OB Final (Old Information)
1/787
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
788 Terms
obstetrical timeline
birth rate
number of births per one thousand people annually
unplanned pregnancies
50% of US pregnancies
barriers to prenatal care
cost, lack of insurance, transportation, dependant child care, insurance not accepted by the provider
Order of events
medicaid coverage for delivery
43% covered
integrative healthcare
includes complementary and alternative therapies with western medicine, 40% of the population uses complementary and alternative therapies, most people don't tell providers
integrative healthcare examples
chiropractor, herbal medicine, massages
prenatal care
associated with better outcomes, early risk assessment, health promotion behaviors, nutrition, smoking cessation, treatment program for substance abuse
birth providers
physicians and nurse midwives, physicians more common in US, other country's midwives more common (Sweden)
midwife vs physician for birth provider
physicians more expensive due to malpractice insurance needed for MD's, liability coverage cheaper for nurse-midwife
midwife training
in michigan no formal training for "lay midwife", certification available for "certified nurse midwife"
birth settings in the US
most births take place in hospital, small percentage at home or free standing birth center
free standing birthing center
outside of hospital, no anesthesia capability's aka no epidurals and no cesarean, cannot handle complicated births
cesarean birth rates (vaginal bypass delivery)
32.8% of births are cesarean, first-time mothers = 23.9 %, history of cesareans = 81.7%
cesarean birth (vaginal bypass delivery)
surgical incision into abdomen to deliver the baby
VBAC (vaginal birth after cesarean)
vaginal birth of an infant to a woman who has had at least one previous cesarean delivery, higher risk for uterus rapturing
assisted reproduction
recent uptick in these types of births due to societal later pregnancies, the use of medical techniques, such as drug therapy, artificial insemination, or in vitro fertilization, to enhance fertility
early discharge legislation
caginal delivery 48 hours, c-section delivery 96 hours, much teaching required in this time, early outpatient visits after, home visits prn
passed due to "drive through deliveries" where people would be sent home and have complications at home without any help
quiz 1
has lots of stats
be able top put this in order
primarily left side
j=Know mitosis and meiosis and zygoats and gametes
videos?
infant mortality rate
number of deaths per 1000 ;ove births
us infant mortality rates
6.3-6.8 from 1990 onwards, 29.2 from 1950-1990
poverty and poor prenatal care
34.8 versus 6.2 mortality rate if no prenatal care
US rank for infant mortality rate
1-22/28 developed countries
world infant mortality
2 million die in first 24 hours
maternal mortality rates/trends
worldwide 1600 women die each day with problems r/t pregnancy and childbirth
maternal mortality
number of maternal deaths per 100,000 live births related to pregnancy and labor up to 42 days post partum
major causes of maternal mortality
infection, hypertension, hemorrhage (ectopic pregnancy), sepsis, amniotic fluid embolism, a complication of abortions
indirect causes of maternal mortality
malaria, anemia, HIV/AIDS, cardiovascular problems
when do postpartum deaths occur
45% occur within 24 hours
2004 maternal mortality rate spike
caused by obesity, advanced maternal age, number of c-sections
to reduce maternal mortality
improve access to skilled attendants at birth, post abortion care, improved family planning, adolescents reproductive health
point of care testing
Tests performed at the patient's bedside or work of area, using a portable instrument.
