IPFC 1 - Menopause
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
Menopause
is the last spontaneous episode of physiologic uterine bleeding (the last period)
Menopause is identified retrospectively 12 months after amenorrhea and marks the end of menstrual cycling
Amenorrhea
the absence of menstruation
Menstrual cycle transition
is the time from the cycle irregularity to the final period
Perimenopause
(aka climacteric phase) is the 4-5 year period between the transition and the months after the last period
Premature ovarian failure
happens when you reach menopause before age 40.
Average age of menopause
51 (range is 40-58)
Menopausal age depends on...
It’s about genes not race, physical characteristics, age at menarche, age at last pregnancy, socioeconomic status or oral contraceptive use
What causes menopause to happen early?
- Smoking (1-2 years earlier)
- Chemotherapy
- Radiotherapy
- Bilateral oophorectomy
When do females have the highest number of follicles
20 weeks gestation in utero
COME BACK TO SLIDES 9-11
YES SIR
If you had a hysterectomy and don't have a period, how would you know when you are menopausal?
Can monitor FSH and LH levels
very high levels demonstrate that the body is working overtime to try to produce more
particularly helpful in women with hysterectomy
What hormones drop around menopause
estradiol (and Inhibin A and B)
What happens during the EARLY menopausal transition period
- Menstrual cycles vary in length (by ≥7 days)
- FSH levels start to increase
- low follicle count
What happens during the LATE menopausal transition period
- Intervals of amenorrhea of >60 days
- high FSH levels
- low follicle count
- Vasomotor symptoms likely begin
What happens during the early postmenopausal period (first 2-6 years after menopause)
- FSH levels stabilize
- AMH and inhibin are very low
- Follicle count very low
- Vasomotor symptoms most likely in first 2 years after menopause
What symptoms occur in latte menopause (remaining lifespan)
increasing urogenital atrophy
Vasomotor symptoms
• Hot flashes, night sweats
• Spontaneous sensation of warmth, often with perspiration, palpitations, anxiety
• Most common concern of menopause
– ~80% of perimenopausal women and ~40% of
post menopausal have >3 hot flashes per day
What causes vasomotor symptoms
Associated with the decline in estrogen
when do vasomotor symptoms (VMS) occur
Starts 2 years before menopause
- Worst 2 years after last menstrual period
- Often lasts ~5 years after last period
- Can last for 7- 8 years
In which population do VMS tend to last longer
- Start menopause earlier
- Higher BMI
- Smoke
- Low socioeconomic status
- Depressive symptoms, stress, anxiety at start of symptoms
Menopausal Symptoms
Vasomotor symptoms
Mood
Vulvovaginal atrophy
Aches & pains
Genitourinary syndrome
Aches & Pains
• Joint pain common during menopause
