Animal Science Lab Practical
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
What is the length of pregnancy for sheep
144 days - 152 days ( 5 Months)
Stages of lambing
Stage 1 Preparation: ends when water breaks
Stage 2 Lambing: 30 minutes- 2 hours (active labor)
Stage 3 Placenta Delivery: may be expelled with lamb or shortly after
Lamb birthing position
“superman position” = front feet and nose first, one fot in front of the other
Post-lambing care
lambs must breathe, stand, and nurse within the first hour
umbilicus dipped in antiseptic
Zoonotic disease transmission
direct contact
indirect contact
inhaled
ingested
5 kinds of PPE
coveralls
gloves
boots
masks
goggles
Why should lambs be weighed during processing
make sure they’re growing well
make sure they’re eating
track health
Why are ears tagged during lamb processing?
for identification
what are the numbers for on ear tags?
1st: last digit of the year they were born
2nd and 3rd: sex and birth order (1-50 = boys, 51-99 = girls)
why is tail docking performed in lambs?
to prevent fly strike (manure cakes on and attracts flies to lay eggs)
tools used for castration in lambs
hot docker (cauterizes)
burdizzo clamp (crushes nerves/vascular supply)
elastrator band (cuts off circulation and tail dies)
why are ewes supplemented with selenium/ lambs being injected with selenium/vitamin E after birth?
northeastern soil is deficient and deficiency in selenium leads to immune, muscle, and neurological dysfunction
Signs of a healthy ruminants
chewing cud
alert and interested
eating/drinking
lying down
normal herd behavior
no wounds
urinating/defecating
healthy breathing
signs of unhealthy ruminants
restless pacing
lethargy
isolation
loss of appetite
abnormal breathing
open wounds
limping
diarrhea/constipation
environmental factors that influence health
cleanliness
size of enclosure
availability of food and water
temperature
ventilation
population size
Normal vital signs of sheep
Temperature (F)
101-103.5
Heart rate (bpm)
60-120
respiratory rate (bpm)
12-24
Ruminations
1-2 per minute
Normal vital signs for goats
Temperature (F)
101-103.5
Heart rate (bpm)
60-120
respiratory rate (bpm)
12-24
Ruminations
1-2 per minute
Normal vital signs for cattle
Temperature (F)
100-102.8
heart rate (bpm)
40-80
respiratory rate (bpm)
10-36
ruminations
3 every 2 minutes
normal vital signs for horses
Temperature (F)
99-101
Heart rate (bpm)
24-44
respiratory rate (bpm)
