UARK Anatomy Lecture Exam 4
1/264
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
265 Terms
What is the composition of blood?
plasma (liquid matrix), buffy coat (platelets and leukocytes), Erythrocytes (RBC)
What percent mass is blood in the body?
7%
Where are the proteins in blood?
plasma
What are plasma donations used for?
making immunoglobins from proteins of the plasma
What does the extracellular fluid contain?
interstitial fluid, plasma, lymph, cerebrospinal, synovial, serous, etc.
What is interstitial fluid?
fluid between cells, NOT in blood
Where do we get lymph?
from plasma filtrate
Where is most fluid in the body?
intracellular
Chemical composition of plasma
high O2
low CO2
high proteins
Chemical composition of interstitial fluid
low O2
high CO2
low proteins
thrombocytes are cell _____
fragments
What kind of diffusion takes place in aveoli?
simple diffusion
Composition of hemoglobin
- 4 heme units (where O2 and CO2 bind to Hb)
What is the Bohr effect on hemoglobin?
Higher/Lower pHs cause hemoglobin binding affinity to change to O2
Hb in RBCs allow for what?
a higher concentration of CO2 and O2 in blood
Hb increases the ______ of O2 in blood
carrying capacity
Decreased pH = Hb ______ of CO2
release
Increased pH = Hb ______ of O2
uptake
Normal pH (where enzymes function)
7.35-7.45
The renal system _____ pH regulation
slows (retains or releases H+ or HCO3-)
carbonic acid-bicarbonate buffer system
chemical system that helps maintain pH homeostasis of the blood
Type A blood
A antigens and anti-B antibodies
Type B blood
B antigens and anti-A antibodies
Type AB blood
A and B antigens, no antibodies
Type O
no antigens, A and B antibodies
Rh+
has the Rh antigen
Rh-
lack Rh antigen
anti-Rh antibodies
only produced when Rh- individuals are exposed to Rh antigens (pregnancy and blood transfusion)