transition
• Unlike arthritis, aches and pains respond to hormone therapy
Mood symptoms of menopause
• Irritability, tearfulness, anxiety
• Depression, lack of motivation or energy
• Poor concentration and sleep
• More common in women with a history of depression, poor physical health, stressors
Possible causes:
– Declining estrogen levels
– Vasomotor symptoms resulting in poor sleep
Vulvovaginal Atrophy
• Vulva and vagina appear thin, pale and dry
• Vagina can shorten, narrow, constrict, especially in the absence of sex
• Vaginal lining may be thin, lose elasticity, lose the rugal folds and have petechiae
• Decrease in sebaceous gland secretions and in lubrication during sexual stimulation
- treatment becomes harder the longer we waitAtrophic vaginitis refers to vaginal inflammation
When does Vulvovaginal Atrophy occur
• Starts a few years after LMP
• Does not improve over time (unlike other symptoms)
• Symptoms include dryness, itchiness, dyspareunia (painful intercourse)
• Lower libido
*Key to treat this before it perpetuates a cycle of poor sexual health
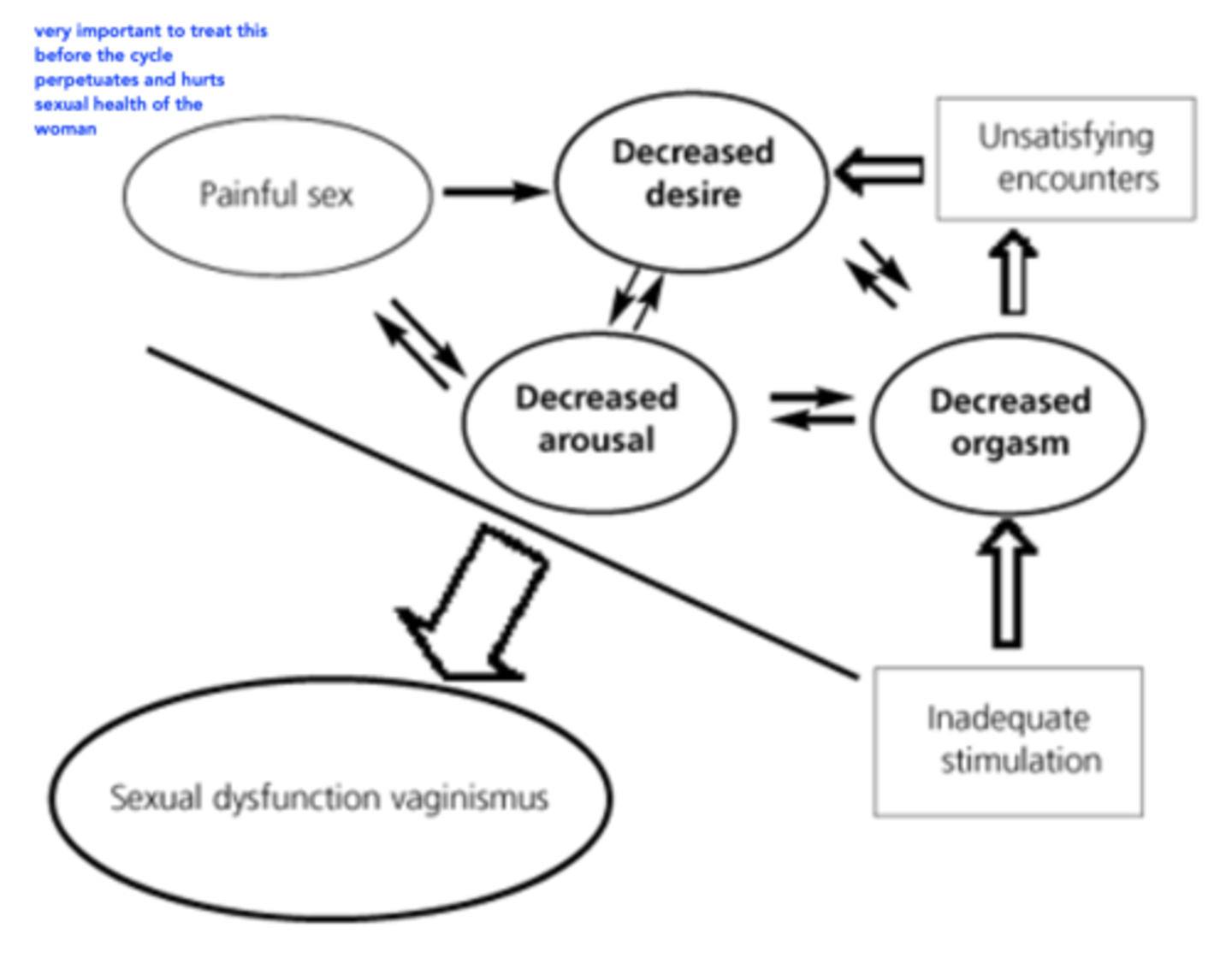
Atrophic vaginitis
Refers to vaginal inflammation
Genitourinary Syndrome
• Genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) is a more comprehensive term (includes genital, sexual, urinary)
• Frequent UTIs, dysuria, increased frequency and urgency
• Late postmenopause stage
Hormone therapy
• Estrogen Therapy (ET)
• Routes: systemic (oral, transdermal), local (vaginal)
Estrogen HT drug interactions
Carbamazepine increased hepatic metabolism of estrogen
Smoking also increases hepatic metabolism of oral therapy (smoking cessation is key)
Systemic estrogen therapy contraindications (not for local therapy)
• Unexplained vaginal bleeding (after 1y of amenorrhea)
• Acute liver disease
• Active or history of thromboembolic disease
• Estrogen-dependent cancer (breast/endometrial cancer)
• Current or history of breast cancer
• Pregnancy
• Coronary heart disease
• Previous stroke
• Gallstones
Estrogen common adverse effects
Fluid retention, headache, stomach upset, breast tenderness, gallbladder disease, urinary incontinence (w/ systemic therapy)
Estrogen rare but serious ADRs
Myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, venous thromboembolism (clotting), breast cancer
natural forms of estrogen
Estradiol (more potent) > Estrone
– Oral estradiol and estrone are not well absorbed
– Estradiol is converted to estrone in intestines
– Estradiol must be micronized (made really small) to be absorbed but only 5% gets through first pass
Synthetic estrogen
Conjugated Estrogen is a combo of
10 estrogens
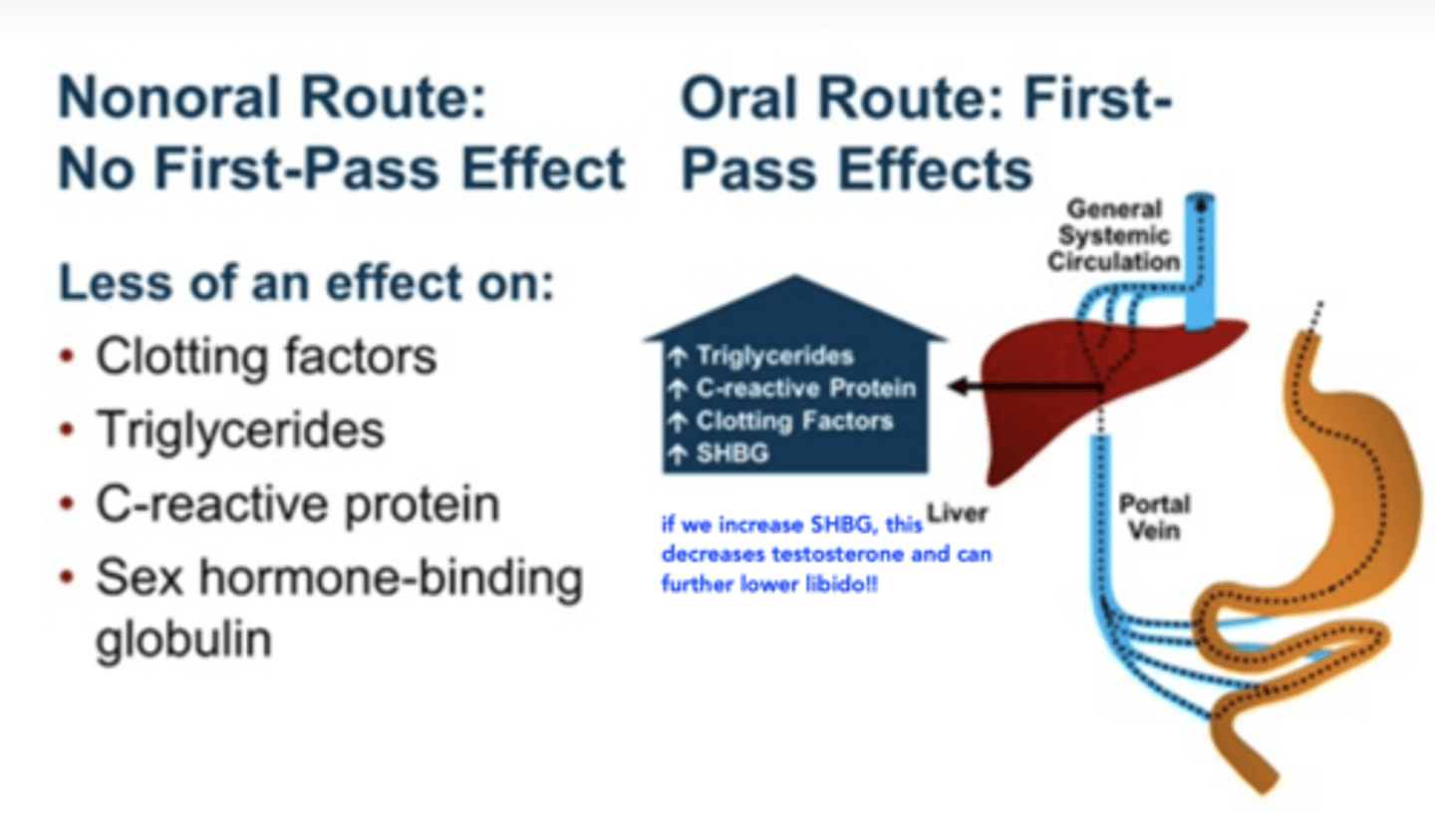
Estrogen first pass
First pass effect increases HDL cholesterol, triglycerides, coagulation factors
Also increases bad cholesterol though :(