association of womens health, obstetric and neonatal nurses (AWHON)
publishes standards of practice and education for perinatal nurses
ethics and OB
abortion, step cell research, impregnation therapy, cord blood banking, cloning
high risk pregnancy
1/5 million out of 4 million total pregnancies in US, defined as one in which life or health of the mother or fetus is jeopardized
categories of pregnancy risks
biophysical, psychosocial, sociodemographic risks, environmental risks

antepartum testing: biophysical assessment
daily fetal movement kick count, done at home, noninvasive, movement is reassuring, should have 10 kicks or movements q2h, less than 3 per hour requires followup
ultrasound biophysical assessment
between 9-12 weeks gestation, another at 18-20 weeks vaginally and abdominally, confirms dates, assesses developmental progress
first trimester ultrasound
confirm pregnancy, confirm viability, determine gestational age, number of baby's, rule out ectopic pregnancy, used for visualisation during chorionic villus sampling, detect maternal abnormalities
second trimester ultrasound
establish or confirm dates, confirm viability, detect polyhydramnios, oligohydramnios, detect congenital anomalies, detect IUGR, confirm placental placement, use for visualization during amniocentesis
polyhydramnios
excessive amniotic fluid
third trimester ultrasound
confirm gestational age, confirm viability, detect macrosomia, detect congenital anomalies, IUGR, determine fetal position, detect placenta abruption, visualization during amniocenteses or version,. BPP, AFI, doppler flow studies, placental maturity
BPP (biophysical profile)
Ultrasound Determination of Fetal Well Being
The higher the score the better the baby is doing, gross body movements, fetal breathing, fetal tone, reactive fetal heart rate,
normal 8-10, equivocal 6, abnormal less than 4
AFI
Amniotic Fluid Index (Determination Made by Ultrasound)
doppler flow analysis
looks at blood flow in the fetus and placenta, fetal adaption and reserve
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1rKWuMoWJbU
amniotic fluid volume
via ultrasound, the vertical depths of the largest pockets is measured in all four quadrants. total = AFI
over 25 - polyhydramnios
10-25 is normal
5-10 low normal
