Oral Embryo and Histology Exam 1
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Embryology
The study of prenatal development
Three groups of embryology
1. Preimplantation (proliferative) period
2. Embryonic period
3. Fetal period
Preimplantation Period
The 1st week, associated with the 1st trimester.
Beginning of week 1
Conception/fertilization: Where the ovum + sperm = zygote and the zygote is formed by meiosis. The zygote receives half chromosomes from male and female because the process allows the ovum and sperm to reduce by 1/2 of chromosomes to prevent doubled chromosomes.
During week 1 after conception
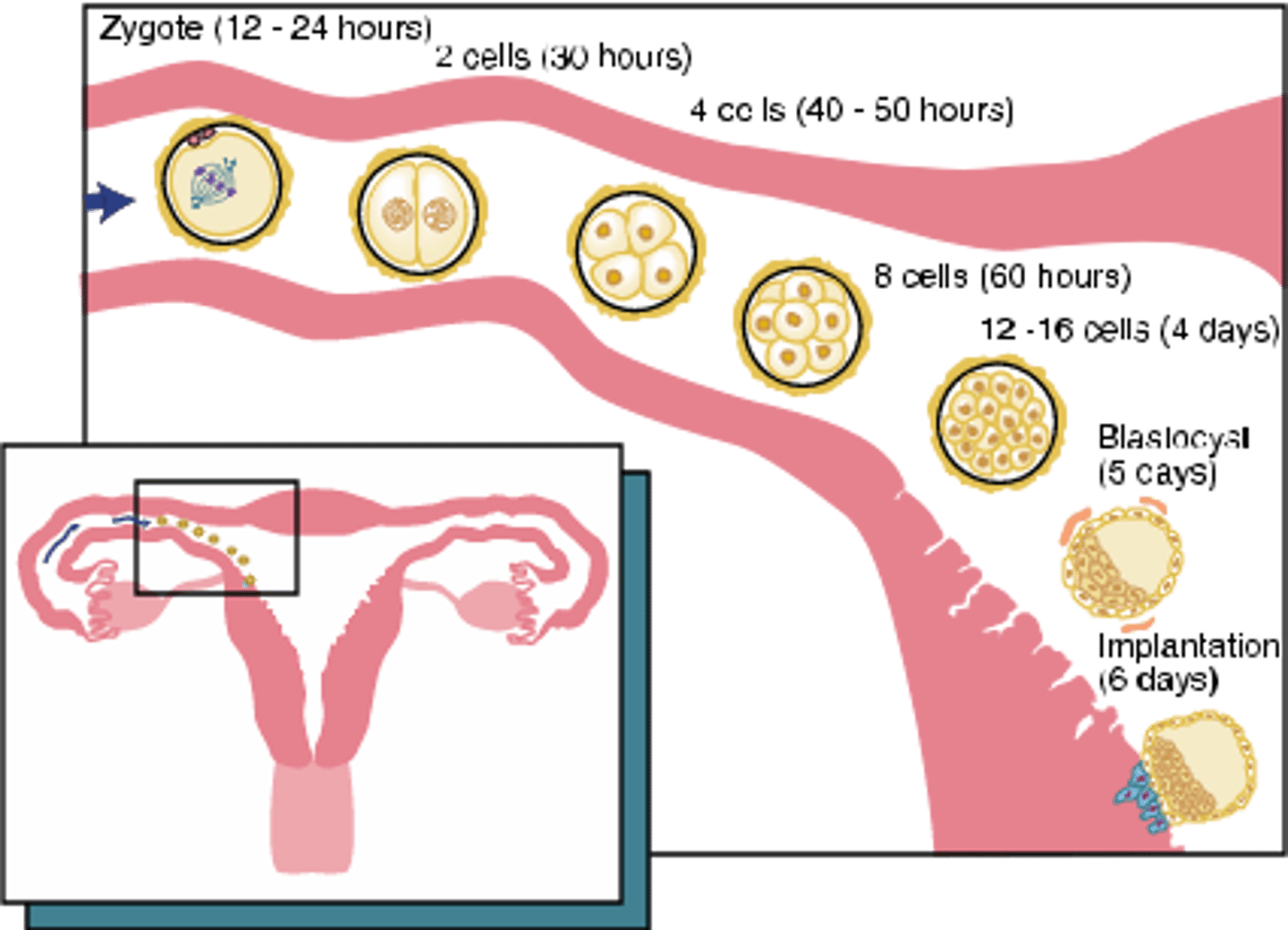
The zygote grows by mitosis which replicates the cell into identical cells. Once the zygote grows and matures, it is now called a blastocyst which then splits and travels down the fallopian tube.
Fertilization
1. Zygote (12-24 hours)
2. 2 cells (30 hours)
3. 4 cells (40-50 hours)
4. 8 cells (60 hours)
5. 12-16 cells (4 days)
6. Blastocyst (5 days)
7. Implantation (6-7 days)
Day 7
By the end of the week, the blastocyst stops traveling and undergoes implantation and becomes embedded into the endometrium. The peripheral cells in the tropoblast layer (outside layer) give rise to supportive tissues and the embryonic cells in the embryoblast layer (inner mass) give rise to the embryo.
The embryonic period
Weeks 2-8, associated with the 1st trimester
Weeks 2-8
Physiological processes occur and help develop and grow the embryo (Induction, Proliferation, Differentiation, Morphogenesis, Maturation)
Induction
Action of one group of cells on another that leads to the establishment of the developmental pathway in the responding tissue.
Proliferation
Controlled cellular growth and accumulation of byproducts.
Differentiation
Change in identical embryonic cells to become distinct structurally and functionally.
Morphogenesis
Development of specific tissue structure or differing form due to embryonic cell migration or proliferation and inductive interactions
Maturation
Attainment of adult function and size due to proliferation, differentiation, and morphogenesis
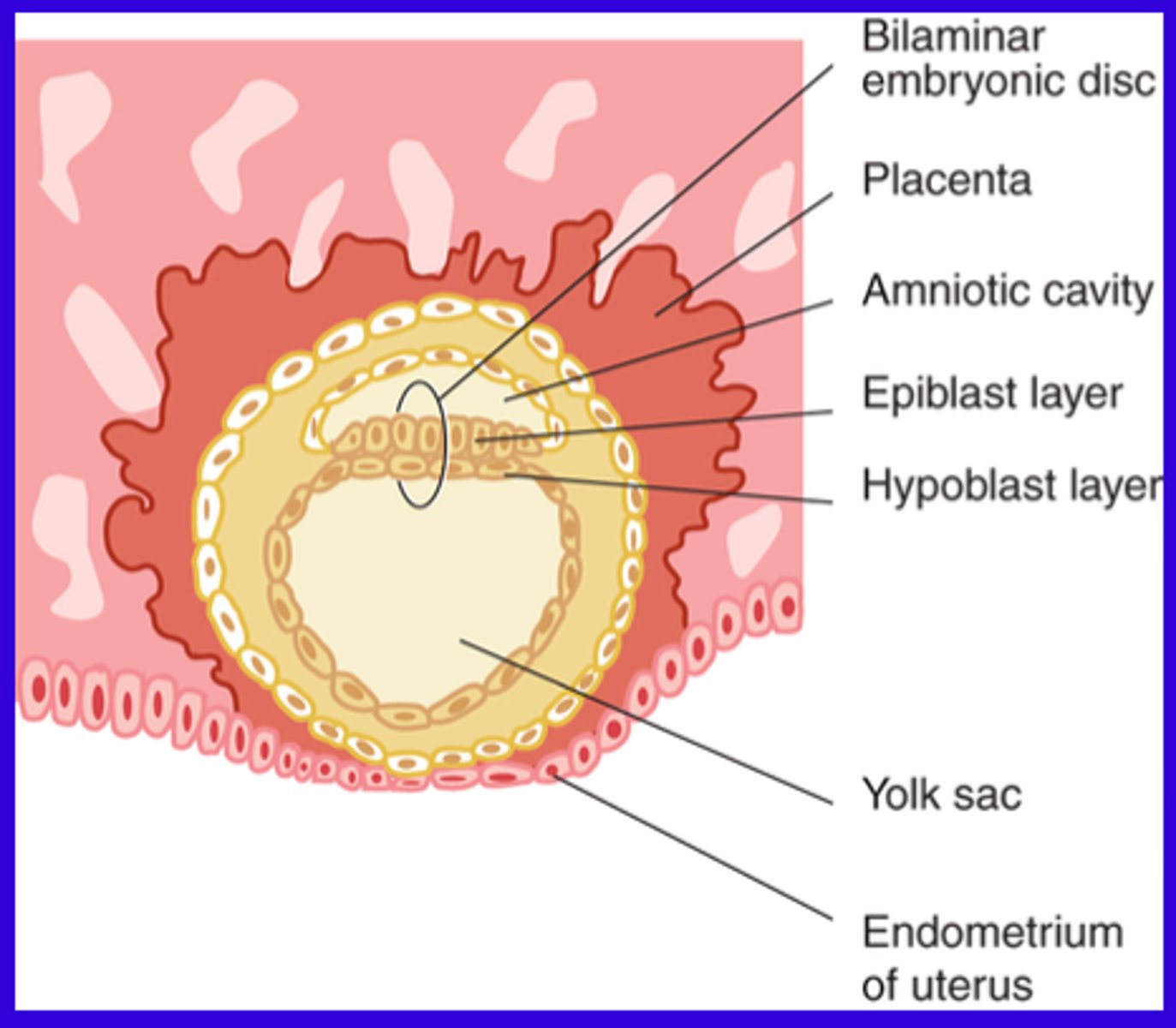
Week 2
The implanted blastocyst grows by increased proliferation, cellular morphogenesis and differentiation. This creates embryonic cell layers within blastocysts creating a bilaminar embryonic disc.