- make sure to check triglyceride and cholesterol levels to make sure they are controlled before beginning HT
Preparations of oral estrogen
Conjugated equine estrogen (CEE)
17β- estradiol (micronized)
Estropipate (discontinued)
Conjugated equine estrogen (CEE) dosing
Premarin
- Oral
- 0.3, 0.625, 1.25mg dosing qd
(1.25mg dosing very uncommon)
17β- estradiol (micronized) dosing
Estrace, Lupin-estradiol
- oral
- 0.5, 1 and 2mg tabs qd
- preferred because its more natural with less CV risk
T/F: doses of estrogen for VM symptoms are higher than contraceptive doses
false, they are lower
So there is some overlap in years where a woman may have VM symptoms almost starting menopause and can get pregnant - so we can actually use this as both contraception and for VM symptoms and use the higher dose
T/F Transdermal estradiol does not go through first pass metabolism
True
Transdermal estrogen
- Does not go through first pass metabolism
• Patches are changed 1-2x/wk
• Gel is applied daily and is absorbed in 1-2 min
- More expensive
When should women use transdermal estrogen > oral
Used for women at risk (clotting)
• Hypertriglyceridemia
• High risk of VTE
• Malabsorption
• Obese women with metabolic syndrome
• History of gallstones or pancreatitis
17β- estradiol - Transdermal patch (Applied twice weekly)
Sandoz-Estradiol Derm® (matrix)
50, 75, 100 mcg/24 hr patches
Oesclim® (matrix)
25, 50 mcg/24 hr patches
Estradot® (matrix)
25, 37.5, 50, 75, 100 mcg/24 hr patches
17β- estradiol - Transdermal patch (Applied once weekly)
Climara® (matrix) 25, 50, 75, 100 mcg/24 hr patches
17β- estradiol - Transdermal gel (Applied once daily)
Estrogel® 0.06% Divigel® 0.1%
0.75mg, 1.5mg 0.25mg, 0.5mg, 1mg
lower strength gives more flexibility in how to treat and dose. start low, go slow
Sex-hormone binding globulin (SHBG)
If SHBG is increased, testosterone is decreased which can further lower libido
Non-oral route has less effect on SHBG
Estrogen efficacy
VERY effective!
• 18 fewer episodes/week of hot flashes compared to placebo
• At does of 17-beta estradiol 1mg/day or equivalent
• Eliminated VMS in ~80% of women
• Reduced severity and frequency in the rest
Why might we add on progestogen HT on top of the estrogen
estrogen will promote endometrial hyperplasia which can increase risk of cancer, so we HAVE to take progestogen in some form along with estrogen therapy
Progestogen HT
• Progestogen includes natural progesterone
and synthetic progestins
• In women with an intact uterus taking systemic ET, oral progesterone must be taken to prevent endometrial hyperplasia and cancer
• Hyperplasia can occur within 6 months of ET
• Occasionally used alone for vasomotor symptoms if CI to estrogen
Progestogen Contraindications
• Unexplained vaginal bleeding
• Current or history of breast cancer
• Pregnancy
