Class #1: International Brands & Branding Nations
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Where and when is marketing considered to have been born?
Around 25–35 AD in Pompeii, with branded garum by Aulus Umbricius Scaurus.
What product made Aulus Umbricius Scaurus famous?
Garum (fermented fish sauce).
What market share did “Garum Flower by Scaurus” hold around 79 AD?
About 30% of its regional market.
What is market segmentation?
Dividing a market into distinct groups with different needs or behaviours.
What is a market segment?
A group of consumers who respond similarly to a given marketing effort.
What is nano-segmentation?
Hyper-precise segmentation where each consumer becomes a unique segment.
What is target marketing?
Selecting the most attractive segments to enter and serve.
What is market positioning?
Placing a product clearly and distinctively in the consumer’s mind.
What is portfolio analysis?
Evaluating all a company's businesses to allocate resources efficiently.
How many types of segmentation are there ?
4
What does geographic segmentation focus on?
Regions, climates, density, and location-based needs.
What does demographic segmentation focus on?
Age, gender, income, education, nationality, etc.
What does psychographic segmentation focus on?
Lifestyle, personality, and social class.
What does behavioural segmentation focus on?
Purchase occasions, loyalty, usage rate, attitudes, benefits sought.
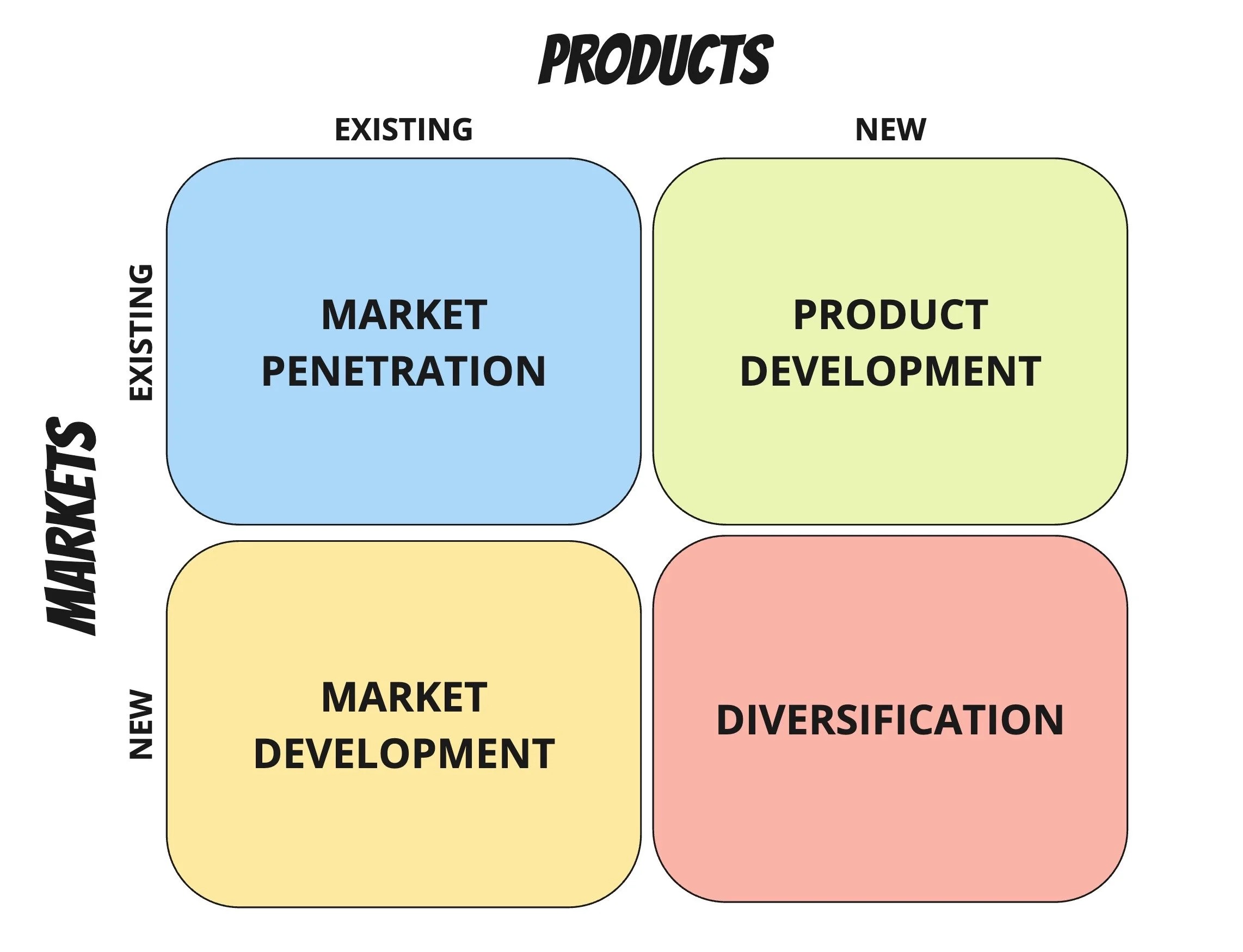
What is market penetration strategy?