O-
universal donor
AB+
universal recipient
Leukocytes
white blood cells, fight infection
Diapedisis (emigration)
The migration of intact blood cells between endothelial cells of a blood vessel such as a venule.
Chemotaxis
Cell movement that occurs in response to chemical stimulus
Agranulocytes
lack cytoplasmic granules
Which side of the heart is oxygen rich?
left
Which side of the heart is oxygen poor?
right
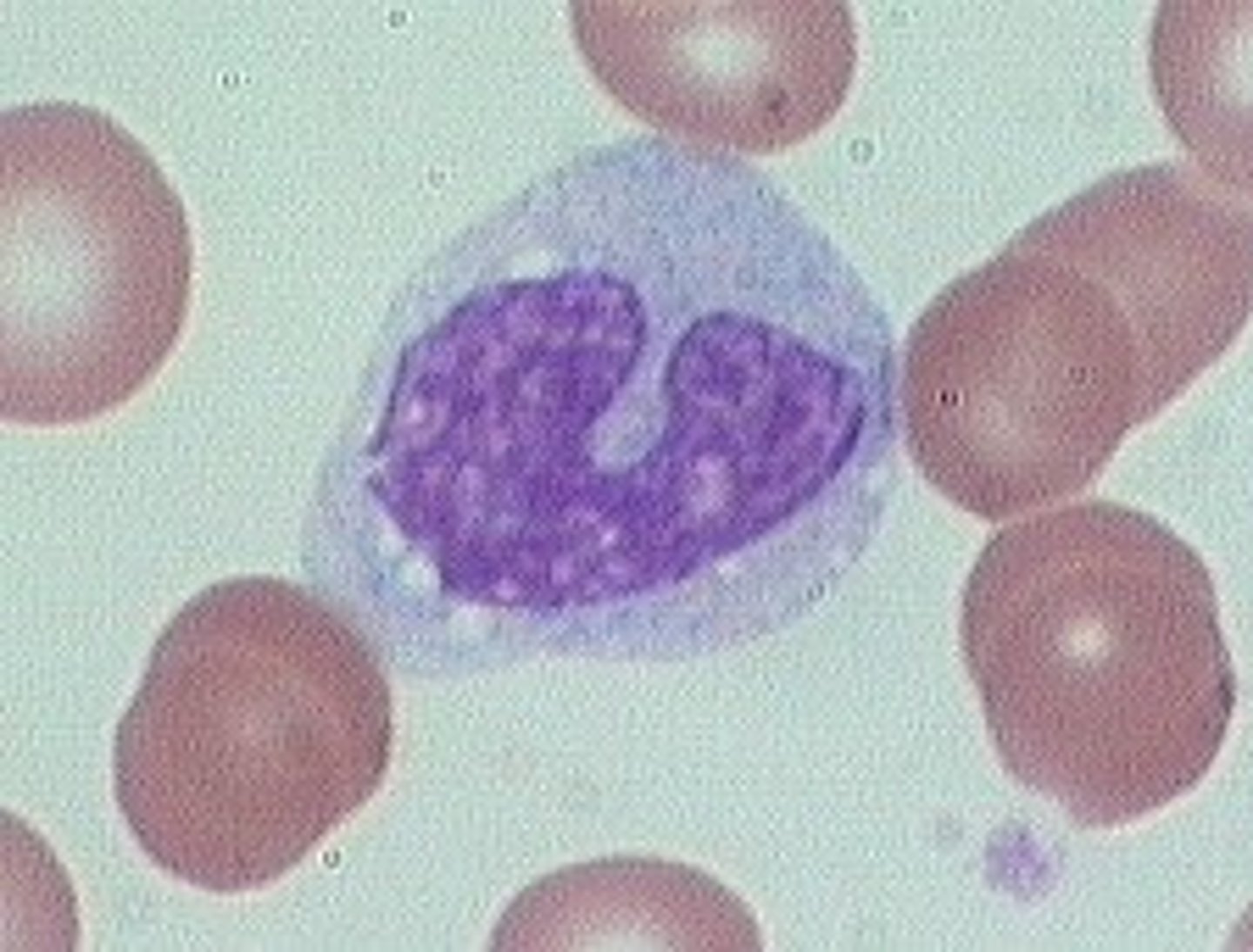
Monocytes
- large cells with kidney shaped nucleuses
- use chemotaxis
- attract fibroblast to encase pathogen in collagen
- produce scar tissue
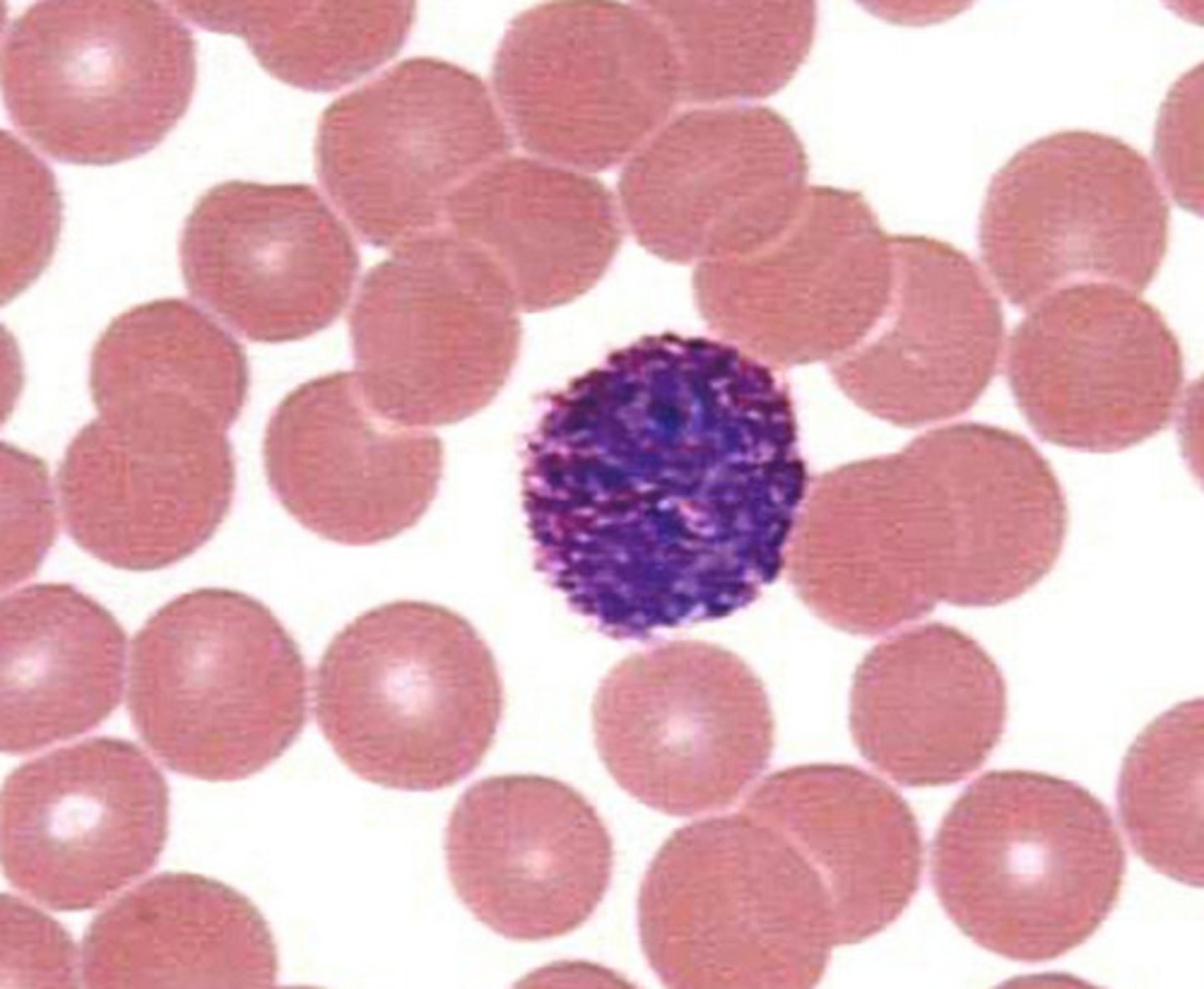
lymphocytes
- round nucleases; responsible for specific immunity
- primary cells of lymphatic system
- differentiates into T cells, B cells, and NK cells
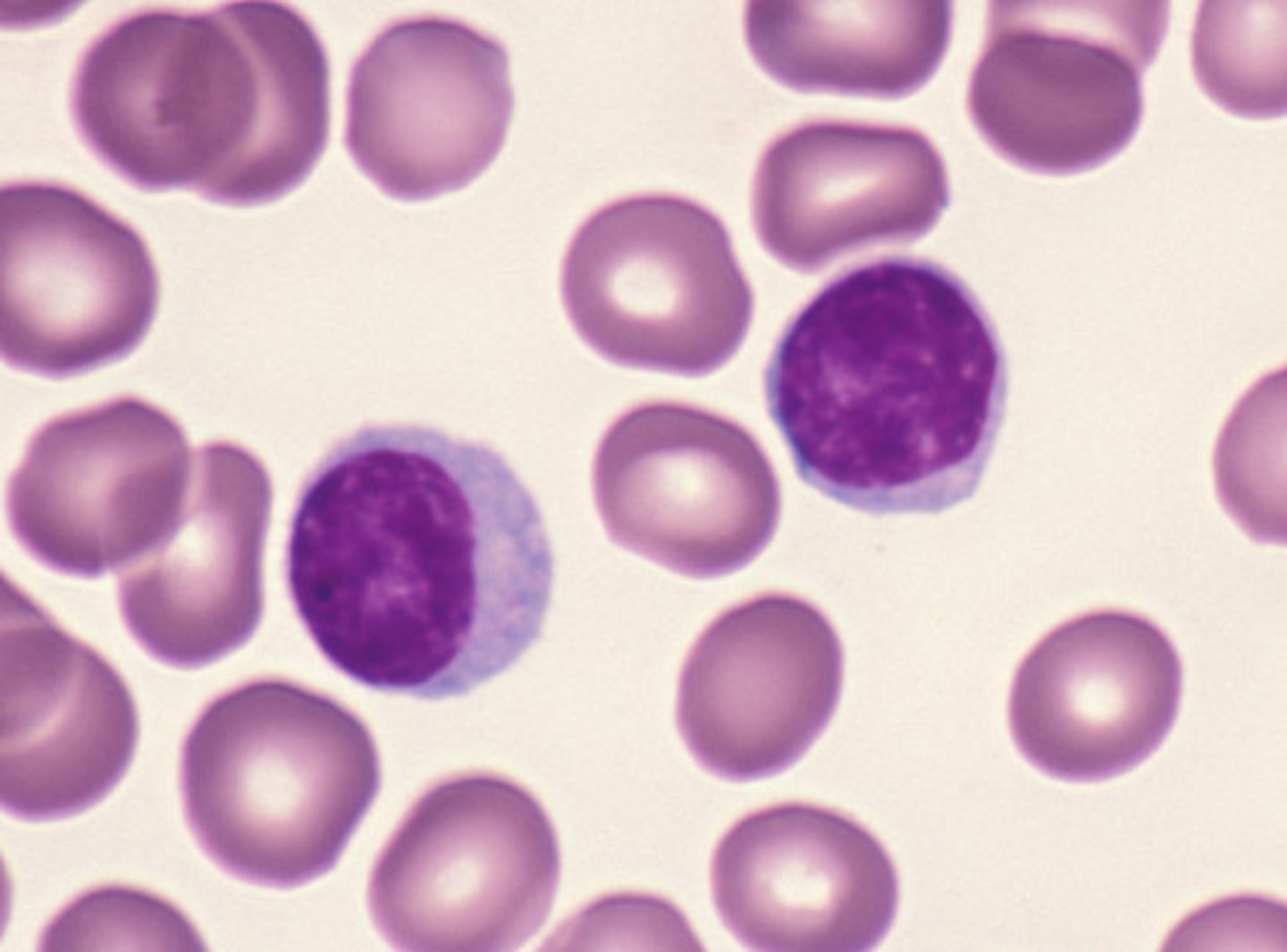
T cells