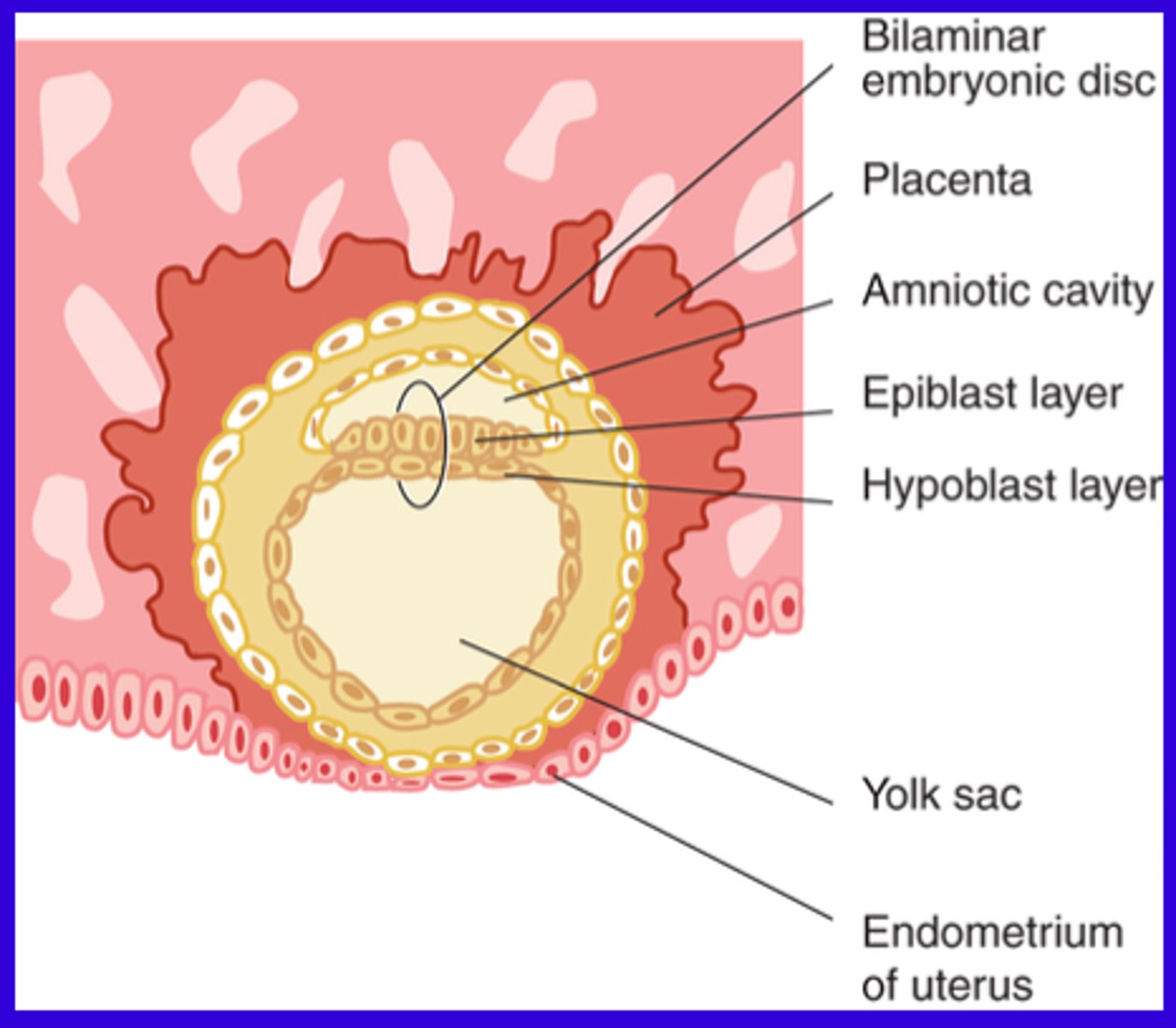
Bilaminar embryonic disc layers
1. Epiblast layer: The superior layer, made of columnar epithelial cells
2. Hypoblast layer: The inferior layer, made of cuboidal epithelial cells
3. Suspended between the two fluid-filled cavities: The amniotic cavity and the yolk sack
Week 3
The primitive streak forms which causes cells from the epiblast layer to migrate to the middle, creating a new middle layer called the mesoderm and turning the bilaminar disk to the trilaminar disk. Epiblast cells form into the ectoderm and endoderm (and hypoblasts). The CNS starts to develop by a group of ectoderm cells differentiating into the neuroectoderm, forming neural crest cells from the creation of the neural plate. Neural crest cells and the mesoderm join together to form the mesenchyme. The mesoderm then differentiates and divides on each side of the developing CNS (neural tube).
