LAB 4: STAINING ii = DIFFERENTIAL STAINING
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
what type of staining is Gram staining? - RM
differential - RM
what is the main difference between a gram+ and gram- bacterium? - QUEEN
+G=thick cell wall and -G=thin cell wall an outer membrane - QUEEN
what type of staining is acid-fast staining? - JIN
differential - JIN
what’s an acid-fast bacteria? - YUHH
bacteria that has mycolic acid - YUHH
what’s an non-acid fast bacterium? - NAHHH
bacteria doesn’t have mycolic acid - NAHH
what type of staining is endospore staining? - SUGA
differential - SUGA
when do endospore-forming bacteria produce endospores? - JINNN
during harsh conditions - JINNN
1st stains/reagents used in gram staining
crystal violet
2nd stains/reagents used in gram staining
grams iodine
3rd stains/reagents used in gram staining
decolorizer
4th stains/reagents used in gram staining
safranin
simple gram staining step 1
create a smear slide - START
simple gram staining step 2
crystal violet (sit for 1 minute)
simple gram staining step 3 - JISOO
wash - JISOO
simple gram staining step 4
gram’s iodine (sit for 1 minute)
simple gram staining step 5 - JK
wash - JK
simple gram staining step 6
decolorize for 5 sec
gram staining step 7 - HOBI
wash - HOBI
simple gram staining step 8 - HOBI
safranin (sit for 1 minute)
simple gram staining step 9
wash and blot - FINAL
differential staining purpose
distinguish different bacteria
what are the three types of differential staining?
gram, acid-fast, and endospore
gram and acid-fast staining are based on
differences in bacteria’s cell envelope
three layers of bacteria’s cell envelope
membrane, wall, and outer membrane
bacteria’s cell membrane composition
bilayer of phospholipids
bacteria’s cell wall composition
peptidoglycan
bacteria’s outer membrane composition
bilayer of phospholipids and lipopolysaccharides
who developed a staining technique to differentiate the cell envelopes of different bacteria?
hans christian gram
grams staining technique purpose
distinguish based on thickness of cell wall
gram-positive bacteria cell wall
thick cell wall
gram-negative bacteria cell wall
thin cell wall
what are the +G and -G bacteria stain with beginning?
crystal violet (purple)
what are the +G and -G bacteria stain with second?
gram iodine
what does gram iodine do to +G
helps trap crystal violet in +G
why is there less trapping of crystal violet in -G?
its cell wall in thinner
what are the +G and -G bacteria stain with third?
decolorizer of ethanol
who stain is lost during decolorizing? - ROSE
gram negative - ROSE
the ethanol destroys what of the gram negative cell?
outer membrane
who retains the purple color during decolorization?
gram positive
who looses the purple color and becomes colorless during decolorization? - RM
gram negative - RM
what are the +G and -G bacteria stain with finally?
safranin (counterstain)
the safranin (counterstain) stains -G what color?
pink/red
in conclusion , gram positive bacteria are stained
purple
in conclusion , gram negative bacteria are stained
pink/red
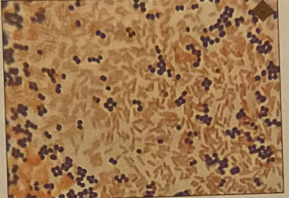
gram staining
pink=negative, purple=positive
why can’t gram staining be used on some bacteria? - RIT
they have mycolic acid - RIT
what is mycolic acid?
hydrophobic molecule
what method is used on bacteria with mycolic acid?
ziehl-neelsen method
ziehl-neelsen method purpose
distinguish between those with and without mycolic acid
what are acid-fast cells? - SUGA
bacteria with mycolic acid - SUGA
what non acid-fast cell? - DUDE
bacteria without mycolic acid - DUDE
in acid-fast staining what’s the 1st dye used
carbol fuchsin
when u add carbol fuchsin, acid-fast cells are what color
red
what is the counterstain in acid fast staining
methylene blue
when do bacterial species form a resistant endospore? - FUN
when environment is too harsh for vegetative cell - FUN
what is the vegetative cell in bacteria?
metabolically active bacteria cell
when nutrients return, what happens to the endospore
it germinates
what does it mean when the endospore germinates?
forms new vegetative cell and metabolically active
in endospore staining, endospores are stained with
malachite green
in endospore staining, what color is the endospore?
green
in endospore staining, vegetative cell are stained with - VEGE
safranin - VEGE
in endospore staining, what color is the vegetative cell?
red
endospore staining purpose
to differentiate between vegetative cell and endospore
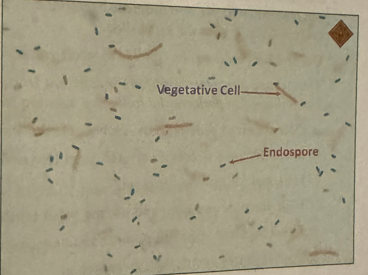
endospore staining: vegetative cell location
long and red
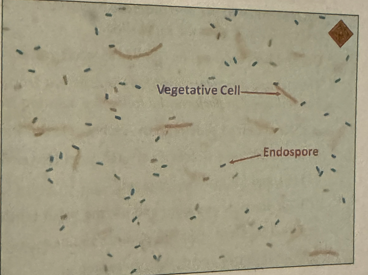
endospore staining: endospore location
green pea

gram stain step 1
get clean slide

gram stain step 2
add drop of water in center

gram stain step 3
add first bacteria, sterilize, add second then smear (circular motion)
gram stain step 4
air dry
gram stain step 5
heat fix 3 times

gram stain step 6 - JIN
add crystal violet and let sit 1 minute - JIN

gram stain step 7 - LISA
wash at 45 degree angle - LISA
gram stain step 8 - GASSED UP
add grams iodine and let sit for 1 minute - GASSED UP

gram stain step 9 - ROSE
wash at 45 degree angle - ROSE
gram stain step 10 (DONT OVERDO)
decolorize at 45 degree angle for 5-10 seconds until colorless
gram stain step 11 - JISOO
wash at 45 degree angle - JISOO

gram stain step 12 - OG
add counterstain safranin and let sit for 1 minute - OG

gram stain step 13
wash at 45 degree angle

gram stain step 14 (BIBULOUS PAPER) - DRY
blot until dry - DRY
gram stain step 15
view cells under 100x with oil
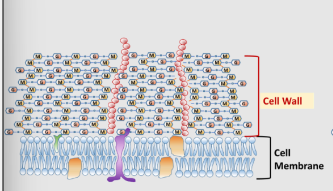
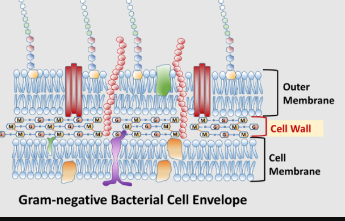
in diagram form, show the similarities and differences between a cell envelope found in a gram-positive bacterium vs. the cell envelope found in a gram-negative bacterium. - PUS
+G=thick cell wall, -G=thin cell wall & outer membrane - PUS
what bacteria is this?
+G, thick cell wall and NO outer membrane
what bacteria is this?
-G, thin cell wall WITH outer membrane
what is the purpose of the decolorizer in gram staining produce?
to destain the gram negative cells
what would be the color of the cells of a gram stain if you forget to use the ethanol?
purple and blue
acid-fast cells do not stain well using the gram staining method - WHY?
they have hydrophobic mycolic acid - WHY?
under what conditions do bacteria produce an endospore? - DRAKE
harsh conditions - DRAKE
are endospores hard to kill?
yes
what d we do to destroy endospores?
autoclave (high pressure sterilize)