Chapter 10 - Characters, C-Strings, and More About the string Class
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
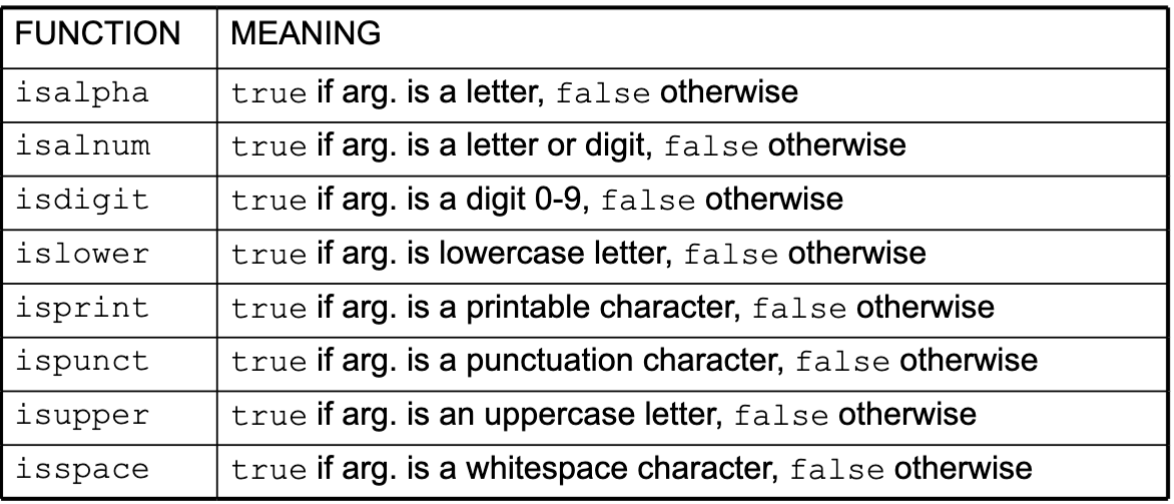
Character Testing
requires
<cctype>header file
Character Case Conversion
toupperif
charargument is lowercase letter, return the ASCII code for the uppercase equivalent; otherwise, return the argument’s ASCII code unchangedif you want to send the returned value to
cout, use a cast expression to display it as a charactercout << static_cast<char>toupper(char1);
tolowerif
charargument is uppercase letter, return the ASCII code for its lowercase equivalent; otherwise, return the argument’s ASCII code unchangeduse case expression for
cout
C-Strings
C-String: sequence of characters stored in adjacent memory locations and terminated by
NULLcharacterString literal (string constant): sequence of characters enclosed in double quotes “ “
ex: “Hi there!“
an array of chars can be used to define storage for a string
leave room for
NULLat the endcan enter a value using
cinor>>input is whitespace-terminated
no check to see if there’s enough space
for input containing whitespace, and to control amount of input, use
cin.getline()