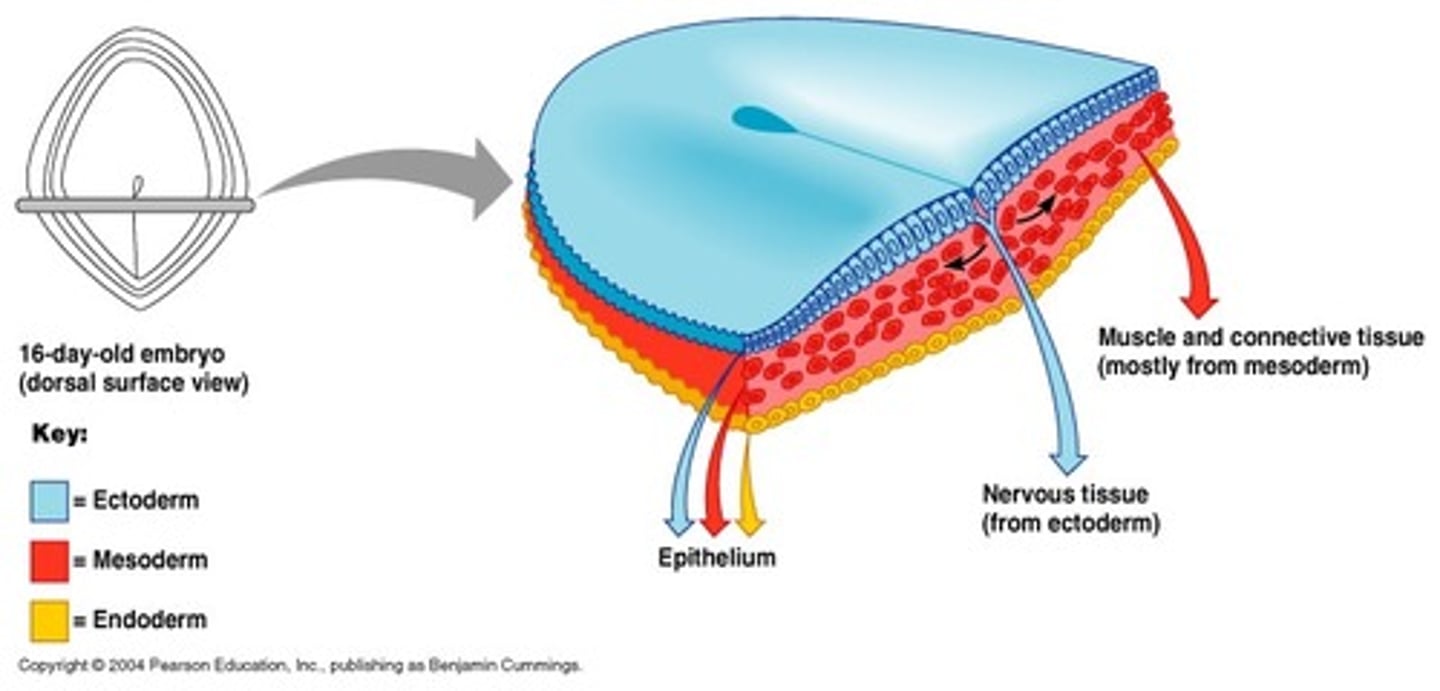
Ectoderm
1. Originated from the epiblast layer
2. Made of columnar epithelial cells
3. Forms the epithelium, sensory epithelium of eyes, ears, nose, nervous system, neural crest cells, mammary and cutaneous glands
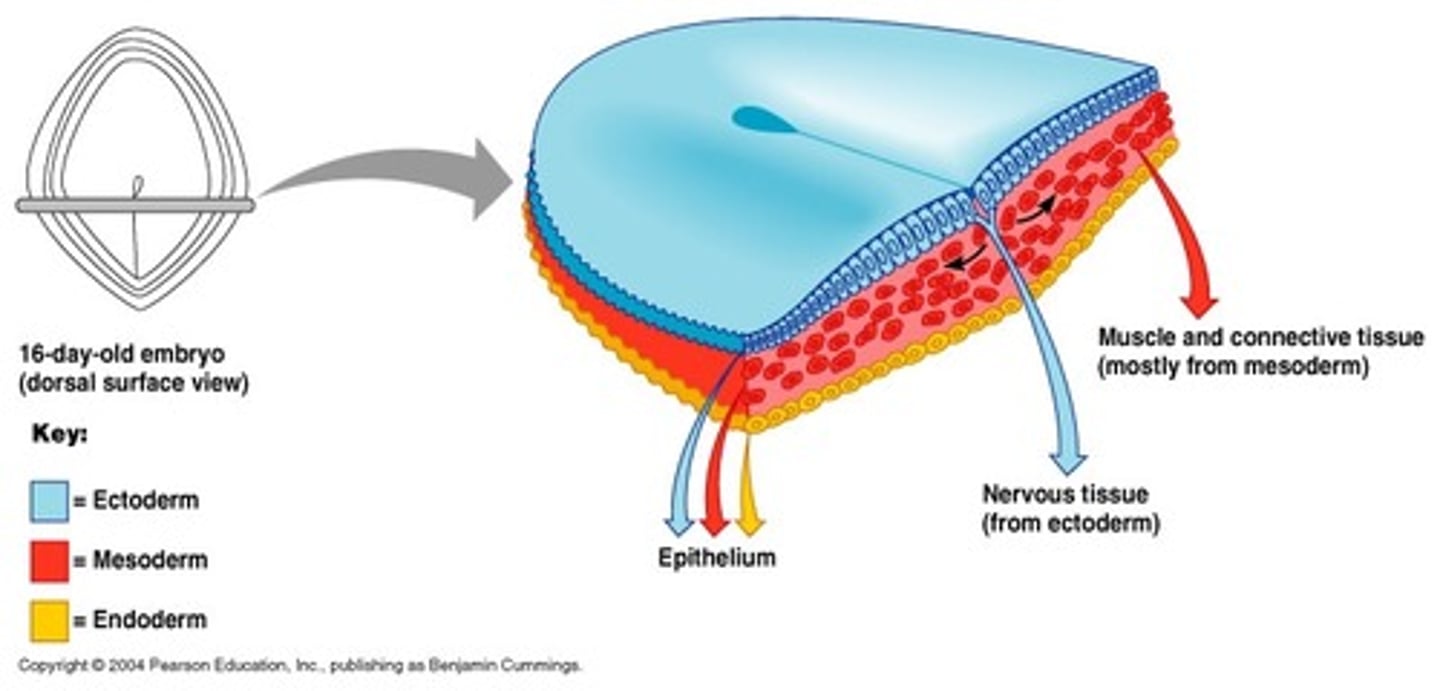
Mesoderm
1. Originated from migrating cells from epiblast
2. Histological features vary
3. Forms the Dermis, muscle, bone, lymphatics, blood cells, bone marrow, cartilage, reproductive and excretory organs
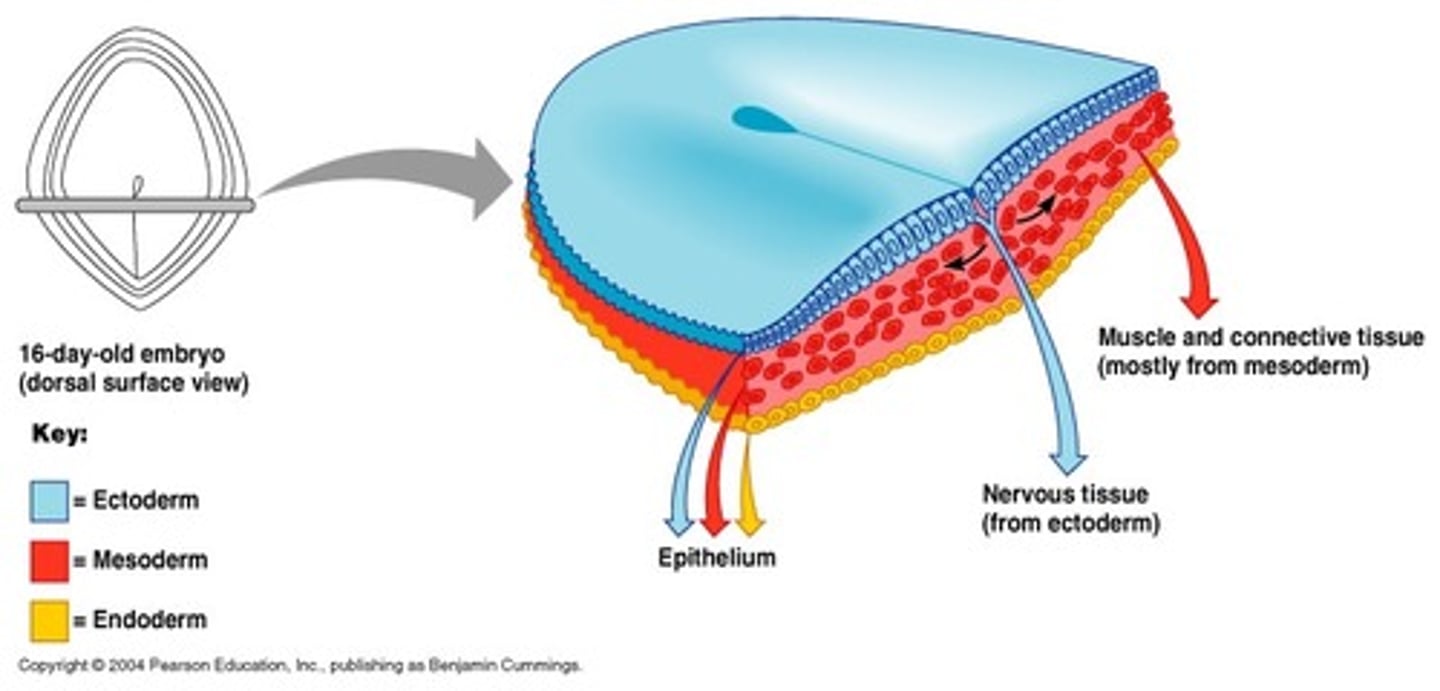
Endoderm
1. Originated from Migrating cells from the epiblast and hypoblasts
2. Made of cuboidal epithelium cells
3. Forms the respiratory and digestive system, liver, pancreatic cells
Neural Crest cells (characteristics)
1. Originated from migrating neuroectoderm
2. Histological features vary
3. Forms components of the nervous system pigment cells. connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone and certain dental tissue
Primitive streak
Where cells from the epiblast layer migrate to the middle, creating the new layer between the epiblast and the hypoblast called the mesoderm. The primitive streak gives bilateral symmetry L/R.