enter tissues to directly attack pathogens
B cells
produce plasma cells that secrete antibodies
NK cells
attack abnormal cells; immune surveillance
Granulocytes
have cytoplasmic granules
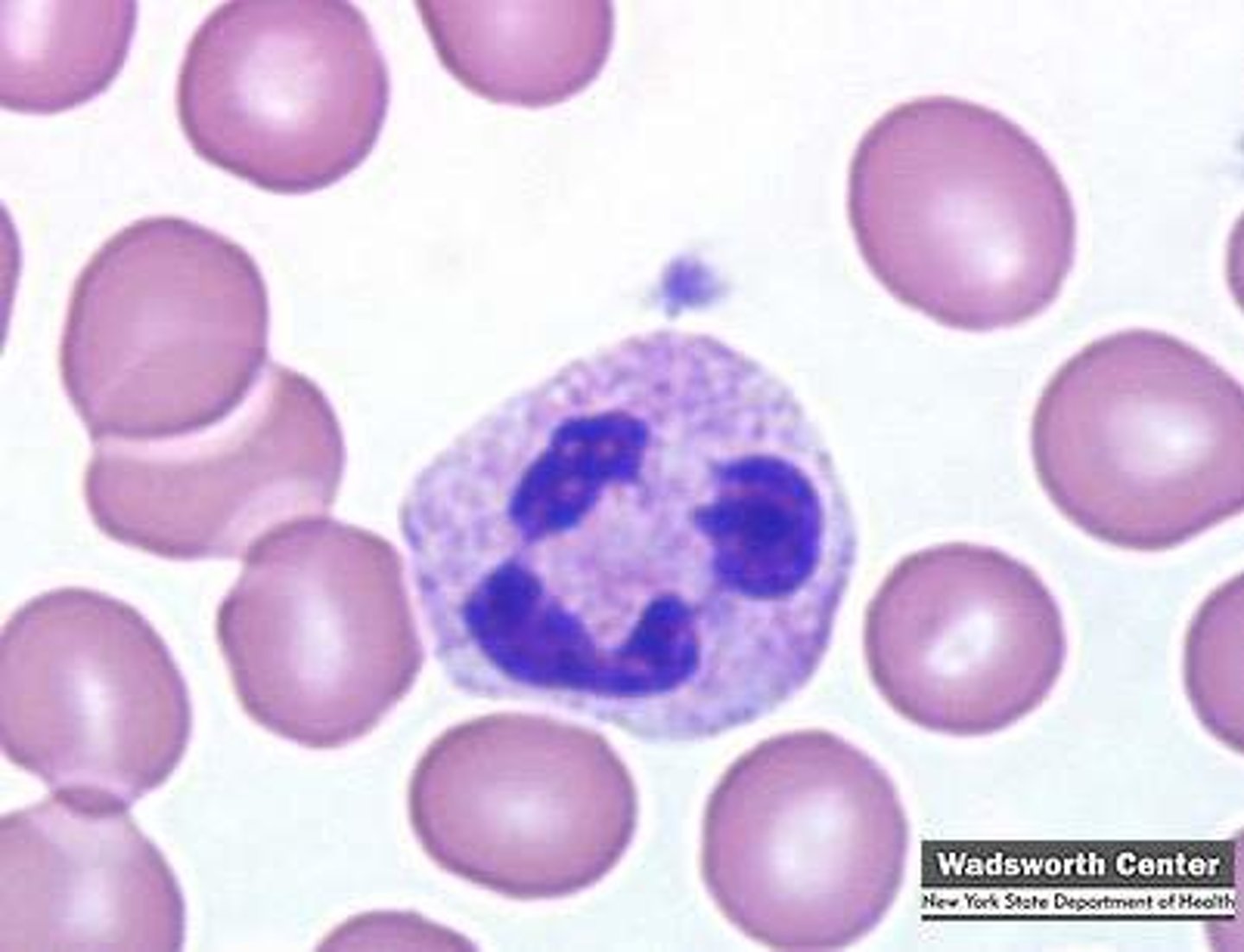
Neutrophils
- multi lobed nucleus
- vacuoles with lysosomal enzymes and bactericidal compounds
- phagocytotic
- short-lived; will secret chemotaxic chemicals upon death
Eosinophils
- bilobed nucleus
- attack objects marked with antibodies
- involved with allergies and parasites
- secrete compounds that reduce inflammation
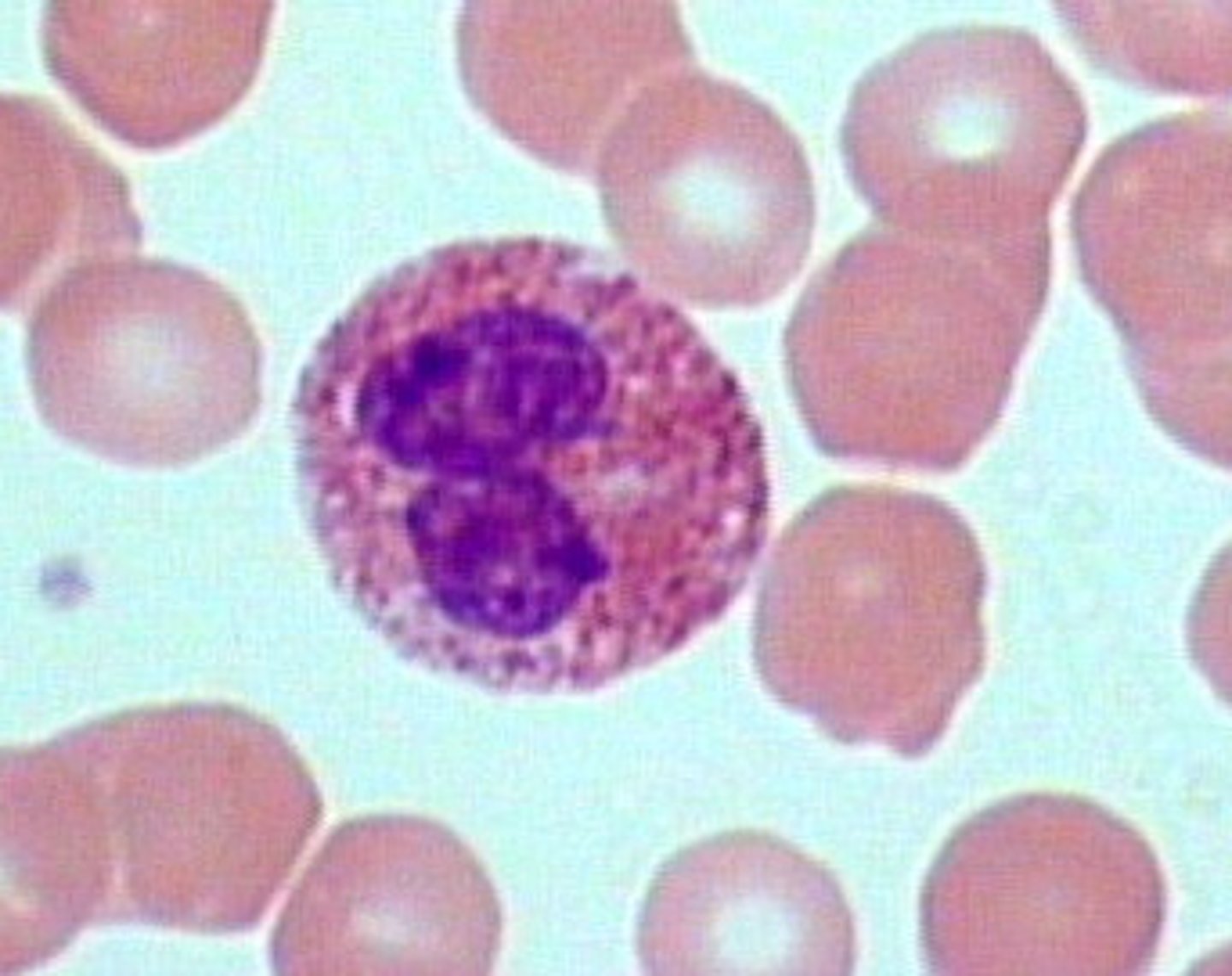
Basophils
- very high density of granules
histamines
- dilate blood vessels
Heparin
- prevents blood clots
Platelets (thrombocytes)
- derived from megakaryocytes (fragement forming bit and pieces of membrane-enclosed packets of chemicals)
Hemostasis
- blood clotting
What do platelets do to help clotting process?
