RHMS - lecture 5 - qualitative design and data collection
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what is qualitative research
form of social inquiry that focuses on the way people make sense of their experiences of life and the world in which they live.
behaviour
feelings
experiences
perspectives
difference quantitative and qualitative research
hypothesis is only in quantitative research, not in qualitative! (do not know before what you will find)
four aims of qualitative research
explore - seeks to explore what is happening
describe - to provide a picture of a phenomena as it naturally occurs
explain - explains and accounts for the descriptive information
interprete - explores peoples experiences and views
deductive and inductive reasoning
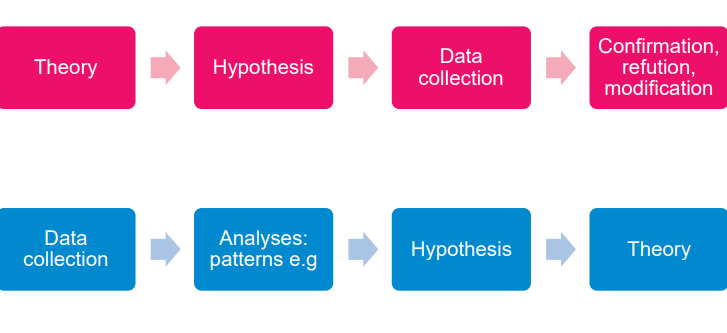
what 4 steps are supposed to be in your research proposal
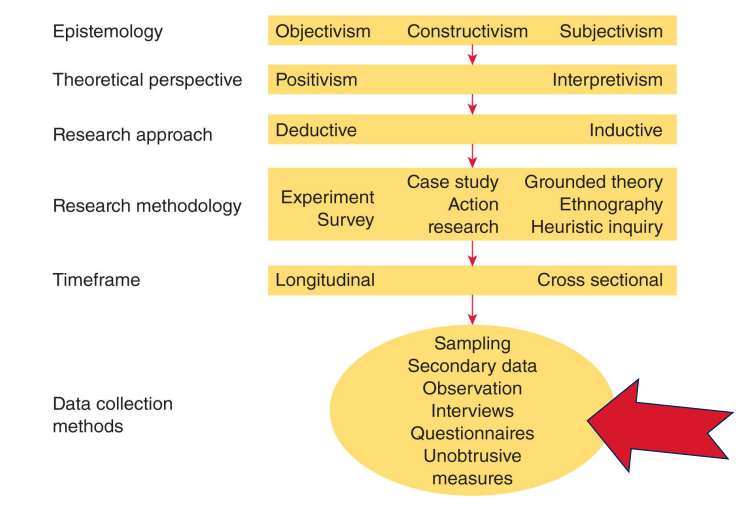
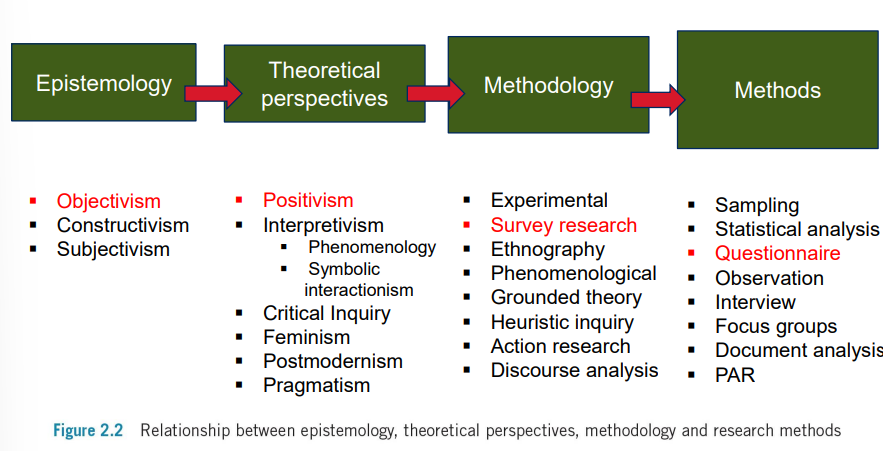
epistemology → definition; the study of knowledge itsef. how we know what we know
theoretical perspectives → the overarching stance that guides the research (which lens are you looking through)
methodology → the plan that links the theoretical perspective to the actual methods (what strategy will you use)
methods → specific techniques and tools that will be used
wheel of critical choices
1st circle epistomology (represent your epistemological stance
2nd ring theoretical perspectives
3rd circle is the methods
4rth circle is the analysis
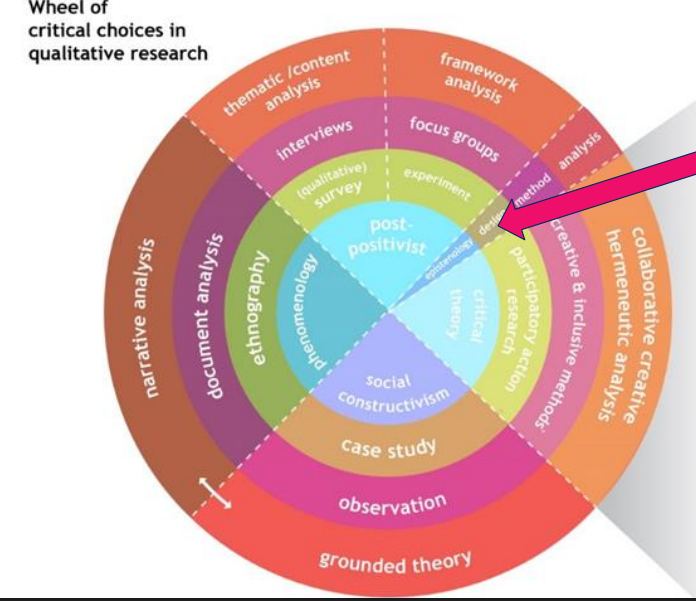
major research paradigms to know (positivism, interpretivism, critical enquiry, pragmatism)
positivism → the world is external and objective (can be measured)
interpretivism → the world is socially constructed and subjective
critical enquiry → need to questions values and assumptions
pragmatism → reality is complex, and what matters is what works in practice
cascade when choosiing a research approach
sampling in qualitative data
not randomized
purposeful and criterion based
choose target population → study population → then choose the sampling frame
target population →
study population →
sampling frame →