• Peanut allergy (generic uses micronized progesterone; Prometrium® uses sunflower oil now)
• Soy allergy
Progestogen ADRs
• Menstrual irregularities
• Weight gain (38% gain >10lbs over 2y)
• Irritability
• Fatigue
• Breast tenderness
• Decrease in libido
Progestogen IUD
- Levonorgestrel-released IUDs with Estrogen-Therapy (ET) for endometrial protection
- Acts locally to protect the endometrium
- Benefits also includes contraception, ease of use, amenorrhea
- Good option for patients with s/e to oral progesterone
- As effective, or perhaps more effective, than oral progesterone regimens for endometrial protection
- Off-label, but viable option as per SOGC
Progestogen preparations used for endometrial protection
Medroxy- progesterone (MPA)
Micronized progesterone
Medroxy- progesterone (MPA) dosing
Oral (synthetic progestogen)
Provera® + generics
5-10mg/day x 12-14days/mth or 2.5mg continuous daily
Micronized progesterone dosing
Oral
Prometrium® + generics
200-300mg/dy for 12-14 days/mth or 100mg continuous daily
Better! more commonly used, closer to what is found in the body
Continuous vs cyclical progestogen dosing
The daily dosing is what prevents withdrawal bleed, while the cyclical dosing will have the bleed
- But using continuous dosing for someone who just hit menopause may actually increase random spotting/BTB, so better to do cyclical for them and have predictable WBs
Combination HT products
17β-estradiol / Norethindrone acetate (Oral, TD)
17β-estradiol/ drospirenone (Oral)
17β-estradiol / Norethindrone acetate (Oral) dosing
Oral
Activelle®, Activelle LD®
0.5mg/0.1mg QD
1mg/0.5mg QD
17β-estradiol/ drospirenone (Oral) dosing
Oral
Angeliq®
1mg/1mg QD
17β-estradiol / Norethindrone acetate (transdermal) dosing
Trans- dermal Patch (matrix)
Estalis®
0.05mg/140ug per 24 hrs;
0.05mg/250ug per 24 hrs
1 patch twice weekly
When can we use hormonal contraceptives for menopausal symptoms
Hormonal contraceptives can be used in perimenopausal women
• Useful when need to control irregular or heavy bleeding
Ethinyl estradiol (EE)/levonorgesterol Oral (Alesse®) If needed for contraception
Ethinyl estradiol (EE)/levonorgesterol Oral (Alesse®) dose
0.02mg/0.1mg
Ethinyl estradiol (EE)/levonorgesterol
Oral
(Alesse®) If needed for contraception
0.02mg/0.1mg
Vaginal estrogen indications
• Symptoms of vulvovaginal atrophy (including dyspareunia)
• Urinary urge incontinence (not stress incontinence)
• Recurrent UTIs
Benefit seen within weeks, f/u appt monitoring in 4-6 weeks
Vaginal estrogen mechanism
Improves blood supply to urogenital tissues, induces normal mucous proliferation/lubrication, restores normal flora, makes acidic pH
T/F Very little vaginal estrogen is absorbed systemically
True
T/F Concurrent progesterone is required with vaginal estrogen
False - not required
Vaginal estrogen contraindications