release chemicals and enzymes to initiate it
What clumps together to form platelet plug?
fibrin
What contracts a clot?
actin and myosin
Platelets are not
cells
Hemopoises
- blood cell formation
- red marrow
- yellow marrow can be converted to red
Lymphatic stem cells
NK cells, T cells, B cells
Myeloid stem cells
Neutrophils, Basophils, Eosinophil, Macrophages, Megakaryocyte (platelets), Erythrocytes
Erythropoiesis
- production of red blood cells
- requires B12, amino acids, and Fe
Erythropoietin
- glycoprotein hormone by kidneys and liver in response to low O2 (hypoxia)
- stimulate erythroblast and stem cell division
- speed up Hb formation
Leukopoiesis
- differentiation of myeloid cells into leukocytes
colony stimulating factors (CSF)
- hormones that stimulate leukocyte production
Lymphopoiesis
- differentiation of lymphoid cells into lymphocytes
Lymphoid stem cells are also in
thymus, spleen, lymph nodes
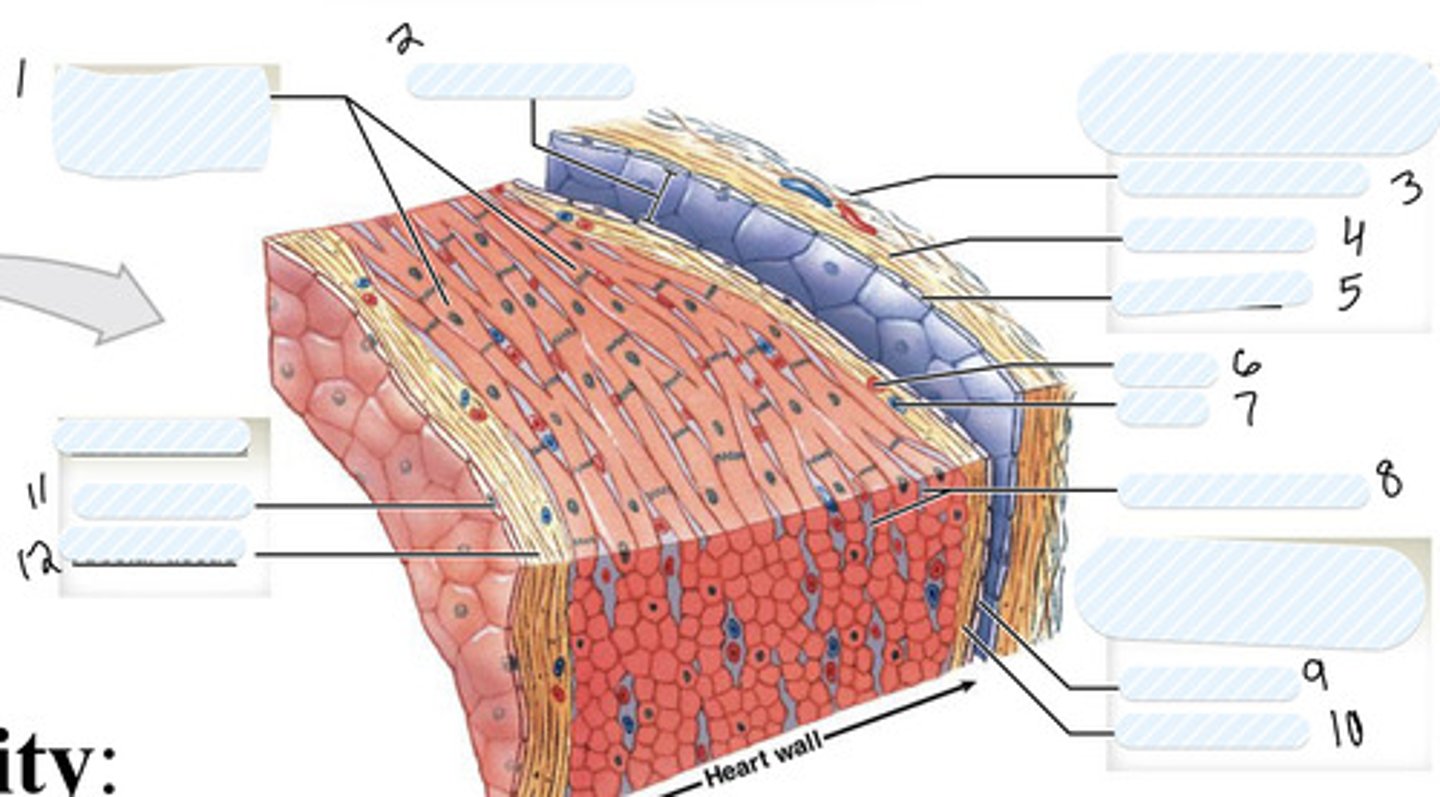
superior vena cava
1
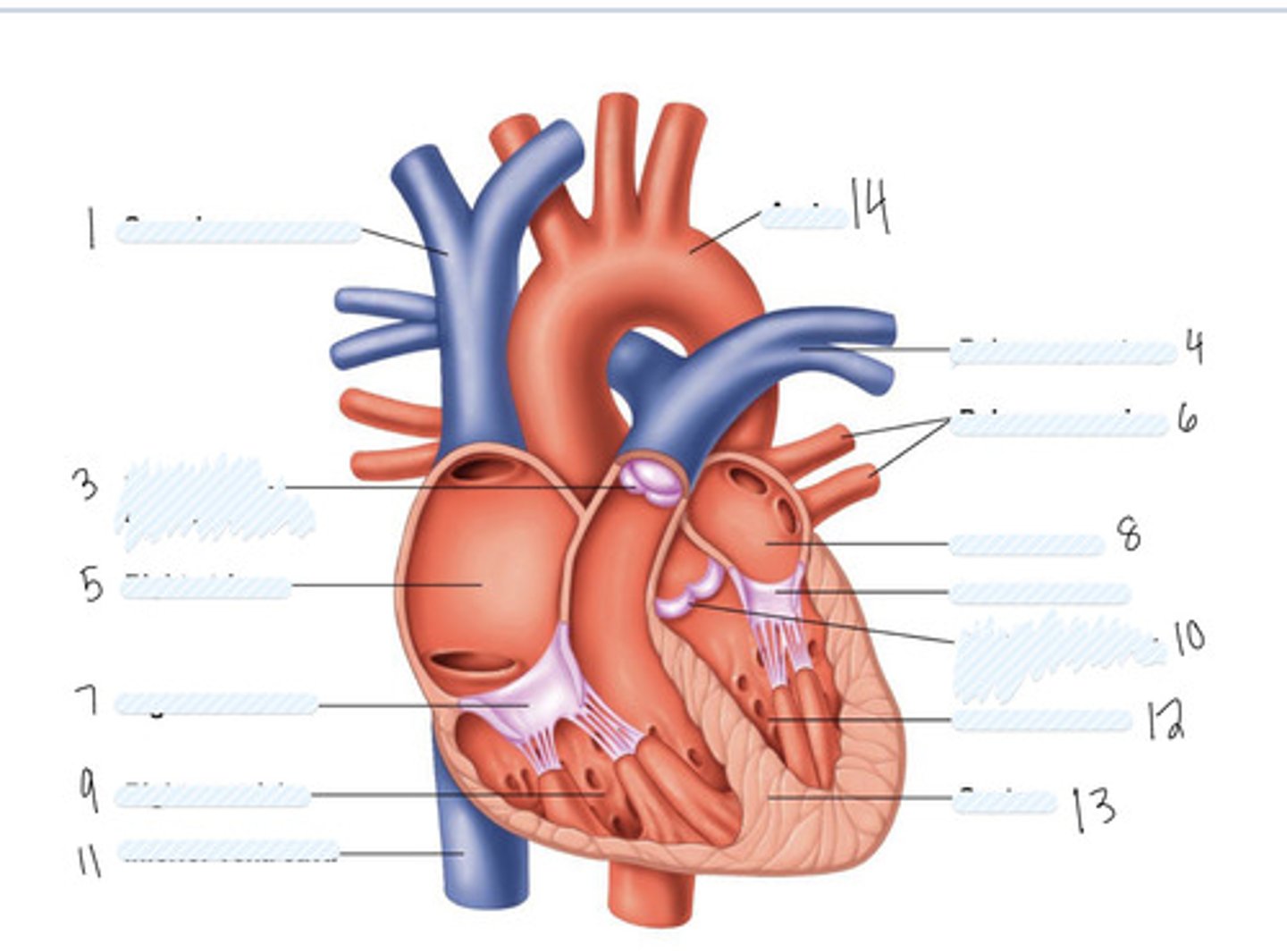
pulmonary semilunar valve
3
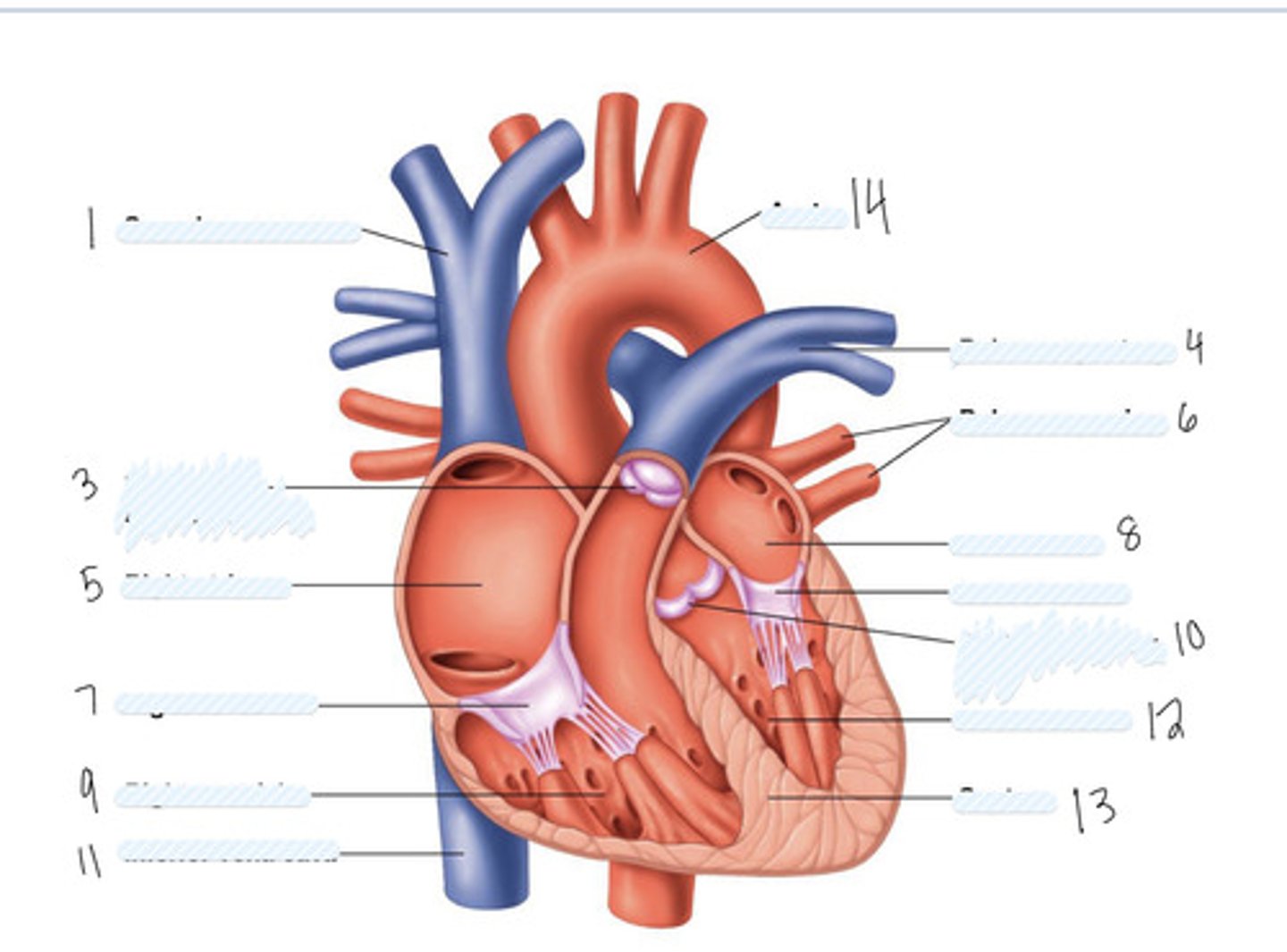
right atrium
5
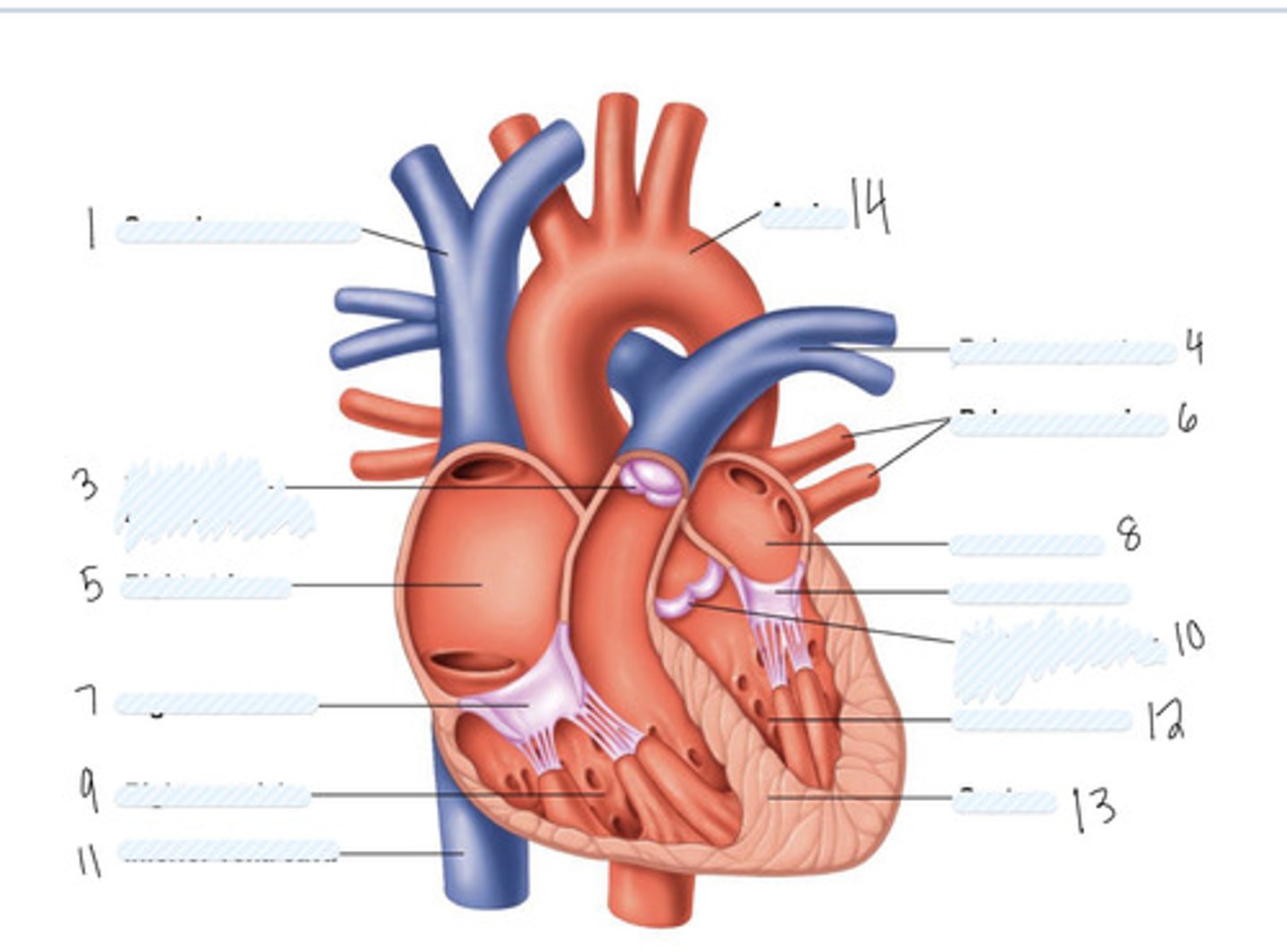
Right AV (tricuspid) valve
7
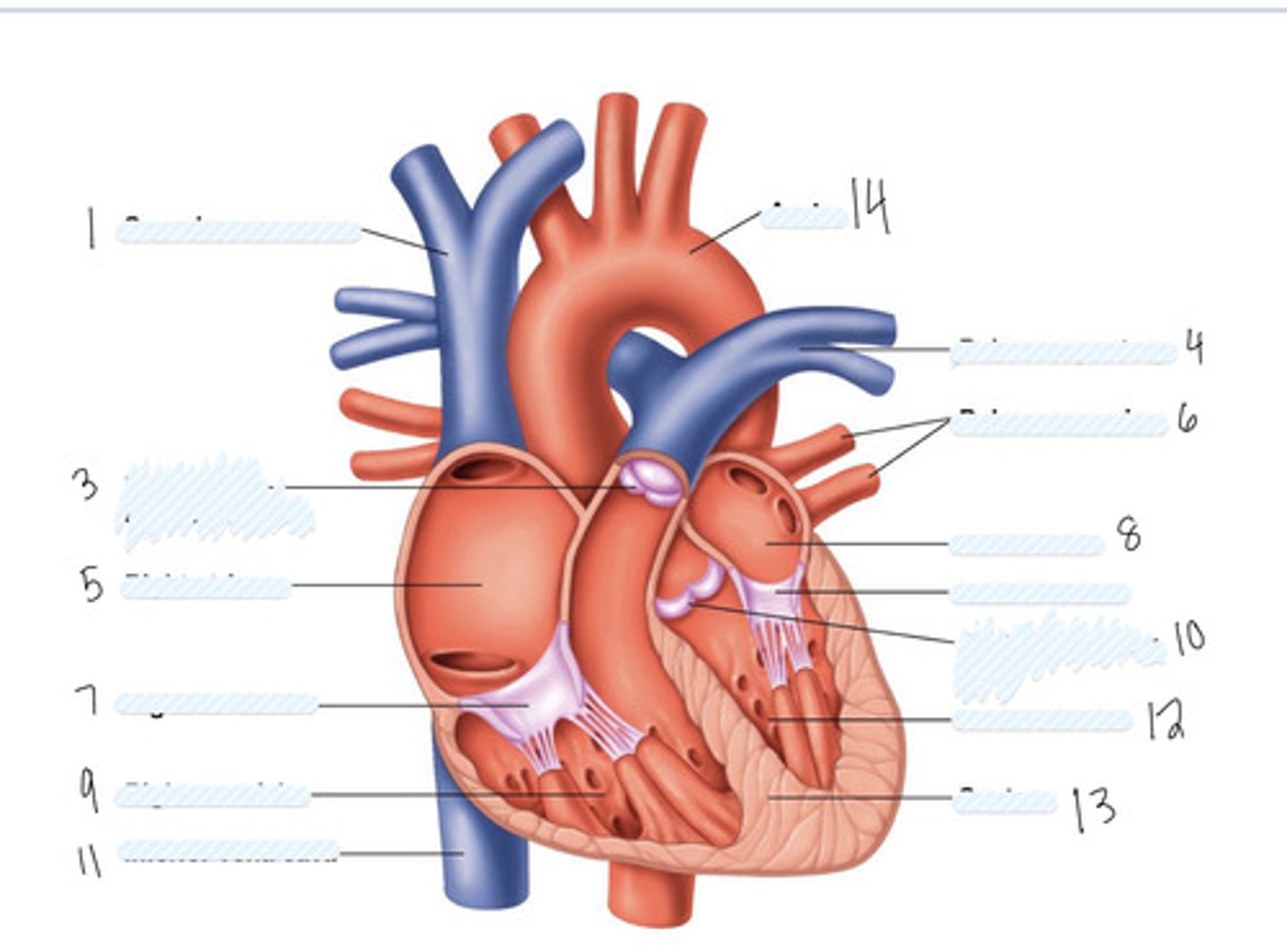
right ventricle
9
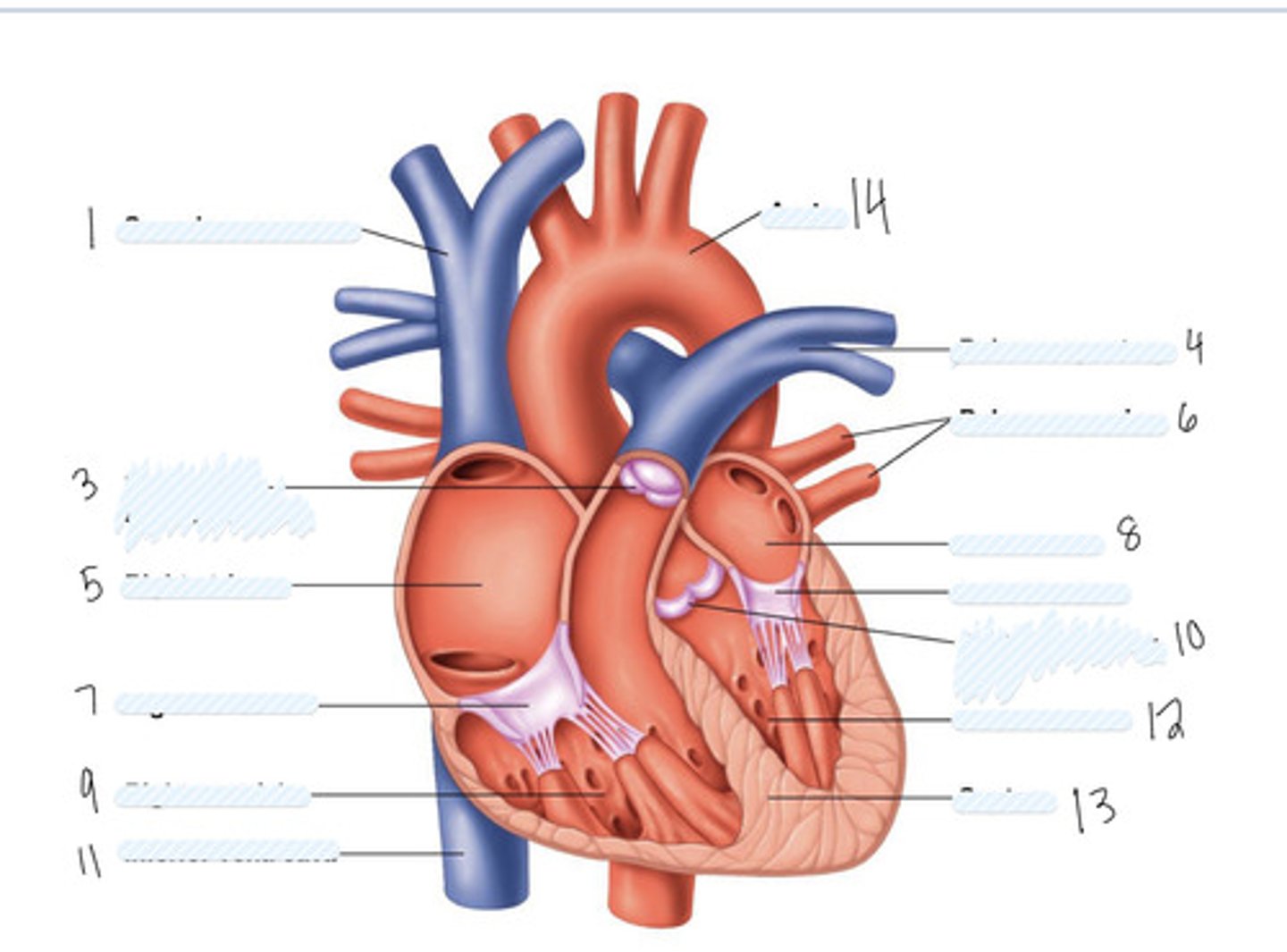
inferior vena cava
11
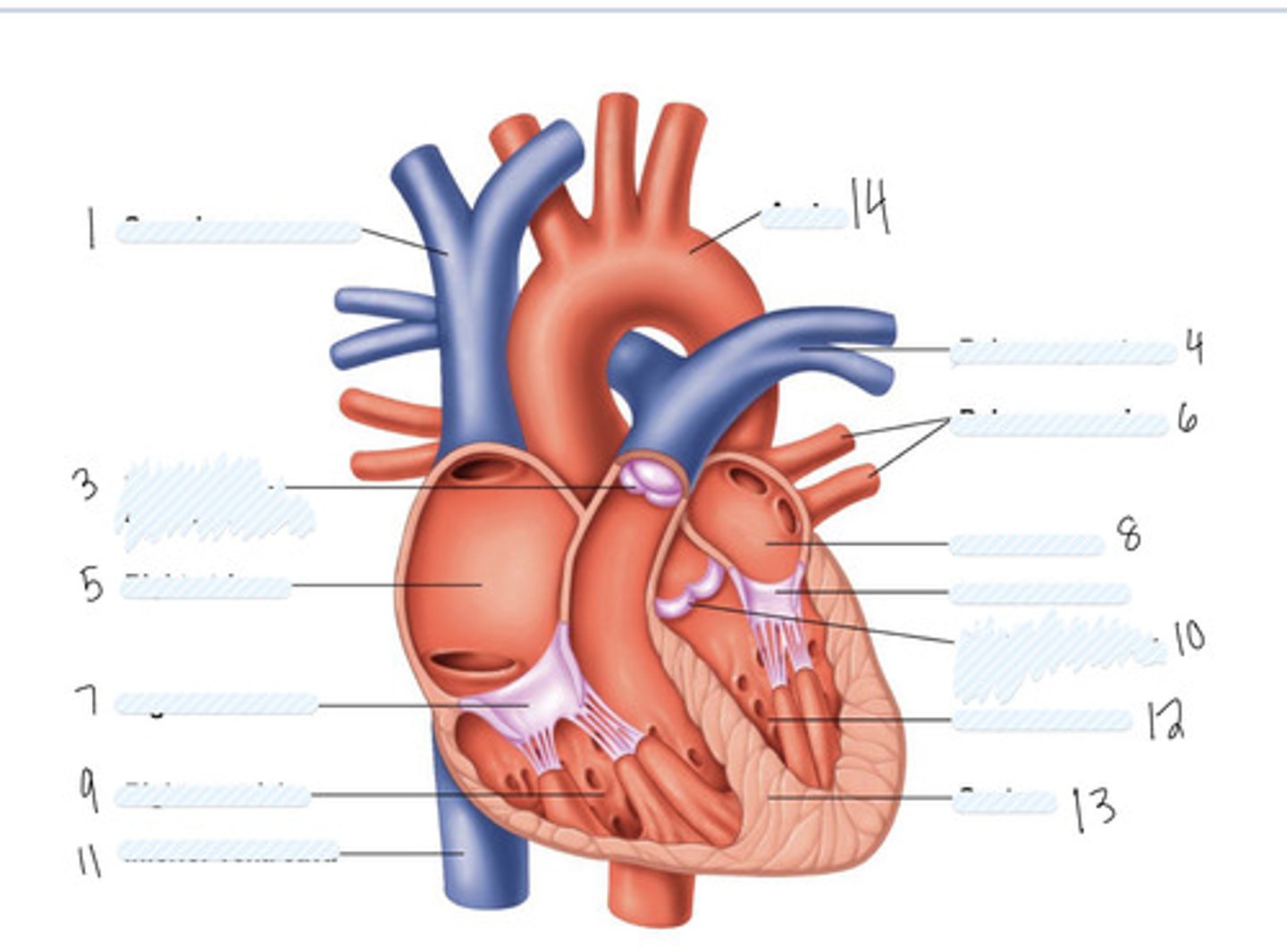
aorta
14
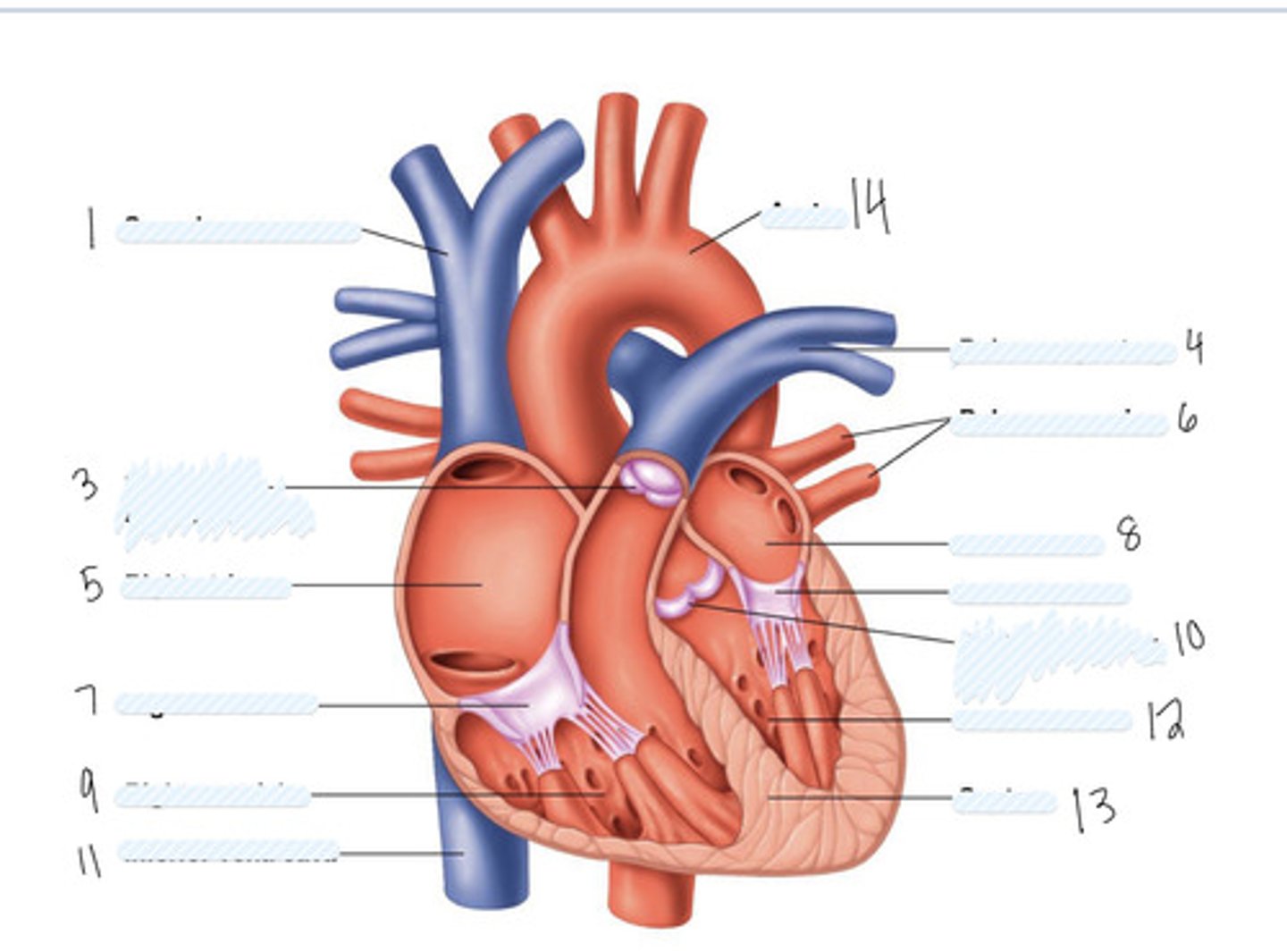
pulmonary artery
4
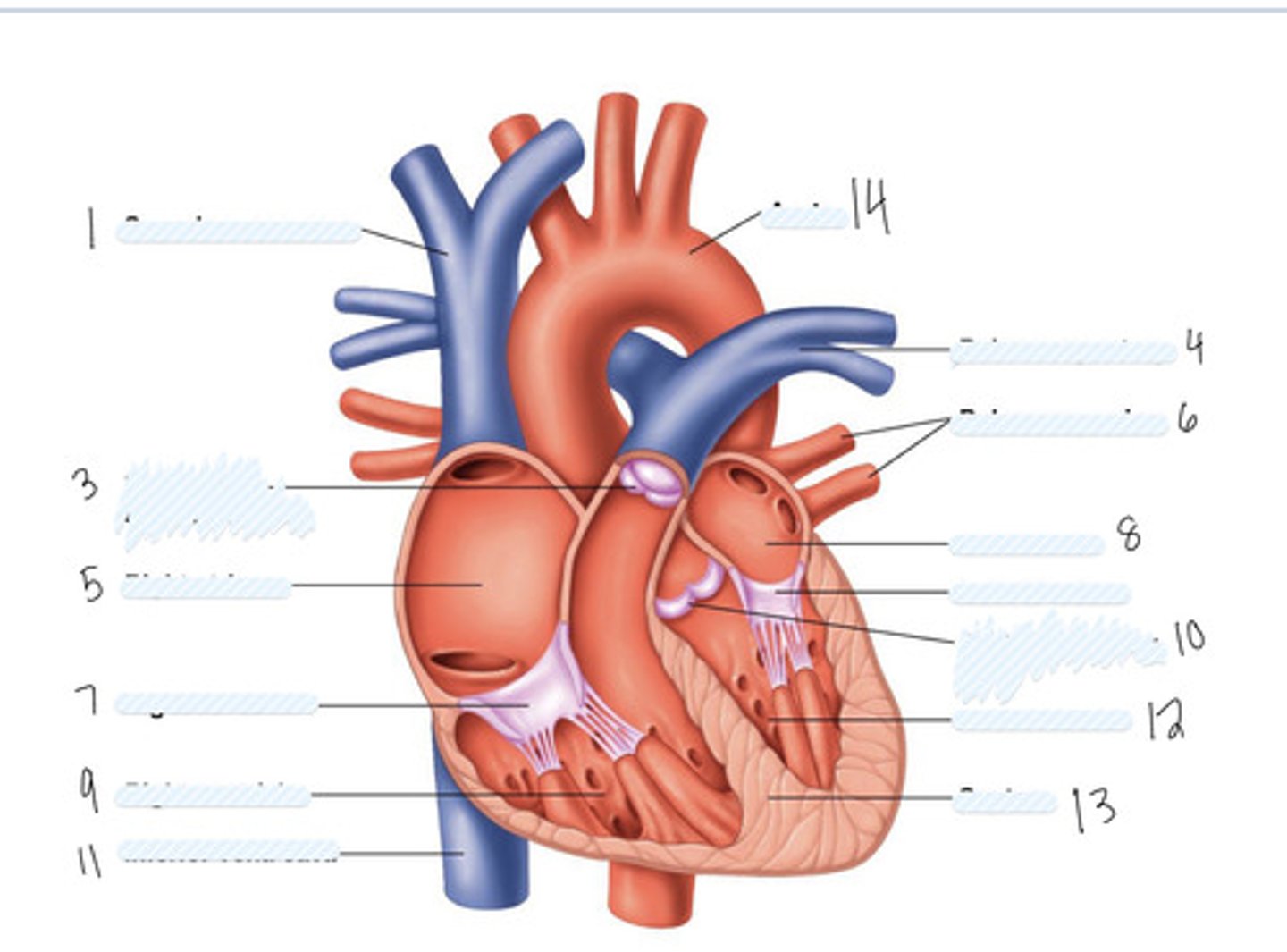
pulmonary veins
6
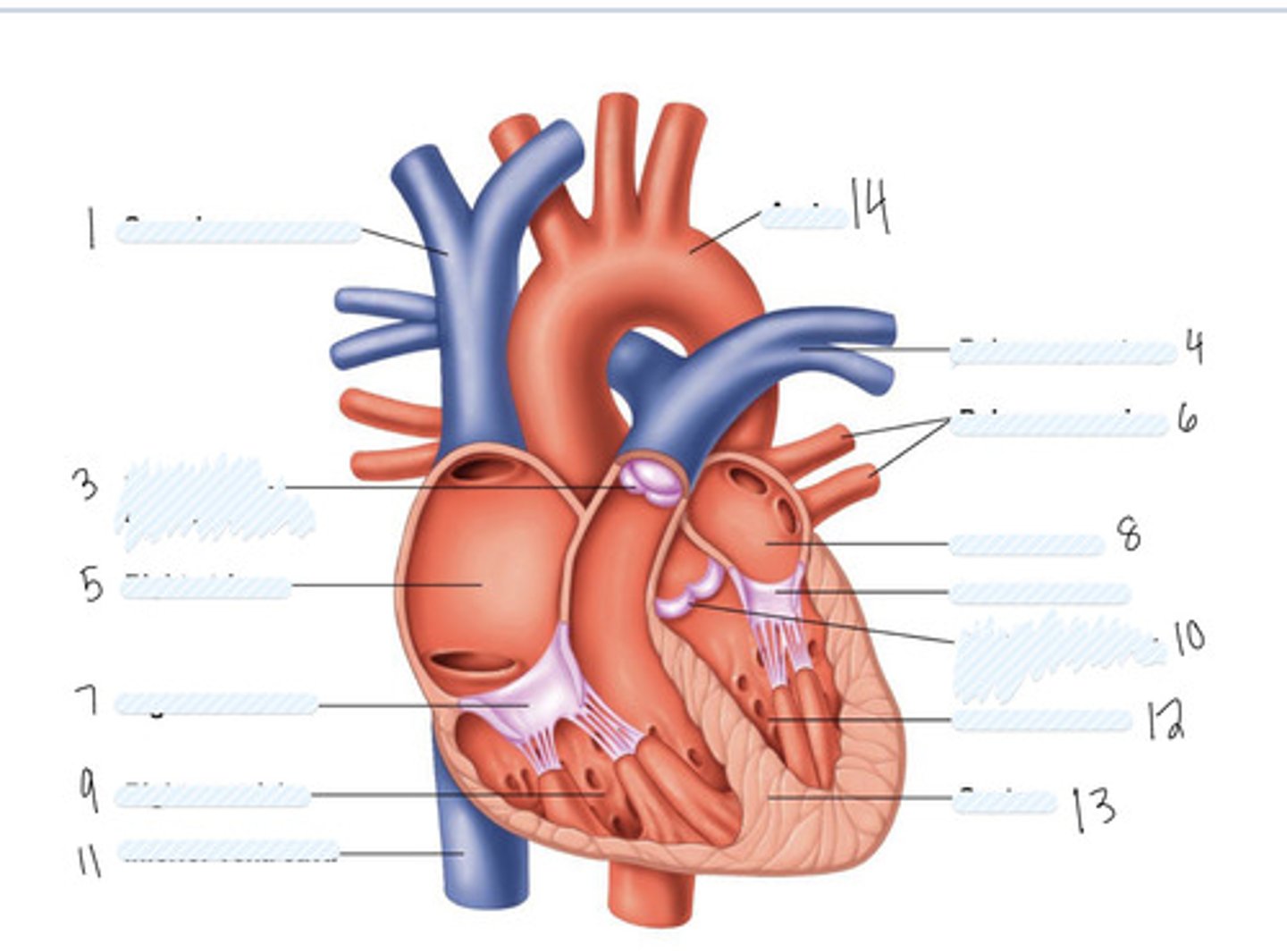
left atrium
8
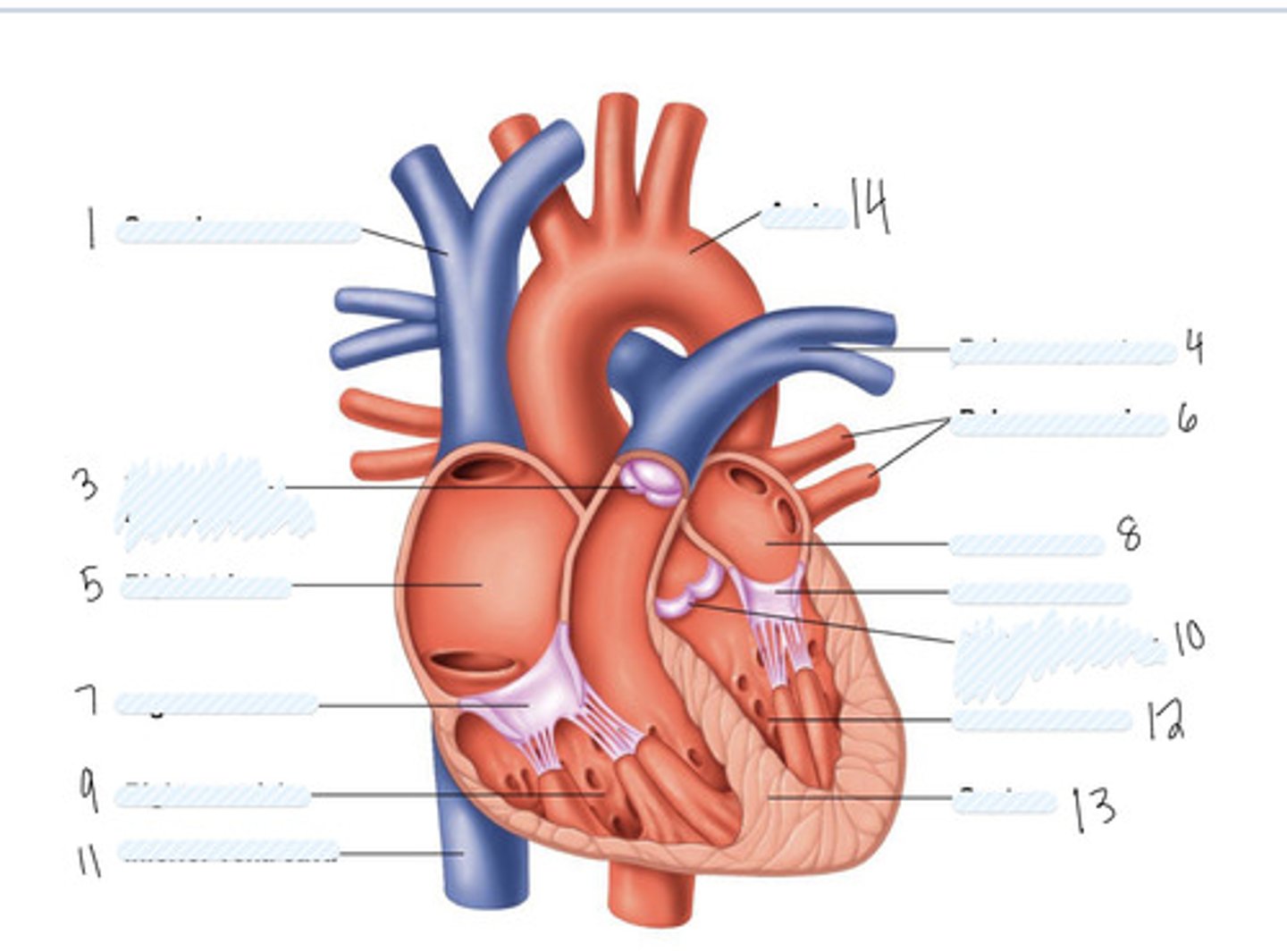
Left AV Valve (bicuspid)
not numbered
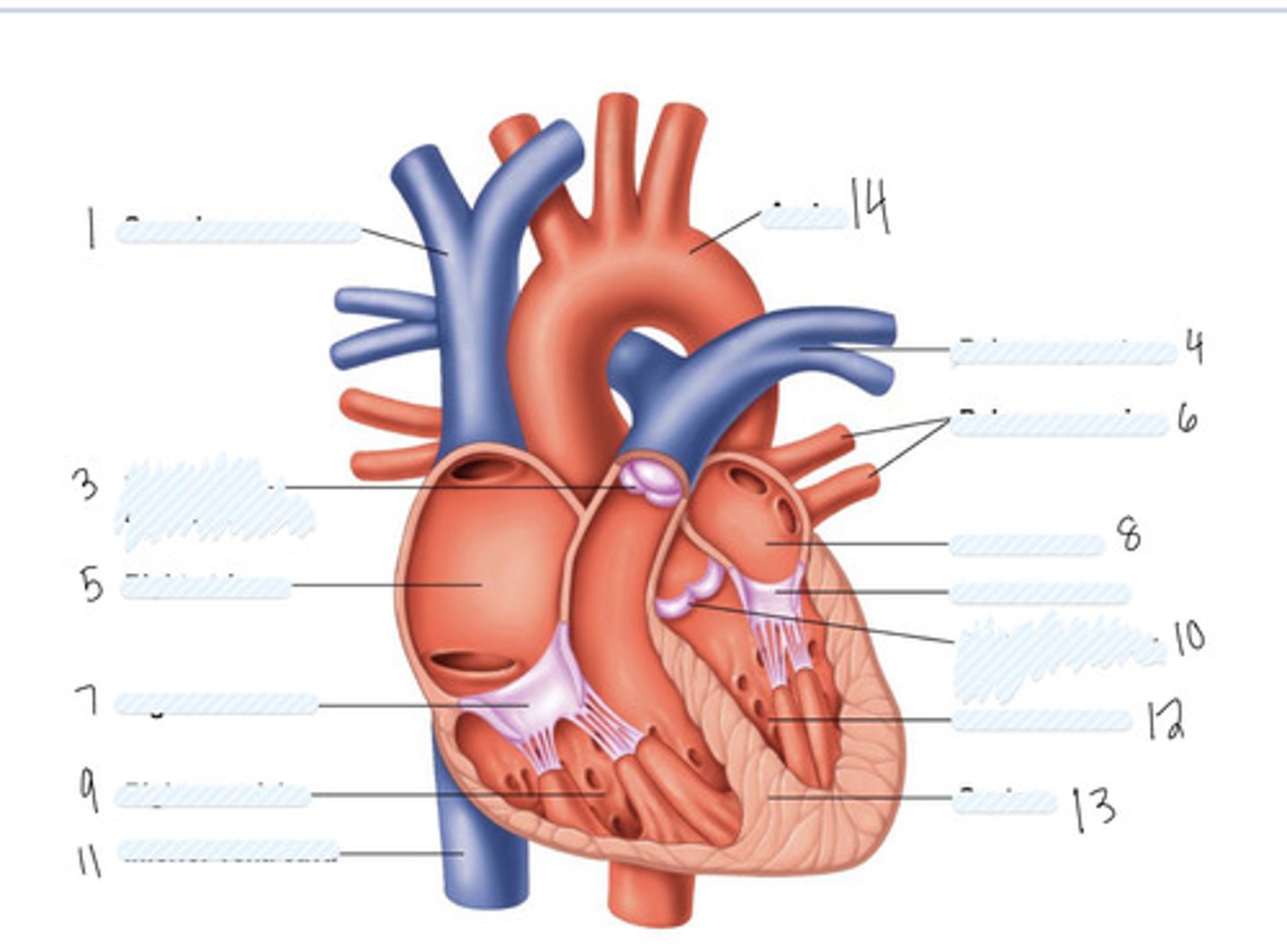
aortic semilunar valve
10
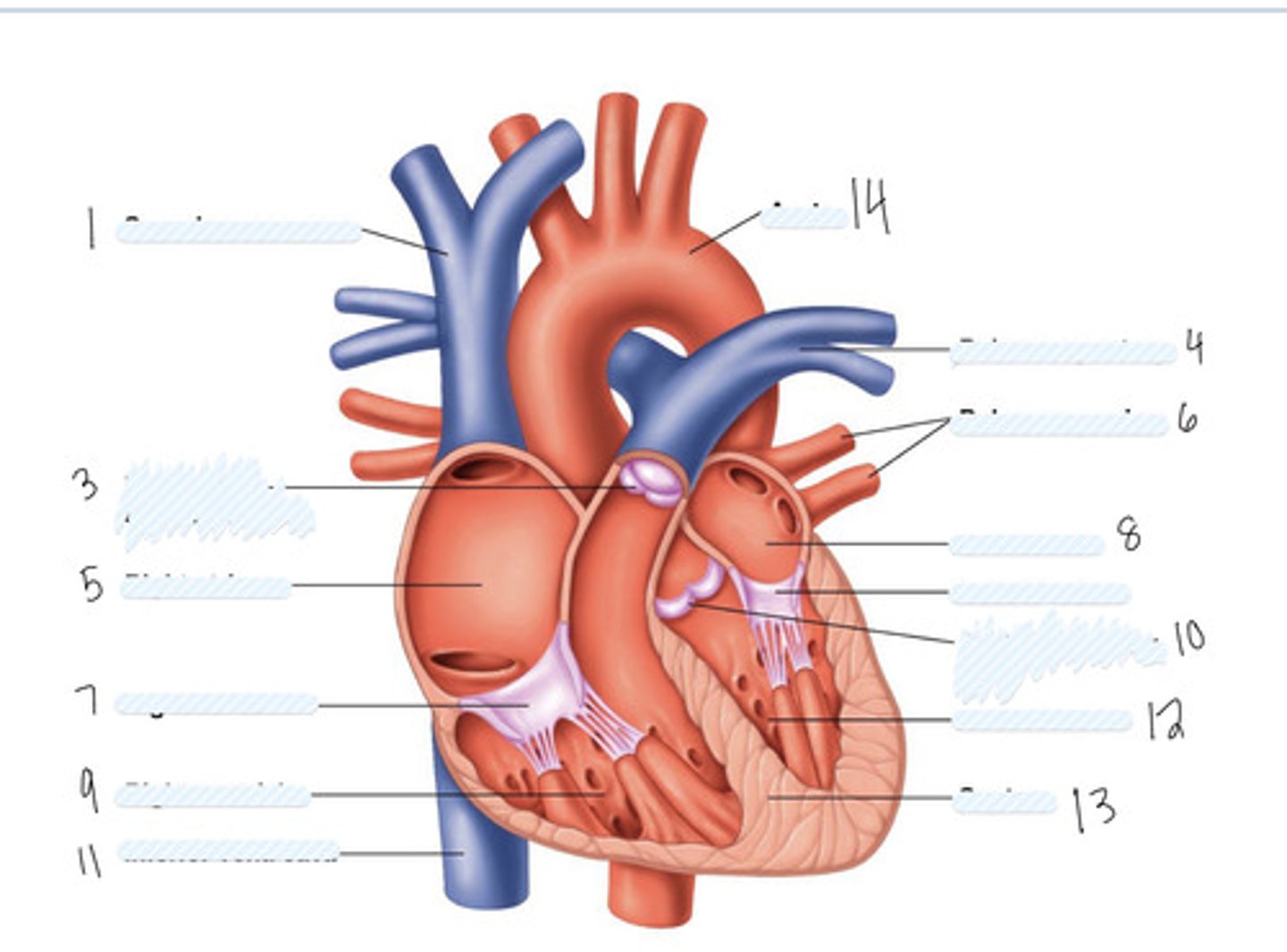
left ventricle
12
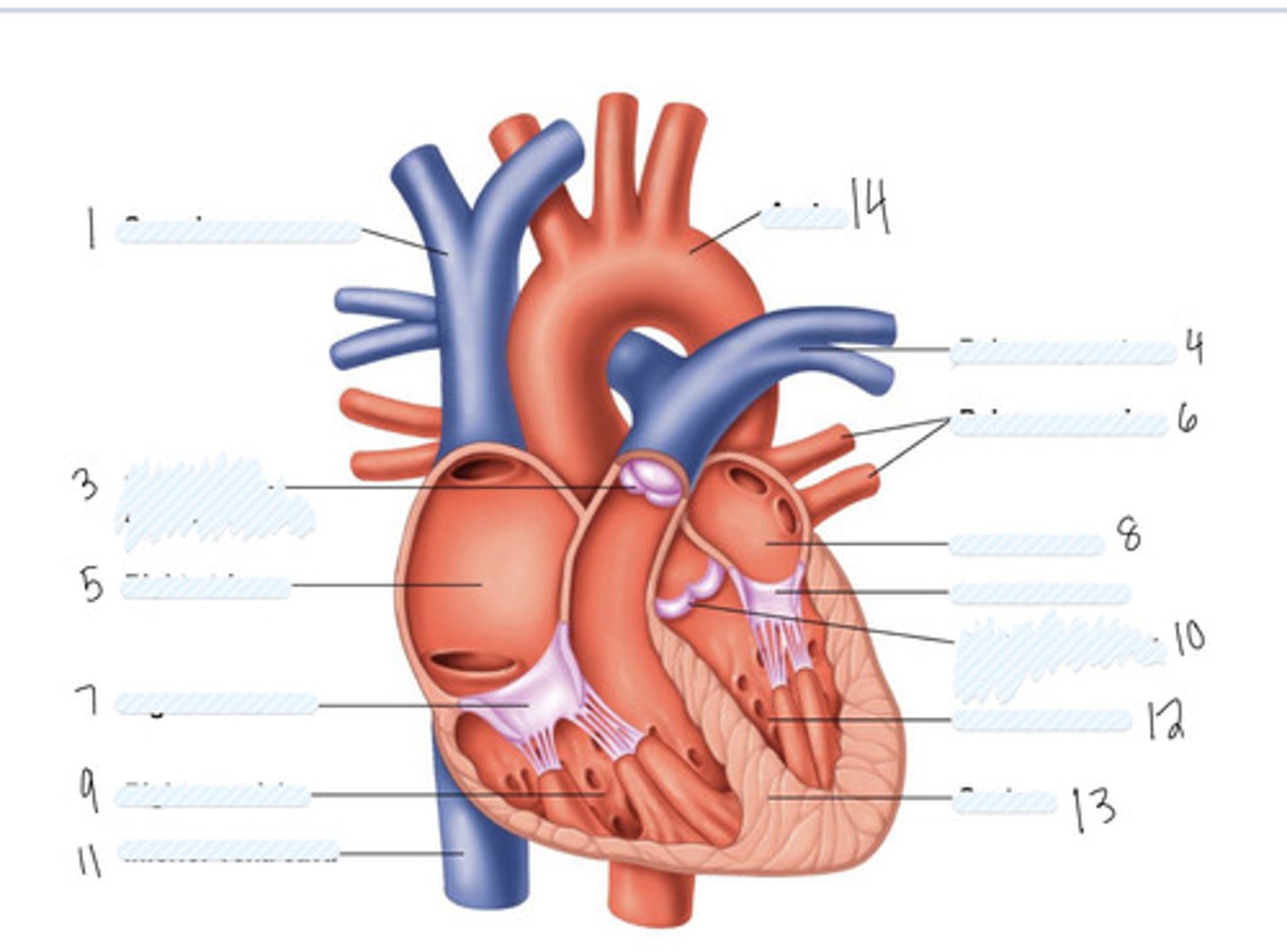
septum
