CNIM: Guidelines 9C (Clinical) & 11C (IOM) Auditory Evoked Potentials
1/233
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
234 Terms
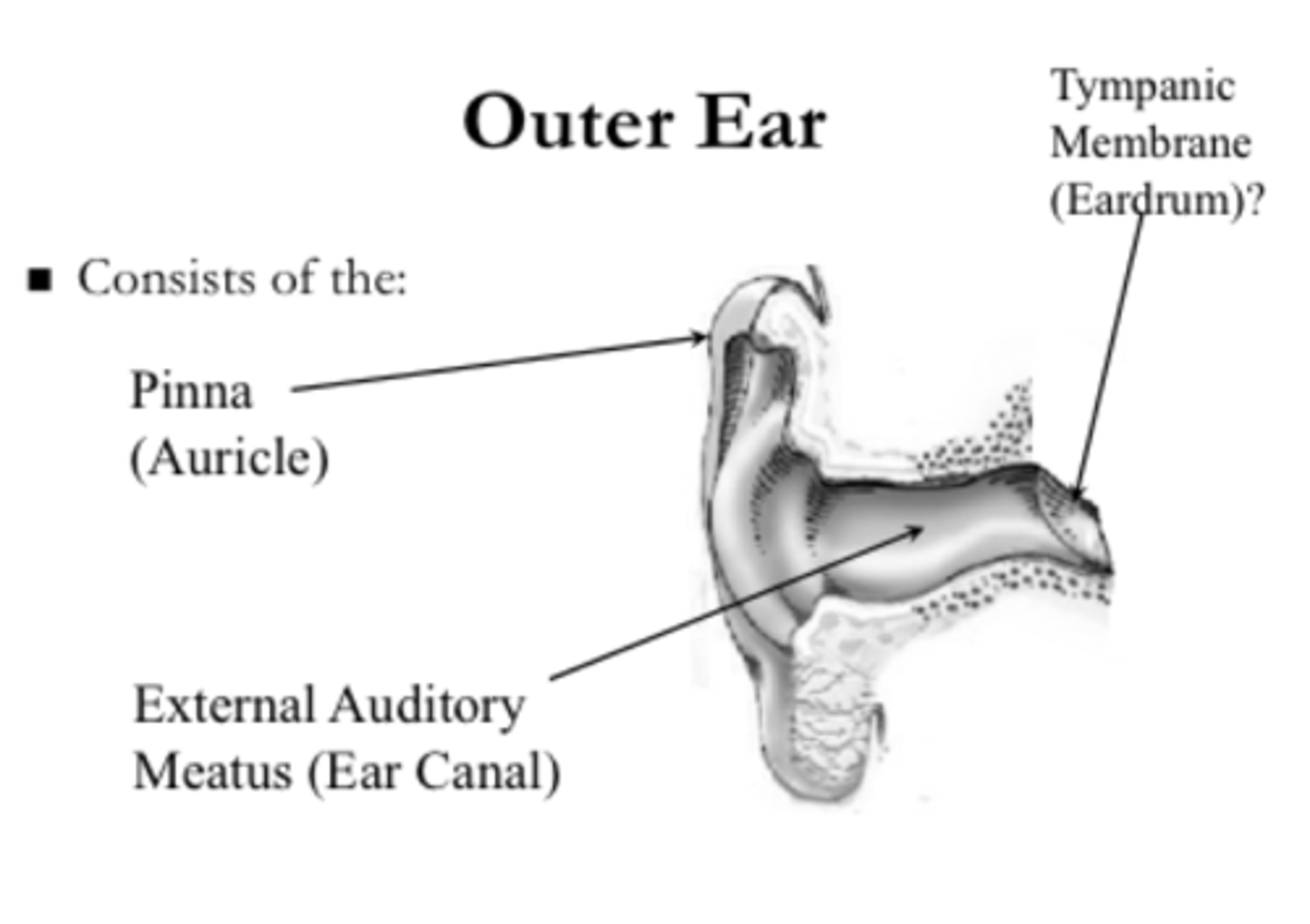
outer ear consists of __
pinna and external auditory canal
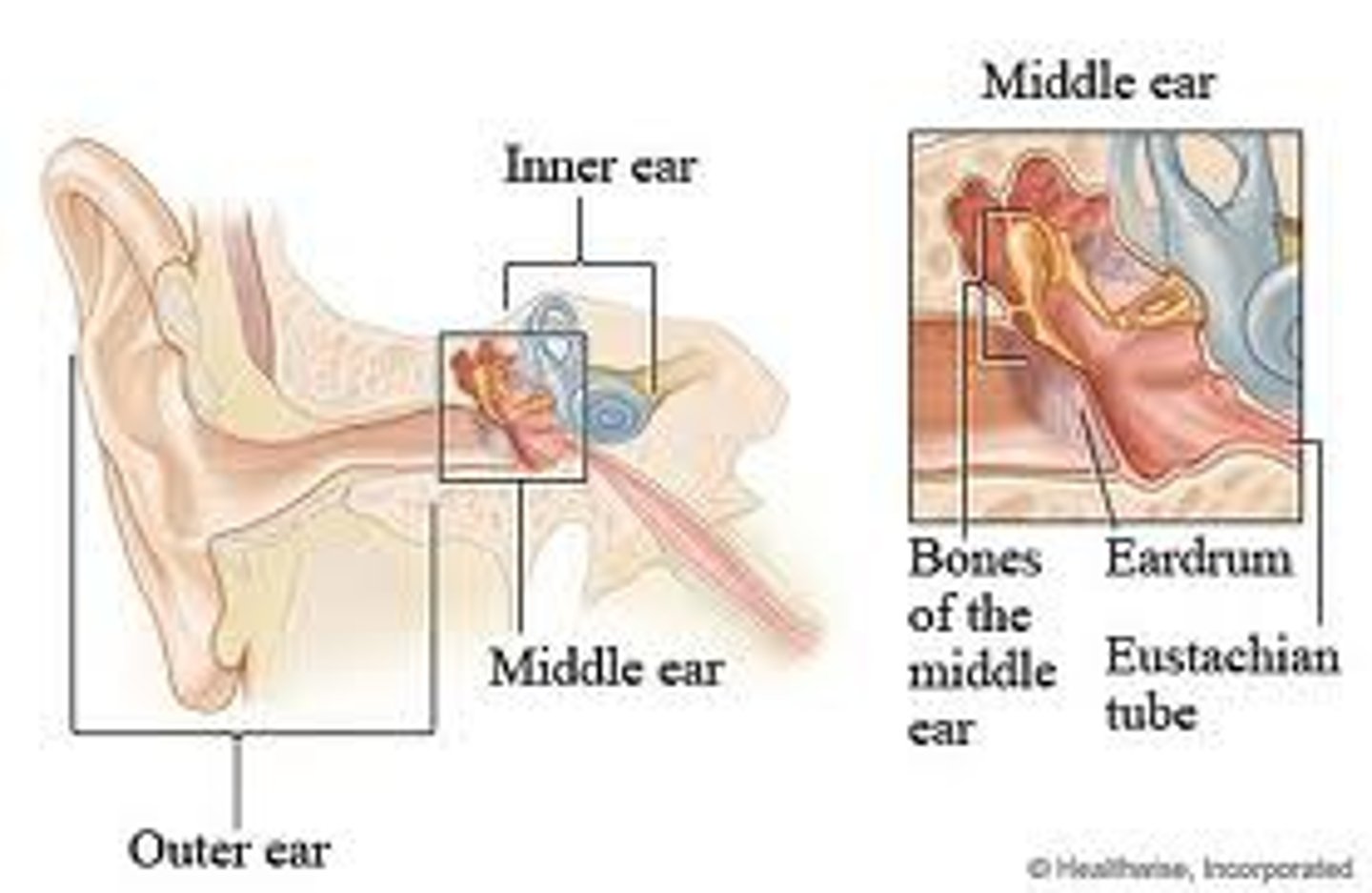
middle ear consists of __
tympanic membrane & ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes)
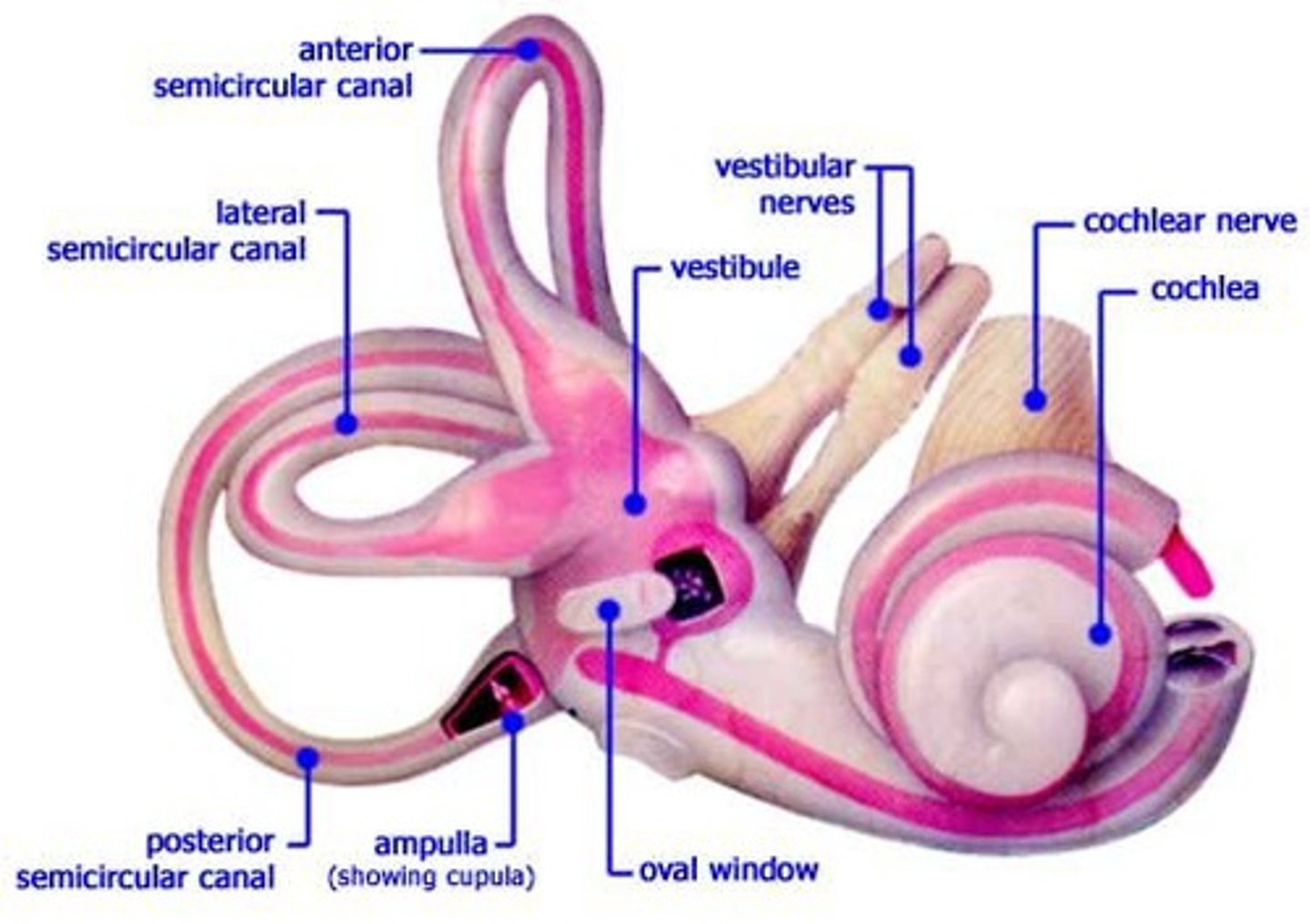
inner ear consists of __
vestibule, semicircular canals, cochlea
incoming sound enters the __
external acoustic meatus (auditory canal)
sound waves vibrate the ___ which cause the ossicles to vibrate
tympanic membrane
ossicles connect to the ___ via ___ which causes movement of fluid and hair cells
cochlea; oval window
hair cells generate what kind of AP?
depolarization
what 2 nerves form the vestibulocochlear nerve
cochlear & vestibular
hearing pathway
sound --> external acoustic meatus --> tympanic membrane --> ossicles --> cochlea --> hair cells --> vestibulocochlear nerve
brainstem is supplied by what arteries?
vertebral (2) & basilar = vertebrobasilar
cochlea is supplied by what arteries?
basilar/vertebrobasilar --> AICA (anterior inferior cerebellar artery) --> internal auditory artery (labyrinthine artery)
cochlear branch of vestibulo-cochlear artery
another name for cochlea
labyrinth
what branch of the basilar artery goes toward the cochlea
anterior inferior cerebellar artery
what is the main branch of the AICA that perfuses the cochlea
internal auditory artery/labyrinthine artery
short-latency auditory evoked potentials (SAEPs)
electrical responses of auditory pathways
consist of BAEP & ECoG
occur within 10-15 ms
brainstem auditory evoked potentials can also be referred to as?
