Functional Anatomy of Brain
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
cerebral cortex
superficial thin layer of gray matter
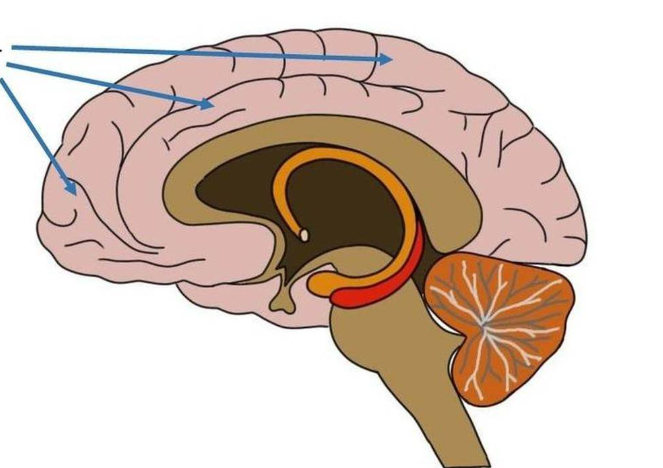
functions of cerebral cortex
conscious thought, memory storage & processing, sensory processing, control of skeletal muscle
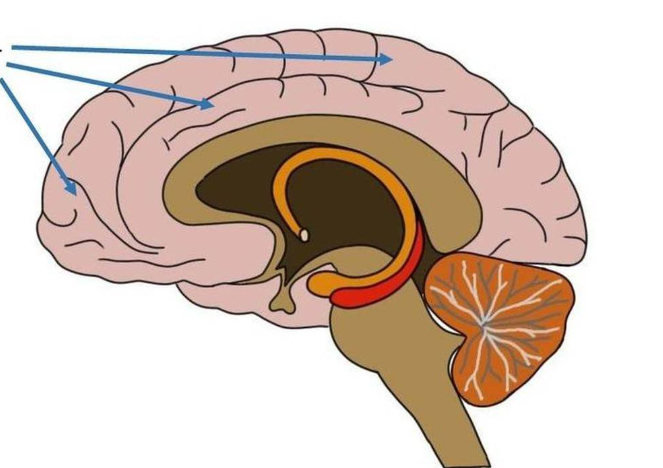
cerebellum
automatic processing center that coordinates and modulates motor commands from cerebral cortex
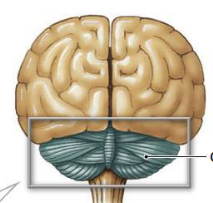
specific functions of cerebellum
proprioceptor, visual, tactile, balance, and auditory sensations
cerebellum: adjusting postural muscles
modifies activities of brainstem centers
cerebellum: programming movements controlled at conscious/subconscious levels`
refines learned movement patterns, compares motor commands w/ proprioceptive info, makes adjustments as needed
ataxia
results from cerebellum damage/impairment. inability to coordinate muscle movement. if severe, person cannot sit or stand
gray matter function in cerebellar cortex
involuntary coordination and control of ongoing movements
gray matter function in cerebellar nuclei
involuntary coordination and control of ongoing body movements
white matter function in arbor vitae
connects cerebellar cortex and nuclei w/ cerebellar peduncles
white matter function in cerebellar peduncles superior
link cerebellum w/ midbrain, diencephalon, and cerebrum
white matter function in cerebellar peduncles middle
carry communications between the cerebellum and pons
white matter in cerebellar peduncles inferior
link cerebellum w/ medulla oblongata and spinal cord
white matter function in transverse pontine fibers
interconnected pontine nuclei w/ opposite cerebellar hemisphere
midbrain contains nuclei that
process visual & auditory info, control reflexes triggered by them, helps maintain consciousness, send info to thalamus
pons - connect cerebellum/brainstem
tracts and relay centers, somatic and visceral motor control
medulla oblongata
relays sensory info thru brainstem and to thalamus, regulates many autonomic functions
inferior olivary complex
relays info from red nucleus, other midbrain centers, and cerebral cortex to cerebellum
cardiovascular centers
regulate heart rate and force of contraction
respiratory rhythmicity centers
set basic pace of respiratory movements
gracile nucleus & cuneate nucleus
relay somatic info to the thalamus
cranial nerves
sensory and motor nuclei of five cranial nerves; nuclei relay ascending info from the spinal cord to higher centers
reticular formation
contains nuclei and centers that regulate vital autonomic functions; extends into pons and midbrain
ascending and descending tracts w/i funiculi
link the brain w/ the spinal cord
descending tracts
carry motor commands from higher centers of brain to nuclei of cranial or spinal nerves
ascending tracts
carry sensory info from brainstem nuclei to thalamus
transverse pontine fibers
link pontine nuclei w/ the cerebellum of opposite side
tectum (roof)
superior colliculi and inferior colliculi
superior colliculi
integrate visual info w/ other sensory inputs; initiate reflex response to visual stimuli
inferior fcolliculi
relay auditory info to medial geniculate body; initiate reflex responses to auditory stimuli
red nuclei
provide subconscious control of upper limb position and background muscle tone
substantia nigra
secretes neurotransmitter dopamine and inhibits activity in basal nuclei
reticular formation
processes incoming sensations and outgoing motor commands automatically; can initiate involuntary motor responses to stimuli; helps maintain consciousness
other nuclei/centers
are associated w/ cranial nerves III and IV
cerebral peduncles
connect primary motor cortex w/ motor neurons in brain and spinal cord; carry ascending sensory info to thalamus
diencephalon
structural/functional link between cerebral hemispheres and rest of CNS
thalamus
sensory relay/processing
hypothalamus
has centers involved w: emotions, autonomic function, and hormone production
corpora quadrennia
reflex centers for vision and hearing
pineal gland
responds to decreasing light from CN II to make melatonin; induces sleep
posterior commissure
connects language processing centers of both cerebral hemispheres
anterior commissure
connects structures of olfactory pathway, frontal cortex
choroid plexus
production and secretion of CSF and forms blood-CSF barrier
corpus collosum
connects corresponding regions of cerebral cortex of two hemispheres
interventricular foramen
connects 3rd and lateral ventricles to allow CSF to flow
fornix
extends form hippocampus to mammillary bodies and functions in cognition, memory, and emotions
interthalamic adhesion
connects right and left thalamus
septum pellucidum
membrane separating left and right ventricles