13
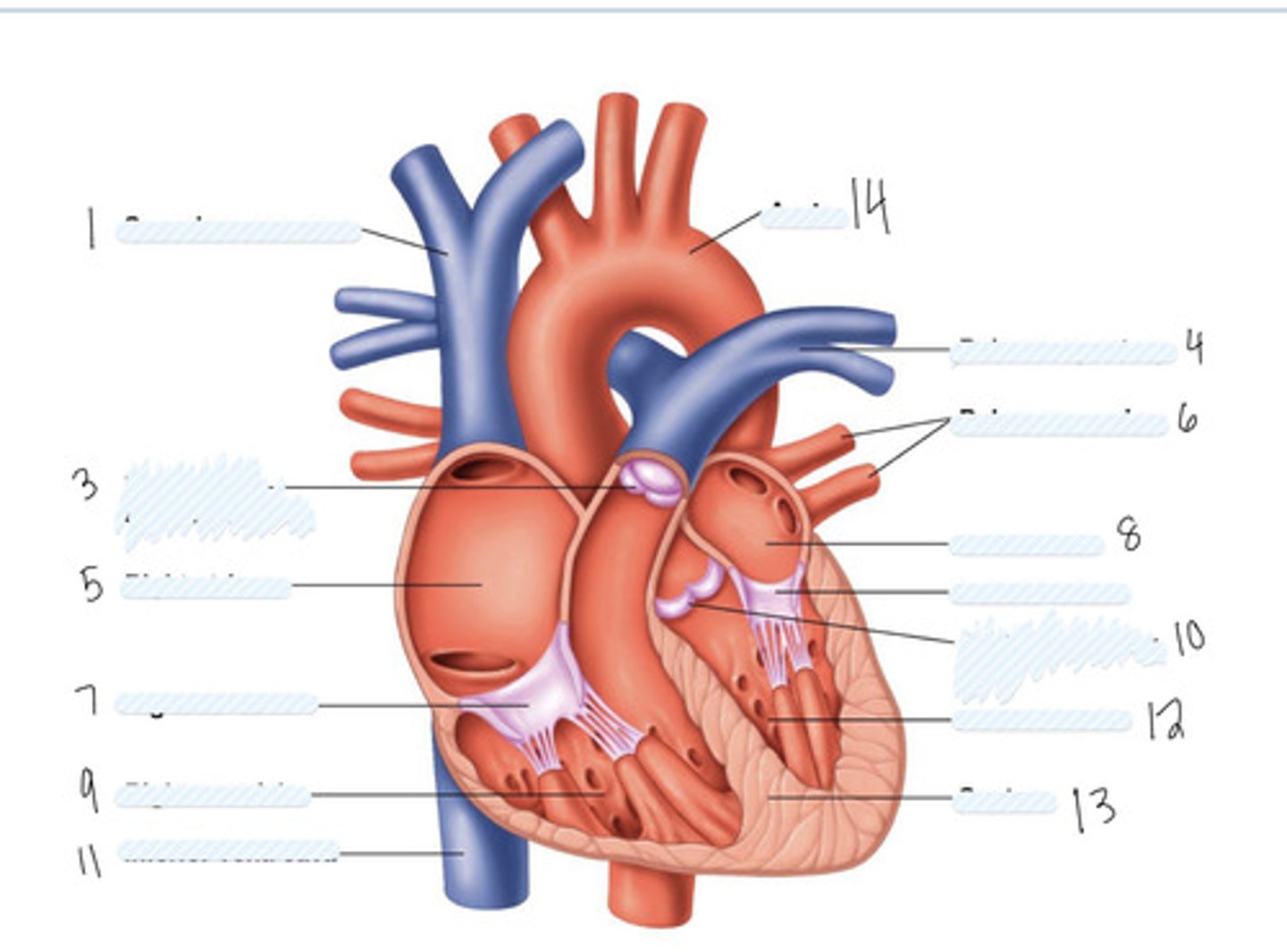
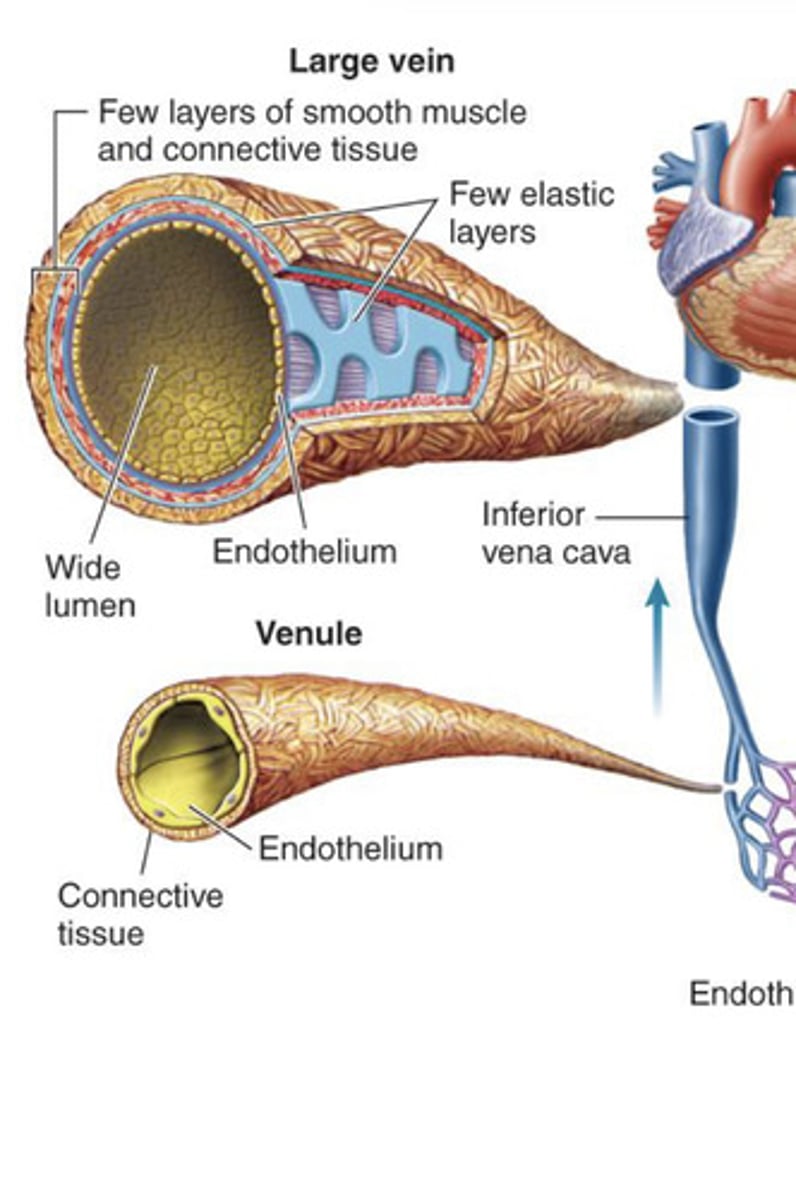
Large vein
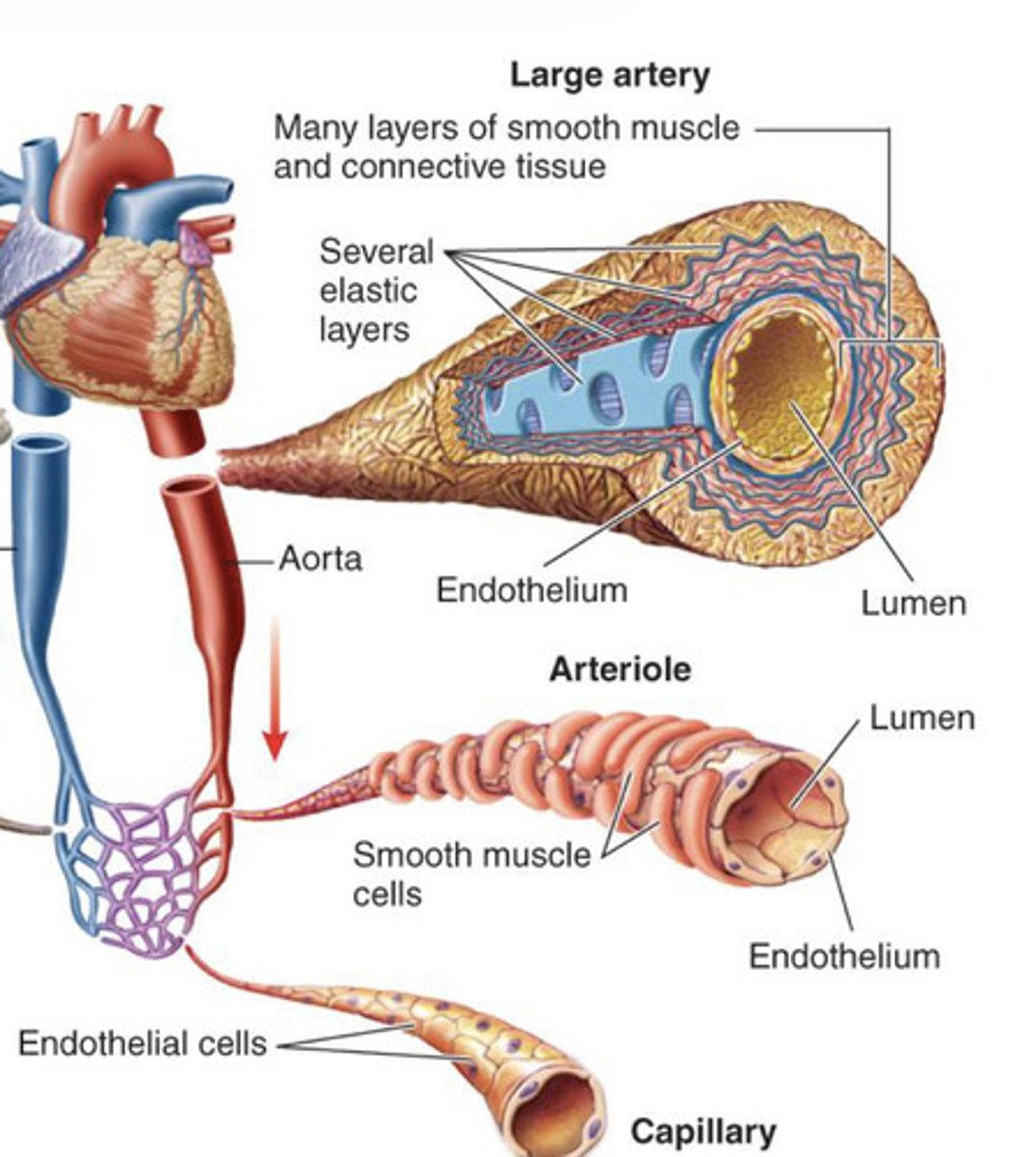
large artery
fibrous pericardium
- fibrous outer layer that attaches to diaphragm
serous pericardium
- inner layer that secrets pericardial fluid
parietal serous pericardium
outer layer of pericardial cavity, fused to fibrous pericardium
visceral serous pericardium
exterior of heart; epicardium
myocardium
1
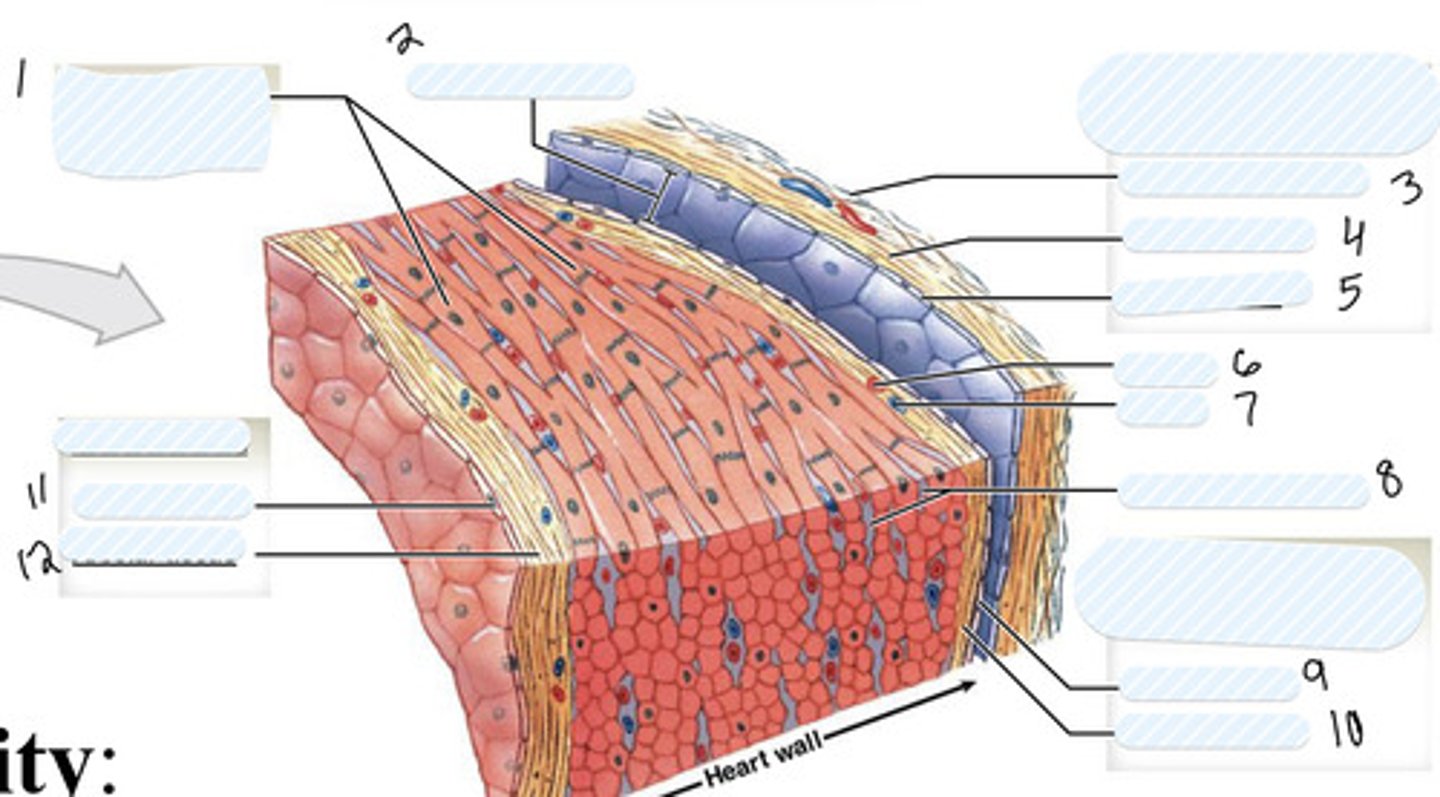
pericardial cavity
2
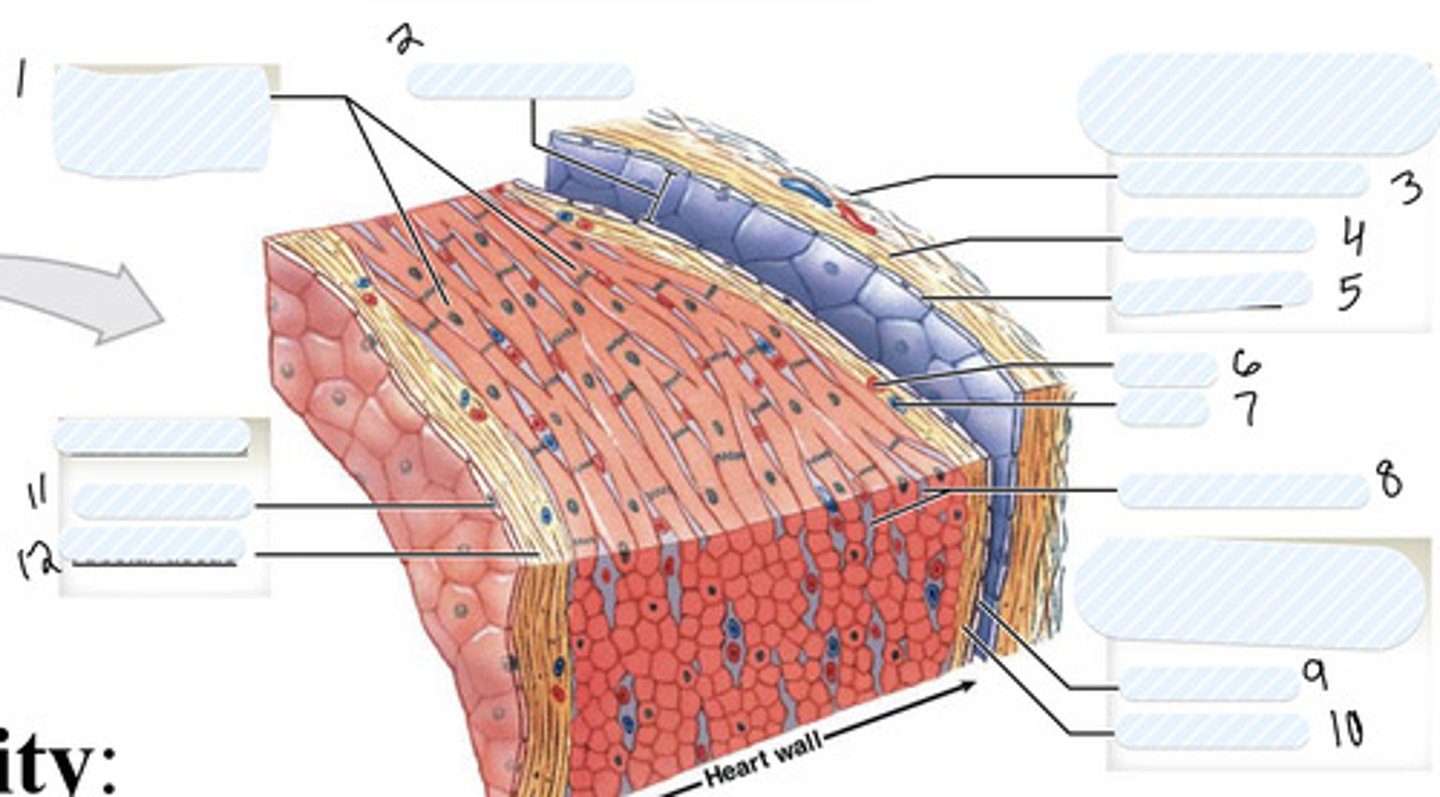
dense fibrous layer
3
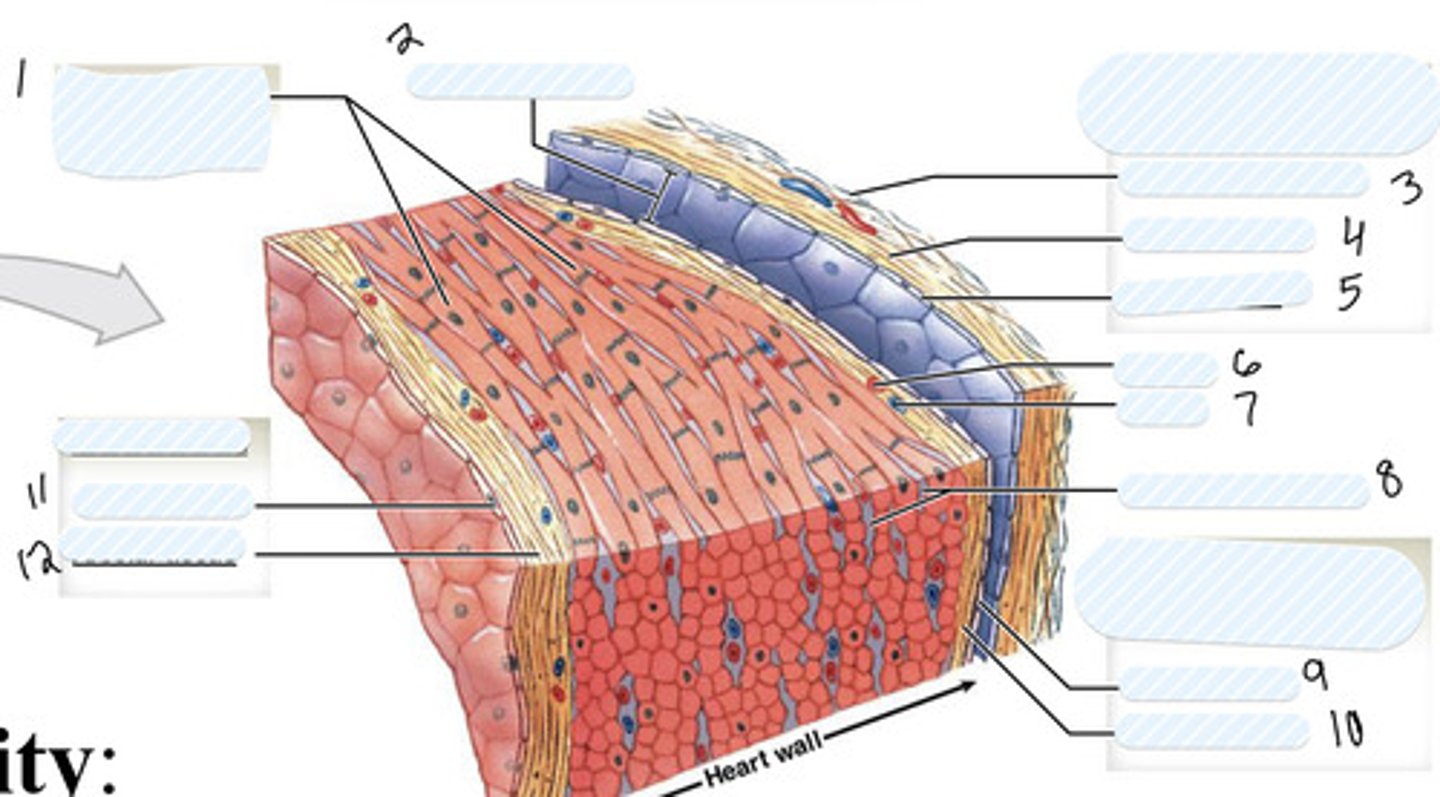
areolar tissue (parietal)
4
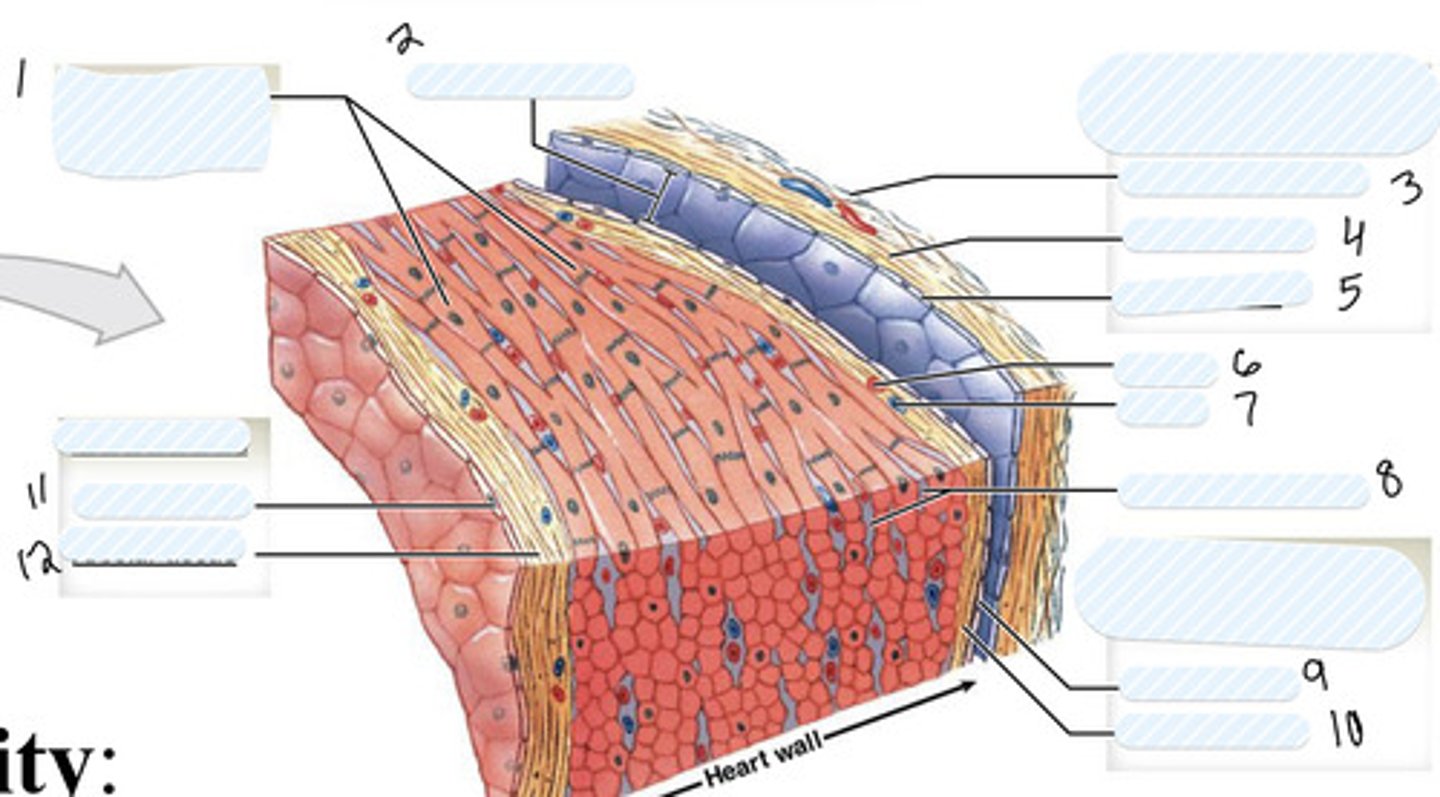
mesothelium
5
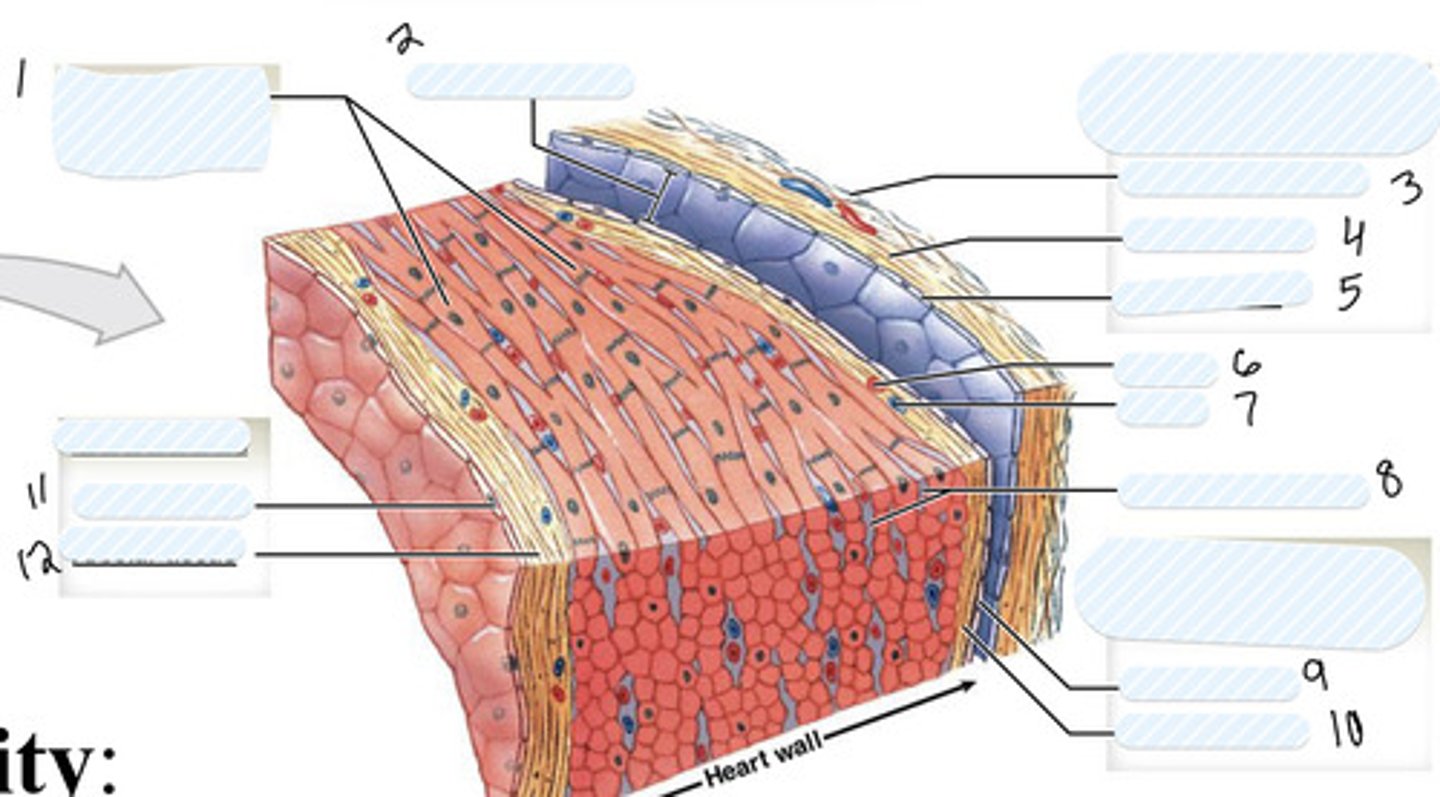
artery
6
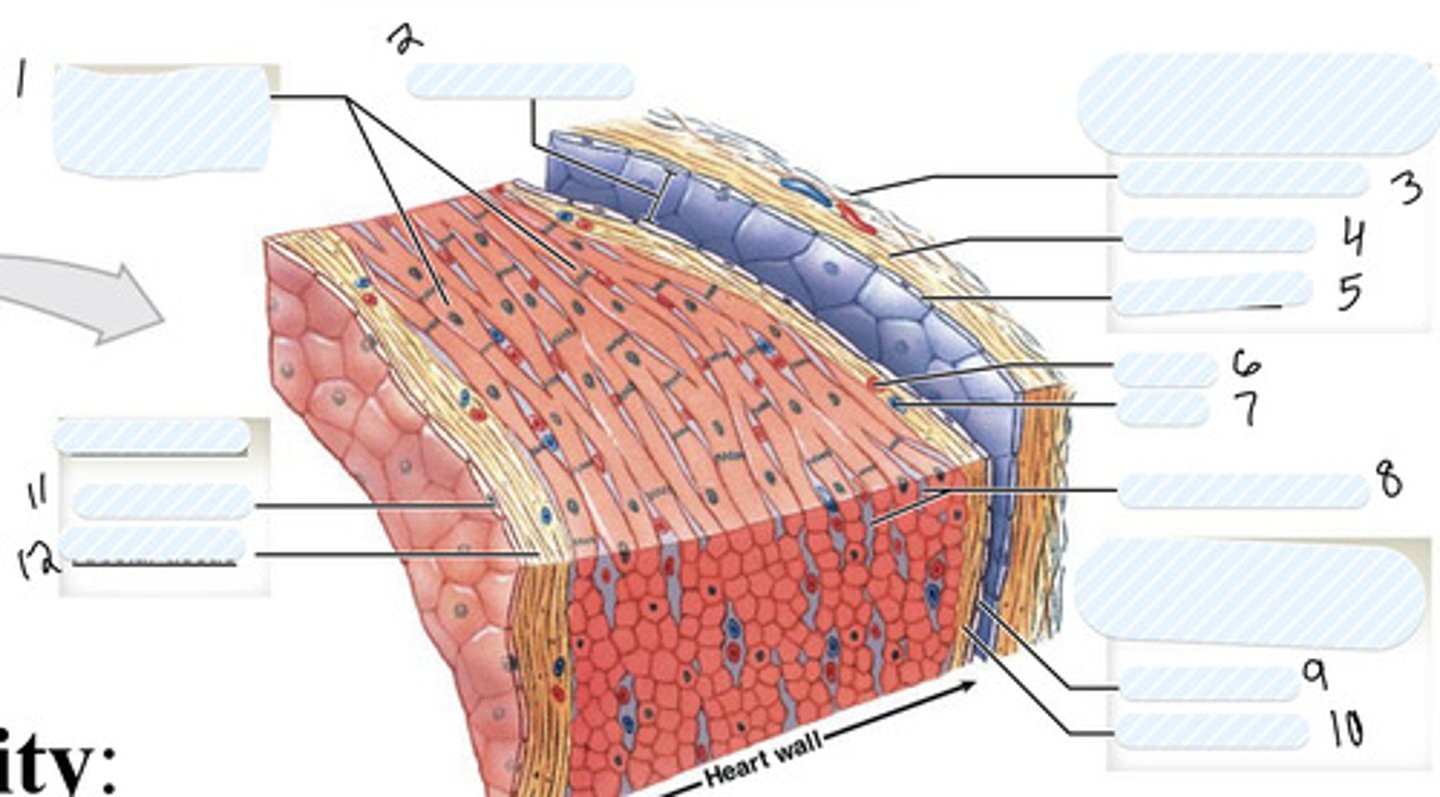
vein
7
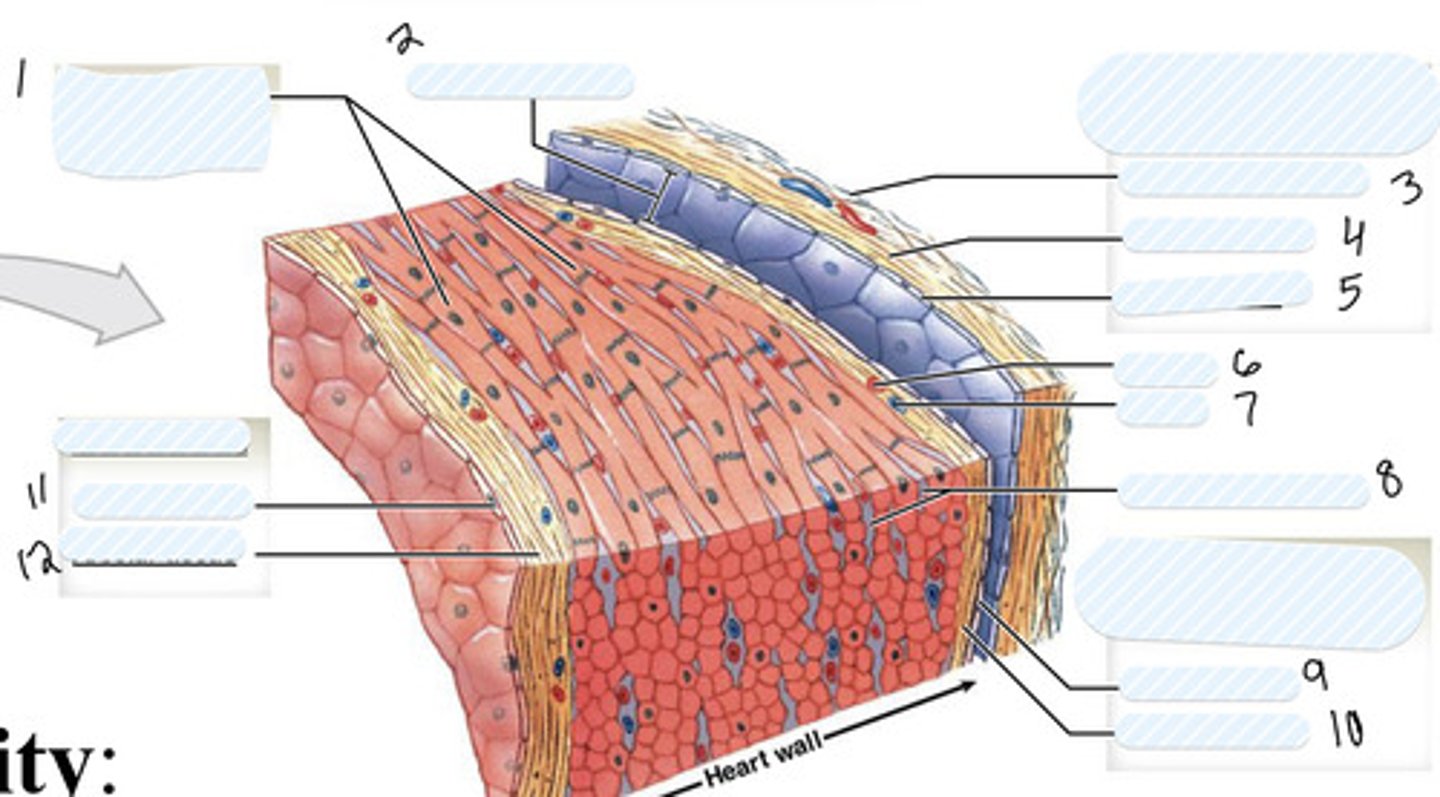
connective tissue
8
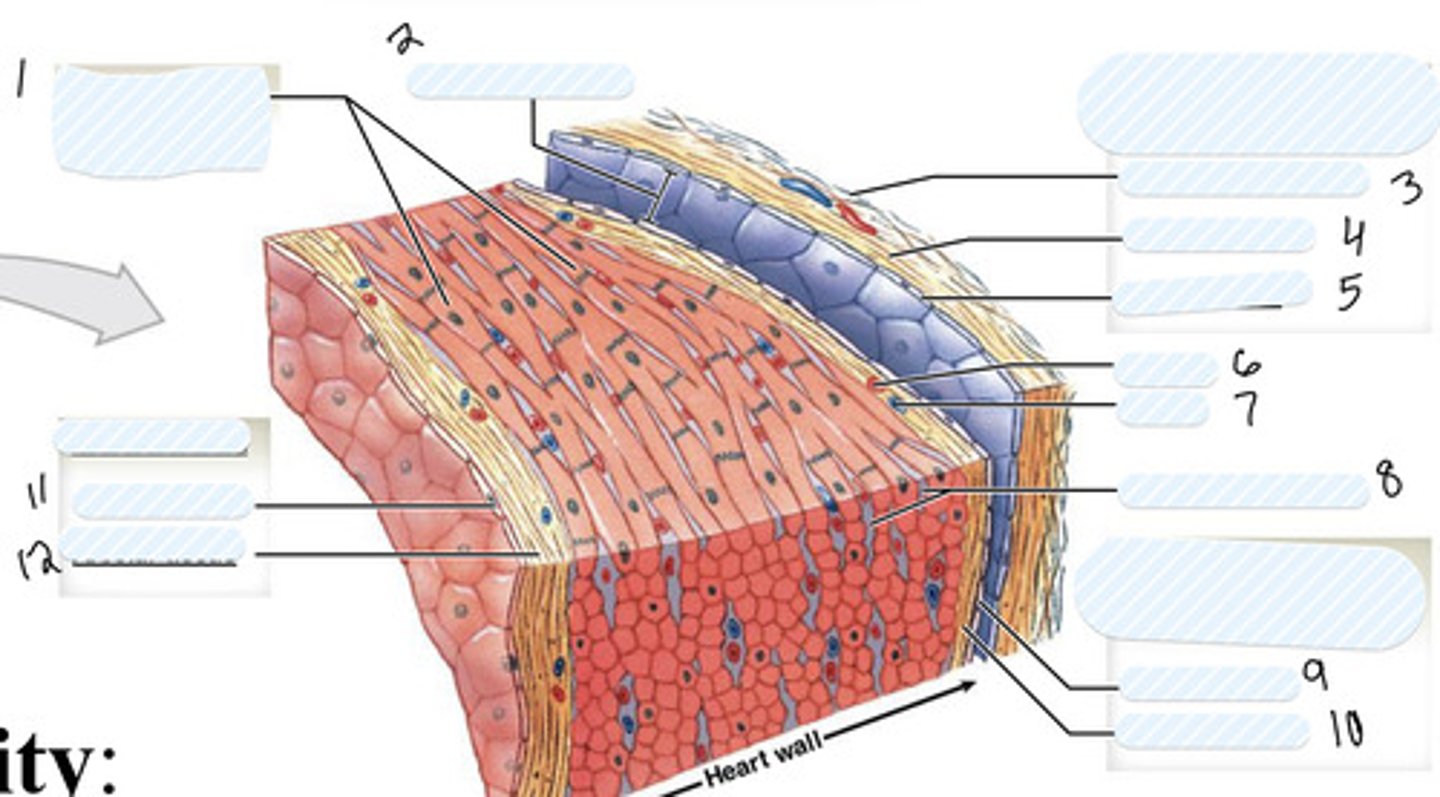