10-24
normal vital signs for swine
Temperature (F)
101-103.5
Heart rate (bpm)
60-80
respiratory rate (bpm)
10-20
what is a withdrawal period?
the time from last drug treatment before an animal or animal product can enter food supply
PO
per os (by mouth)
ID
intradermal (neck or tail folds)
SC or SQ
subcutaneous (under all layers of skin, usually neck)
IP
intraperitineal (in the abdomen)
IM
intramuscular (in the neck of food animals)
IV
intraveinous (in veins)
IC
intracardial (inside the heart)
Which government agency assures the safety and efficacy of drugs and regulates labels?
Food and Drug administration
How is manure managed and stored at mapeline?
stored in tanks and used for fertilizer later
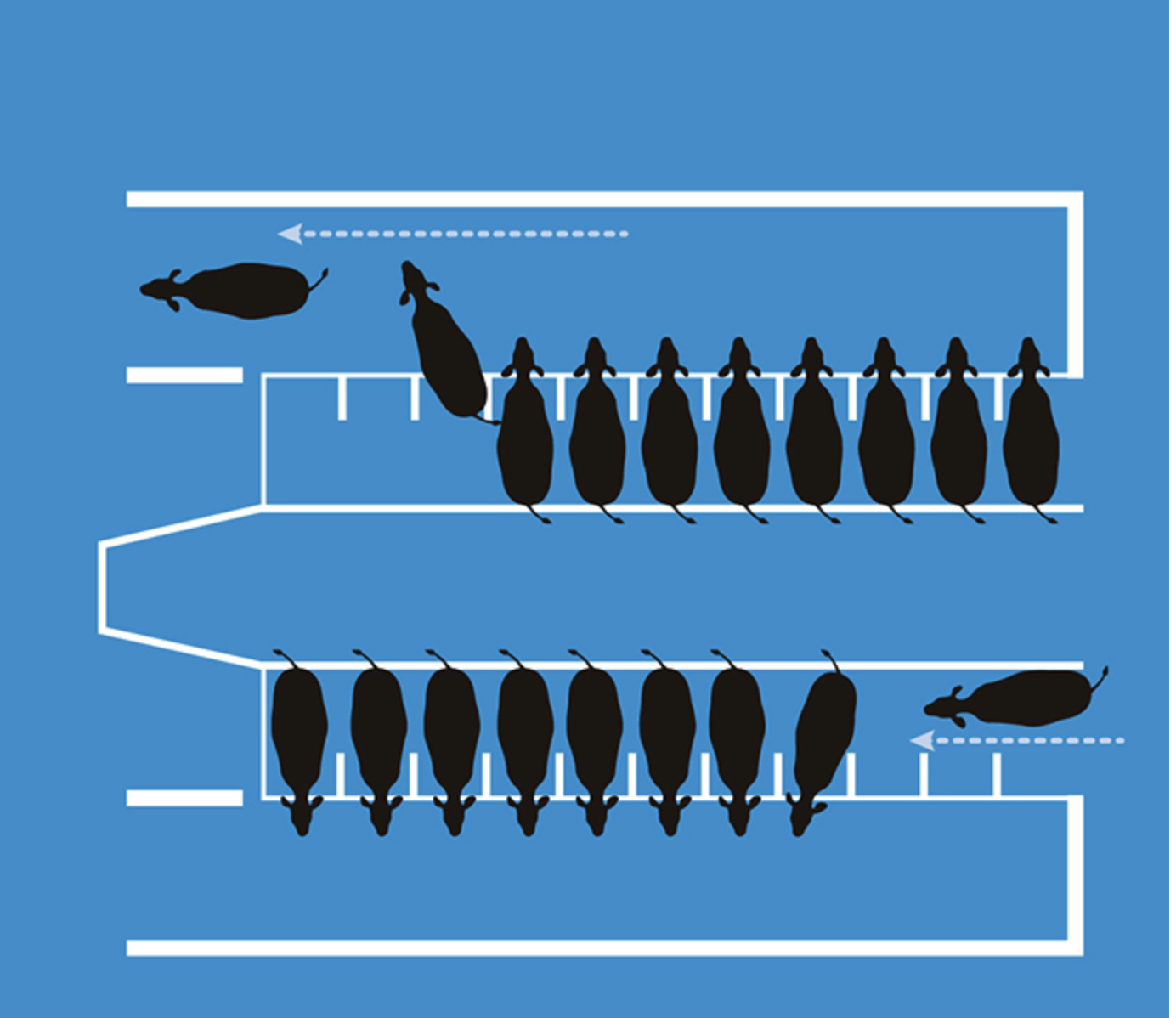
Parallel Parlor
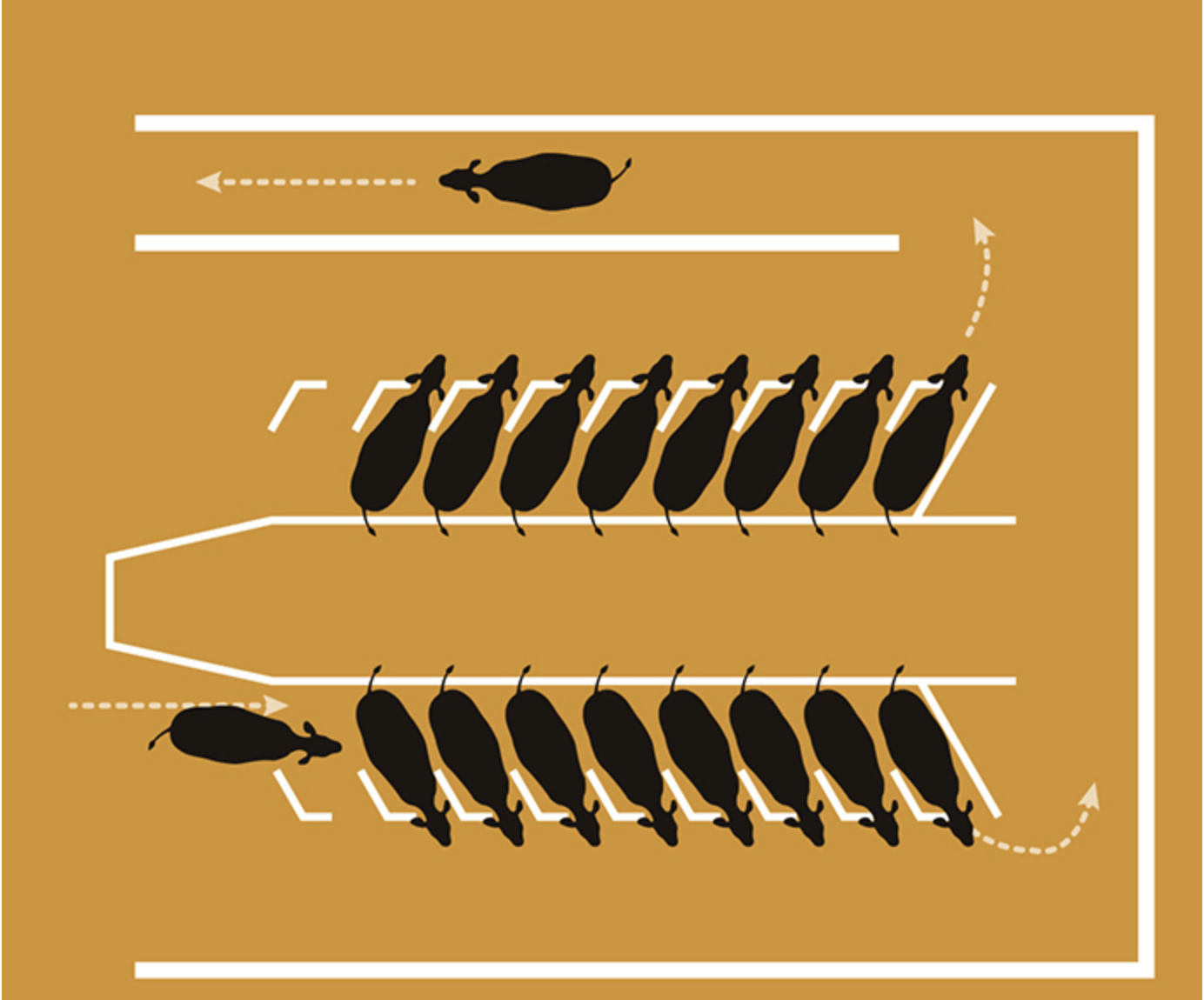
Herringbone Parlor
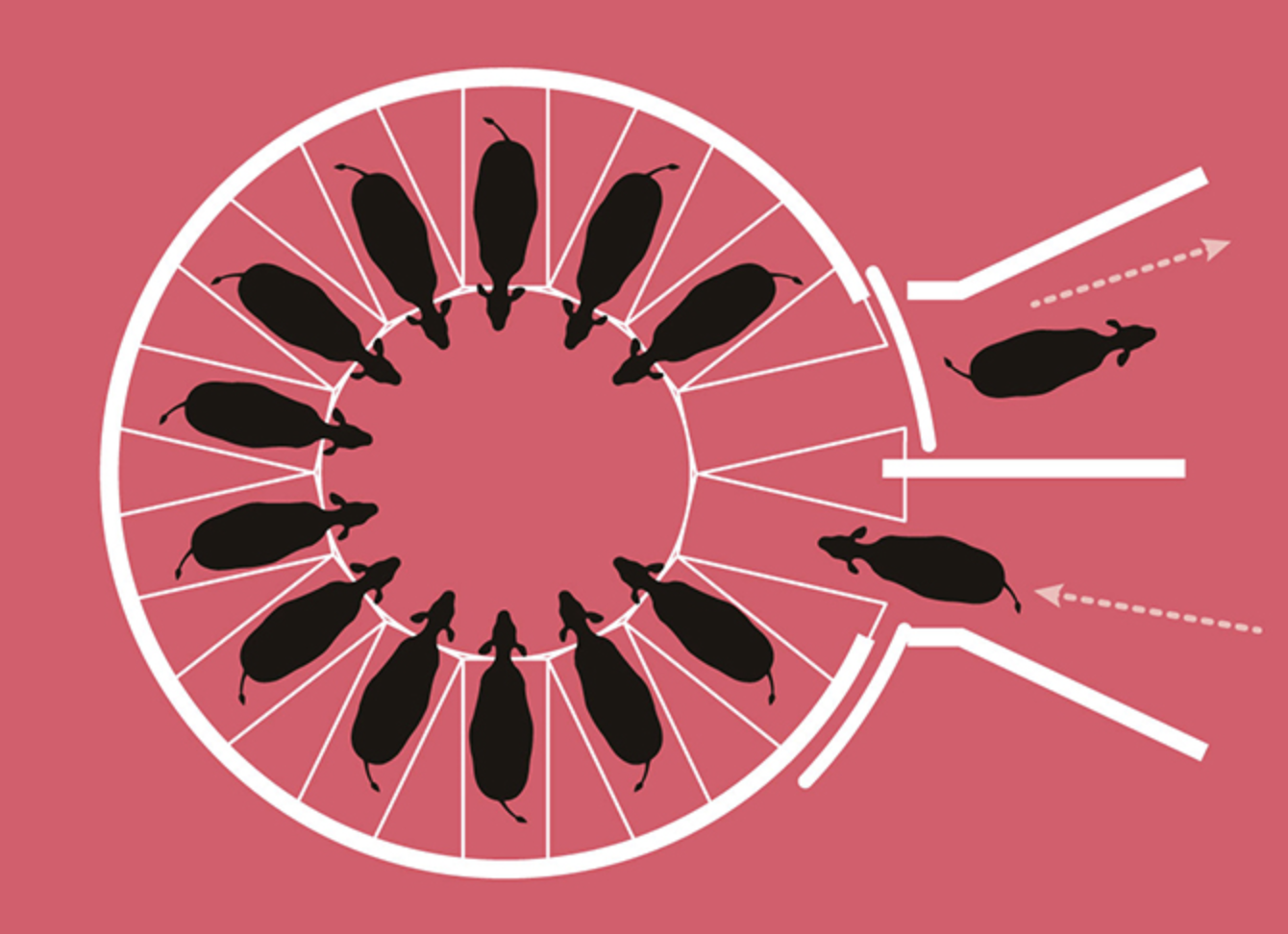
Rotary Parlor
What is restraint?
physical, chemical, and psychological methods to limit or control animal movement
Why is restraint necessary?
maximize animal safety
maximize human safety
complete medical procedures
minimize animal stress
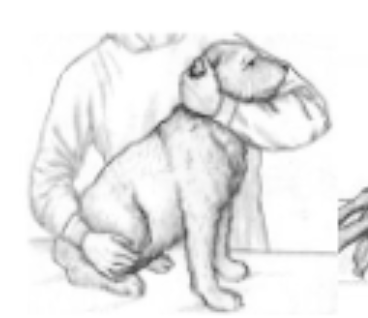
head restraint
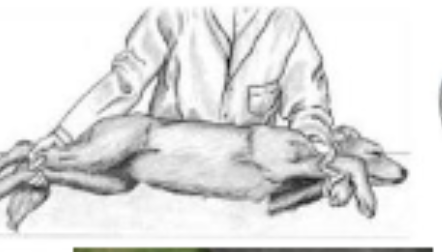
lateral restraint