Display Contents of Character Array

Library Functions for Working with C-Strings
<cstring>header filefunctions take one or more C-strings as arguments:
C-string name
pointer to C-string
literal string
strlen(str)returns length of C-string
str
strcat(str1, str2)appends
str2to the end ofstr1
strcpy(str1, str2)copies
str2tostr1
note:
strcatandstrcpyperform no bounds checkingstrstr(str1, str2)finds the first occurernce of
str2instr1, returns a match, orNULLif no match
C-String/Numeric Conversion Functions
<cstdlib>header fileif C-string contains non-digits, results are undefined
function may return result up to non-digit
function may return 0
itoadoes no bounds checking
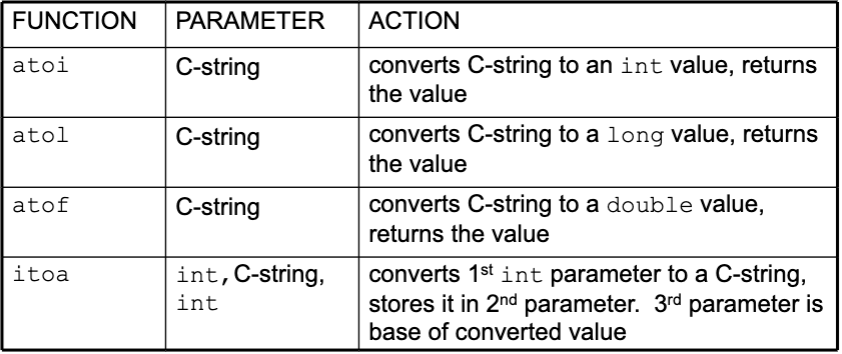
string to Number Conversion
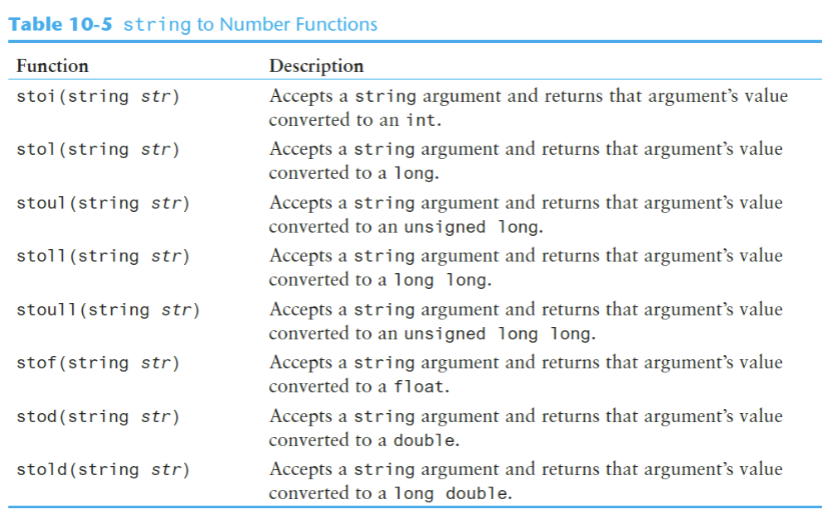
The to_string Function
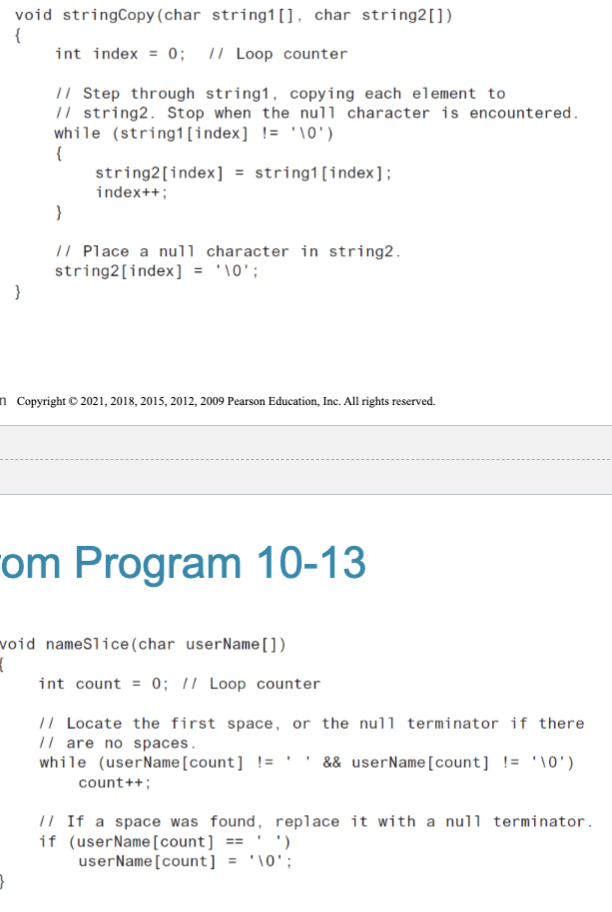
Writing Your Own C-String Handling Functions
can pass arrays or pointers to
chararrayscan perform bounds checking to ensure enough space for results
can anticipate unexpected user input
see examples: stringCopy() & nameSlice()
The C++ string Class
special data type that supports working with strings
#include <string>
can define
stringvariables in programscan receive values with assignment operator
can be displayed via
coutuse
cinuse
getlineto put a line of input (spaces) into a stringcan use relational operators directly to compare string objects
performed similar to
strcmp
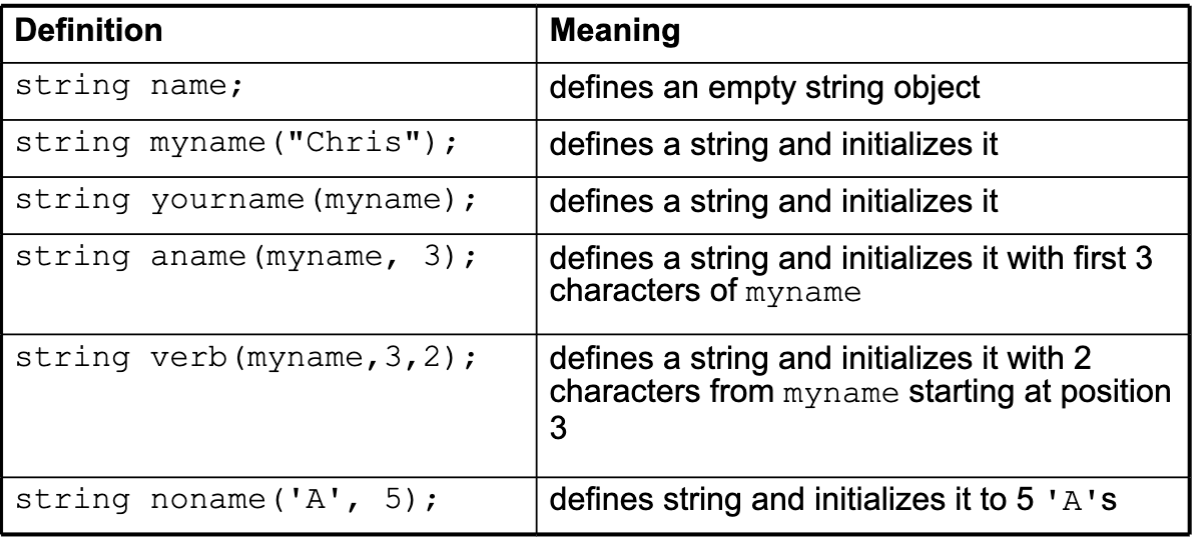
Other Definitions of C++ strings
Using auto To Define a string Object
auto str = "Hello World!";
defines str as either const char * or const char[12]
when using
auto, append thessuffix to the string literalauto str = "Hello World!"s;defines str as a string object
string operators

string Member Functions
behind many overloaded operators
assignment
assign,copy,data
modification
append,clear,erase,insert,replace,swap
space management
capacity,empty,length,resize,size
substrings
find,front,back,at,substr
comparison
compare
see Table 10-9 string Class Member Functions