less than 5 - oligohydramnios
amniocentesis
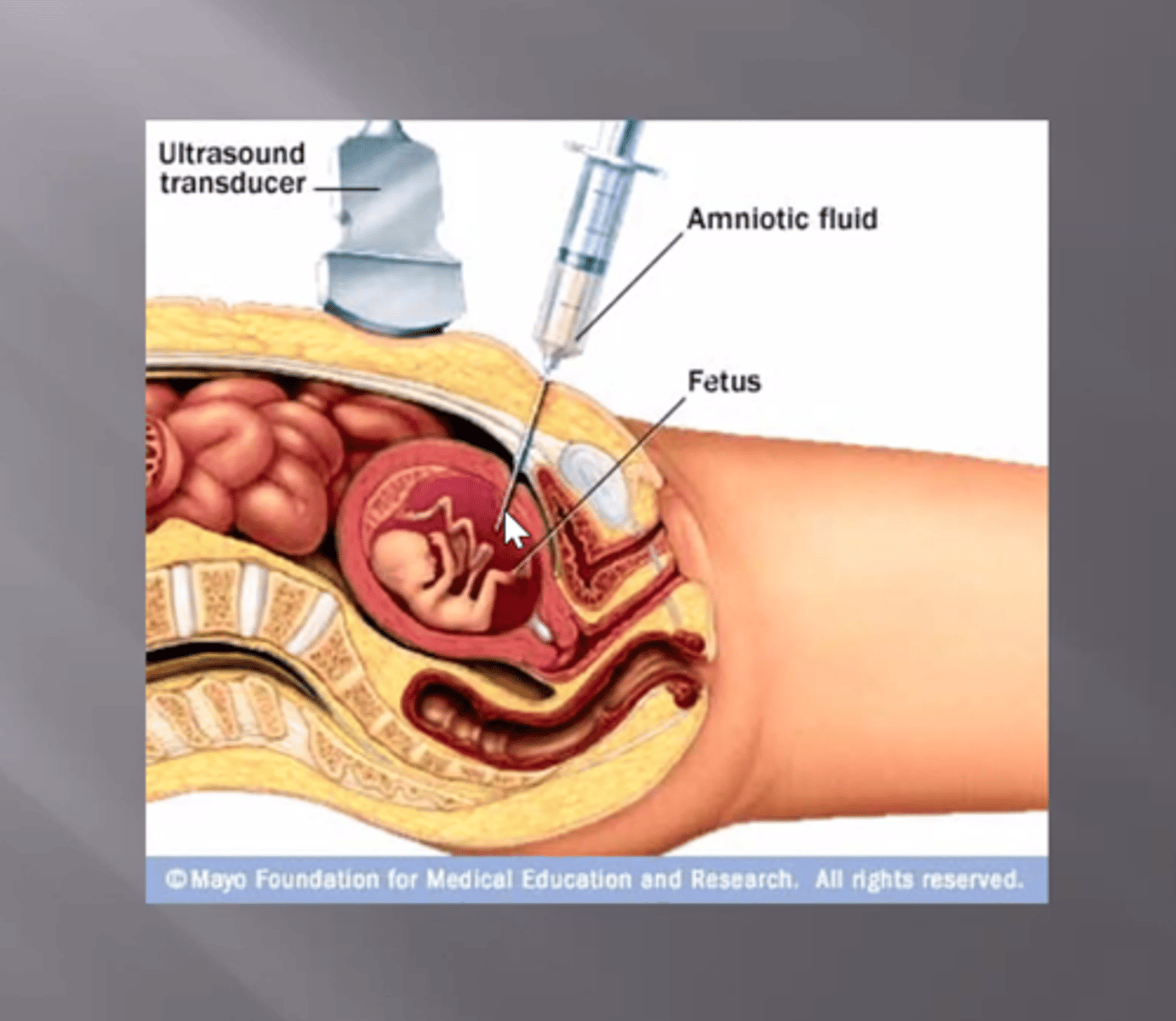
amniotic fluid (amniocenteses) risks for mom
hemorrhage, Rh isoimmunization (give rhogam), infection, labor, abruption, amniotic fluid embolism
fetal risks amniocentesis
death, hemorrhage, infection, miscarriage. preterm labor
chorionic villus sampling
10-12 weeks, removes tissue specimen from fetus for genetic screening
PUBS percutaneous umbilical sampling
insertion of needle directly into a fetal umbilical vessel under ultrasound guidance for sampling
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Hg10v0Pa5Sc
AFP
maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein, screens for NTD, test of maternal blood, AFP produced by fetal liver, screening ID's those who need follow up, done at 16-18 weeks is preferred, may do 15-20 weeks
NTD
neural tube defects
quad screen
alphas feto protein, estriol, inhibin, hcg
estriol test
one of the three main estrogens, secreted in significant amount in pregnancy
inhibin test
protein complex produced by placenta
coombs test
screening for Rh Incompatibility in RH - mom
fetal monitoring
Nonreactive stress test is not reassuring, contraction stress test, variability (98% accurate in predicting fetal well-being)
gametes
sex cells, either sperm or egg
fertilization
egg and sperm joining together to make zygoat
zygote
made by combination of sperm and egg
ampulla
where fertilization occurs
germinal stage
conception through week 2
embryonic stage
3-8 weeks
fetal stage
9-42 weeks
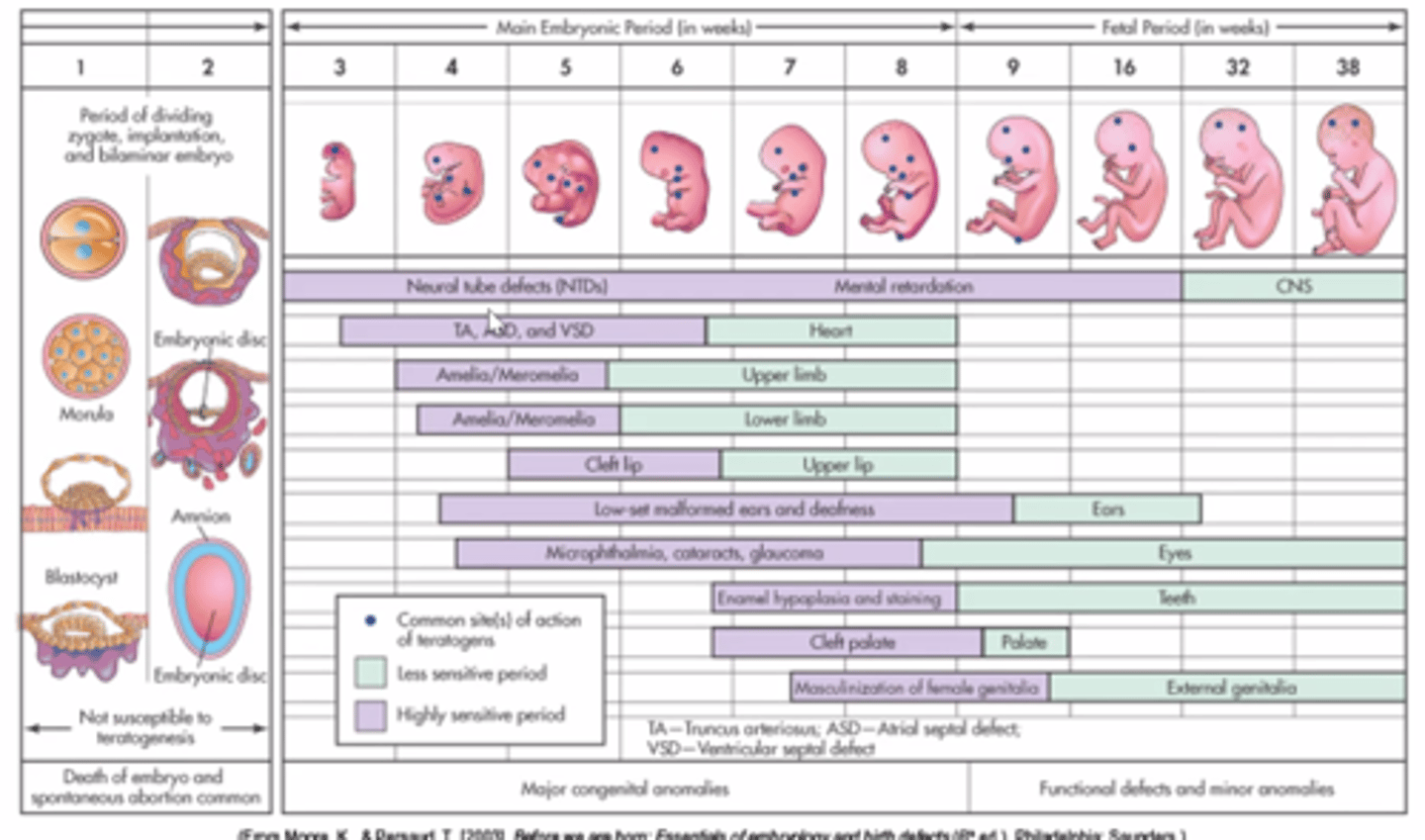
threats to prenatal development
certain aspects of mothers and fathers behavior, both before and after conception, can produce lifelong consequences
illnesses in a pregnant woman
rubella, chicken pocks
embryonic disk germ layers
ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
membranes of the placenta
amnion and chorion
amnion
inner cell membrane develops from interior cells of the blastocyst
chorion
outer cell membrane, develops from trophoblasts, contains chorionic villi on its surface, becomes covering of fetal side of placenta
amniotic fluid
comes from maternal blood via diffusion, increased weekly, term 800-1200 ml total, fetus swallows in and out of lungs, should be clear (thick water)
menscis
smells like merigold