Increasing sales of current products to current markets.
Why is market penetration difficult?
It often leads to price wars and strong competition.
What is market development?
Selling current products to new markets.
What is product development?
Creating modified or new products for existing customers.
What is diversification?
Entering new markets with new products.
Give an example of product adaptation in exports.
Orange Bank succeeding in African markets but not Europe.
Product/Market Expansion (Ansoff Grid)
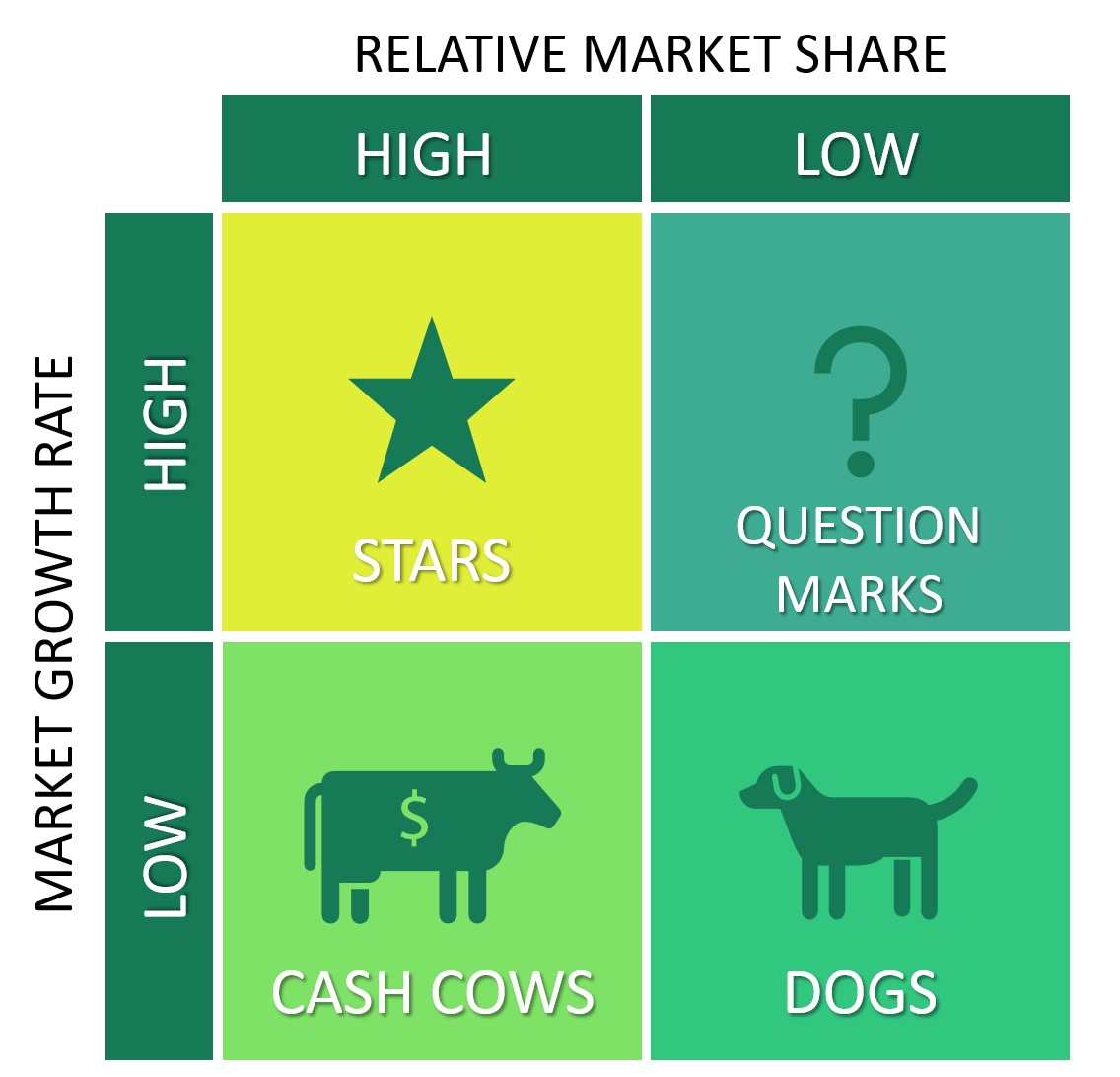
What characterizes a “Question Mark” product?
Low share in a high-growth market, requiring heavy investment.
What is a recommended strategy for a Question Mark?
Invest, acquire competitors, or abandon it.
What characterizes a “Cash Cow”?
High market share in a low-growth market with strong profitability.
What pricing rule applies to Cash Cows?
Never reduce prices, as they generate stable cash flow.
BCG Matrix
How does Starbucks practice market penetration?
By adding stores, improving menus, and increasing promotion.
How does Starbucks use market development?
By entering new demographic or geographic markets.
How does Starbucks use product development?
By adding food, supermarket coffee, and co-branded items.
How does Starbucks diversify?
By testing restaurants or selling branded lifestyle items.
What are the 8P ?
Product, Price, Place, Promotion, Physical Evidence, Process, People, Partnership
What does the “Product” P include?
Design, technology, warranty, and branding.
What is Cost-Plus pricing?
Pricing based on production cost plus a margin.
What is COD pricing?
