Microeconomics: Elasticity
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What is price elasticity of demand (PED)?
Elasticity of demand is how responsive the quantity demanded is for a good or service when price or income changes.
How is PED calculated?
What are the degrees of PED?
PED > 1: Price elastic demand
PED = 1: Unitary elastic demand
PED < 1: Price inelastic demand
PED = 0: Perfectly inelastic demand
PED = ∞: Perfectly elastic demand
What are the determinants of PED?
Number and closeness of substitutes
Degree of necessity
Proportion of income spent on the good
Time period considered
What is the relationship between PED and total revenue?
If demand is elastic (PED > 1), a price fall increases total revenue.
If demand is inelastic (PED < 1), a price fall decreases total revenue.
If demand is unitary elastic (PED = 1), total revenue remains unchanged.
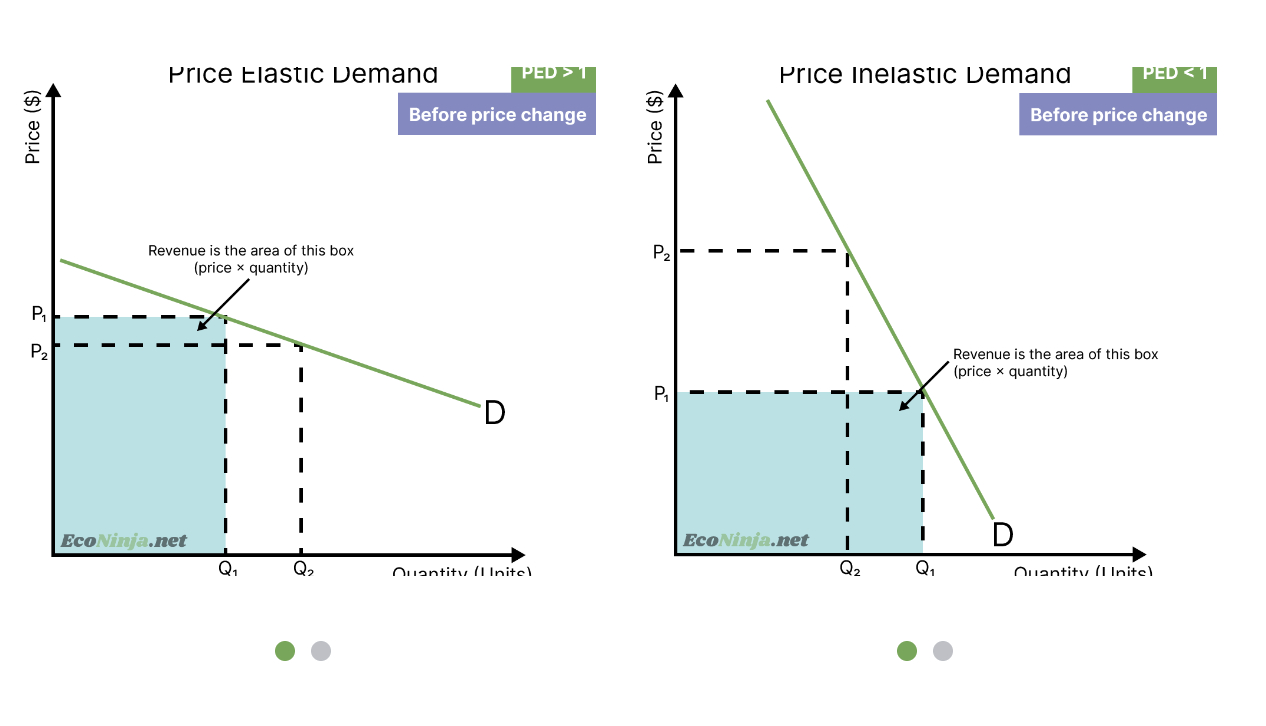
Why is PED important for firms and governments?
Firms use it to set prices and maximize revenue.
Governments use it to predict tax impacts and revenue changes.
What is income elasticity of demand (YED)?
Income elasticity of demand refers to how responsive the quantity demanded is for a good or service when income of consumers changes.
How is YED calculated?
What do positive and negative YED values mean
Positive YED = Normal goods (demand rises as income rises).
Negative YED = Inferior goods (demand falls as income rises).
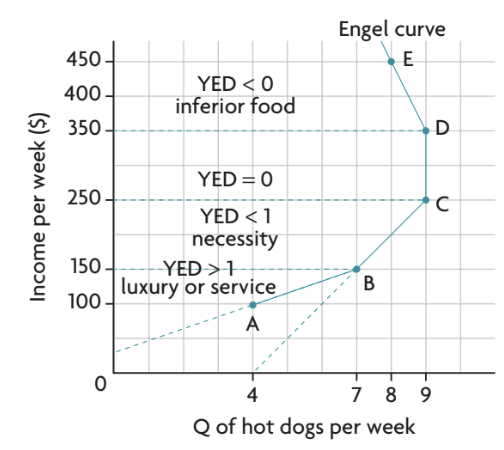
What’s the difference between necessities and luxuries
Necessities: Income inelastic (YED < 1).
Luxuries: Income elastic (YED > 1).
What is price elasticity of supply (PES)?
Price elasticity of supply refers to how responsive the quantity supplied is for a good or service when price changes
How is PES calculated?
What are the degrees of PES?
PES > 1: Elastic supply
PES = 1: Unit elastic supply
PES < 1: Inelastic supply
PES = 0: Perfectly inelastic supply
PES = ∞: Perfectly elastic supply
What are the determinants of PES?
Time period (more time → more elastic)
The more time producers have to adjust production, the more price elastic supply tends to be.
Mobility of factors of production
Example: A factory that can switch from making shirts to making jackets.
Example: A vineyard with very specific soil/climate; you can’t just move it.
Unused capacity
Firms with significant unused capacity can respond more easily to price changes, leading to more elastic supply.
Ability to store stocks
The easier and cheaper it is to store a product, the more elastic supply tends to be.
Rate at which costs rise
When marginal costs rise quickly as output expands, supply tends to be more inelastic, as firms are reluctant to increase production.