elizabethan collar

Grooming Sling

catch pole

cat hoods/muzzles

towel/bag

holding scruff
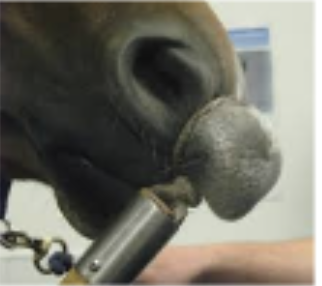
nose twitch

neck twitch

hobbles

stocks

cross tie
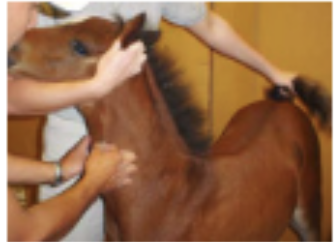
ear twitch

halter/lead rope

cattle chute

tail jack

hobbles

head locks

pig boards
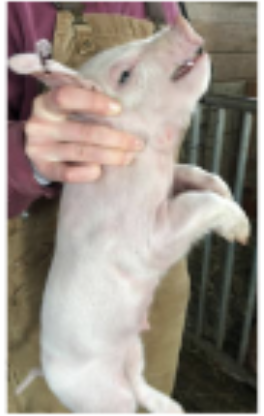
chin hold
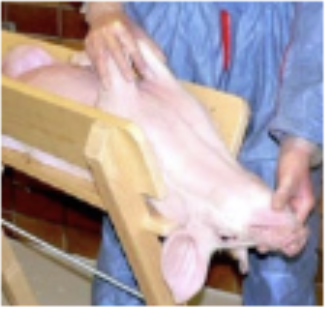
v trough
leg hold

