Ch. 6 Adaptations to Aerobic Endurance Training
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What does aerobic mean?
Relating to or denoting exercise that improves the efficiency of the body's cardiovascular system in absorbing and transporting oxygen.
What energy pathway is primarily used during aerobic exercise?
The oxidative phosphorylation pathway.
What is the Heart Rate Reserve (HRR) of a 38-year-old male with a resting heart rate of 64 bpm?
118 bpm (HRR = HRmax - HRrest).
Using the Karvonen method, what should a 22-year-old female with a resting heart rate of 55 bpm maintain to work at 75% intensity?
162 bpm (HRtarget = HRrest + (training % x HRR)).
What happens to cardiac output from rest to steady-state aerobic exercise?
Cardiac output initially increases rapidly, then more gradually, and subsequently reaches a plateau.
What is stroke volume?
The amount of blood pumped by the heart in liters per minute, calculated as stroke volume (SV) times heart rate (HR).
What physiological mechanisms increase stroke volume during exercise?
Increased end-diastolic volume and sympathetic stimulation leading to more forceful ventricular contractions.
What is the Frank-Starling mechanism?
An increase in end-diastolic volume leads to a greater stretch on ventricular walls, enhancing contraction strength.
How does heart rate respond to increases in exercise intensity?
Heart rate increases linearly with increases in intensity due to anticipatory stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system.
What is maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max)?
The greatest amount of oxygen that can be used at the cellular level during maximal exercise.
What is systolic blood pressure (SBP)?
The pressure exerted against arterial walls during ventricular contraction.
What is diastolic blood pressure (DBP)?
The pressure exerted against arterial walls when the heart is at rest and no blood is being forcefully ejected.
What occurs to blood flow during aerobic exercise?
Blood flow to active muscles increases due to local arteriolar dilation, while flow to other organs decreases.
What are the acute responses to aerobic exercise?
Increased cardiac output, stroke volume, heart rate, oxygen uptake, systolic blood pressure, and blood flow to active muscles.
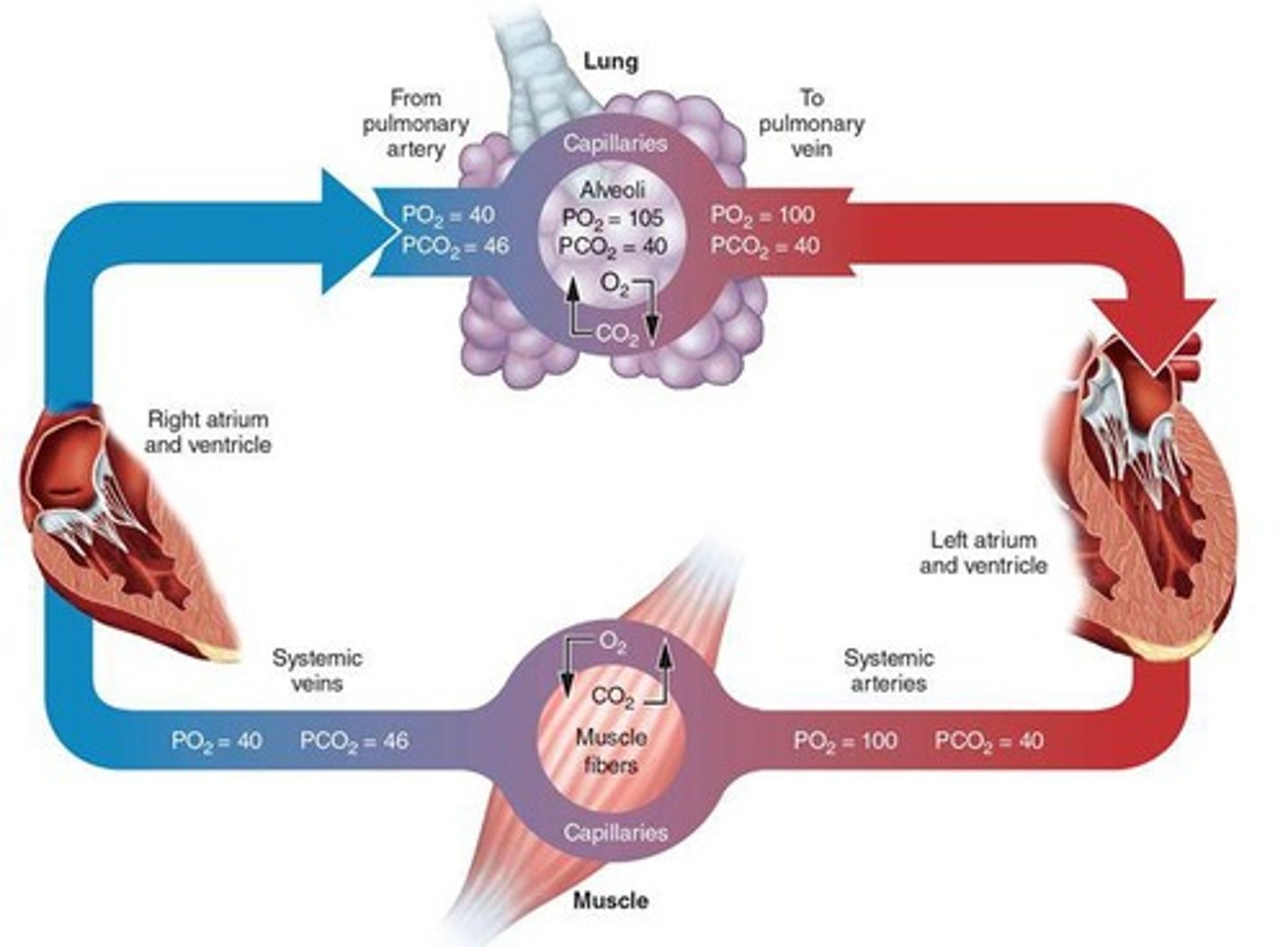
What happens to oxygen and carbon dioxide during high-intensity aerobic exercise?
Oxygen diffuses from capillaries into tissues, and carbon dioxide moves from blood into alveoli.
What is the onset of blood lactate accumulation (OBLA)?
The exercise intensity at which lactic acid begins to accumulate in the blood.
What are chronic adaptations to aerobic endurance training?
Increased maximal cardiac output, stroke volume, fiber capillary density, and decreased resting heart rates.
How does aerobic exercise affect hormonal responses?
It increases hormonal circulation and alters receptor levels, with trained athletes showing blunted responses to submaximal exercise.
What external factors can affect aerobic performance?
Altitude, smoking, doping, age, and sex can all impact aerobic capacity and performance.
What is the effect of overtraining on performance?
It can lead to decreased body fat loss, increased muscle soreness, and reduced VO2max.

What is detraining?
The loss of training adaptations due to inactivity following exercise.
What is tapering in the context of training?
A planned reduction of training volume before an athletic competition or recovery period.