“Cheapest on Display,” always setting the lowest visible price.
What does the “Place” P refer to?
Distribution channels and value delivery.
Give an example of Place evolution in an industry.
Music shifting from CDs to streaming platforms.
What does the “Promotion” P include?
Advertising, social media, sales communication, exhibitions.
What is “Physical Evidence” in marketing?
Proof of legitimacy: testimonials, storytelling, brand signals.
What does the “Process” P include?
UX, CX, ease of doing business, customer-mirroring structures.
UX
User Experience
CX
Customer Experience
What does the “People” P cover?
Employees, founders, culture, and customer service quality.
What does “Partnership” P include?
Co-branding, alliances, or co-contracting (e.g., McDonald’s + Coca-Cola).
What does supplier power represent?
How strongly suppliers can influence price and access.
Give an example of high supplier power.
China controlling most rare earth minerals.
What does customer power represent?
Buyers’ ability to impose conditions on sellers.
Example of strong customer power?
Spotify’s leverage over music artists.
What is technological disruption?
Innovations that change or eliminate industries.
What is the threat of new entrants?
How easily new competitors can enter a market.
Give an example of high new-entry risk.
Drone companies rapidly entering the market.
What is the threat of substitutes?
Alternative products that can replace yours.
Give a substitution example.
Smartphones replacing multiple devices.
What role do authorities and lobbies play?
Regulating markets and influencing competition.
What does competitive rivalry assess?
The intensity of competition within an industry.