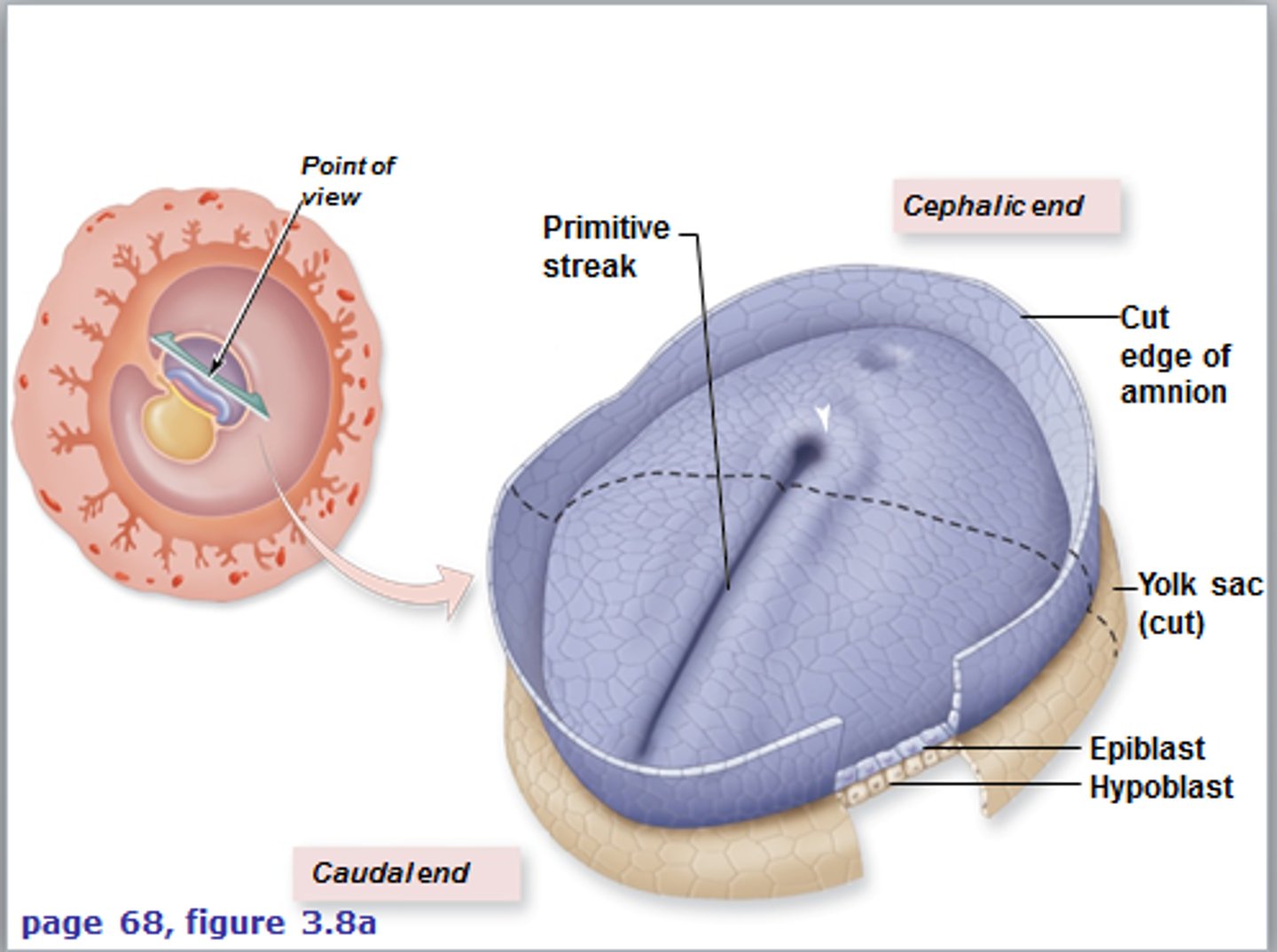
Trilaminar embryonic disc
Has three germ layers including: the ectoderm, the mesoderm and the endoderm
Anatomical structures of the trilaminar disk
1. Cephalic end: head-oropharyngeal
2. Caudal end: tail-cloacal membrane
3. Both ends have ectoderm externally and endoderm internally and no mesoderm layers are fused
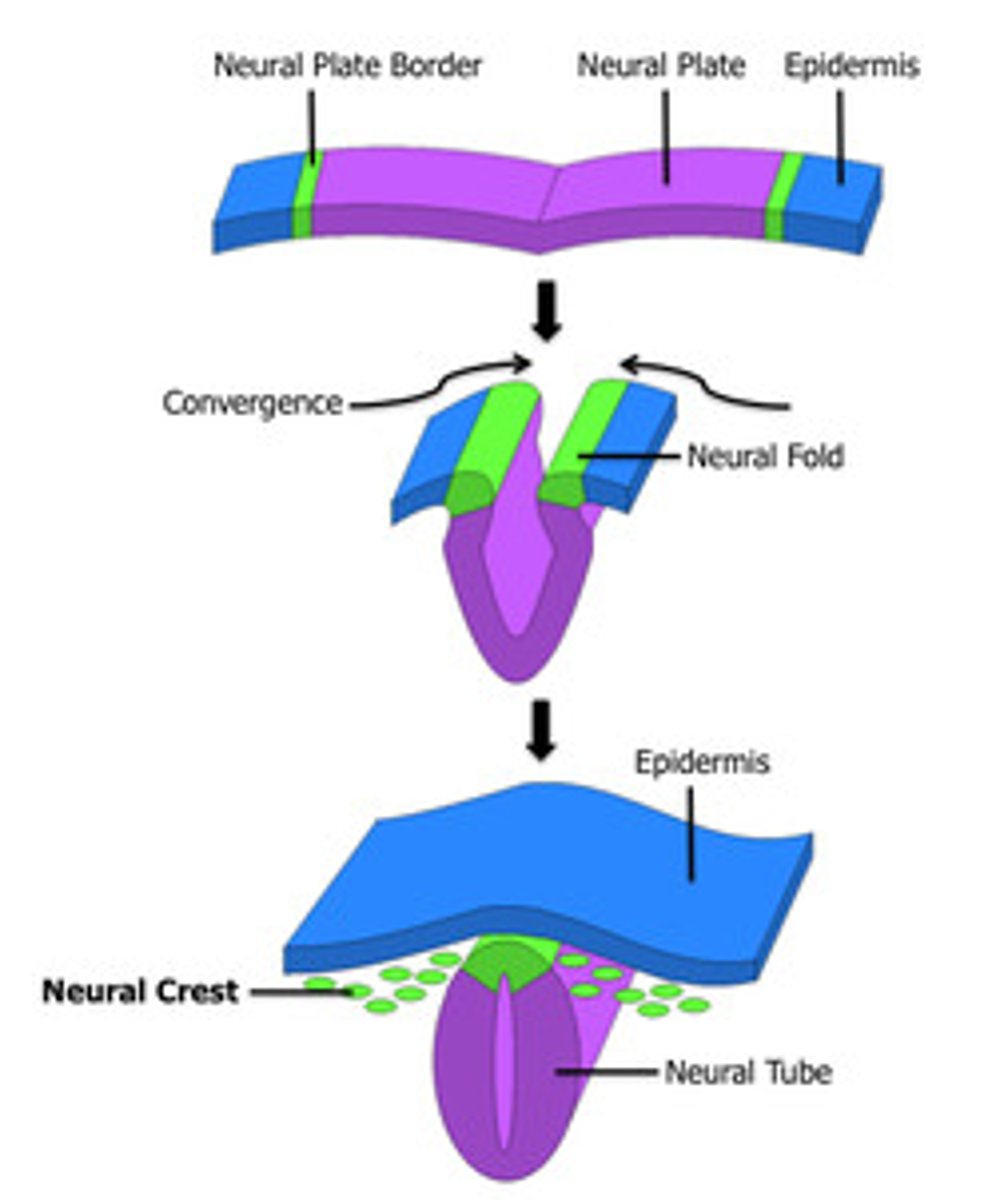
Neuroectoderm
A group of ectoderm cells differentiate into the neuroectoderm located within the neural plate of the embryo. This plate then thicken and grows into the neural groove which deepens and is then surrounded by neural folds. The neural tube is formed during week 4 from the fusion of neural tissue
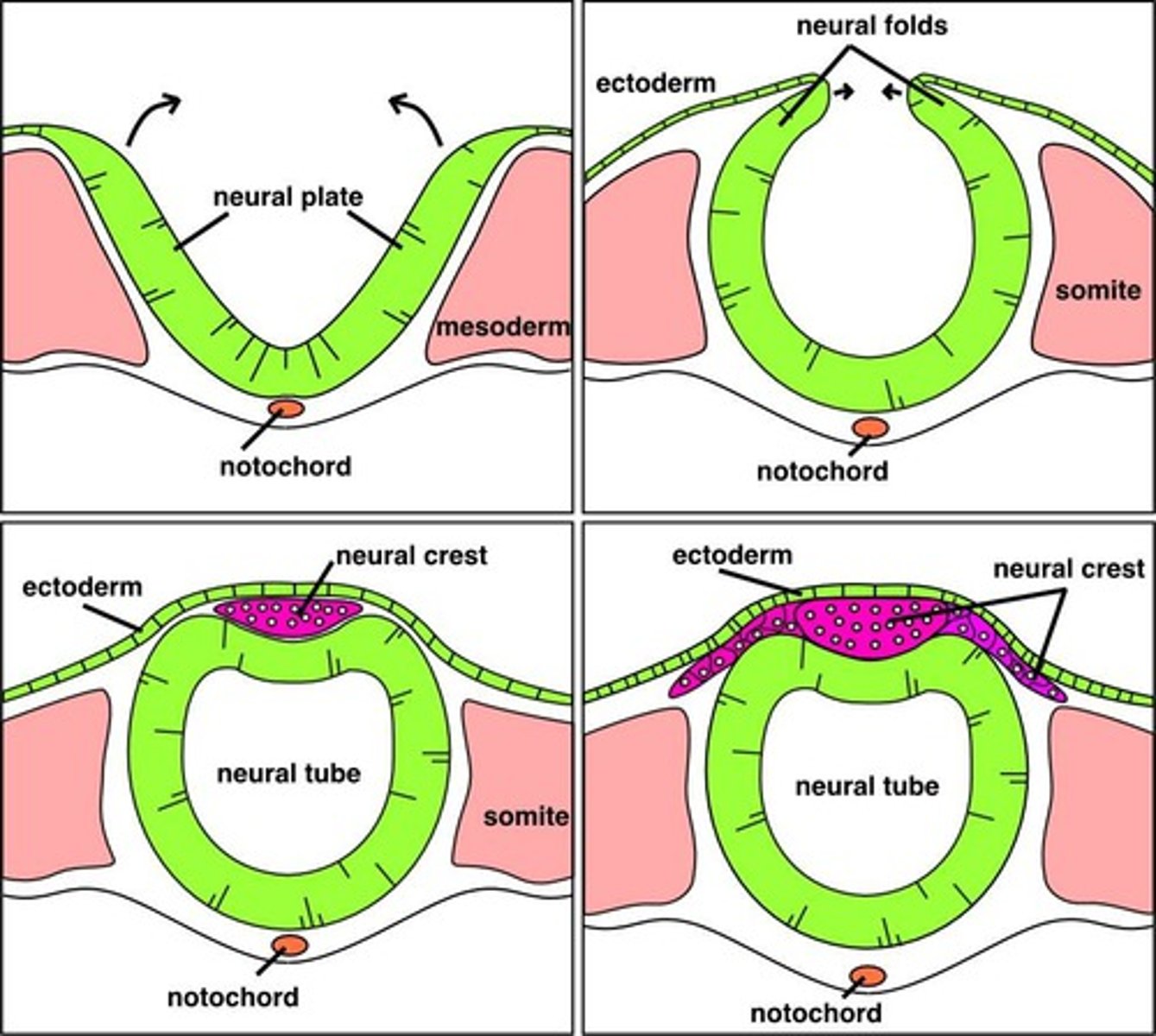
Neural crest cells
The sometimes considered 4th layer that develops the neuroectoderm. They give rise to portions of the nervous system, pigment cells, connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone, most dental tissues (as ectomesenchyme), pulp, dentin, cementum, alveolar process and PDL
Mesenchyme