BAER
ABR = auditory brainstem responses
AEP
SAEP = short latency auditory evoked potentials
ECoG records electrical responses of the __ to assess ___
cochlea; cochlear function
is ECoG used to assess the brainstem
NO even though it does collect the auditory nerve compound action potential
3 components of ECoG
1) cochlear microphonics
2) summating potential
3) auditory nerve compound action potential
cochlear microphonics
receptor potentials of cochlear hair cells
aka "stim artifact" b/c of LOW latency
ONLY ECoG
summating potential
receptor potentials of cochlear hair cells
ECoG & ABR
auditory nerve compound action potential
AP of CN VIII
EQUIVALENT to WI with BAEP --> WI = NI (negative 1 on the ECoG)
ECoG & ABR
BAEPs are used to assess __
auditory nerve and/or brainstem & possibly a higher subcortical structure to acoustic stimulation
does BAEP have a summating potential & auditory nerve compound action potential
YES
why does NI exceed WI in amp
b/c there is an electrode in the external auditory meatus
does ECoG use a cephalic electrode (CZ)
no --> A1-EAM1 vs BAEP that uses CZ-A1
why is ECoG used intraoperatively
to get a NI/WI response but it is MOSTLY a clinical modality
ECoG:
analysis time
channel
types of clicks
analysis time = 5 ms
channel = A1-EAM1 (ipsilateral earlobe to ipsilateral external auditory meatus/canal)
clicks = condensation or rarefaction
can you use alternating clicks in ECoG
NO b/c it will cancel out the cochlear microphonic --> it changes direction (up or down) with condensation & rarefaction clicks
how is Wave 1 differentiated from cochlear microphonic
based on click polarity
what does reversing polarity (switch from rarefaction to condensation or vice versa) do
change direction of cochlear microphonic but WI (NI) will stay pointed UP
what do BAEPs record
responses of the auditory nerve & brainstem to acoustic stimulation
do BAEPs assess the thalamus or auditory cortex
no b/c of short latency (how short the CN VIII is)
what are the most important BAEP waves per ACNS
I
III
V
since we ONLY monitor waves I, III, & V, the generators for waves ___ are grouped together
II & III
IV & V
wave I
distal auditory nerve (CN VIII)
neg polarity
wave II
proximal auditory nerve (CN VIII)
junction of pons & medulla
wave III
superior olivary complex (CONTRALATERAL side) --> AKA "cochlear nucleus"
from rostral medulla to mid-pons
pos polarity
wave IV
lateral lemniscus
pons to midbrain
wave V
inferior colliculus (CONTRALATERAL side) --> AKA "lateral lemniscus"
midbrain
pos polarity
waves IV & V are merged to form the?
IV-V complex --> better seen on the CONTRALATERAL side
do BAEPs have specific latencies
NO --> just expected/standard
absolute latency
expected latency of each waveform
interpeak latency
time between waveforms
effect tubing has on absolute or interpeak latencies
absolute latencies: adds 0.9-1 ms delay to ALL
interpeak latencies: NOT affected
interpeak latencies:
I-III
III-V
I-V
2 ms
2 ms
4 ms
absolute latencies:
I
III
V
1.5 ms
3.5 ms
5.5 ms
absolute latencies with tubing (+0.9 ms):
I
III
V
2.4 ms
4.4 ms
6.4 ms
what does dB SPL mean?
sound pressure level
dB SPL
physical measure of lowest sound intensity
what we consider to be 0 dB
what does dB pe SPL mean?
peak equivalent sounds pressure level
dB pe SPL
measurement unit by sound level meters
uses pressure to quantify sound intensity
compare peak-to-peak amplitude of the stimulus (click) with amp of a sine wave of a pure tone with known SPL
what is a click's pe SPL
SPL of a pure tone which matches the peak-to-peak amp of the click's acoustic waveform
pressure measured by a certain sound correlates to its amp on a tool using SPL
output of dB pe SPL equipment
standardized
what does dB HL or dB nHL mean?
decibels hearing level; NORMAL hearing level
dB HL/dB nHL
dB ABOVE the average hearing threshold of a group of normal young adults
determined for different frequencies since some people have difficulty hearing low or high sounds
what is the softest sound that can be heard by the average person with NORMAL hearing
0 dB HL
hearing level for individuals ABOVE average hearing
LOW
EX: -10 dB HL
normal hearing level
0-20 dB HL
what does dB SL mean?
