Articulation & Phonological Disorders: Key Concepts and Processes
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
Phoneme
The smallest unit of sound in speech.
Place
The location in the vocal tract where a consonant sound is produced.
Manner
The way in which a consonant sound is produced.
Voice
The use of vocal cord vibration in producing sounds.
/p/
Bilabial Stop voiceless
/b/
Bilabial Stop voiced
/t/
Alveolar Stop voiceless
/d/
Alveolar Stop voiced
/k/
Velar Stop voiceless
/g/
Velar Stop voiced
/ʔ/
Glottal Stop voiceless
/f/
Labiodental Fricative voiceless
/v/
Labiodental Fricative voiced
/θ/
Interdental Fricative voiceless
/ð/
Interdental Fricative voiced
/s/
Alveolar Fricative voiceless
/z/
Alveolar Fricative voiced
/ʃ/
Palatal Fricative voiceless
/ʒ/
Palatal Fricative voiced
/h/
Glottal Fricative voiceless
/dʒ/
Alveolar Affricate voiced
/tʃ/
Alveolar Affricate voiceless
/m/
Bilabial Nasal voiced
/n/
Alveolar Nasal voiced
/ŋ/
Velar Nasal voiced
/l/
Alveolar Liquid voiced
/r/
Palatal Liquid voiced
/w/
Labio-velar Glide voiced
/j/
Palatal Glide voiced
Distinctive Feature Theory
Attempts to determine the specific properties of a sound that serve to signal meaning differences in a language.
Binary System in Distinctive Features
Uses a plus (+) and minus (-) system to signal the presence (+) or absence (-) of certain features.
Broad Transcription
Symbols representing target sounds in a speech sample.
Narrow Transcription
Includes broad transcription symbols & symbols that describe slight variations in the production of target sounds.
Diacritics
Marks added to sound transcription symbols to give them a particular phonetic value.
Dentalization
An articulatory variation in which the tongue approaches the upper incisors.
Palatalization
Only sound for which the palate is not the place of articulation can be palatalized.
Velarization
Refers to a more posterior tongue placement for palatal sounds.
Lateralization
[l] is the only lateral in GA. It cannot be lateralized because it is already lateral.
Syllabic Consonants
Unstressed syllables easily become reduced syllable.
Derhotacization
Loss of r-coloring typically for the central vowels with r-coloring.
Nasalization
If a nasal follows a vowel, nasality often seeps into the vowel segment.
Stress Markers
Primary and secondary= [ˈ] primary and [ˌ ] secondary.
Duration Symbols
Lengthening- [fiːt] [jɛsːɝ].
Tense Vowels
Longer duration.
Lax Vowels
Shorter duration.
Diphthong
A vowel sound that demonstrates articulatory movement resulting in a qualitative change during its production.
Coarticulation
The concept that the articulators are continually moving into position for other segments over a stretch of speech.
Assimilation
Refers to adaptive articulatory changes through which one speech sound becomes similar to a neighboring sound.
Progressive Assimilation
When a segment influences a following sound in a linear manner.
Regressive Assimilation
When a sound segment influences a preceding sound.
Phonotactics
Refers to the description of the allowed combinations of phonemes in a particular language.
Articulation Disorder
When an individual's articulation deviates significantly from the norm; characterized by substitutions, omissions, distortions, and additions (SODA) that may interfere with intelligibility.
Phonological Disorder
Refers to impaired comprehension of the sound system of a language and the rules that govern the sound combinations; includes syllable structure, substitution, and assimilatory
Cluster Reduction
Clusters are reduced to a single consonant; usually the natural member of the cluster remains. E.g., [pun] for spoon. (syllable structure)
Reduplication
Second syllable becomes a repetition of the first. E.g., [/bɑbɑ/] from bottle. (syllable structure)
Weak Syllable Deletion
Unstressed syllable is deleted. E.g., [nænə] from banana. (syllable structure)
Fronting
E.g., [ti] for key. (substitution- changes in place)
Labialization
E.g., [fʌm] for thumb. (substitution- changes in place)
Alveolarization
E.g., [sʌm] for thumb. (substitution- changes in place)
Voicing
E.g., [du] for two. (substitution- changes in voicing)
Devoicing
E.g., [pit] for beet. (substitution- changes in voicing)
Consonant Cluster Substitution
E.g., [stwit] for street. (substitution- changes in voicing)
Stopping
Gliding of liquids/fricatives. E.g., [dus] for juice. (substitution- changes in manner)
Affrication
E.g., [tʃu] for shoe. (substitution- changes in manner)
Deaffrication
E.g., [ʃiz] for cheese. (substitution- changes in manner)
Denasalization
E.g., [dud] for noon. (substitution- changes in manner)
Labial Assimilation
E.g., [fwɪŋ] for swing. (assimilatory)
Velar Assimilation
E.g., [gɑg] for dog. (assimilatory)
Nasal Assimilation
E.g., [mʌnɪ] for bunny. (assimilatory)
Liquid Assimilation
E.g., [lɛloʊ] for yellow. (assimilatory)
Generative Phonology
Represents the application of principles of generative grammar to phonology; Noam Chomsky and Morris Halle; Assumes two levels of sound representation:
Phonological representation- an abstract, underlying form and Phonetic representation- modified, surface form; Phonological rules- govern how this phonological representation (underlying representation or deep form) is transformed into the actual pronunciation (surface form)
Natural Phonology
Incorporates features of naturalness theories and was specifically designed to explain the normal development of children's phonological systems; Patterns of speech are governed by an innate, universal set of phonological processes; Suggested by David Stampe: phonological processes are innate and universal; all children are born with the capacity to use the same system and processes; This theory points out prominent developmental steps that children go through until the goal of adult phonology is reached in the children's early years; Stampe thought these phonological processes explained the replacement of the difficult property of the sound or sound class with a simpler form.