mesothelium
9
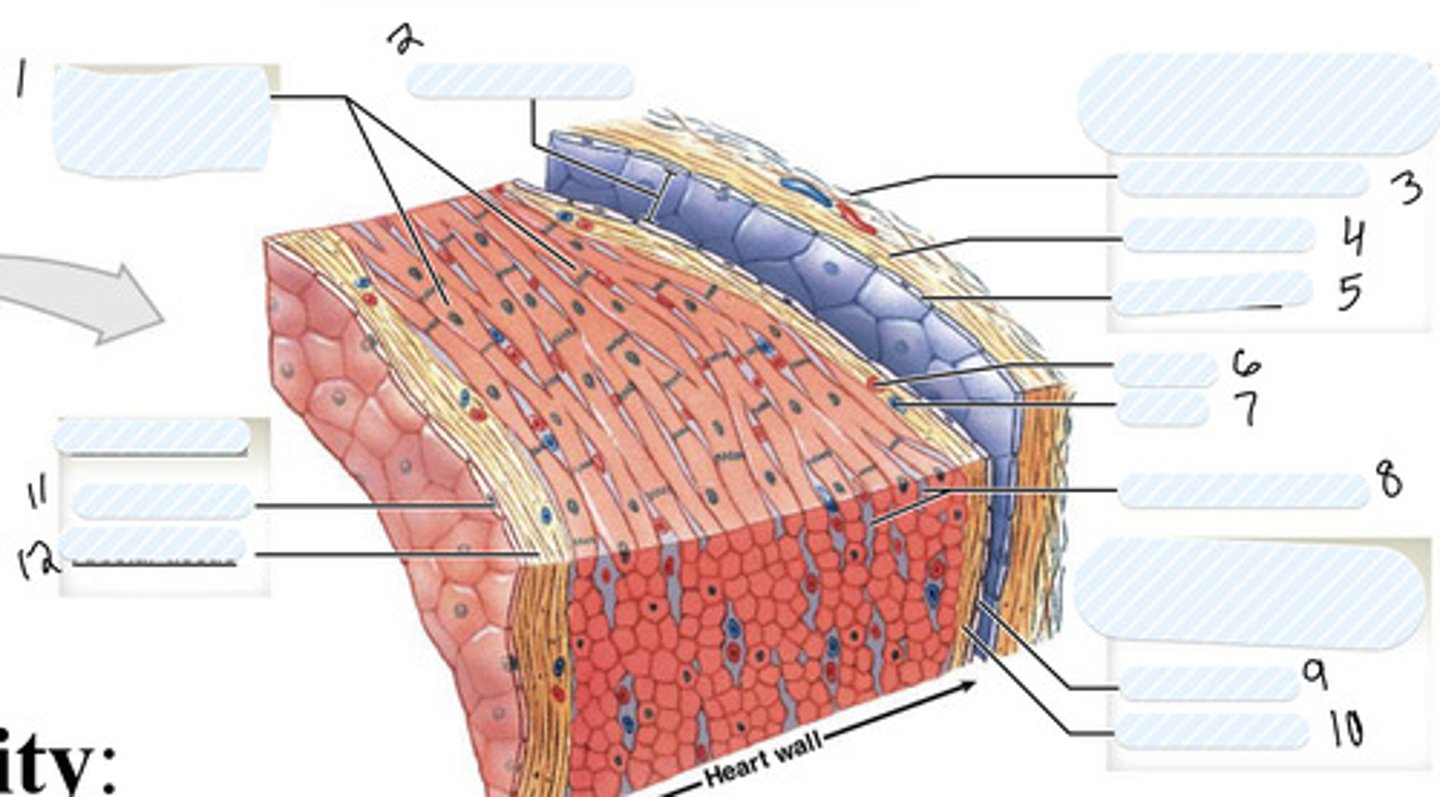
areolar tissue (visceral)
10
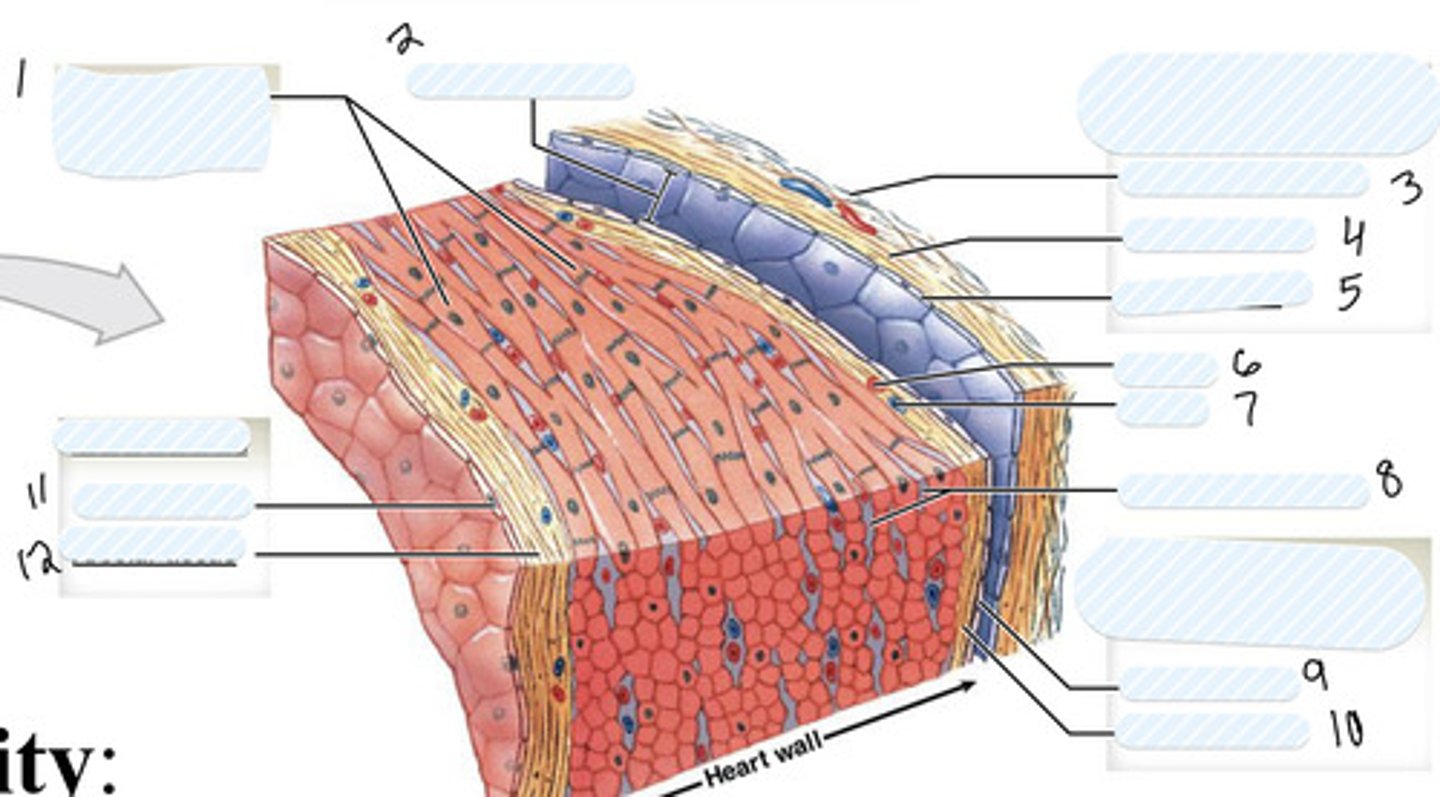
endothelium
11
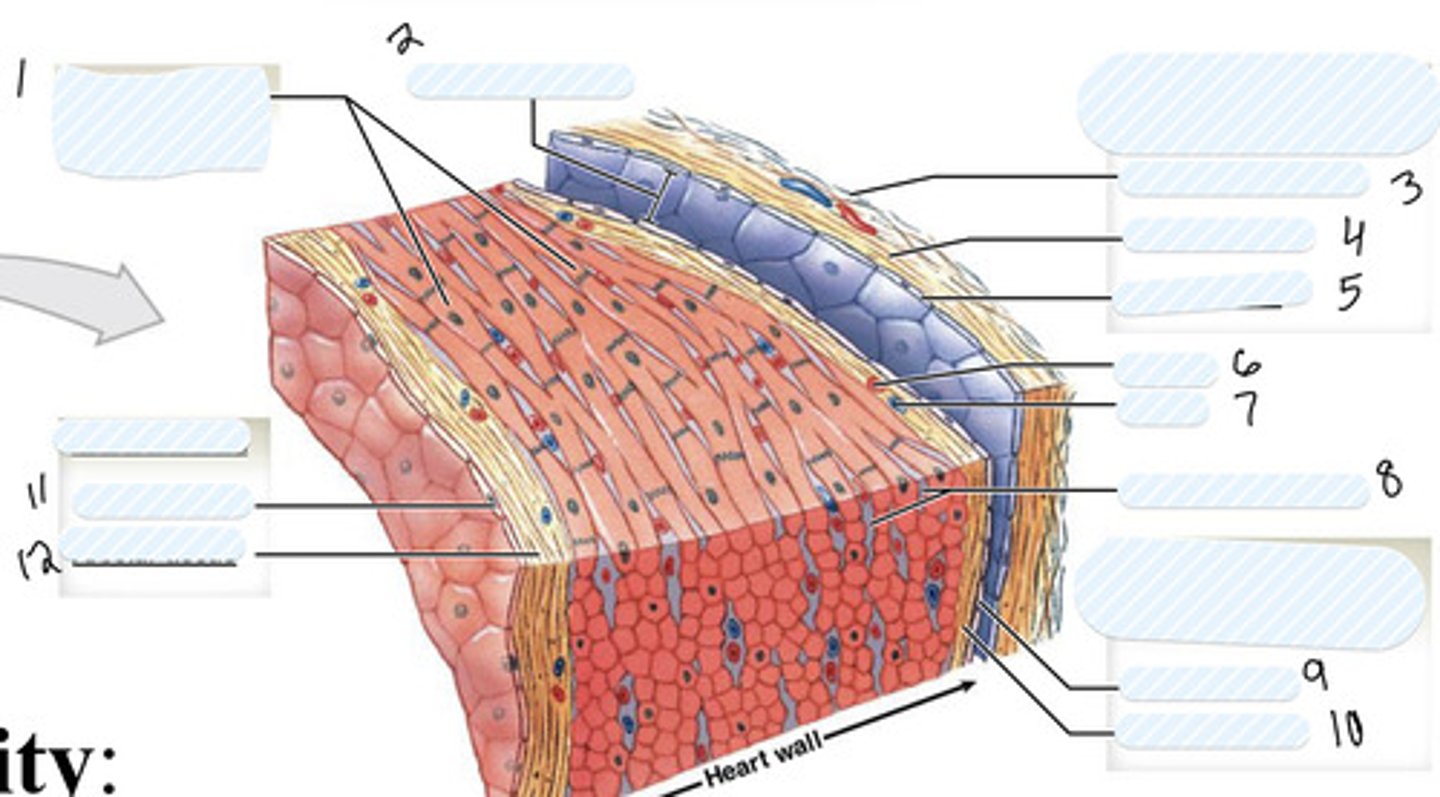
areolar tissue (endocardium)
12
epicardium
on external surface of heart
myocardium
Thick middle muscle layer of the heart (includes cardiac muscle cells, connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves)
endocardium
- internal surface of the heart (includes endothelial surface which is simple squamous)
Cardiac muscle characteristics
- myogenic
- aerobic respiration
- high amts of myoglobin and mitochondria
- one nucleus per cell
- highly vascularized
- short t-tubules
- intercalated discs: gap junctions and fascia aherens
- branching arragments
desmosomes
lock adjacent cells together (z discs)
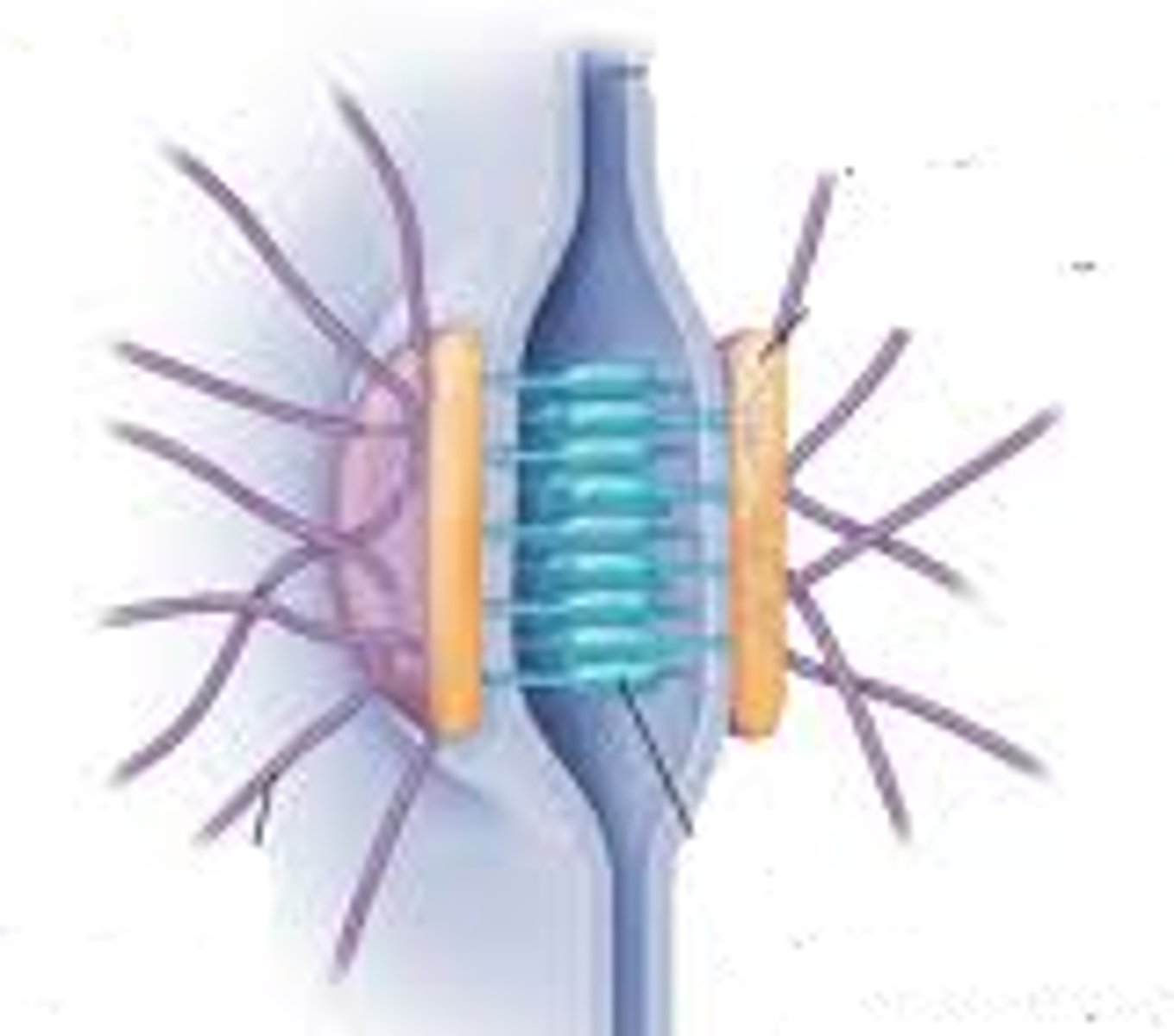
gap junctions
allow for transfer of ions and APs (2)