amniotic fluid function
cushion for fetus and cord, temperature, wastes, oral fluid, amniotic band syndrome
amniotic band syndrome
when fibrous bands of the amniotic sac (the lining inside the uterus that contains a fetus) get tangled around a developing fetus
oligohydramnios
too little amniotic fluid, <300 ml, can cause rennal abnormalities
polyhydraminos
>2 liters, can cause gi and other malformations
gtpal and gpal
must practice and know
https://www.registerednursern.com/gtpal-nursing-practice-questions-quiz/
nagel's rule practice
must know
amniocentesis
L/S ratio, karyotyping, chromosomal abnormalities, gender
yolk sac
aids in transferring maternal nutrients and oxygen for the first 5-6 weeks, before the placenta takes over, blood cells and plasma made here
umbilical cord
2 arteries and a vein, at term 2cm diameter, 30-90cm long, wharton's jelly
umbilical cord blood
arteries DEoxygenated, vein OXYGENATED
placenta
metabolic exchange, respiration, nutrition, excretion and storage
placenta hormones
HcG, human placenta lactogen, progesterone
fetal circulation
ductus arteriosis, ductus venosis, foramen ovale
pulmonary surfactants
Surface-active phospholipids that must be present in fetal and newborn lungs to facilitate breathing after birth. keeps them from collapsing.
lecithin
critical alveolar surfactant, increases in amount as pregnancy continues
sphingoomyelin
critical alveolar surfactant, remains constant through pregnancy
L/S ration
2/1 indicates maturity
sensory awareness in utero
24 weeks, taste, temperature changes, light through abdomen, REM
multiple gestations
Twins, triplets, etc
- < 3% if all pregnancies
- 1 in 10 couples using fertility drugs have dizygotic twins
- More likely in older mom
Higher risk pregnancies
- More likely for complications
More likely to deliver prematurely
- Associated problems
Monozygotic Twins
Genetically identical; form a cluster of cells in the ovum splits off within the first 2 weeks following fertilization
Dizygotic Twins
2 separate ova are fertilized by 2 separate sperm; no more genetically similar than 2 siblings
pregnancy testing
detects HcG, false positives and false negatives
false positives pregnancy tests
anticonvulsants, tranquilizers
false negative pregnancy tests
diuretics, promethezine