Embryonic connective tissue that is formed by the joining of the mesoderm and neural crest cells. The mesenchyme proliferates and differentiates into diverse types of connect tissue-forming cells.
Mesoderm differentiation
The mesoderm (somites) differentiates and divides on each side of the developing CNS or the neural tube. 38 pairs of cuboidal mesoderm give rise to most of the skeletal structures of the head, neck, and trunk and the associated muscles and dermis of the skin
Week 4
Embryonic folding takes place where the disk folds into an embryo. The face, neck and digestive system start developing.
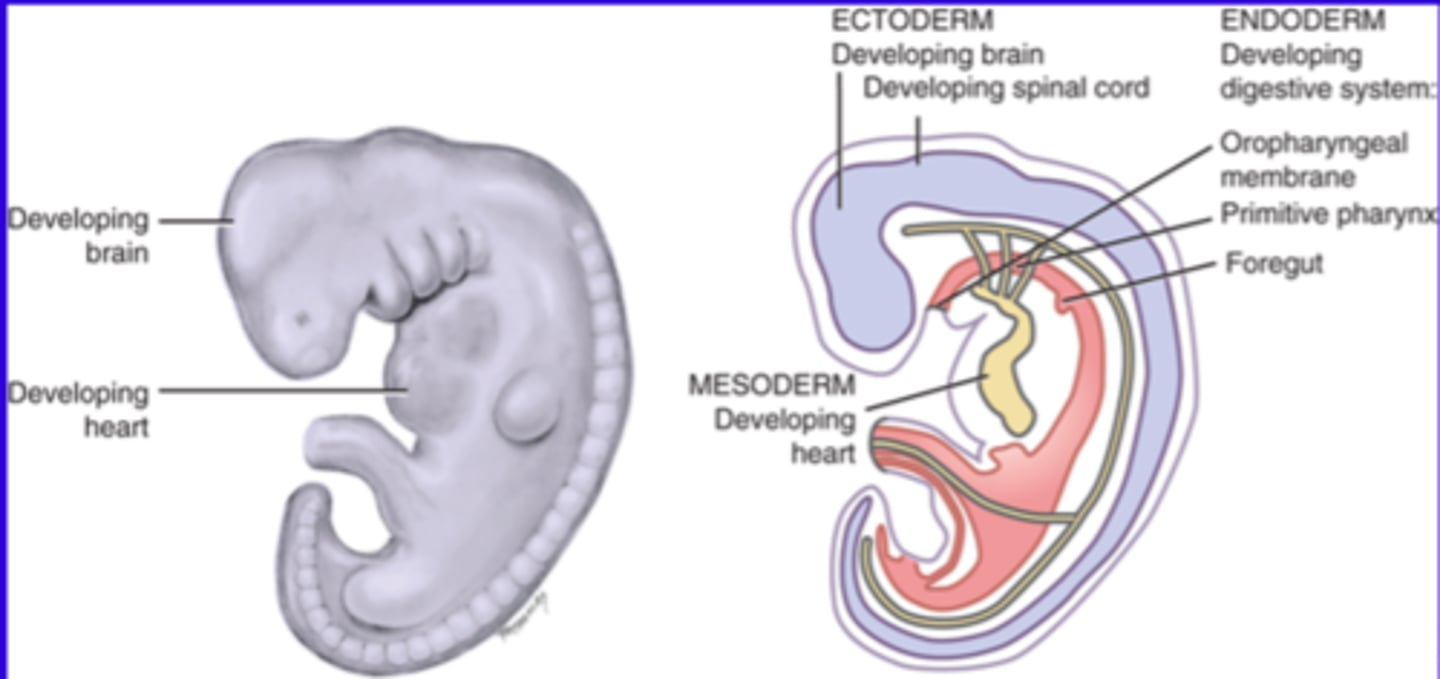
Embryonic folding
The disk folds into an embryo due to the proliferation of the ectoderm and the differentiation of basic tissues. It includes anterior and lateral folding with growth that occurs primarily at the cephalic end (head). Sometimes growth also occurs at the caudal end and the sides of the embryo. Embryonic areas are placed in proper areas for further development (ectoderm = outside, mesoderm = middle, endoderm = inside)
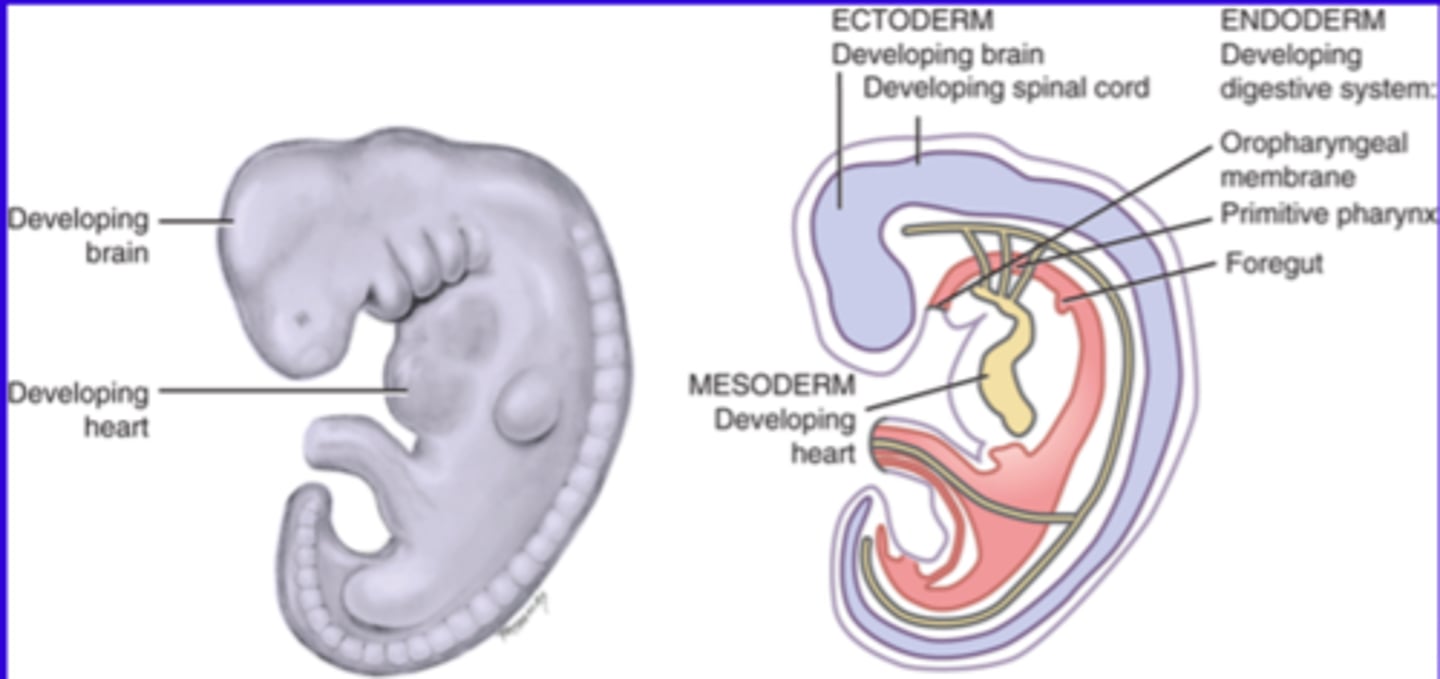
Digestive tract development