sensation level
dB SL
dB ABOVE the subject's INDIVIDUAL hearing threshold in the ear tested
individual hearing theshold
stim intensity in db HL formula
individuals threshold (dB HL) + 60 db SL = stim intensity in dB HL
EX: If a patient is tested to hear a 2,000 Hz frequency at 12 dB HL, their BAEPs should be tested at: 12dB HL + 60db SL = 72dB HL
just focus on dB HL
what type of stimulation does BAEPs use
broad band clicks
broad band clicks frequency
2000-4000 Hz (2-4 KHz)
broad band clicks
wide range of frequencies; used for neurologic applications
examples of narrow-broad band clicks
tone bursts
tone pips
filtered clicks
single-cycle clicks
why AREN'T narrow broad band clicks used for BAEPs
they have a more restricted frequency spectrum (less range)
more suited for audiologic applications
clicks should be delivered one/two ears at a time?
one (monoaurally)
the non-stimulated (contralateral) ear should be masked with ___
white noise to eliminate bone crossover (bone-conducted responses)
can you use interleaving stimulation for ABRs
NO b/c it does NOT allow for contralateral masking
bone conducted crossover
when unilateral stimulation is performed without sufficient contralateral masking tone or simultaneous stimulation
failure to use white noise masking introduces __
false negatives
false negative
data does NOT change; pt wakes up with a deficit
do we want to use bilateral stimulation for ABRs
NO
what does the BAEP sound stim intensity at the tympanic membrane depend on
acoustic coupling between the sound stimulus generator & the ear
sound waves are transduced to mechanical movement/vibrations in the outer/inner/middle ear?
outer & middle
mechanical movement is transduced to electrical potentials via ___ at the hair cells in the inner ear
depolarization
how often should calibration of the stimulus delivery system (head phones or ear inserts) be repeated
every 6 mo
earplugs are connected to a ___
transducer
what does obstruction of the tubing system lead to
failure of sound transmission (EX: kinking)
what should ear plus be protected from
blood & fluid by waterproof tape
purpose of bone wax
secure earphone
DOESN'T completely protect the canal from fluid entry
purpose of otoscopic visualization
- used before placing ear plugs
- visualize excessive cerumen that could interfere with stimulation
cerumen
ear wax
an otoscope is used to examine:
external ear
auditory canal
tympanic membrane

BAEP duration (pulse width)
100 usec (0.1 msec) rectangular pulse (singular monophasic square wave)
BAEP stim rate/rep rate:
9C
11C
avoid anything divisible by 60 Hz ! !
9C: 8-10/sec
- ranges from 5-200/sec
- HIGHER than 10/sec = reduces WI, II, IV, VII amp
- HIGH rates (50-70/s) = FASTER identification of WV
11C: 5-12 sec - 30.1/sec
- OPTIMAL for WI, III, V = 5-12/sec
- HIGHER rates of 30/sec = FASTER acquisition of WI & V, but WIII is DEGRADED
WV disappears __ dB HL above/below threshold?
1 dB HL below
do you have to reset baselines if the stim rate is changed during the procedure
YES
stim intensity & white noise masking:
9C
11C
9C: 40-120 dB pe SPL
- white noise = 60 dB SPL
11C: 100 dB pe SPL or 60-70 dB HL
- white noise = 60 dB SPL or 30-35 dB HL
^ use HIGHER stim intensity if the pt has pre-existing hearing loss or fluid in middle ear
sound pressure levels measurements are used as a ___
reference level
0 dB =?
20 micopascals (Pa) = 0.0002 dyne2/cm2
types of stimulus polarities
1) rarefaction
2) condensation
3) alternating
rarefaction polarity
apply NEGATIVE pressure
pulls AWAY from tympanic membrane
best WI amp
condensation polarity
apply POSITIVE pressure
pushes TOWARD tympanic membrane
best WV amp
alternating polarity
NEG & POS pressure
BEST for IOM
cancel stim artifact & cochlear microphonic
can you use alternating polarity for ECochG
NO
stim polarity 9C
NO clear rational for preferring rarefaction over condensation clicks or vice versa
normative data needs to be collected using stim polarity or polarities to be used in clinical setting
summating responses is acceptable whenever NO differences exist
stim polarity 11C
alternating clicks
HIGH int = high stim artifact --> use alternating to reduce it
bandpass:
9C
11C
9C: 10-30 to 2,500-3,000 Hz
- raise LFF to 100-200 Hz if muscle artifact is present
11C: 100-150 to 2,500-3,000 Hz
- reduce HFF to 1,000 Hz for OR noise