differnet sampling
availability / convenience sampling → just ask on instagram, if someone wants to participate
purposive sampling → researcher purposely selects the respondents because they satisfy specific inclusion and exclusion criteria.
quota sampling → try to get the same kind of population (age, sex, ect.)
respondent-assisted sampling / snowball → from one patient to another.
examples purposive sampling
typical case sampling
extreme or deviant case sampling
maximum variation sampling
intensity sampling
homogenous sampling
snowball sampling
statified purposeful sampling
random purposeful sampling
critical case sampling
sampling politically important cases
criterion sampling
theoretical sampling
confirming or disconfirming case sampling
opportunistic samplig
survey study
questionnaire → open questions
drawing a representative sample from the population
generating both qualitative and quantitative data
generalizability of results
how a survey study should look
interview study
To understand experiences, attitudes, values and processes
To attain highly personalized data
When opportunities for probing are required
When a good return rate is important
When respondents are not fluent in the native language of the country, or where they have difficulties with written language
various interview studies
open → flexible, no fixed questions
semi-open → has guiding questions but allows flexibility
structured → highly standardized, fixed set of questions in the same order
in depth → long, detailed one on one conversations
narrative → encourages participants to tell their story in their own words
how does interview fit the phenomological approach
phenomological → philosophy of experience
Producing thick descriptions of participants experiences
Seeks subjective accounts and interpretations of participants
Constructivist, using qualitative data
Relatively less structured, inductive (although thorough understanding of related theories and concepts gives structured guidelines)
narrative studies
a qualitative research method that explores how people make sense of their experiences by analyzing stories, or narratives.