Forms the long, hollow tube from the oropharyngeal membrane to the cloacal membrane (ecto = outside, meso = middle, endo = inside). It also forms the foregut-primitive pharynx, the mid-gut and the hindgut.
Face and neck development
Forms the primitive eyes, ears, nose, oral cavity and jaw.
Congenital malformation (birth defects)
These orofacial congenital malformations occur mostly during the 1st trimester in the preimplantation and the embryonic periods. They are due to genetic factors and teratogens and are traceable to a specific time in the embryological development.
Ectodermal dysplasia
Abnormal development of one or more structures from the ectoderm leading to possible oral effects. This includes partial or complete anodontia and developmental defects in teeth. It can involve teeth, skin, hair, nails, eyes, inner ears, fingers, toes, facial structure and glands.
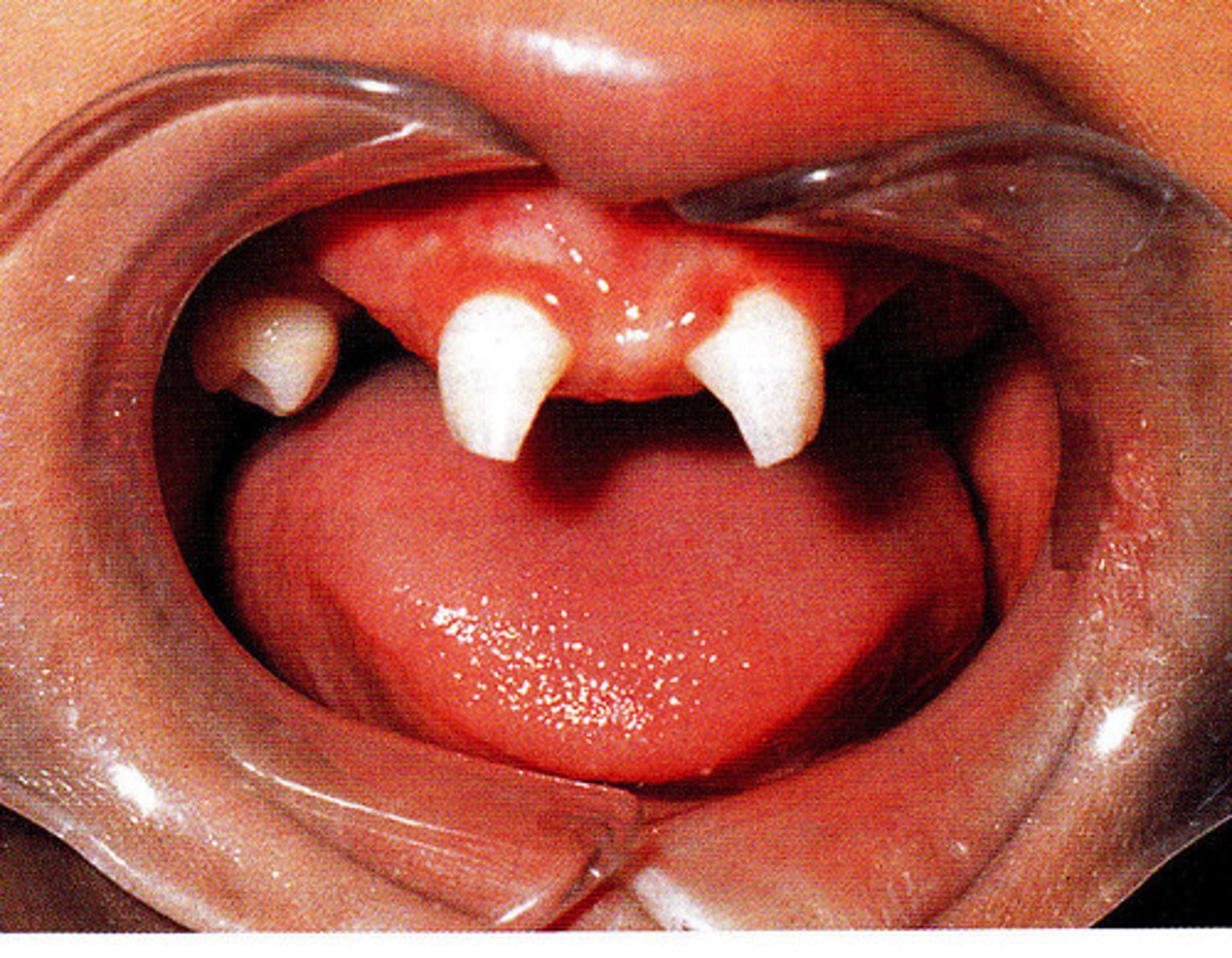
Chromosomal abnormalities
Down syndrome, or trisomy 21 can have possible oral effects such as, fissured tongue, weak tongue muscles, lingual papillae hypertrophy, arched palate, increased risk of periodontal disease, microdontia and delayed eruption.