Not contraindicated in women with contraindications to systemic estrogen (e.g. recent stroke, VTE) but avoid in women with breast cancer who are taking aromatase inhibitors
- May consider for patients on tamoxifen after consultation with oncologist
Vaginal Estrogen preparations
Conjugated estrogens - Premarin® Vag. Cream
Estrone - Estragyn® Vag. Cream
17β-estradiol - Estring®, Vaginal ring
17β-estradiol - Vagifem® Vaginal Tablet
Conjugated estrogens - Premarin® Vag. Cream DOSING
0.625mg/g
0.5g QD x 14 days, then 0.5g 2-3x weekly
Estrone - Estragyn® Vag. Cream DOSING
1mg/g
0.5-4g QD cyclic (3 weeks on, 1 week off)
OR 2-3x weekly
17β-estradiol - Estring®, Vaginal ring DOSING
2mg/ring Releases 0.0075mg/d
Insert & replace q3m
17β-estradiol - Vagifem® Vaginal Tablet DOSING
0.010 mg
1 vaginal tab QD x 2wks then 2/week
Bioidentical hormones
By definition are identical to the hormones we
produce in our body
• Do not naturally occur outside of humans, so must be produced in labs
• Promoted as “natural” and “safe”
• Estradiol, estrone, estriol, progesterone, testosterone
• Providers usually target a specific hormone level, despite lack of evidence to do so
"Compounded bioidentical HT should be avoided, given concerns about safety, including the possibility of overdosing or underdosing, lack of efficacy"
Commercially available bioidentical hormones
Estrace®, Estrogel®, Prometrium®
When should compounded HT be used (bioidentical hormones)
Compounded HT should only be used by women allergic to approved products
HERS/HERS II trials
Showed that ET caused more CV events, more DVTs, more PEs, more strokes, more breast cancer, heart attacks
Less colorectal cancer, less hip and vertebral fractures
WHI - ET Outcomes
• HT is not for chronic disease management
• Greatest benefit is in symptom management
• For long-term therapy, risks generally outweigh benefits, even in younger women
Menopause & HT - when is CVD & Stroke risk minimized
• Low risk of CVD & stroke if started right after
menopause and used for
Menopause & HT - when is CVD & Stroke risk incrceased
Increased risk if started >10y postmenopause
EPT riskier than ET
Oral riskier than transdermal
When does HT have the most risk for VTE (blood clots)
Risk increases with age
EPT riskier than ET
Oral riskier than transdermal
- Use TD if older (>65), obese, or with DVT history
HT risk of breast cancer
Risk persists after stopping (for 3 -13 years)
• Can prescribe when a woman has increased risk of breast cancer, but with counselling and surveillance
• Increased breast cancer risk first seen 3-4 years after
starting EPT (so
Hormone therapy benefits
• Vasomotor symptoms
• Vaginal irritation or dryness
• Sleep disturbances/ mood disorders
• Aches, pains
• Osteoporosis
• GSM (vaginal ET)
Hormone therapy risks
• VTE
• Stroke
• Breast cancer (after ~4 years on EPT)
• CHD if >60y, or >10 years after menopause