type of interview study
observational study methods
observational methods provide data on phenomena (such as behaviour), as well as on people’s accounts of those phenomena
can be purely observational or actively involve the researcher
can be covert or overt
covert versus overt observational observation
overt → those being observed are aware the observation is taking place
covert → those being observed are unaware the observation is taking place
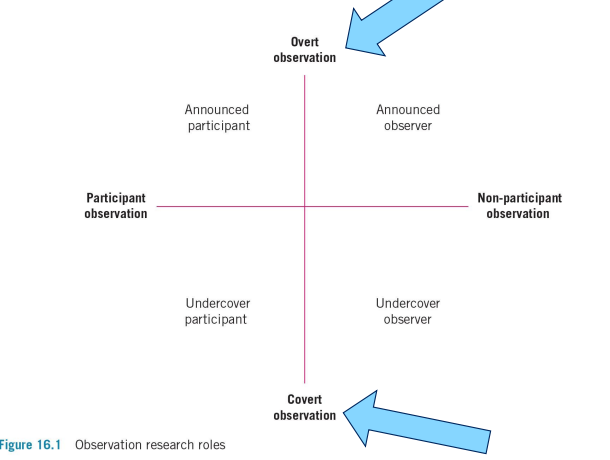
what is non-participant (naturalistic) observation
often a deep and long term engagement in the field
field notes are most common data tool
researcher hidden
data gathering process
what is ethnography
A qualitative research method that seeks to understand cultural phenomena that reflect the knowledge and meanings that guide the life of cultural groups within their own environment.
focuses more on culture instead of individual
old way of doing research
both descriptive and interpretive
data may involve observation, interviews and documents
an outsider perspectives for insider knowledge.
guidelines for ethnography (for fieldwrok)
be invisible
data collection is co-prodcution between researvher and participant
researcher is a miner (data already there), or a traveller (data will emerge through the journey)
Select the field: nature of the setting may define before the start, but ethnographic data can help define the research problem
Gain access: consider gatekeepers & hurdles
Gain informed consent
Become ‘invisible’ for full immersion
Build rapport with key informants
Maintain a balance between ‘insider’ and ‘outsider’ status
Get out: physically and emotionally disengage
ethnographic data collection
phase 1 → In-depth interviews to patients focused on obtaining insights regarding patients’ attitudes to cope with the disease
phase 2 → Ethnographic interviews to patients and healthcare professionals focused on understanding the patients’ journey and unmet needs throughout the disease according to differ-ent attitudinal profiles.
ethonographic interviewing tips
listen well and respectfully → develop ethical engagement with participants
acquire a self awareness of your role in the construction of meaning within the interview process
be aware of the ways in which both the ongoing relationship and broader social contexts affect participants
recognize that what emerges from the interview is only partial knowledge.
what is a focus group
An organized discussion with a selected group of individuals with the aim of eliciting information about their views
Generate a range of views and stimulate interactions and discussions between participants
key to succesful focus grouo
participants contribute equally
participants feel comforable
the moderators questions mimic a natural exchange
aim of focus group
Consolidating old knowledge
Gaining insight on different perspectives & interaction within a group
First diverge (looking for contrast) and then converge
handy when you want to generate new ideas
positives of doing a focus group
the low-cost way of collecting data, but require a considerable amount of cooperation and enthusiasm from participants
funneling approach of focus groups
start very broad

limitations focus groups
Moderators have less control or influence over processes and outcomes
Challenging to locate participants and persuade them to respond
Sample is often one of convenience
Not conducive to confidentiality
Moderators can contaminate results
what is visual research
capacity to interpret the world through our sense of sight. help to provide insights into difficult, emotional, sensitive issues and experiences
photographs
video
websites
images
podcast
when do you use visual data
Be used at any stage of research
Provide a means of getting inside a programme
Bridge psychological and physical realities
Allow for combining visual and verbal language
Assist in building trust and rapport
Produce unpredictable data
Promote longer and more detailed interviews
Be used in conjunction with other methods
advantage visual data
Allows for a more sophisticated understanding of the nature of cultures and their complex networks of interrelationships
It may be less restrictive than other methods where faulty recall may generate bias
Capture a wide range of voices in real-time
Draw attention to the embodied identity of the researcher and force the researcher to empathize
challenges visual data
Significant resource requirements (time, money and technical expertise)
The danger of respondent fatigue/withdrawal
Ethical issues around the covert observation
May only capture a version of reality, not objective reality → challenging to determine meaning and context