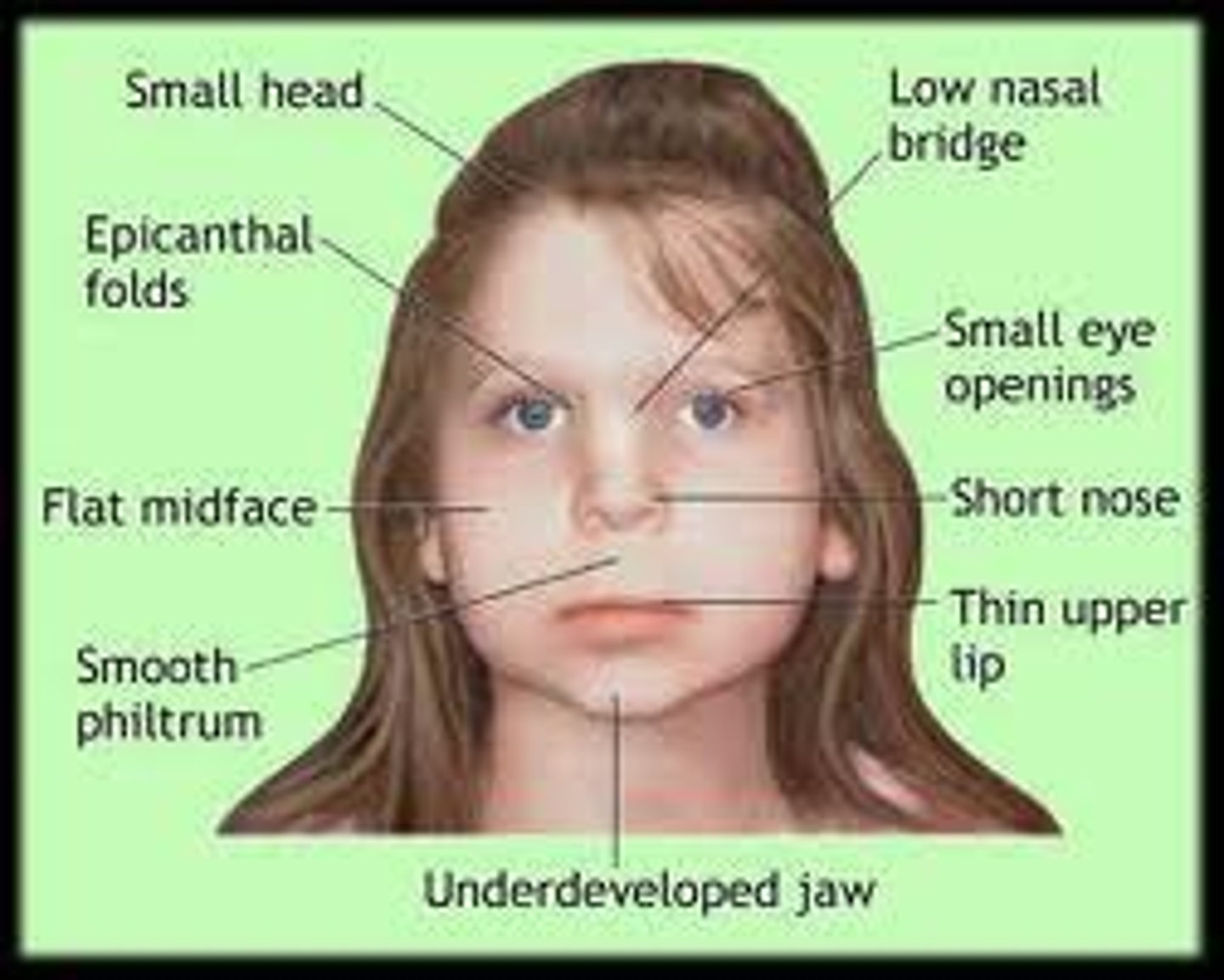
Fetal alcohol syndrome
High levels of drugs such as tetracycline, ethanol, lithium, etc. can lead to possible oral effects such as crowded teeth, open bite and gingivitis.
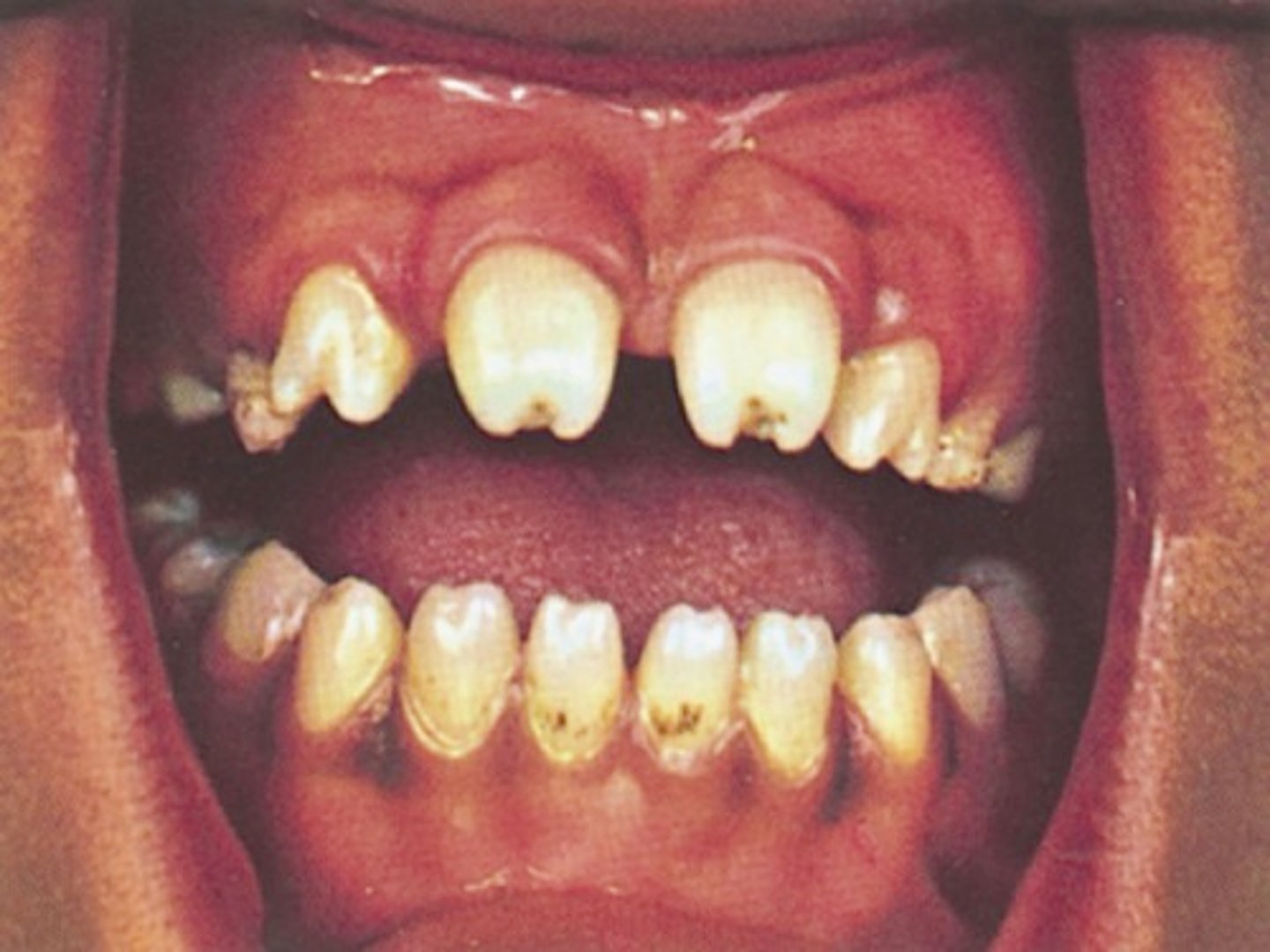
Congenital Syphilis
The bacterial spirochete present in this disease can lead to blindness, deafness and paralysis. It can also lead to possible oral effects such as, Hutchinson's incisors and mulberry molars.
Radiation
High levels may lead to cancers in embryos, chromosome injury, retardation, delayed development and physical growth (no congenital abnormalities have bee directly linked).
