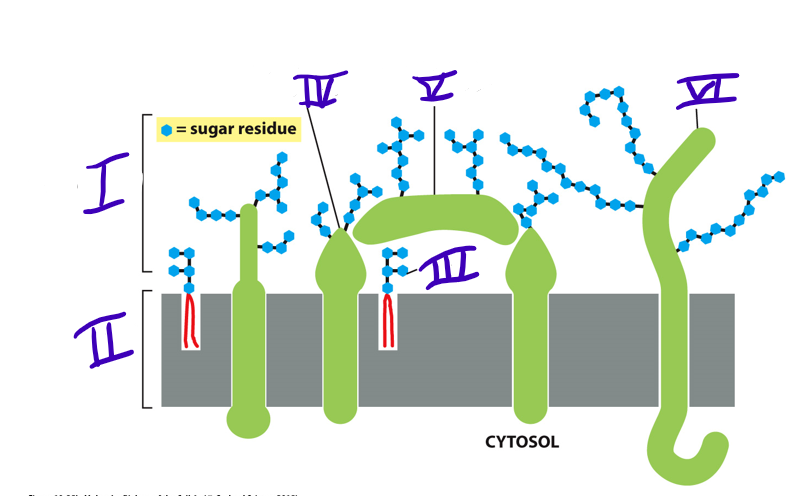
carbohydrate layer
what is I
39
New cards
lipid bilayer
what is II
40
New cards
glycolipid
what is III
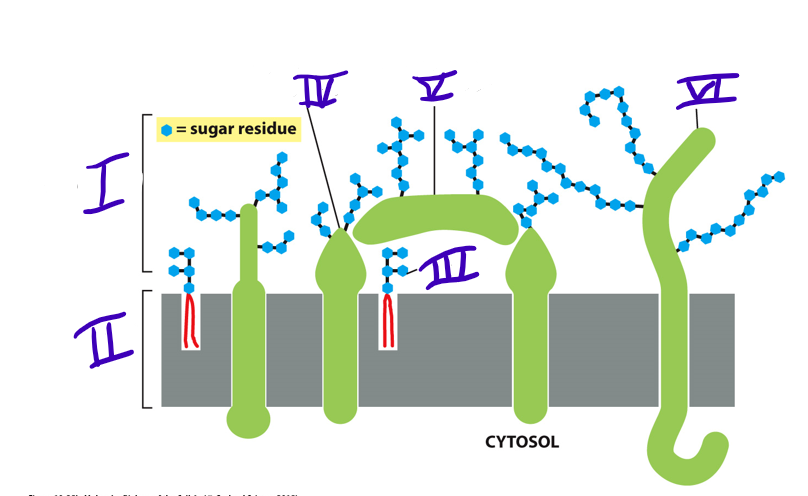
41
New cards
transmembrane glycoprotein
what is IV
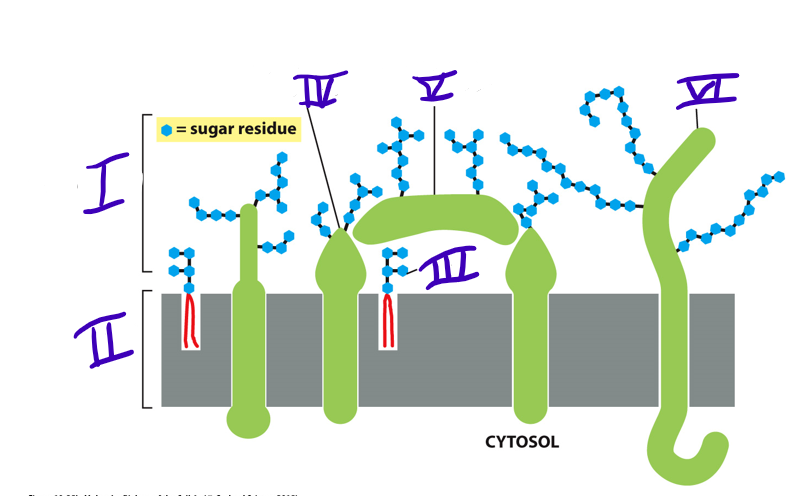
42
New cards
adsorbed glycoprotein
what is V
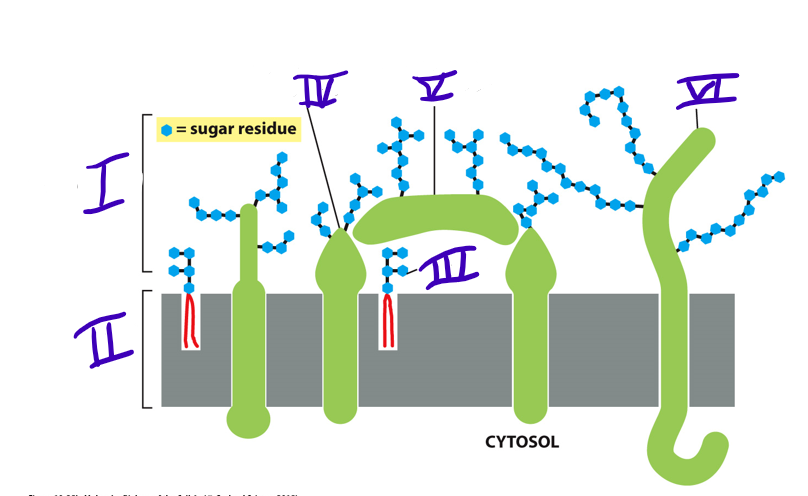
43
New cards
transmembrane proteoglycan
what is VI
44
New cards
glycoprotein
what type of protein is made when there are short oligosaccharides side chains attached?
45
New cards
proteoglycan (heavily glycosylated)
what type of protein is made when there are long polysaccharide side chains attached?
46
New cards
glycocalyx
what do the glycoprotein and proteoglycan make up together?
47
New cards
adsorption
what is it when a slimy surface is made to allow movement?
48
New cards
lectin
a type of receptor protein that binds to carbohydrates on cell and allow for interactions (cell recognition)
49
New cards
fluorescence recovery after photobleaching
what is FRAP?
50
New cards
fluorescent antibody or GFP (green fluorescent protein)
what two things can be used to label a protein that interacts with the membrane?
51
New cards
not able to see any fluorescence and the bleach is irreversible
what happens when there is excess radiation with intense light on a small patch of membrane?