shaker paddle

pig snare

bull ring

set on rump

show chain

chin hold

show stand

halter/lead rope

horn hold
What is the length of pregnancy in pigs?
3 months, 3 weeks, 3 days (114 days)
Normal farrowing for pigs
10-12 piglets per litter, 2-4.5 lbs, 2-3 hours, 15-20 minutes between each piglet, can be delivered backwards
need 85-90 degrees as newborns
gestation vs farrowing crate
gestation crate is only for pregnancy and has more space, farrowing crate is for birth and not long-term
Wean to estrus interval for sows
4-7 days
Weighing piglets
1-3 days old
to gauge health, monitor weight gqain, make breeding decisions
clip needle teeth/wolf teeth for piglets
1-3 days old
to limit piglet injuries and prevent damaging teats
dock tails for piglets
1-3 days old
prevent tail biting/chewing
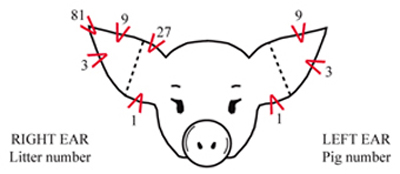
Ear notching for piglets
1-3 days old
gives each piglet an ID # on left ear
right ear has litter #
Inject iron
1-3 days old
prevent iron deficiency and anemia
Castrate
3-14 days old
surgically
prevent breeding and lower aggression
What could alter a horse’s vital signs
environmental temperature
illness
exercise
stress
age
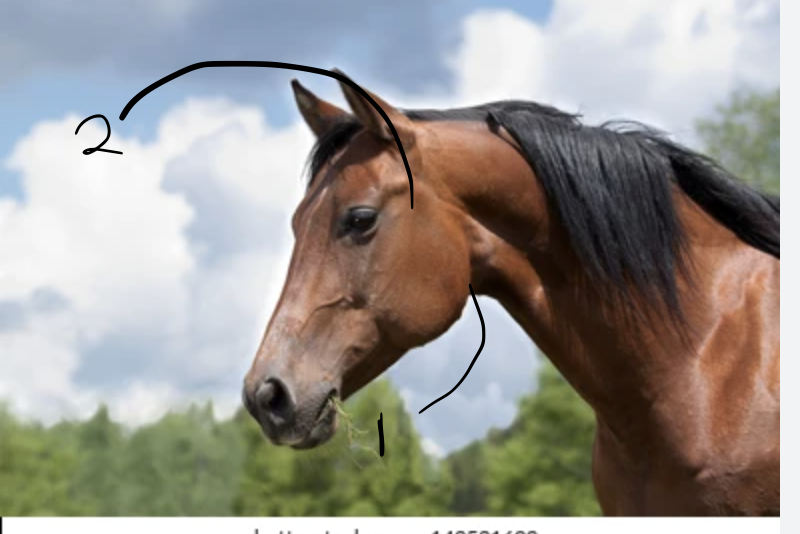

Submandibular facial artery
Transversal facial artery
Where should you feel for a digital pulse on a horse
underneath the fetlock
what is the significance of a bounding digital pulse
can signal inflammation/injury/etc
where should you listen to a horses heart, lungs, and cecum?
lungs = barrel of the horse on both sides
heart = underneath the armpit, can be either side
cecum = back, right side of the barrel
6 areas to assign a BCS on a horse
right behind the shoulder
over the ribs
either side of tailhead/doclk
loin
either side of the wither
crest of the neck
3 reasons for shoeing a horse and how often?
treatment of medical conditions
traction/support during sports or jobs
basic hoof protection
farrier should come every 6-8 weeks
What is passive stay apparatus
PSA is made of ligaments, tendons, and muscles
allows sleep by locking front legs and ONE hind leg and requires very little energy
How is the California Mastitis Test performed
it is a somatic cell count done by adding a stained reagent to see the reaction in the milk