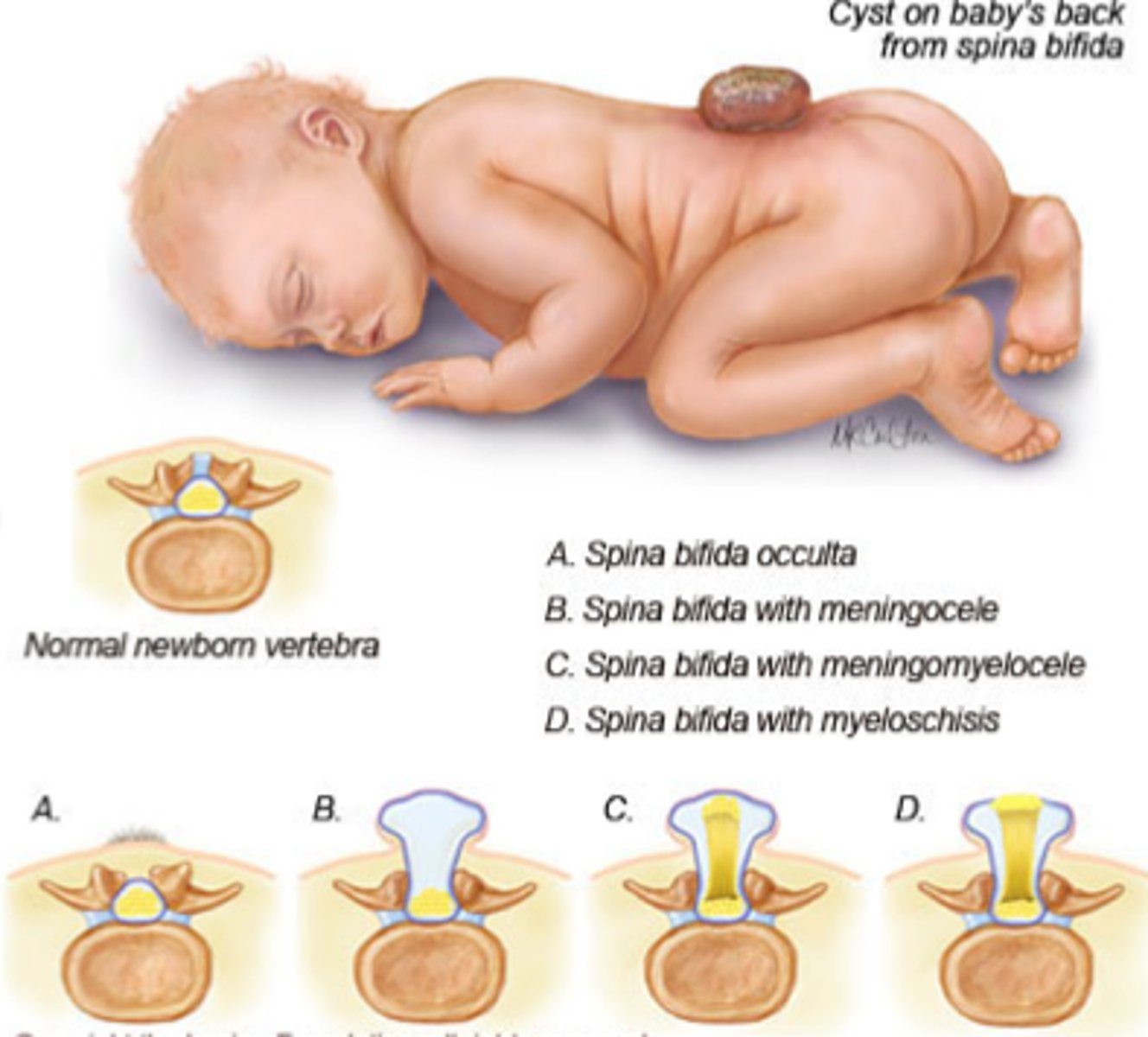
Spina Bifida
The failure of the neural tube fusion that leads to vertebral defect due to lack of folic acid (nutritional deficit). This can cause paralysis, incontinence, learning difficulties, and fluid on the brain.
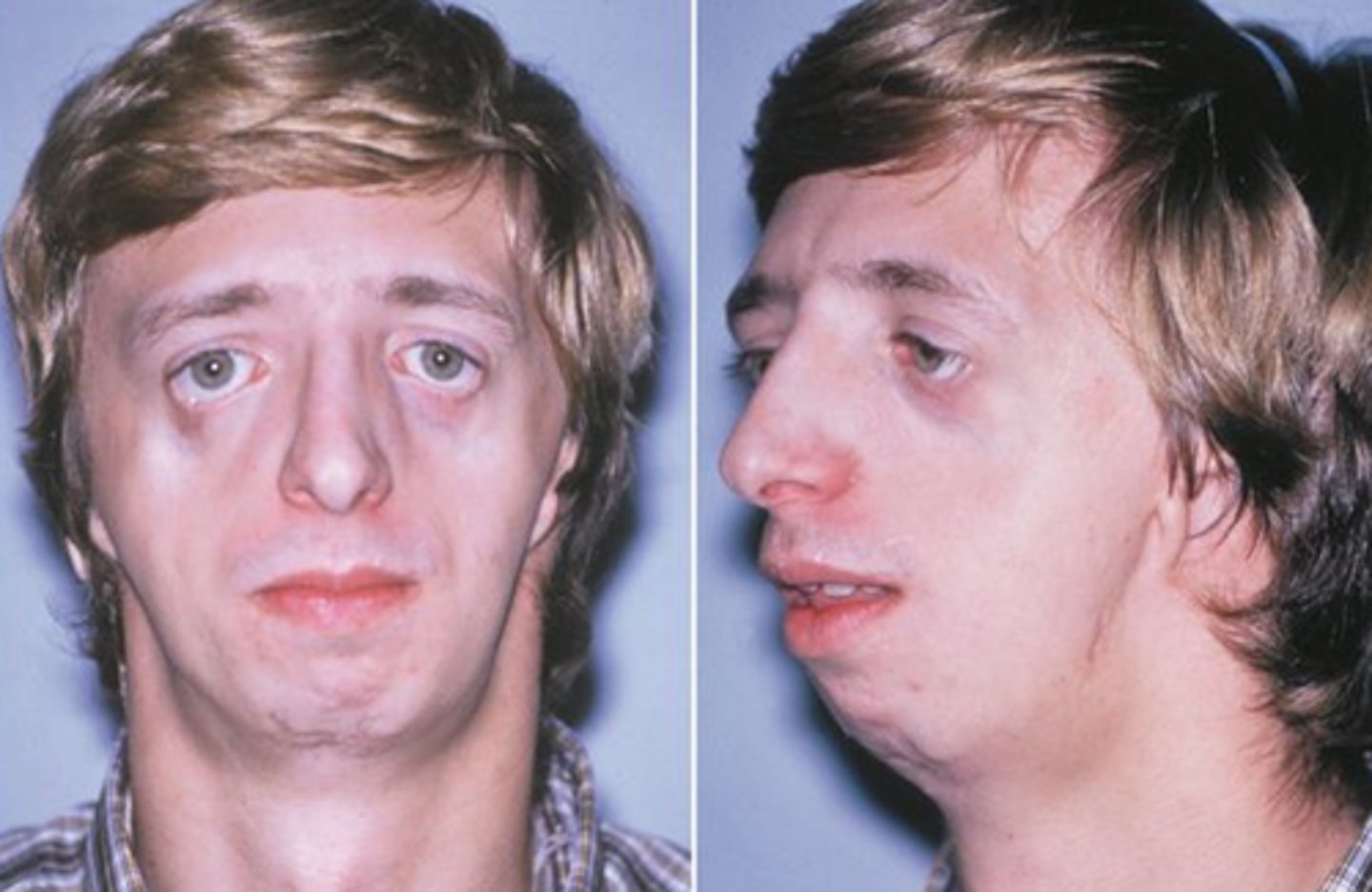
Treacher collins syndrome
The failure of neural crest cells migration to the facial region which can cause downward slanting eyes, micrognathia (small lower jaw), hearing loss, underdeveloped zygomatic bone, drooping lower eyelids, malformed or absent ears, missing teeth, and enamel dysplasia.
Fetal Period
Lasts from week 9 to birth and is where existing structures mature, the embryo becomes a fetus and more proliferation, differentiation, and morphogenesis.
Tetracycline staining
A systemic antibiotic that binds irreversibly to dentin and stains both sets of dentition.