Limitation
Occurs when differences between child's and adult's system become limited to specific sounds, sound classes, or sound sequences. (natural phonology)
Ordering
Occurs when substitutions that appear unordered and random become more organized. (natural phonology)
Suppression
One or more phonological processes are suppressed as children move from innate speech patterns to the adult form. (natural phonology)
Articulation
The motor production of speech sounds.
Fluency
The flow of speaking including rate and rhythm.
Language
Complex and dynamic system of convention symbols that is used in various modes for thought and communication.
Phonology
The study of the sound system of language and includes the rules that govern its spoken form.
Morphology
Studies the structure of words; analyzes how words can be divided into parts labeled morphemes.
Morpheme
The smallest meaningful unit of a language.
Syntax
Consists of organizational rules denoting word, phrase, and clause order; sentence organization and the relationship between words.
Semantics
The study of linguistic meaning and includes the meaning of words.
Pragmatics
The study of language used to communicate within various situational contexts.
Phonetics
The study of speech emphasizing the description and classification of speech sounds according to their production, transmission, and perceptual features.
Speech sound
Represent physical sound realities; they are end products of articulatory motor processes.
Phonemes
The smallest linguistic unit that is able to distinguish meaning between words.
Articulatory phonetics
Categorization/Classification of speech sounds
Acoustic phonetics
Transmission properties of speech (i.e. frequency, intensity)
Auditory phonetics
How we perceive sounds
Normative phonetics
setting good speech standards, or establishing norms for good or acceptable speech
Clinical phonetics
remediates unintelligible or disordered speech
Label speech chain
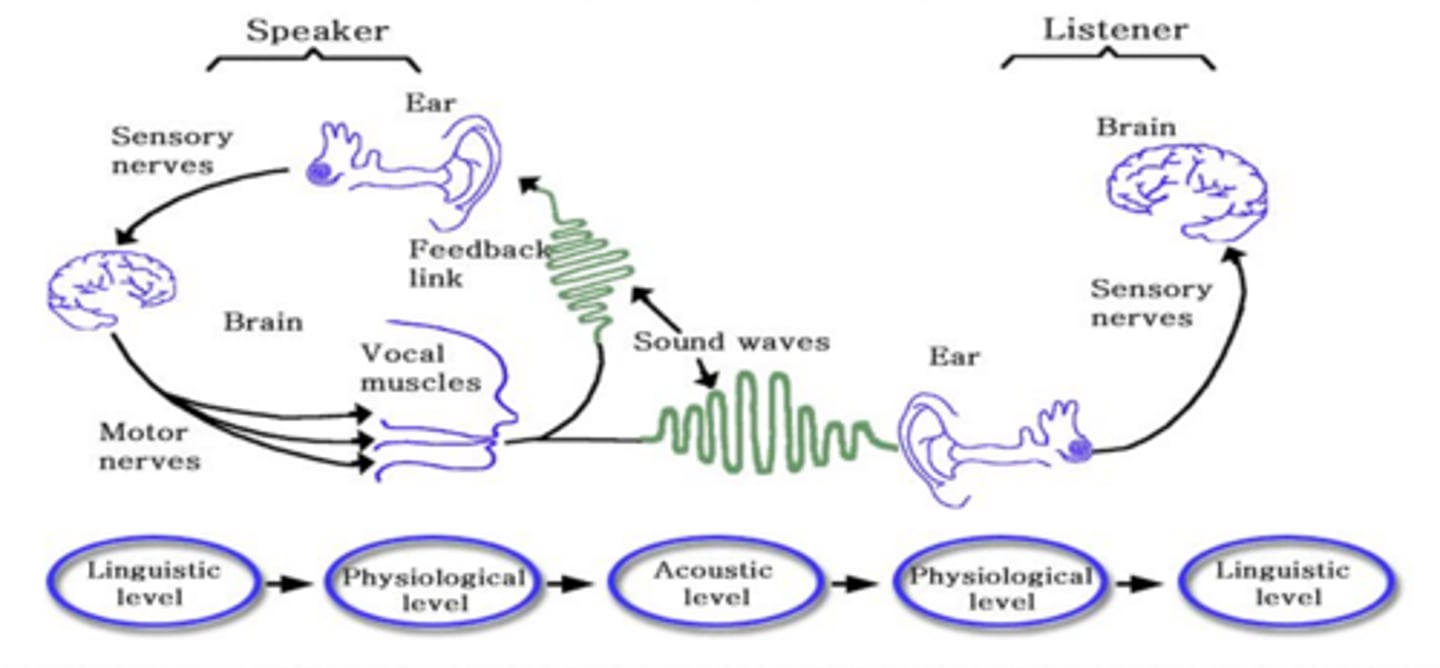
Phonetic level is to "surface level form" as phonemic level is to...
underlying function
When speaking about phonology, why would a child with difficulties in phonological skills also have difficulties with other areas of language (such as syntax, semantics, etc.)?
They are all interconnected- if they don't know the rules of the language, they will have a hard time understanding sentence structure and vocabulary
Stampe believed that a child tends to produce forms that are more....
natural
What 2 aspects are necessary for effective verbal communication?
form and function
Why is the distinctive theory not widely used now?
outdated and difficult to use
What is the difference between articulation and phonology?
phonology is the rules that govern the sounds and articulation is how the sounds are produced
What is the difference between an articulation vs. a phonological disorder?
articulation disorder is when the client has trouble producing sound, phonological disorders are when the client has difficulty with phonological rules