• Endometrial hyperplasia, cancer (when unopposed systemic ET in a woman with a uterus)
Unknown risks:
• CHD if
HRT associated with _______________ surrogate markers of atherosclerosis
improved
• Reduced carotid intima-media thickness (KEEPS, ELITE)
• Reduced coronary artery calcium (KEEPS)
HRT associated with a(n) ____________ risk of a
composite outcome of mortality, heart failure, or myocardial infarction (DOPS)
reduced
In someone with moderate - severe hot flashes and/or night sweats and no CIs, how should they be treated?
Can use estrogen and progesterone (or if they have had hysterectomy, then only estrogen)
If someone has GSM and no CIs, how should they be treated?
Vaginal lubricants and/or moisturizer
consider low-dose vaginal estrogen
If someone has GSM and has CIs (breast cancer, endometrial cancer etc.), how should they be treated?
Vaginal lubricants and/or moisturizers
In someone with moderate - severe hot flashes and/or night sweats and has a contraindication (hormone dependent cancer, VTE, CHD, stroke etc.), how should they be treated?
treat with a low dose SSRI (paroxetine
if still not controlled or SSRI contraindicated, try gabapentin/pregabalin
When to avoid HT in women for CVD risk
if they are at high risk, or moderate risk with >10 years since menopause onset
If moderate risk
Alternatives to traditional HT for vasomotor symptoms
Tibolone
Bazedoxifene (SERM)
Antidepressants (SSRIs, SSNRIs)
NHPs, lifestyle changes
Tibolone
• Synthetic steroid (“prohormone”) that metabolizes to 3 metabolites with estrogenic, progestogenic and androgenic activity
• Start at least 12 months after LMP due to the risk of breakthrough vaginal bleeding
Who is tibolone indicated for
Only indicated in patients with intact uterus
Tibolone dosing
Typical dosage: 2.5mg PO once daily
Tibolone efficacy
• Less effective than EPT in reducing vasomotor
symptoms
• More effective than EPT at improving sexual dysfunction
Other benefits: Reduced vertebral fractures, improved BMD, improved vaginal dryness, improved mood
Tibolone short-term safety
Side effect profile similar to EPT, with
additional acne and hirsutism (male pattern hair growth)
• Substrate of CYP3A4, possible fibrinolytic activity
• Less unscheduled bleeding compared to EPT
Tibolone long-term safety
• Increased risk of stroke vs. placebo in women
> 60 years old
• Increased risk of breast cancer recurrence vs. placebo
Tibolone adherence
• More expensive and not on ODB
• Lower pill burden (single daily pill)
• Classified as a controlled drug, similar to
testosterone
- not first line for most patients. consider for those who do not tolerate EPT
Bazedoxifene (SERM)
• Does not require a progestogen (no endometrial hyperplasia)
• Works for vasomotor symptoms, vulvovaginal symptoms, osteoporosis
• Less vaginal bleeding, less breast tenderness